Bhopawar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bhopawar Agency was a sub-agency of the Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 8, p. 145.
/ref>
Dictionaries of South Asia Library, Chicago University
{{coord, 22, 55, N, 75, 15, E, source:kolossus-cawiki, display=title Agencies of British India Historical Indian regions History of Madhya Pradesh 1882 establishments in India 1947 disestablishments in India de:Central India Agency#Bhopawar Agency
Central India Agency
The Central India Agency was created in 1854, by amalgamating the Western Malwa Agency with other smaller political offices which formerly reported to the Governor-General of India. The agency was overseen by a political agent who maintained ...
in British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
with the headquarters at the town of Bhopawar, so the name. Bhopawar Agency was created in 1882 from a number of princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
s in the Western Nimar
Nimar is the southwestern region of Madhya Pradesh state in west-central India. This region has sub-regions which include Nimad, Khandya and Bhuwana.
The region lies south of the Vindhya Range, and consists of two portions of the Narmada and ...
and Southern Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also sy ...
regions of Central India
Central India is a loosely defined geographical region of India. There is no clear official definition and various ones may be used. One common definition consists of the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh, which are included in al ...
belonging to the former Bhil Agency and Bhil Sub-agency with the capitals at Bhopawar and Manpur. The agency was named after Bhopawar, a village in Sardarpur tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its adminis ...
, Dhar District
Dhar district is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The historic town of Dhar is administrative headquarters of the district.
The district has an area 8,153 km2. It is bounded by the districts of Ratlam to the north, Ujja ...
of present-day Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
state. Manpur remained a strictly British territory.
The other chief towns of this region were: Badnawar
Badnawar (or Badnavar) is a Town, former pargana and a Nagar Parishad of the Dhar district in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. This is a tehsil place having 170 villages. Badnawar is around 95 km from Indore - the business capital of Madhya ...
, Kukshi
Kukshi is a town in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh state, India. Kukshi has population of around 37,482 making it a Tier-3 city and a Semi-Urban centre. It is a Nagar Parishad. Kukshi is famous for the business of cotton, mirchi, gold and sil ...
, Manawar and Sardarpur, Chadawad Estate, Dattigaon. The mighty Vindhya
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.
Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the ...
and Satpura
The Satpura Range is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range parallels the Vindhya Range to the north, and ...
ranges crossed the territory of the agency roughly from east to west, with the fertile valley of the Narmada River lying between them. The agency also included the "Bhil Country", inhabited by the Bhil people
Bhil or Bheel is an ethnic group in western India. They speak the Bhil languages, a subgroup of the Western Zone of the Indo-Aryan languages. As of 2013, Bhils were the largest tribal group in India.
Bhils are listed as tribal people of ...
./ref>
History
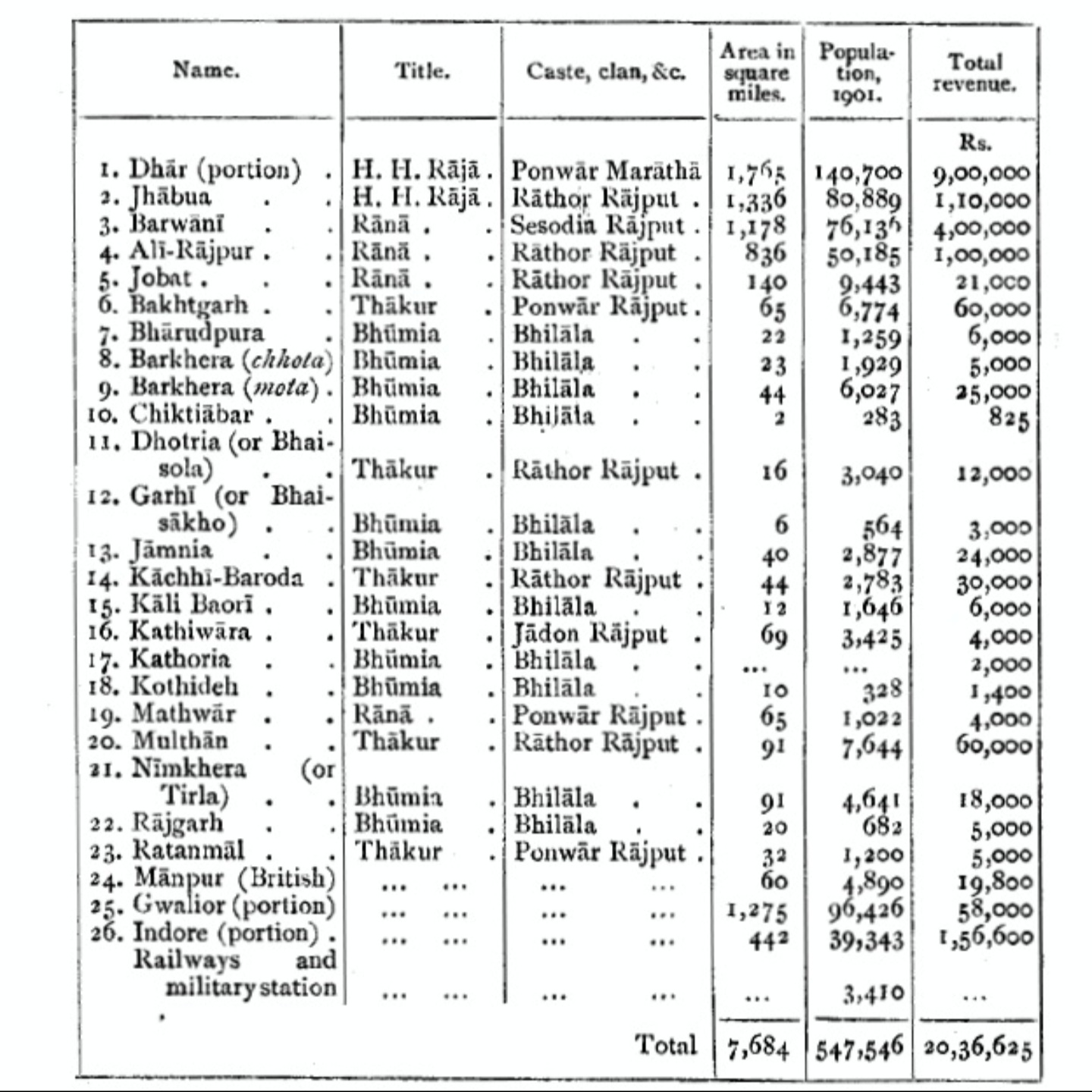
At the time of its 1882 establishment, the agency had a total area of , and its population was 547,546 according to the 1901 census. In 1904 certain districts were transferred from this agency to theIndore Residency
Indore was one of the residencies of British India. Indore Residency included most of Indore State, and, after 1933, Rewa State, which formerly belonged to Bagelkhand Agency. It was part of Central India Agency
The Central India Agency was ...
, created in 1899, and the area of Bhopawar was thus reduced by .
In 1925 Bhopawar Agency was merged into Malwa Agency
Malwa Agency was an administrative section of India's Central India Agency. The headquarters of the political agent was at Mandsaur (Mandasor) / Neemuch (Nimach). The other chief towns of the region were : Ratlam and Jaora.
History
The Malw ...
, and in 1927 the agency was renamed the Malwa-Bhopawar States Agency, which was renamed again as the Malwa Agency in 1934.
After Indian Independence in 1947, the rulers of the princely states within Malwa-Bhopawar Agency acceded to the Union of India, and the region became part of the new state of Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat, also known as Malwa Union, was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jiwajirao Scindia as its Rajpramukh. ...
. Madhya Bharat was merged into Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
on 1 November 1956.
Princely states and their feudatory estates

Salute States
Salute state
A salute state was a princely state under the British Raj that had been granted a gun salute by the British Crown (as paramount ruler); i.e., the protocolary privilege for its ruler to be greeted—originally by Royal Navy ships, later also ...
s in the agency, by precedence, with their feudatories :
# Dhar
Dhar is a city located in Dhar district of the Malwa region in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. The city is the administrative headquarters of the Dhar district. Before Indian independence from Great Britain, it was the capital of the Dh ...
, title Maharaja, Hereditary salute of 15-guns
# Alirajpur
Alirajpur is a city in the Alirajpur tehsil in Alirajpur district in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India.
Alirajpur State was formerly a princely state of India, under the Bhopawar Agency in Central India. It lay in the Malwa region of Madhya Pr ...
, title Raja, Hereditary salute of 11-guns
#* including the extinct State of Phulmaal, which was incorporated into it earlier as well as Fiefs
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
(Jagirs)
## Ondhwa
## Sondhwa.
# Barwani
Barwani or Badwani ( hi, Baḍwāni) is a municipal town in Barwani district of Madhya Pradesh, India, that is situated near the left bank of the Narmada River. It is the administrative headquarters of Barwani district and has also served a ...
, title Maharana, Hereditary salute of 11-guns
#Jhabua
Jhabua is a town and a municipality in Jhabua district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of Jhabua District.
Recently the district has got international recognition because of its endemic hen species ...
, title Raja, Hereditary salute of 11-guns (till 1927, later shifted to (Malwa Agency
Malwa Agency was an administrative section of India's Central India Agency. The headquarters of the political agent was at Mandsaur (Mandasor) / Neemuch (Nimach). The other chief towns of the region were : Ratlam and Jaora.
History
The Malw ...
)
Non-salute states
Minor and pettyPrincely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
s in the agency included (alphabetically, with their feudatories) :
# Amjhera, title Rao
# Bakhatgarh
# Chhadawad, title Rao
# Jobat, title Raja
# Kathiwara, title Thakur
# Mathwar, title Rana
# Multhan.
# Ratanmal, title Thakur.
# in Indore State
Indore State, also known as Holkar State, was a kingdom in India. Its rulers belonged to the Holkar dynasty. After 1857, Indore became a 19- gun salute Maratha princely state (a rare high rank) under the British Raj.
Indore stat ...
Territory's few enclaves like - Petlawad
Petlawad is a town and a Nagar Panchayat in the Jhabua district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, formerly the Central Provinces. The town received nationwide media coverage on 12 September 2015 when an explosion killed approximately 100 ...
Tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its adminis ...
, Dahi Jagir etc.
# also including around about seventeen Feudal lords
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
( Jagirdars) who paid direct tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conq ...
(nazarana/khillat) to Indore Durbar .
Further estates, not named above, include :
*
References
External links and Sources
Dictionaries of South Asia Library, Chicago University
{{coord, 22, 55, N, 75, 15, E, source:kolossus-cawiki, display=title Agencies of British India Historical Indian regions History of Madhya Pradesh 1882 establishments in India 1947 disestablishments in India de:Central India Agency#Bhopawar Agency