Big Dig on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
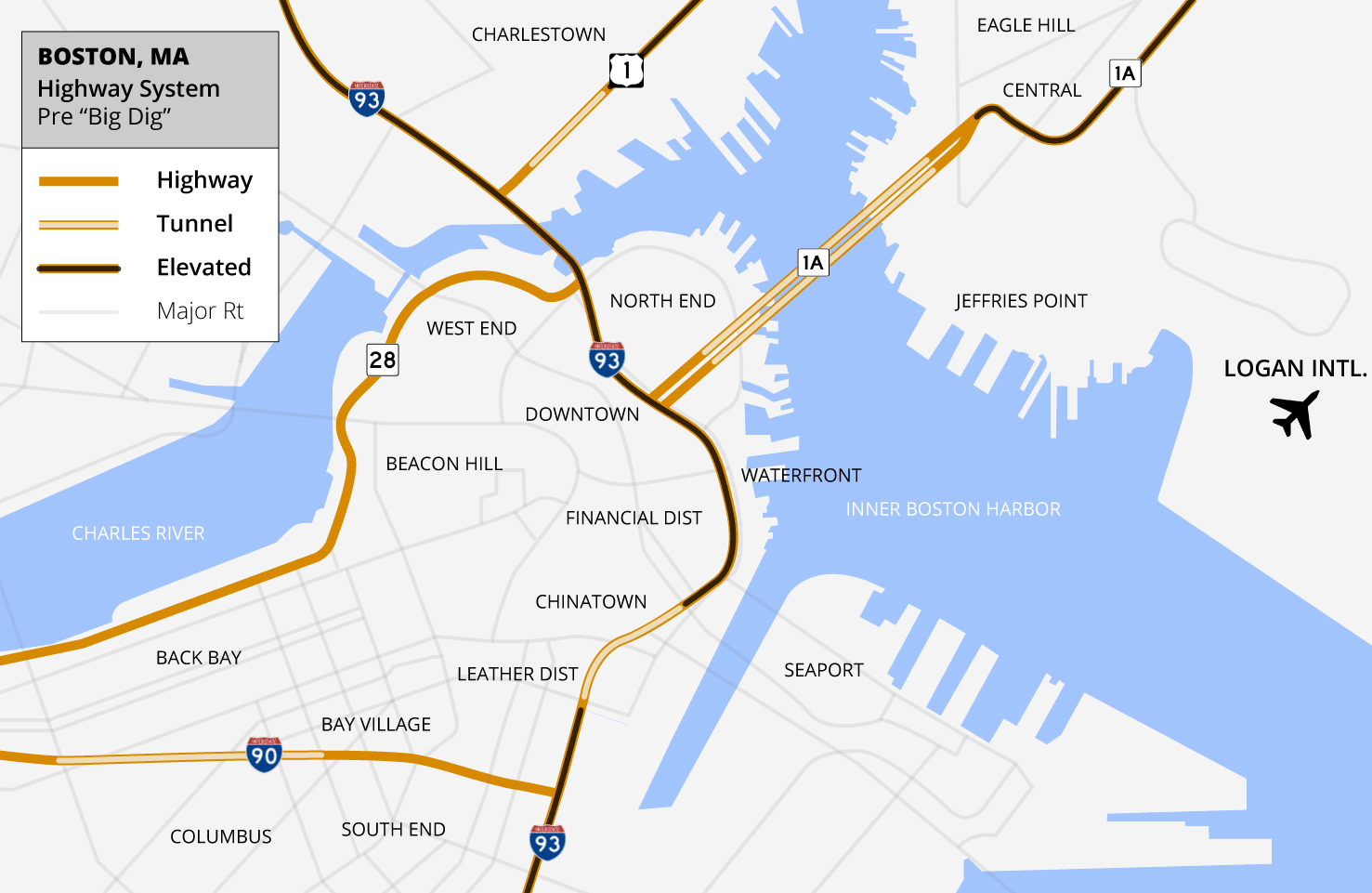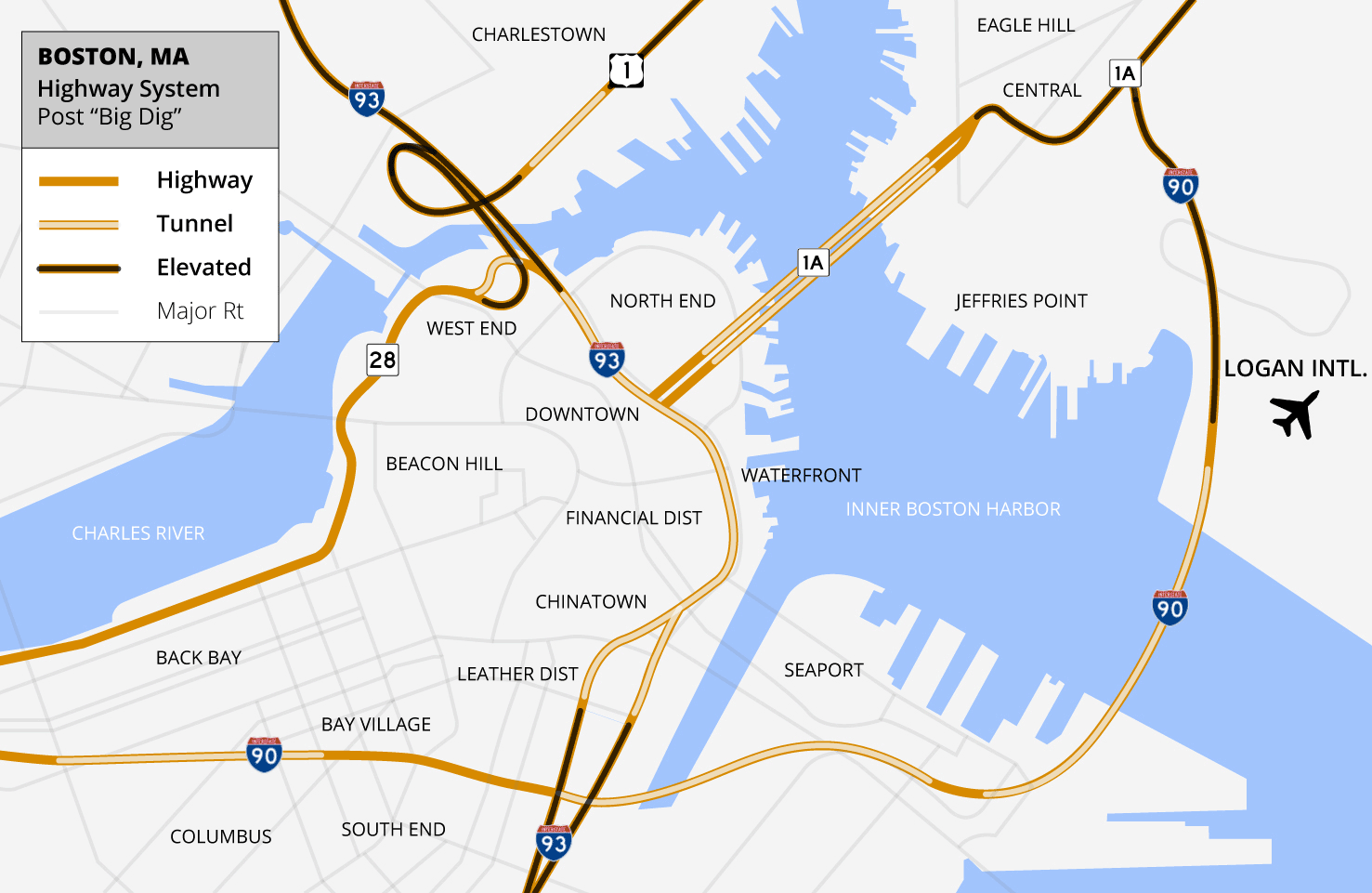 The Central Artery/Tunnel Project (CA/T Project), commonly known as the Big Dig, was a
The Central Artery/Tunnel Project (CA/T Project), commonly known as the Big Dig, was a
 Another important motivation for the final form of the Big Dig was the abandonment of the Massachusetts Department of Public Works' intended expressway system through and around Boston. The Central Artery, as part of Mass. DPW's Master Plan of 1948, was originally planned to be the downtown Boston stretch of Interstate 95, and was signed as such; a bypass road called the Inner Belt, was subsequently renamed Interstate 695. (The law establishing the
Another important motivation for the final form of the Big Dig was the abandonment of the Massachusetts Department of Public Works' intended expressway system through and around Boston. The Central Artery, as part of Mass. DPW's Master Plan of 1948, was originally planned to be the downtown Boston stretch of Interstate 95, and was signed as such; a bypass road called the Inner Belt, was subsequently renamed Interstate 695. (The law establishing the
 On January 18, 2003, the opening ceremony was held for the I-90 Connector Tunnel, extending the Massachusetts Turnpike (Interstate 90) east into the
On January 18, 2003, the opening ceremony was held for the I-90 Connector Tunnel, extending the Massachusetts Turnpike (Interstate 90) east into the
(presentation) to the Charles River Basin, including the construction of North Point Park in Cambridge and
 A fatal accident raised safety questions and closed part of the project for most of the summer of 2006. On July 10, 2006, concrete ceiling panels and debris weighing and measuring fell on a car traveling on the two-lane ramp connecting northbound I-93 to eastbound I-90 in
A fatal accident raised safety questions and closed part of the project for most of the summer of 2006. On July 10, 2006, concrete ceiling panels and debris weighing and measuring fell on a car traveling on the two-lane ramp connecting northbound I-93 to eastbound I-90 in
Official siteProject map
on page vi of ''Highway to the Past: The Archaeology of Boston's Big Dig'' (
Map of Central Artery Project
on page 21 of report on Climate Change Vulnerability
List of Massachusetts State Reports on Central Artery Project in BostonBoston CA/T Project History at MIT Rotch Library
– Central Artery * 2007 establishments in Massachusetts 2007 in Boston Engineering projects Interstate 93 Megaprojects North End, Boston Road tunnels in Massachusetts Transport infrastructure completed in 2007 Tunnels completed in 2007 Tunnels in Boston U.S. Route 1
 The Central Artery/Tunnel Project (CA/T Project), commonly known as the Big Dig, was a
The Central Artery/Tunnel Project (CA/T Project), commonly known as the Big Dig, was a megaproject
A megaproject is an extremely large-scale investment project.
According to the ''Oxford Handbook of Megaproject Management'', "Megaprojects are large-scale, complex ventures that typically cost $1 billion or more, take many years to develop and ...
in Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
that rerouted the Central Artery
The Central Artery (officially the John F. Fitzgerald Expressway) is a section of freeway in downtown Boston, Massachusetts; it is designated as Interstate 93, US 1 and Route 3.
The original Artery, constructed in the 1950s, was named aft ...
of Interstate 93 (I-93), the chief highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-acces ...
through the heart of the city, into the 1.5-mile (2.4 km) tunnel named the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Tunnel. The project also included the construction of the Ted Williams Tunnel
The Ted Williams Tunnel is a highway tunnel in Boston, Massachusetts. The third in the city to travel under Boston Harbor, with the Sumner Tunnel and the Callahan Tunnel, it carries the final segment of Interstate 90 (the Massachusetts Turnpik ...
(extending I-90 to Logan International Airport
General Edward Lawrence Logan International Airport , also known as Boston Logan International Airport and commonly as Boston Logan, Logan Airport or simply Logan, is an international airport that is located mostly in East Boston and partial ...
), the Leonard P. Zakim Bunker Hill Memorial Bridge
The Leonard P. Zakim () Bunker Hill Memorial Bridge (also known as “The Zakim”) is a cable-stayed bridge completed in 2003 across the Charles River in Boston, Massachusetts. It is a replacement for the Charlestown High Bridge, an older trus ...
over the Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
, and the Rose Kennedy Greenway
The Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy Greenway is a linear park located in several Downtown Boston neighborhoods. It consists of landscaped gardens, promenades, plazas, fountains, art, and specialty lighting systems that stretch over one mile through Chin ...
in the space vacated by the previous I-93 elevated roadway. Initially, the plan was also to include a rail connection between Boston's two major train terminals. Planning began in 1982; the construction work was carried out between 1991 and 2006; and the project concluded on December 31, 2007, when the partnership between the program manager and the Massachusetts Turnpike Authority ended.
The Big Dig was the most expensive highway project in the United States, and was plagued by cost overruns
A cost overrun, also known as a cost increase or budget overrun, involves unexpected incurred costs. When these costs are in excess of budgeted amounts due to a value engineering underestimation of the actual cost during budgeting, they are known ...
, delays, leaks, design flaws, charges of poor execution and use of substandard materials, criminal arrests, and the death of one motorist. The project was originally scheduled to be completed in 1998 at an estimated cost of $2.8 billion (in 1982 dollars, US$7.4 billion adjusted for inflation ). However, the project was completed in December 2007 at a cost of over $8.08 billion (in 1982 dollars, $21.5 billion adjusted for inflation, meaning a cost overrun of about 190%) . ''The Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe'' is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes, and has a total circulation of close to 300,000 print and digital subscribers. ''The Boston Glob ...
'' estimated that the project will ultimately cost $22 billion, including interest, and that it would not be paid off until 2038. As a result of a death, leaks, and other design flaws, Bechtel and Parsons Brinckerhoff
WSP USA, formerly WSP, Parsons Brinckerhoff and Parsons Brinckerhoff, is a multinational engineering and design firm with approximately 14,000 employees. WSP stands for Williams Sale Partnership. The firm operates in the fields of strategic con ...
—the consortium that oversaw the project—agreed to pay $407 million in restitution and several smaller companies agreed to pay a combined sum of approximately $51 million.
The Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy Greenway
The Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy Greenway is a linear park located in several Downtown Boston neighborhoods. It consists of landscaped gardens, promenades, plazas, fountains, art, and specialty lighting systems that stretch over one mile through Chin ...
is a roughly series of parks and public space
A public space is a place that is open and accessible to the general public. Roads (including the pavement), public squares, parks, and beaches are typically considered public space. To a limited extent, government buildings which are open to ...
s, which were the final part of the Big Dig after Interstate 93 was put underground. The Greenway was named in honor of Kennedy family
The Kennedy family is an American political family that has long been prominent in American politics, public service, entertainment, and business. In 1884, 35 years after the family's arrival from Ireland, Patrick Joseph "P. J." Kennedy beca ...
matriarch Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy
Rose Elizabeth Fitzgerald Kennedy (July 22, 1890 – January 22, 1995) was an American philanthropist, socialite, and matriarch of the Kennedy family. She was deeply embedded in the " lace curtain" Irish American community in Boston. Her fathe ...
, and was officially dedicated on July 26, 2004.
Origin
This project was developed in response to traffic congestion on Boston's historically tangled streets which were laid out centuries before the advent of theautomobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarde ...
. As early as 1930 the city's Planning Board recommended a raised express highway running north–south through the downtown district in order to draw through traffic off the city streets. Commissioner of Public Works William Callahan promoted plans for the Central Artery, an elevated expressway which eventually was constructed between the downtown area and the waterfront. Governor John Volpe
John Anthony Volpe (; December 8, 1908November 11, 1994) was an American businessman, diplomat, and politician from Massachusetts. A son of Italian immigrants, he founded and owned a large construction firm. Politically, he was a Republican in ...
interceded in the 1950s to change the design of the last section of the Central Artery, putting it underground through the Dewey Square Tunnel
The Dewey Square Tunnel in Boston, Massachusetts, is part of Interstate 93 (concurrent with US 1 and Route 3), running under the heart of the city's financial district, including Dewey Square. Built in 1959, it was part of Boston's Central Arte ...
. While traffic moved somewhat better, the other problems remained. There was chronic congestion on the Central Artery (I-93), the elevated six-lane highway through the center of downtown Boston, which was, in the words of Pete Sigmund, "like a funnel full of slowly-moving, or stopped, cars (and swearing motorists)."
In 1959, the 1.5-mile-long (2.4 km) road section carried approximately 75,000 vehicles a day, but by the 1990s, this had grown to 190,000 vehicles a day. Traffic jams of 16 hours were predicted for 2010.
The expressway had tight turns, an excessive number of entrances and exits, entrance ramps without merge lanes, and as the decades passed and other planned expressways were cancelled, continually escalating vehicular traffic that was well beyond its design capacity. Local businesses again wanted relief, city leaders sought a reuniting of the waterfront with the city, and nearby residents desired removal of the matte green-painted elevated road which mayor Thomas Menino
Thomas Michael Menino (December 27, 1942 – October 30, 2014) was an American politician who served as the 53rd mayor of Boston, from 1993 to 2014. He was the city's longest-serving mayor. He was elected mayor in 1993 after first serving three ...
called Boston's "other Green Monster
The Green Monster is a popular nickname for the left field wall at Fenway Park, home to the Boston Red Sox of Major League Baseball. The wall is from home plate and is a popular target for right-handed hitters.
Overview
The wall was part ...
" (as an unfavorable comparison to Fenway Park
Fenway Park is a baseball stadium located in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, near Kenmore Square. Since 1912, it has been the home of the Boston Red Sox, the city's American League baseball team, and since 1953, its only Major League Bas ...
's famed left-field wall). MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
engineers Bill Reynolds and (eventual state Secretary of Transportation) Frederick P. Salvucci envisioned moving the whole expressway underground.
Cancellation of the Inner Belt project
 Another important motivation for the final form of the Big Dig was the abandonment of the Massachusetts Department of Public Works' intended expressway system through and around Boston. The Central Artery, as part of Mass. DPW's Master Plan of 1948, was originally planned to be the downtown Boston stretch of Interstate 95, and was signed as such; a bypass road called the Inner Belt, was subsequently renamed Interstate 695. (The law establishing the
Another important motivation for the final form of the Big Dig was the abandonment of the Massachusetts Department of Public Works' intended expressway system through and around Boston. The Central Artery, as part of Mass. DPW's Master Plan of 1948, was originally planned to be the downtown Boston stretch of Interstate 95, and was signed as such; a bypass road called the Inner Belt, was subsequently renamed Interstate 695. (The law establishing the Interstate highway system
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. T ...
was enacted in 1956.) The Inner Belt District was to pass to the west of the downtown core, through the neighborhood of Roxbury and the cities of Brookline, Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
, and Somerville. Earlier controversies over impact of the Boston extension of the Massachusetts Turnpike
The Massachusetts Turnpike (colloquially "Mass Pike" or "the Pike") is a toll highway in the US state of Massachusetts that is maintained by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT). The turnpike begins at the New York state li ...
, particularly on the heavily populated neighborhood of Brighton, and the additional large amount of housing that would have had to be destroyed led to massive community opposition to both the Inner Belt and the Boston section of I-95.
By 1970, building demolition and land clearances for had been completed along the I-95 right of way through the neighborhoods of Roxbury, Jamaica Plain
Jamaica Plain is a neighborhood of in the City of Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Settled by Puritans seeking farmland to the south, it was originally part of the former Town of Roxbury, now also a part of the City of Boston. The commun ...
, the South End and Roslindale
Roslindale is a primarily residential neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, bordered by Jamaica Plain, Hyde Park, West Roxbury and Mattapan.
It is served by an MBTA Commuter Rail line, several MBTA bus lines and the MBTA Orange Line in nearby J ...
, which led to secession threats by Hyde Park, Boston's youngest and southernmost neighborhood (which I-95 was also slated to go through). By 1972, with relatively little work done on the Southwest Corridor portion of I-95 and none on the potentially massively disruptive Inner Belt, Governor Francis Sargent
Francis Williams Sargent (July 29, 1915 – October 22, 1998) was an American politician who served as the 64th governor of Massachusetts from 1969 to 1975. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as the 63rd Lieutenant Govern ...
put a moratorium on highway construction within the Route 128 corridor, except for the final short stretch of Interstate 93. In 1974, the remainder of the Master Plan was canceled.
With ever-increasing traffic volumes funneled onto I-93 alone, the Central Artery became chronically gridlocked. The Sargent moratorium led to the rerouting of I-95 away from Boston around the Route 128 beltway and the conversion of the cleared land in the southern part of the city into the Southwest Corridor linear park, as well as a new right-of-way for the Orange Line subway and Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
. Parts of the planned I-695 right-of-way remain unused and under consideration for future mass-transit projects.
The original 1948 Master Plan included a Third Harbor Tunnel plan that was hugely controversial in its own right, because it would have disrupted the Maverick Square Maverick Square is a section of the neighborhood of East Boston in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. It is East Boston's oldest commercial center. At the heart of the square is Maverick Station, which is part of the Blue Line of the MBTA.
In ...
area of East Boston
East Boston, nicknamed Eastie, is a neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts annexed by the city of Boston in 1637. Neighboring communities include Winthrop, Revere, and Chelsea. It is separated from the Boston neighborhood of Charlestown and d ...
. It was never built.
Mixing of traffic
A major reason for the all-day congestion was that the Central Artery carried not only north–south traffic, but it also carried east–west traffic. Boston's Logan Airport lies acrossBoston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, and is located adjacent to the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the northeastern United States.
History
...
in East Boston; and before the Big Dig, the only access to the airport from downtown was through the paired Callahan and Sumner tunnels. Traffic on the major highways from west of Boston—the Massachusetts Turnpike and Storrow Drive
Storrow Drive, officially James Jackson Storrow Memorial Drive, is a major crosstown parkway in Boston, Massachusetts, running east–west along the southern bank of the Charles River. It is restricted to cars; trucks and buses are not perm ...
—mostly traveled on portions of the Central Artery to reach these tunnels. Getting between the Central Artery and the tunnels involved short diversions onto city streets, increasing local congestion.
Mass transit
A number ofpublic transportation
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
projects were included as part of an environmental mitigation for the Big Dig. The most expensive was the building of the Phase II Silver Line tunnel under Fort Point Channel
Fort Point Channel is a maritime channel separating South Boston from downtown Boston, Massachusetts, feeding into Boston Harbor. The south part of it has been gradually filled in for use by the South Bay rail yard and several highways (specif ...
, done in coordination with Big Dig construction. Silver Line buses now use this tunnel and the Ted Williams Tunnel to link South Station
South Station, officially The Governor Michael S. Dukakis Transportation Center at South Station, is the largest railroad station and intercity bus terminal in Greater Boston and New England's second-largest transportation center after Logan In ...
and Logan Airport.
, promised projects to connect the Red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
and Blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between violet and cyan on the spectrum of visible light. The eye perceives blue when ...
subway lines, and to restore the Green Line streetcar service to the Arborway
Arborway (also known as The Arborway) consists of a four-lane, divided parkway and a two lane residential street in the Jamaica Plain neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It was designed by Frederick Law Olmsted in the 1890s as the south most ...
in Jamaica Plain
Jamaica Plain is a neighborhood of in the City of Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Settled by Puritans seeking farmland to the south, it was originally part of the former Town of Roxbury, now also a part of the City of Boston. The commun ...
have not been completed. Construction of the extension beyond Lechmere has begun. The Union Square Green Line station opened March 21, 2022. The Red and Blue subway line connection underwent initial design, but no funding has been designated for the project. The Arborway Line restoration has been abandoned, following a final court decision in 2011.
The original Big Dig plan also included the North-South Rail Link
''North-South'' ( hy, Հյուսիս-Հարավ) or ''Four Buddies and the Bride'' is an Armenian comedy directed by Davit Babakhanyan and Vazgen Muradyan, starring Diana Malenko, Sona Shahgeldyan and David Tovmasyan. The film was produced by ...
, which would have connected North and South Stations (the major passenger train stations in Boston), but this aspect of the project was ultimately dropped by the state transportation administration early in the Dukakis administration. Negotiations with the federal government had led to an agreement to widen some of the lanes in the new harbor tunnel, and accommodating these would require the tunnel to be deeper and mechanically-vented; this left no room for the rail lines, and having diesel trains (then in use) passing through the tunnel would have substantially increased the cost of the ventilation system.
Early planning
The project was conceived in the 1970s by theBoston Transportation Planning Review
Boston Transportation Planning Review (BTPR), published in 1972, was a transportation planning program for metropolitan Boston, Massachusetts, which was responsible for analyzing and redesigning the entire area-wide transit and highway system in ...
to replace the rusting elevated six-lane Central Artery. The expressway separated downtown from the waterfront, and was increasingly choked with bumper-to-bumper traffic. Business leaders were more concerned about access to Logan Airport
General Edward Lawrence Logan International Airport , also known as Boston Logan International Airport and commonly as Boston Logan, Logan Airport or simply Logan, is an international airport that is located mostly in East Boston and partiall ...
, and pushed instead for a third harbor tunnel. In their second terms, Michael Dukakis
Michael Stanley Dukakis (; born November 3, 1933) is an American retired lawyer and politician who served as governor of Massachusetts from 1975 to 1979 and again from 1983 to 1991. He is the longest-serving governor in Massachusetts history a ...
(governor) and Fred Salvucci (secretary of transportation) came up with the strategy of tying the two projects together—thereby combining the project that the business community supported with the project that they and the City of Boston supported.
Planning for the Big Dig as a project officially began in 1982, with environmental impact studies starting in 1983. After years of extensive lobbying for federal dollars, a 1987 public works bill appropriating funding for the Big Dig was passed by the US Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washin ...
, but it was vetoed by President Ronald Reagan for being too expensive. When Congress overrode the veto, the project had its green light and ground was first broken in 1991.
In 1997, the state legislature created the Metropolitan Highway System and transferred responsibility for the Central Artery and Tunnel "CA/T" Project from the Massachusetts Highway Department and the Massachusetts Governor's Office to the Massachusetts Turnpike Authority (MTA).
The MTA, which had little experience in managing an undertaking of the scope and magnitude of the CA/T Project, hired a joint venture to provide preliminary designs, manage design consultants and construction contractors, track the project's cost and schedule, advise MTA on project decisions, and (in some instances) act as the MTA's representative. Eventually, MTA combined some of its employees with joint venture employees in an integrated project organization. This was intended to make management more efficient, but it hindered MTA's ability to independently oversee project activities because MTA and the joint venture had effectively become partners in the project.
Obstacles
In addition to political and financial difficulties, the project received resistance from residents of Boston's historic North End, who in the 1950s had seen 20% of the neighborhood's businesses displaced by development of the Central Artery. In 1993, the North End Waterfront Central Artery Committee (NEWCAC) created, co-founded by Nancy Caruso, representing residents, businesses, and institutions in the North End and Waterfront neighborhoods of Boston. The NEWCAC Committee's goal included lessening the impact of the Central Artery/Tunnel Project on the community; representing the neighborhoods to government agencies; keeping the community informed; developing a list of priorities of immediate neighborhood concerns; and promoting responsible and appropriate development of the post-construction artery corridor in the North End and Waterfront neighborhoods. The political, financial and residential obstacles were magnified when several environmental and engineering obstacles occurred. The downtown area through which the tunnels were to be dug was largely land fill, and included existing Red Line and Blue Line subway tunnels as well as innumerable pipes and utility lines that would have to be replaced or moved. Tunnel workers encountered many unexpected geological and archaeological barriers, ranging from glacial debris to foundations of buried houses and a number of sunken ships lying within the reclaimed land. The project received approval from state environmental agencies in 1991, after satisfying concerns including release of toxins by the excavation and the possibility of disrupting the homes of millions of rats, causing them to roam the streets of Boston in search of new housing. By the time the federal environmental clearances were delivered in 1994, the process had taken some seven years, during which time inflation greatly increased the project's original cost estimates. Reworking such a busy corridor without seriously restricting traffic flow required a number of state-of-the-art construction techniques. Because the old elevated highway (which remained in operation throughout the construction process) rested on pylons located throughout the designated dig area, engineers first utilizedslurry wall
A slurry wall is a civil engineering technique used to build reinforced concrete walls in areas of soft earth close to open water, or with a high groundwater table.
This technique is typically used to build diaphragm (water-blocking) walls surro ...
techniques to create concrete walls upon which the highway could rest. These concrete walls also stabilized the sides of the site, preventing cave-ins during the continued excavation process.
The multi-lane Interstate highway also had to pass under South Station
South Station, officially The Governor Michael S. Dukakis Transportation Center at South Station, is the largest railroad station and intercity bus terminal in Greater Boston and New England's second-largest transportation center after Logan In ...
's seven railroad tracks, which carried over 40,000 commuters and 400 trains per day. To avoid multiple relocations of train lines while the tunneling advanced, as had been initially planned, a specially designed jack
Jack may refer to:
Places
* Jack, Alabama, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack, Missouri, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack County, Texas, a county in Texas, USA
People and fictional characters
* Jack (given name), a male given name, ...
was constructed to support the ground and tracks to allow the excavation to take place below. Construction crews also used ground freezing
Ground freezing is a construction technique used in circumstances where soil needs to be stabilized so it will not collapse next to excavations, or to prevent contaminants spilled into soil from being leached away.
Ground freezing has been used f ...
(an artificial induction of permafrost) to help stabilize surrounding ground as they excavated the tunnel. This was the largest tunneling project undertaken beneath railroad lines anywhere in the world. The ground freezing enabled safer, more efficient excavation, and also assisted in environmental issues, as less contaminated fill needed to be exported than if a traditional cut-and-cover method had been applied.
Other challenges included existing subway tunnels crossing the path of the underground highway. To build slurry walls past these tunnels, it was necessary to dig beneath the tunnels and to build an underground concrete bridge to support the tunnels' weight, without interrupting rail service.
Construction phase
The project was managed by the Massachusetts Turnpike Authority, with the Big Dig and the Turnpike's Boston Extension from the 1960s being financially and legally joined by the legislature as theMetropolitan Highway System
The Massachusetts Turnpike (colloquially "Mass Pike" or "the Pike") is a toll highway in the US state of Massachusetts that is maintained by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT). The turnpike begins at the New York state li ...
. Design and construction was supervised by a joint venture of Bechtel Corporation
Bechtel Corporation () is an American engineering, procurement, construction, and project management company founded in San Francisco, California, and headquartered in Reston, Virginia. , the '' Engineering News-Record'' ranked Bechtel as ...
and Parsons Brinckerhoff
WSP USA, formerly WSP, Parsons Brinckerhoff and Parsons Brinckerhoff, is a multinational engineering and design firm with approximately 14,000 employees. WSP stands for Williams Sale Partnership. The firm operates in the fields of strategic con ...
. Because of the enormous size of the project—too large for any company to undertake alone—the design and construction of the Big Dig was broken up into dozens of smaller subprojects with well-defined interfaces between contractors. Major heavy-construction contractors on the project included Jay Cashman
Jay Cashman, Inc. is a privately held multi-disciplinary construction and development company, founded and owned by Jay M. Cashman. It is one of the largest privately held contracting firms in the northeastern United States.
The company has moved ...
, Modern Continental, Obayashi Corporation
is one of five major Japanese construction companies along with Shimizu Corporation, Takenaka Corporation, Kajima Corporation, and Taisei Corporation. It is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and is one of the Nikkei 225 corporations. Its head ...
, Perini Corporation, Peter Kiewit Sons' Incorporated, J. F. White, and the Slattery division of Skanska
Skanska AB () is a multinational construction and development company based in Sweden. Skanska is the fifth-largest construction company in the world according to ''Construction Global'' magazine. Notable Skanska projects include renovation of t ...
USA. (Of those, Modern Continental was awarded the greatest gross value of contracts, joint ventures included.)
The nature of the Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
crossing had been a source of major controversy throughout the design phase of the project. Many environmental advocates preferred a river crossing entirely in tunnels, but this, along with 27 other plans, was rejected as too costly. Finally, with a deadline looming to begin construction on a separate project that would connect the Tobin Bridge
The Maurice J. Tobin Memorial Bridge (formerly the Mystic River Bridge) is a cantilever truss bridge that spans more than two miles (3 km) from Boston to Chelsea over the Mystic River in Massachusetts. The bridge is the largest in New Eng ...
to the Charles River crossing, Salvucci overrode the objections and chose a variant of the plan known as "Scheme Z". This plan was considered to be reasonably cost-effective, but had the drawback of requiring highway ramps stacked up as high as immediately adjacent to the Charles River.
The city of Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
objected to the visual impact of the chosen Charles River crossing design. The city sued to revoke the project's environmental certificate and forced the project planners to redesign the river crossing again.
Swiss engineer Christian Menn
Christian Menn (March 3, 1927 – July 16, 2018) was a renowned Swiss civil engineer and bridge designer. He was involved in the construction of around 100 bridges worldwide, but the focus of his work was in eastern Switzerland, especially in can ...
took over the design of the bridge. He suggested a cradle cable-stayed bridge
A cable-stayed bridge has one or more ''towers'' (or ''pylons''), from which cables support the bridge deck. A distinctive feature are the cables or stays, which run directly from the tower to the deck, normally forming a fan-like pattern ...
that would carry ten lanes of traffic. The plan was accepted and construction began on the Leonard P. Zakim Bunker Hill Memorial Bridge
The Leonard P. Zakim () Bunker Hill Memorial Bridge (also known as “The Zakim”) is a cable-stayed bridge completed in 2003 across the Charles River in Boston, Massachusetts. It is a replacement for the Charlestown High Bridge, an older trus ...
. The bridge employed an asymmetrical design and a hybrid of steel and concrete was used to construct it. The distinctive bridge is supported by two forked towers connected to the span by cables and girders. It was the first bridge in the country to employ this method and it was, at the time, the widest cable-stayed bridge in the world, having since been surpassed by the Eastern span replacement of the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge
The eastern span replacement of the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge was a construction project to replace a seismically unsound portion of the Bay Bridge with a new self-anchored suspension bridge (SAS) and a pair of viaducts. The bridge i ...
.
Meanwhile, construction continued on the Tobin Bridge approach. By the time all parties agreed on the I-93 design, construction of the Tobin connector (today known as the "City Square Tunnel" for a Charlestown area it bypasses) was far along, significantly adding to the cost of constructing the US Route 1
U.S. Route 1 or U.S. Highway 1 (US 1) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. It runs from Key West, Florida, north to Fort Kent, Maine, at the Canadian border, making ...
interchange and retrofitting the tunnel.
Boston blue clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
and other soils extracted from the path of the tunnel were used to cap many local landfills, fill in the Granite Rail Quarry in Quincy, and restore the surface of Spectacle Island in the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area
The Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area is a national recreation area situated among the islands of Boston Harbor of Boston, Massachusetts. The area is made up of a collection of islands, together with a former island and a peninsul ...
.
The Storrow Drive Connector, a companion bridge to the Zakim, began carrying traffic from I-93 to Storrow Drive
Storrow Drive, officially James Jackson Storrow Memorial Drive, is a major crosstown parkway in Boston, Massachusetts, running east–west along the southern bank of the Charles River. It is restricted to cars; trucks and buses are not perm ...
in 1999. The project had been under consideration for years, but was opposed by the wealthy residents of the Beacon Hill neighborhood. However, it finally was accepted because it would funnel traffic bound for Storrow Drive and downtown Boston away from the mainline roadway. The Connector ultimately used a pair of ramps that had been constructed for Interstate 695, enabling the mainline I-93 to carry more traffic that would have used I-695 under the original Master Plan.
When construction began, the project cost, including the Charles River crossing, was estimated at $5.8 billion. Eventual cost overruns
A cost overrun, also known as a cost increase or budget overrun, involves unexpected incurred costs. When these costs are in excess of budgeted amounts due to a value engineering underestimation of the actual cost during budgeting, they are known ...
were so high that the chairman of the Massachusetts Turnpike Authority, James Kerasiotes, was fired in 2000. His replacement had to commit to an $8.55 billion cap on federal contributions. The total expenses eventually passed $15 billion. Interest brought this cost to $21.93 billion.
Engineering methods and details
Several unusual engineering challenges arose during the project, requiring unusual solutions and methods to address them. At the beginning of the project, engineers had to figure out the safest way to build the tunnel without endangering the existing elevated highway above. Eventually, they created horizontal braces as wide as the tunnel, then cut away the elevated highway's struts, and lowered it onto the new braces. Three alternative construction methods were studied with their corresponding structural design to address existing conditions, safety measures, and constructability. In addition to codified loads, construction loads were computed to support final design and field execution .Final phases
Ted Williams Tunnel
The Ted Williams Tunnel is a highway tunnel in Boston, Massachusetts. The third in the city to travel under Boston Harbor, with the Sumner Tunnel and the Callahan Tunnel, it carries the final segment of Interstate 90 (the Massachusetts Turnpik ...
, and onwards to Boston Logan International Airport
General Edward Lawrence Logan International Airport , also known as Boston Logan International Airport and commonly as Boston Logan, Logan Airport or simply Logan, is an international airport that is located mostly in East Boston and partial ...
. The Ted Williams tunnel had been completed and was in limited use for commercial traffic and high-occupancy vehicle
A high-occupancy vehicle lane (also known as an HOV lane, carpool lane, diamond lane, 2+ lane, and transit lane or T2 or T3 lanes) is a restricted traffic lane reserved for the exclusive use of vehicles with a driver and one or more passengers, i ...
s since late 1995. The westbound lanes opened on the afternoon of January 18 and the eastbound lanes on January 19.
The next phase, moving the elevated Interstate 93 underground, was completed in two stages: northbound lanes opened on March 29, 2003, and southbound lanes (in a temporary configuration) on December 20, 2003. A tunnel underneath Leverett Circle
Leverett Circle is an intersection in Boston, Massachusetts. Completely rebuilt during the Big Dig, it is no longer a rotary. It marks the confluence of Storrow Drive, Charles River Dam Road ( Northern Artery), Nashua Street, Charles Street, ...
connecting eastbound Storrow Drive to I-93 North and the Tobin Bridge opened December 19, 2004, easing congestion at the circle. All southbound lanes of I-93 opened to traffic on March 5, 2005, including the left lane of the Zakim Bridge, and all of the refurbished Dewey Square Tunnel
The Dewey Square Tunnel in Boston, Massachusetts, is part of Interstate 93 (concurrent with US 1 and Route 3), running under the heart of the city's financial district, including Dewey Square. Built in 1959, it was part of Boston's Central Arte ...
.
By the end of December 2004, 95% of the Big Dig was completed. Major construction remained on the surface, including construction of final ramp configurations in the North End and in the South Bay interchange, and reconstruction of the surface streets.
The final ramp downtown—exit 16A (formerly 20B) from I-93
Interstate 93 (I-93) is an Interstate Highway in the New England states of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont in the United States. Spanning approximately along a north–south axis, it is one of three primary Interstate Highways ...
south to Albany Street
Albany Street is a road in London running from Marylebone Road to Gloucester Gate following the east side of Regent's Park. It is about three-quarters of a mile in length.
History
The street was laid out during the 1820s, and takes its name ...
—opened January 13, 2006.
In 2006, the two Interstate 93 tunnels were dedicated as the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Tunnel, after the former Democratic speaker of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
from Massachusetts who pushed to have the Big Dig funded by the federal government.
Coordinated projects
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts was required under the Federal Clean Air Act to mitigate air pollution generated by the highway improvements. Secretary of Transportation Fred Salvucci signed an agreement with the Conservation Law Foundation in 1990 enumerating 14 specific projects the state agreed to build. This list was affirmed in a 1992 lawsuit settlement. Projects which have been completed include: * Restoration of three Old Colony Commuter Rail lines * Expansion of Framingham Line to serve Worcester full-time * Restoration of the Newburyport/Rockport Line * Six-car trains on the MBTA Blue Line, requiring platform lengthening, station modernization, and all new train cars *MBTA Silver Line
The Silver Line is a system of bus routes in Boston and Chelsea, Massachusetts, operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA). It is operated as part of the MBTA bus system, but branded as bus rapid transit (BRT) as part ...
service to the South Boston waterfront
* 1,000 new commuter parking spaces
As of 2014, several mitigation projects were incomplete:
* Green Line Extension
The Green Line Extension (GLX) was a construction project to extend the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) Green Line light rail system northwest into Somerville and Medford, two inner suburbs of Boston, Massachusetts. The p ...
to Somerville and Medford
* Fairmount Line
The Fairmount Line or Dorchester Branch is a line of the MBTA Commuter Rail system in Boston, Massachusetts, USA. Except for a short portion in Milton, it lies entirely within Boston, running southwest from South Station through the neighborh ...
improvements
* Design of the Red-Blue Connector at Charles Street (under petition to remove from list)
Some projects, such as restoration of Green Line "E" Arborway service, were removed from the list of mitigation projects and replaced with other projects with similar air-quality improvements.
Surface treatments
Some surface treatments that were part of the original project plan were dropped due to the massive cost overruns on the highway portion of the project. $99.1 million was allocated for mitigating improvementsNew Charles River Basin Citizens Advisory Committee, January 17, 2017(presentation) to the Charles River Basin, including the construction of North Point Park in Cambridge and
Paul Revere Park
Paul Revere Park is a park located on the Charles River in Charlestown, Massachusetts. The park was the first park to open along the "Lost Half Mile" of the Charles River as mitigation for the taking of planned parkland for the construction of t ...
in Charlestown. The North Bank Bridge, providing pedestrian and bicycle connectivity between the parks, was not funded until the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) (), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed in response to the Gr ...
. Nashua Street Park on the Boston side was completed in 2003, by McCourt Construction with $7.9 million in funding from MassDOT. As of 2017, $30.5 million had been transferred to the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation
The Department of Conservation and Recreation (DCR) is a state agency of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, situated in the Executive Office of Energy and Environmental Affairs. It is best known for its parks and parkways. The DCR's mission i ...
to complete five projects. Another incomplete but required project is the South Bank Bridge over the MBTA Commuter Rail tracks at North Station (connecting Nashua Street Park to the proposed South Bank Park, which is currently a parking lot under the Zakim Bridge at the Charles River locks).
Improvements in the lower Charles River Basin include the new walkway at Lovejoy Wharf (constructed by the developer of 160 North Washington Street, the new headquarters of Converse
Converse may refer to:
Mathematics and logic
* Converse (logic), the result of reversing the two parts of a definite or implicational statement
** Converse implication, the converse of a material implication
** Converse nonimplication, a logical c ...
), the Lynch Family Skate Park (constructed in 2015 by the Charles River Conservancy), rehabilitation of historic operations buildings for the Charles River Dam
The Charles River Dam is a flood control structure on the Charles River in Boston, Massachusetts, located just downstream of the Leonard P. Zakim Bunker Hill Memorial Bridge, near Lovejoy Wharf, on the former location of the Warren Bridge.
His ...
and lock, a maintenance facility, and a planned pedestrian walkway across the Charles River next to the MBTA Commuter Rail drawbridge at North Station (connecting Nashua Street Park and North Point Park). MassDOT is funding the South Bank Park, and replacement of the North Washington Street Bridge (construction Aug 2018–23). EF Education is funding public greenspace improvements as part of its three-phase expansion at North Point. Remaining funding may be used to construct the North Point Inlet pedestrian bridge, and a pedestrian walkway over Leverett Circle
Leverett Circle is an intersection in Boston, Massachusetts. Completely rebuilt during the Big Dig, it is no longer a rotary. It marks the confluence of Storrow Drive, Charles River Dam Road ( Northern Artery), Nashua Street, Charles Street, ...
. Before being replaced with surface access during the reconstruction of the Science Park
A science park (also called a "university research park", "technology park”, "technopark", “technopole", or a "science and technology park" (STP)) is defined as being a property-based development that accommodates and fosters the growt ...
MBTA Green Line station, Leverett Circle had pedestrian bridges with stairs that provided elevated access between the station, the Charles River Parks, and the sidewalk to the Boston Museum of Science
The Museum of Science (MoS) is a science museum and indoor zoo in Boston, Massachusetts, located in Science Park, a plot of land spanning the Charles River. Along with over 700 interactive exhibits, the museum features a number of live presentat ...
. The replacement ramps would comply with Americans with Disabilities Act requirements and allow easy travel by wheelchair or bicycle over the busy intersection.
Public art
While not a legally mandated requirement,public art
Public art is art in any media whose form, function and meaning are created for the general public through a public process. It is a specific art genre with its own professional and critical discourse. Public art is visually and physically acce ...
was part of the urban design planning process (and later design development work) through the Artery Arts Program. The intent of the program was to integrate public art into highway infrastructure (retaining walls, fences, and lighting) and the essential elements of the pedestrian environment (walkways, park landscape elements, and bridges). As overall project costs increased, the Artery Arts Program was seen as a potential liability, even though there was support and interest from the public and professional arts organizations in the area.
At the beginning of the highway design process, a temporary arts program was initiated, and over 50 proposals were selected. However, development began on only a few projects before funding for the program was cut. Permanent public art that was funded includes: super graphic text and facades of former West End houses cast into the concrete elevated highway abutment support walls near North Station
North Station is a commuter rail and intercity rail terminal station in Boston, Massachusetts. It is served by four MBTA Commuter Rail lines – the Fitchburg Line, Haverhill Line, Lowell Line, and Newburyport/Rockport Line – and the Amtrak ...
by artist Sheila Levrant de Bretteville
Sheila Levrant de Bretteville (born 1940) is an American graphic designer, artist and educator whose work reflects her belief in the importance of feminist principles and user participation in graphic design. In 1990 she became the director of th ...
; Harbor Fog, a sensor-activated mist, light and sound sculptural environment by artist Ross Miller in parcel 17; a historical sculpture celebrating the 18th and 19th century shipbuilding industry and a bust of shipbuilder Donald McKay
Donald McKay (September 4, 1810 – September 20, 1880) was a Canadian-born American designer and builder of sailing ships, famed for his record-setting clippers.
Early life
He was born in Jordan Falls, Shelburne County, on Nova Scotia's ...
in East Boston
East Boston, nicknamed Eastie, is a neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts annexed by the city of Boston in 1637. Neighboring communities include Winthrop, Revere, and Chelsea. It is separated from the Boston neighborhood of Charlestown and d ...
; blue interior lighting of the Zakim Bridge; and the Miller's River Littoral Way walkway and lighting under the loop ramps north of the Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
.
Extensive landscape planting, as well as a maintenance program to support the plantings, was requested by many community members during public meetings.
Impact on traffic
The Big Dig separated the co-mingled traffic from the Massachusetts Turnpike and the Sumner and Callahan tunnels. While only one net lane in each direction was added to the north–south I-93, several new east–west lanes became available. East–west traffic on the Massachusetts Turnpike/I-90 now proceeds directly through the Ted Williams Tunnel to Logan Airport and Route 1A beyond. Traffic between Storrow Drive and the Callahan and Sumner Tunnels still uses a short portion of I-93, but additional lanes and direct connections are provided for this traffic. The result was a 62% reduction in vehicle hours of travel on I-93, the airport tunnels, and the connection from Storrow Drive, from an average 38,200 hours per day before construction (1994–1995) to 14,800 hours per day in 2004–2005, after the project was largely complete. Transportation Impacts of MTA and CAT project, February 2006, Table 3-6: The savings for travelers was estimated at $166 million annually in the same 2004–2005 time frame. Travel times on the Central Artery northbound during the afternoon peak hour were reduced 85.6%. A 2008 ''Boston Globe'' report asserted that waiting time for the majority of trips actually increased as a result of demand induced by the increased road capacity. Because more drivers were opting to use the new roads, traffic bottlenecks were only pushed outward from the city, not reduced or eliminated (although some trips are now faster). The report states, "Ultimately, many motorists going to and from the suburbs at peak rush hours are spending more time stuck in traffic, not less." The ''Globe'' also asserted that their analysis provides a fuller picture of the traffic situation than a state-commissioned study done two years earlier, in which the Big Dig was credited with helping to save at least $167 million a year by increasing economic productivity and decreasing motor vehicle operating costs. That study did not look at highways outside the Big Dig construction area and did not take into account new congestion elsewhere.Impact on property values
Towards the end of the Big Dig in 2003, it was estimated that the demolition of the Central Artery highway would cause a $732 million increase in property value in Boston's financial district, with the replacement parks providing an additional $252 million in value. Additionally, as a result of the Big Dig, a large amount of waterfront space was opened up, which is now a high-rent residential and commercial area called theSeaport District
The Seaport District, or simply the Seaport, is a neighborhood in Boston, Massachusetts. It is part of the larger neighborhood of South Boston, and is also sometimes called the Innovation District. The Seaport is a formerly industrial area that ...
. The development of Seaport alone was estimated to create $7 billion in private investment and 43,000 jobs.
Operations Control Center (OCC)
As part of the project, an elaborate Operations Control Center (OCC)control room
A control room or operations room is a central space where a large physical facility or physically dispersed service can be monitored and controlled. It is often part of a larger command center.
Overview
A control room's purpose is produc ...
was constructed in South Boston
South Boston is a densely populated neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, located south and east of the Fort Point Channel and abutting Dorchester Bay. South Boston, colloquially known as Southie, has undergone several demographic transformat ...
. Staffed on a " 24/7/365" basis, this center monitors and reports on traffic congestion, and responds to emergencies. Continuous video surveillance
Closed-circuit television (CCTV), also known as video surveillance, is the use of video cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place, on a limited set of monitors. It differs from broadcast television in that the signal is not openly tr ...
is provided by hundreds of cameras, and thousands of sensors monitor traffic speed and density, air quality
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
, water levels, temperatures, equipment status, and other conditions inside the tunnel. The OCC can activate emergency ventilation fans, change electronic display signs, and dispatch service crews when necessary.
Problems
"Thousands of leaks"
As far back as 2001, Turnpike Authority officials and contractors knew of thousands of leaks in ceiling and wall fissures, extensive water damage to steel supports and fireproofing systems, and overloaded drainage systems. Many of the leaks were a result of Modern Continental and other subcontractors failing to remove gravel and other debris before pouring concrete. This information was not made public until engineers at MIT (volunteer students and professors) performed several experiments and found serious problems with the tunnel. On September 15, 2004, a major leak in the Interstate 93 north tunnel forced the closure of the tunnel while repairs were conducted. This also forced the Turnpike Authority to release information regarding its non-disclosure of prior leaks. A follow-up reported on "extensive" leaks that were more severe than state authorities had previously acknowledged. The report went on to state that the $14.6 billion tunnel system was riddled with more than 400 leaks. A ''Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe'' is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes, and has a total circulation of close to 300,000 print and digital subscribers. ''The Boston Glob ...
'' report, however, countered that by stating there were nearly 700 leaks in a single section of tunnel beneath South Station
South Station, officially The Governor Michael S. Dukakis Transportation Center at South Station, is the largest railroad station and intercity bus terminal in Greater Boston and New England's second-largest transportation center after Logan In ...
. Turnpike officials also stated that the number of leaks being investigated was down from 1,000 to 500.
The problem of leaks is further aggravated by the fact that many of them involve corrosive salt water
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish wat ...
. This is caused by the proximity of Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, and is located adjacent to the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the northeastern United States.
History
...
and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, causing a mix of salt and fresh water leaks in the tunnel. The situation is made worse by road salt
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/ ...
spread in the tunnel to melt ice during freezing weather, or brought in by vehicles passing through. Salt water and salt spray
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantiti ...
are well-known issues that must be dealt with in any marine environment
Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental ...
. It has been reported that "hundreds of thousands of gallons of salt water are pumped out monthly" in the Big Dig, and a map has been prepared showing "hot spots" where water leakage is especially serious. Salt-accelerated corrosion has caused ceiling light fixtures to fail (see below), but can also cause rapid deterioration of embedded rebar and other structural steel reinforcements holding the tunnel walls and ceiling in place.
The much larger than expected volume of water that must be continuously pumped consumes a correspondingly larger amount of electrical power, and will cause the pumps to wear out much sooner than originally estimated.
Substandard materials
Massachusetts State Police
The Massachusetts State Police (MSP) is an agency of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts' Executive Office of Public Safety and Security, responsible for criminal law enforcement and traffic vehicle regulation across the state. As of 10/4/2022, it ...
searched the offices of Aggregate Industries
Aggregate Industries, a member of the Holcim Group, is a company based in the United Kingdom with headquarters at Bardon Hill, Coalville, Leicestershire. Aggregate Industries manufactures and supplies a range of heavy building materials, prima ...
, the largest concrete supplier for the underground portions of the project, in June 2005. They seized evidence that Aggregate delivered concrete that did not meet contract specifications. In March 2006 Massachusetts Attorney General
The Massachusetts Attorney General is an elected constitutionally defined executive officer of the Massachusetts Government. The officeholder is the chief lawyer and law enforcement officer of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The officeholder ...
Tom Reilly announced plans to sue project contractors and others because of poor work on the project. Over 200 complaints were filed by the state of Massachusetts as a result of leaks, cost overruns, quality concerns, and safety violations. In total, the state has sought approximately $100 million from the contractors ($1 for every $141 spent).
In May 2006, six employees of the company were arrested and charged with conspiracy to defraud the United States. The employees were accused of reusing old concrete and double-billing loads. In July 2007, Aggregate Industries settled the case with an agreement to pay $50 million. $42 million of the settlement went to civil cases and $8 million was paid in criminal fines. The company will provide $75 million in insurance for maintenance as well as pay $500,000 toward routine checks on areas suspected to contain substandard concrete. In July 2009, two of the accused, Gerard McNally and Keith Thomas, both managers, pled guilty to charges of conspiracy, mail fraud, and filing false reports. The following month, the remaining four, Robert Prosperi, Mark Blais, Gregory Stevenson, and John Farrar, were found guilty on conspiracy and fraud charges. The four were sentenced to probation and home confinement and Blais and Farrar were additionally sentenced to community service.
Fatal ceiling collapse
 A fatal accident raised safety questions and closed part of the project for most of the summer of 2006. On July 10, 2006, concrete ceiling panels and debris weighing and measuring fell on a car traveling on the two-lane ramp connecting northbound I-93 to eastbound I-90 in
A fatal accident raised safety questions and closed part of the project for most of the summer of 2006. On July 10, 2006, concrete ceiling panels and debris weighing and measuring fell on a car traveling on the two-lane ramp connecting northbound I-93 to eastbound I-90 in South Boston
South Boston is a densely populated neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, located south and east of the Fort Point Channel and abutting Dorchester Bay. South Boston, colloquially known as Southie, has undergone several demographic transformat ...
, killing Milena Del Valle, who was a passenger, and injuring her husband, Angel Del Valle, who was driving. Immediately following the fatal ceiling collapse, Governor Mitt Romney ordered a "stem-to-stern" safety audit conducted by the engineering firm of Wiss, Janney, Elstner Associates, Inc. to look for additional areas of risk. Said Romney: "We simply cannot live in a setting where a project of this scale has the potential of threatening human life, as has already been seen". The collapse and closure of the tunnel greatly snarled traffic in the city. The resulting traffic jams are cited as contributing to the death of another person, a heart attack victim who died en route to Boston Medical Center when his ambulance was caught in one such traffic jam two weeks after the collapse. On September 1, 2006, one eastbound lane of the connector tunnel was re-opened to traffic.
Following extensive inspections and repairs, Interstate 90 east- and westbound lanes reopened in early January 2007. The final piece of the road network, a high occupancy vehicle lane connecting Interstate 93 north to the Ted Williams Tunnel
The Ted Williams Tunnel is a highway tunnel in Boston, Massachusetts. The third in the city to travel under Boston Harbor, with the Sumner Tunnel and the Callahan Tunnel, it carries the final segment of Interstate 90 (the Massachusetts Turnpik ...
, reopened on June 1, 2007.
On July 10, 2007, after a lengthy investigation, the National Transportation Safety Board found that epoxy glue used to hold the roof in place during construction was not appropriate for long-term bonding. This was determined to be the cause of the roof collapse. The Power-Fast Epoxy Adhesive used in the installation was designed for short-term loading, such as wind or earthquake loads, not long-term loading, such as the weight of a panel.
Powers Fasteners, the makers of the adhesive, revised their product specifications on May 15, 2007, to increase the safety factor
In engineering, a factor of safety (FoS), also known as (and used interchangeably with) safety factor (SF), expresses how much stronger a system is than it needs to be for an intended load. Safety factors are often calculated using detailed analy ...
from 4 to 10 for all of their epoxy products intended for use in overhead applications. The safety factor on Power-Fast Epoxy was increased from 4 to 16. On December 24, 2007, the Del Valle family announced they had reached a settlement with Powers Fasteners that would pay the family $6 million. In December 2008, Powers Fasteners agreed to pay $16 million to the state to settle manslaughter charges.
"Ginsu guardrails"
Public safety workers have called the walkway safety handrails in the Big Dig tunnels "ginsu
Ginsu () is a brand of direct marketed knives, owned by Scott Fetzer Company, a Berkshire Hathaway Company, that was made popular in the United States by being sold on television using infomercials characterized by hawker and hard sell pitch ...
guardrails," because the squared-off edges of the support posts have caused mutilations and deaths of passengers ejected from crashed vehicles. After an eighth reported death involving the safety handrails, MassDOT
The Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) oversees roads, public transit, aeronautics, and transportation licensing and registration in the US state of Massachusetts. It was created on November 1, 2009, by the 186th Session of t ...
officials announced plans to cover or remove the allegedly dangerous fixtures, but only near curves or exit ramps. This partial removal of hazards has been criticized by a safety specialist, who suggests that the handrails are just as dangerous in straight sections of the tunnel.
Lighting fixtures
In March 2011, it became known that senior MassDOT officials had failed to disclose an issue with the lighting fixtures in the O'Neill tunnel. In early February 2011, a maintenance crew found a fixture lying in the middle travel lane in the northbound tunnel. Assuming it to be simple road debris, the maintenance team picked it up and brought it back to its home facility. The next day, a supervisor passing through the yard realized that the fixture was not road debris but was in fact one of the fixtures used to light the tunnel itself. Further investigation revealed that the fixture's mounting apparatus had failed, due to galvanic corrosion of incompatible metals, caused by havingaluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
in direct contact with stainless steel, in the presence of salt water. The electrochemical
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outc ...
potential difference
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to m ...
between stainless steel and aluminum is in the range of 0.5 to 1.0V, depending on the exact alloys involved, and can cause considerable corrosion within months under unfavorable conditions.
After the discovery of the reason why the fixture had failed, a comprehensive inspection of the other fixtures in the tunnel revealed that numerous other fixtures were also in the same state of deterioration. Some of the worst fixtures were temporarily shored up with plastic ties. Moving forward with temporary repairs, members of the MassDOT administration team decided not to let the news of the systemic failure and repair of the fixtures be released to the public or to Governor Deval Patrick's administration.
, it appeared that all of the 25,000 light fixtures would have to be replaced, at an estimated cost of $54 million. The replacement work was mostly done at night, and required lane closures or occasional closing of the entire tunnel for safety, and was estimated to take up to 2 years to complete. , replacement of the light fixtures continued.
See also
*Massachusetts Turnpike
The Massachusetts Turnpike (colloquially "Mass Pike" or "the Pike") is a toll highway in the US state of Massachusetts that is maintained by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT). The turnpike begins at the New York state li ...
* Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network in ...
* Megaproject
A megaproject is an extremely large-scale investment project.
According to the ''Oxford Handbook of Megaproject Management'', "Megaprojects are large-scale, complex ventures that typically cost $1 billion or more, take many years to develop and ...
* Vincent Zarrilli – critic of the Big Dig who proposed the Boston Bypass
* Alaskan Way Viaduct replacement tunnel
The State Route 99 tunnel, also known as the Alaskan Way Viaduct replacement tunnel, is a bored highway tunnel in the city of Seattle, Washington, United States. The , double-decker tunnel carries a section of State Route 99 (SR 99) under ...
– similar project in Seattle, Washington
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region ...
* Carmel Tunnels
Highway 23, more-commonly known as the "Carmel Tunnels" ( he, מנהרות הכרמל, ''Minharot HaCarmel''), are a set of toll tunnels in Haifa, Israel. The tunnels' purpose is to reduce road congestion in the Haifa area and to provide an alt ...
– similar project in Haifa, Israel
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
* Central–Wan Chai Bypass – similar project in the areas of Central, Wan Chai and Causeway Bay, within Victoria City, Hong Kong
* Cross City Tunnel
The Cross City Tunnel is a twin-road tunnel tollway located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The tunnel links Darling Harbour on the western fringe of the central business district to Rushcutters Bay in the Eastern Suburbs. Each o ...
– similar project in Sydney, New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, Australia
* Dublin Port Tunnel
The Dublin Tunnel (Irish: ''Tollán Bhaile Átha Cliath''), originally and still commonly known as the Port Tunnel, is a road traffic tunnel in Dublin, Ireland, that forms part of the M50 motorway.
The twin tunnels form a two-lane dual carri ...
– similar project on a smaller scale in Dublin, Ireland
* Gardiner Expressway – an elevated freeway in Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
with similar future plans
* Autopista de Circunvalación M-30
The M-30 orbital motorway circles the central districts of Madrid, the capital city of Spain. It is the innermost ring road of the Spanish city, with a length of 32.5 km. Outer rings are named M-40, M-45 and M-50. Its length and the surfac ...
, and – similar project along the banks of Manzanares River
The Manzanares () is a river in the centre of the Iberian Peninsula, which flows from the Sierra de Guadarrama, passes through Madrid, and eventually empties into the Jarama river, which in turn is a right-bank tributary to the Tagus.
In its ...
, Madrid, Spain
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
* Blanka tunnel complex
Blanka Tunnel Complex is a part of the inner Prague Municipal Ring Road. It is the longest road tunnel in the Czech Republic and the longest city tunnel in Europe. The complex connects the area west of Prague Castle with Trója district in the no ...
– similar project in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and List of cities in the Czech Republic, largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 milli ...
, Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and the longest city tunnel in Europe (6.4 km / 4.0 mi)
* Yamate Tunnel
The carries the Central Circular Route (C2) of the Shuto Expressway in Tokyo, Japan, from the Takamatsu on-ramp in Toshima to near the Ōi Junction in Shinagawa. It has a length of .
Lying below the surface, about 70 percent of the tunnel was ...
– similar project on a larger scale in Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
, Japan
References
External links
Official site
on page vi of ''Highway to the Past: The Archaeology of Boston's Big Dig'' (
Massachusetts Historical Commission The Massachusetts Historical Commission (MHC) is a review board for state and federal preservation programs for the United States state of Massachusetts. It consists of 17-member panel of appointed representatives from state and private agencies and ...
, 2001)
Map of Central Artery Project
on page 21 of report on Climate Change Vulnerability
List of Massachusetts State Reports on Central Artery Project in Boston
– Central Artery * 2007 establishments in Massachusetts 2007 in Boston Engineering projects Interstate 93 Megaprojects North End, Boston Road tunnels in Massachusetts Transport infrastructure completed in 2007 Tunnels completed in 2007 Tunnels in Boston U.S. Route 1