Beaufort Sea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Beaufort Sea (; french: Mer de Beaufort, Iñupiaq: ''Taġiuq'') is a 

 There is an unresolved dispute involving a wedge-shaped slice on the International Boundary in the Beaufort Sea, between the Canadian
There is an unresolved dispute involving a wedge-shaped slice on the International Boundary in the Beaufort Sea, between the Canadian
BBC News, 2 August 2010 Because of this, Canada argues that "special circumstances" apply to this border, a position that the U.S. rejects. This dispute is in this respect a mirror image of the dispute between the U.S. and Canada over the
Institute of the North On 20 August 2009,
. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 2013-03-21. though no official document has been released by September 2010.
 Several rivers such as the Kongakut River in Alaska and the Firth River in Yukon empty into the Beaufort. The major river to flow into the sea is the Mackenzie, Canada's longest, which empties into the Canadian part of the sea, west of Tuktoyaktuk. The
Several rivers such as the Kongakut River in Alaska and the Firth River in Yukon empty into the Beaufort. The major river to flow into the sea is the Mackenzie, Canada's longest, which empties into the Canadian part of the sea, west of Tuktoyaktuk. The 
 The Beaufort Sea is frozen over through the year, except for August and September when the ice breaks near the coast and opens what was once a wide strip of open water. During the 2000s, due to
The Beaufort Sea is frozen over through the year, except for August and September when the ice breaks near the coast and opens what was once a wide strip of open water. During the 2000s, due to
Encyclopædia Britannica on-line Hidden changes in the ice cover of the Beaufort Sea were discovered in 2009. Whereas the ice area remain stable, as detected by the observation satellites, so as the associated water temperature and salinity, the ice structure has changed recently. The new ice, called
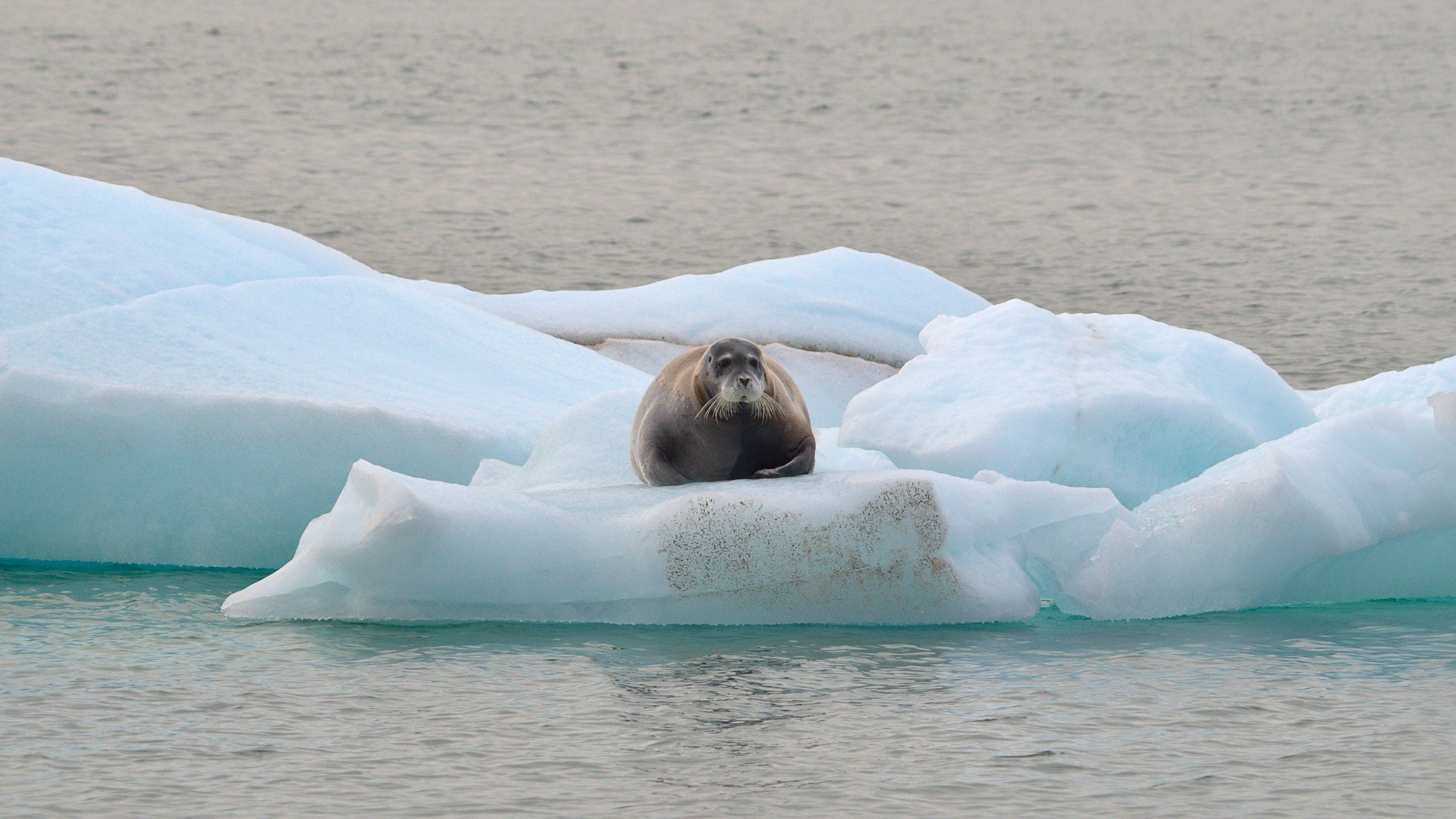 The sea hosts about 80 species of
The sea hosts about 80 species of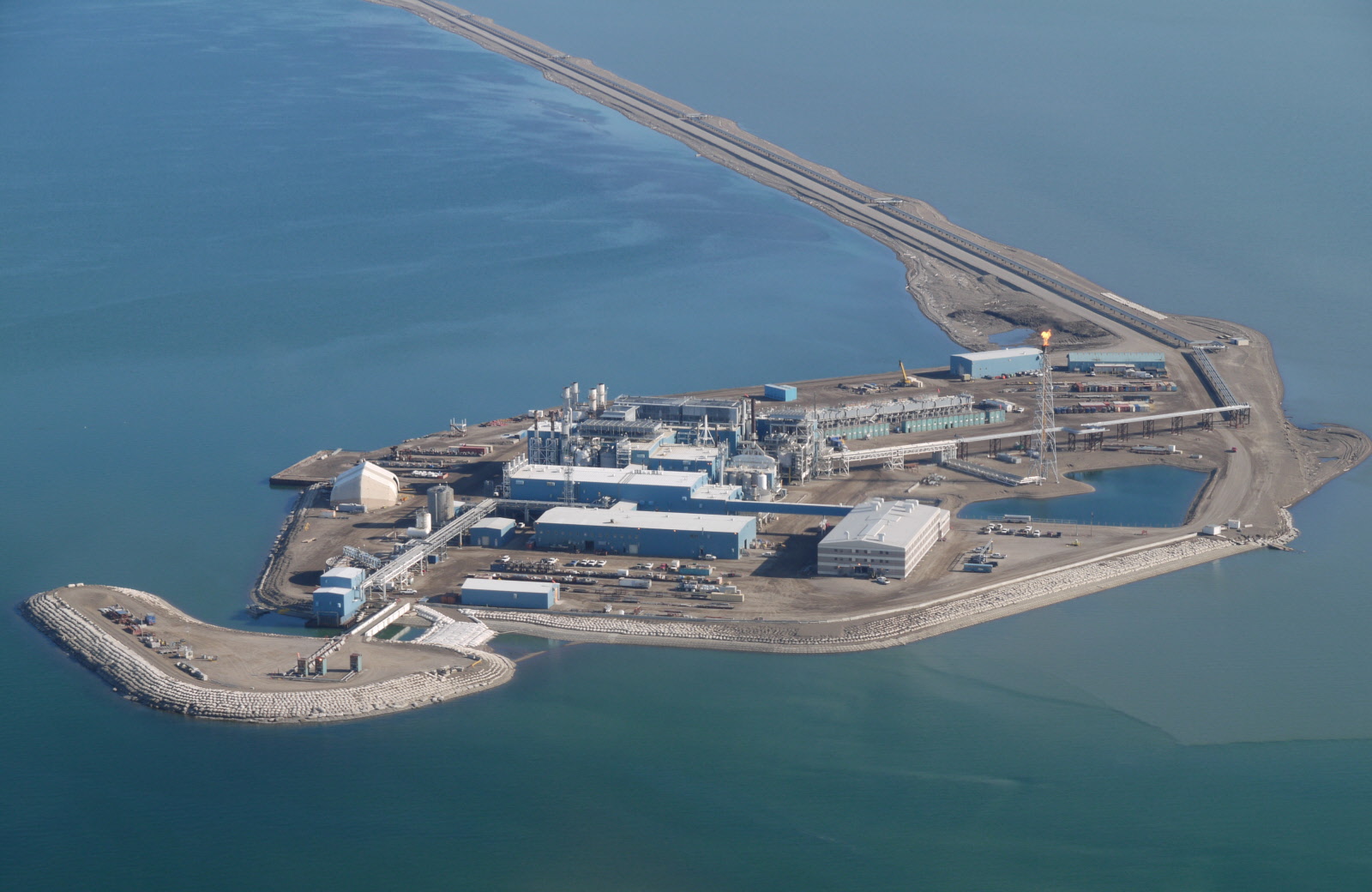  The eastern part of the sea is a major habitat of beluga whales with an estimated population of 39,000. This population is stable and might even be increasing; it is not affected by the offshore oil exploration in the area. Belugas spend summer in the coastal area and Mackenzie River delta, which are free of ice then, and in winter migrate long distances to the polynyas of the deep sea. Genetic analyses have confirmed that belugas of the Beaufort Sea are clearly distinct from those of other Canadian and Alaskan waters, despite often sharing a common wintering habitat.
The food chain of the Beaufort Sea is relatively simple: It starts with phytoplankton and epontic algae (single-cell algae associated with the lower interface of sea ice), which provide energy to zooplankton, and epontic and coastal amphipods. The latter serve as a food for seabirds and fish, primarily as polar cod and Arctic char. Polar cod is a major food of Arctic char, beluga, narwhal, seabirds and seals, which are dominated by the bearded seal (''Erignatus barbatus'') and
The eastern part of the sea is a major habitat of beluga whales with an estimated population of 39,000. This population is stable and might even be increasing; it is not affected by the offshore oil exploration in the area. Belugas spend summer in the coastal area and Mackenzie River delta, which are free of ice then, and in winter migrate long distances to the polynyas of the deep sea. Genetic analyses have confirmed that belugas of the Beaufort Sea are clearly distinct from those of other Canadian and Alaskan waters, despite often sharing a common wintering habitat.
The food chain of the Beaufort Sea is relatively simple: It starts with phytoplankton and epontic algae (single-cell algae associated with the lower interface of sea ice), which provide energy to zooplankton, and epontic and coastal amphipods. The latter serve as a food for seabirds and fish, primarily as polar cod and Arctic char. Polar cod is a major food of Arctic char, beluga, narwhal, seabirds and seals, which are dominated by the bearded seal (''Erignatus barbatus'') and
 "There is only one proposed Early-Entry site in eastern Beringia that still has proponents, Bluefish Caves in the Porcupine River Basin, Yukon Territory, Canada. Claims of great antiquity in the area .g., 30kyahave a convoluted history. A caribou tibia flesher, the most diagnostic human implement from the Old Crow basin, had been dated at near 28 kya. When redated using accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) of small amounts of remnant collagen the bone produced a 1.8 kya date (Yesner 1996b:255)". There is no evidence for anomalous occupation of Beaufort coasts in the context of Arctic cultures generally, including the arrival about 4,000 years ago by
"There is only one proposed Early-Entry site in eastern Beringia that still has proponents, Bluefish Caves in the Porcupine River Basin, Yukon Territory, Canada. Claims of great antiquity in the area .g., 30kyahave a convoluted history. A caribou tibia flesher, the most diagnostic human implement from the Old Crow basin, had been dated at near 28 kya. When redated using accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) of small amounts of remnant collagen the bone produced a 1.8 kya date (Yesner 1996b:255)". There is no evidence for anomalous occupation of Beaufort coasts in the context of Arctic cultures generally, including the arrival about 4,000 years ago by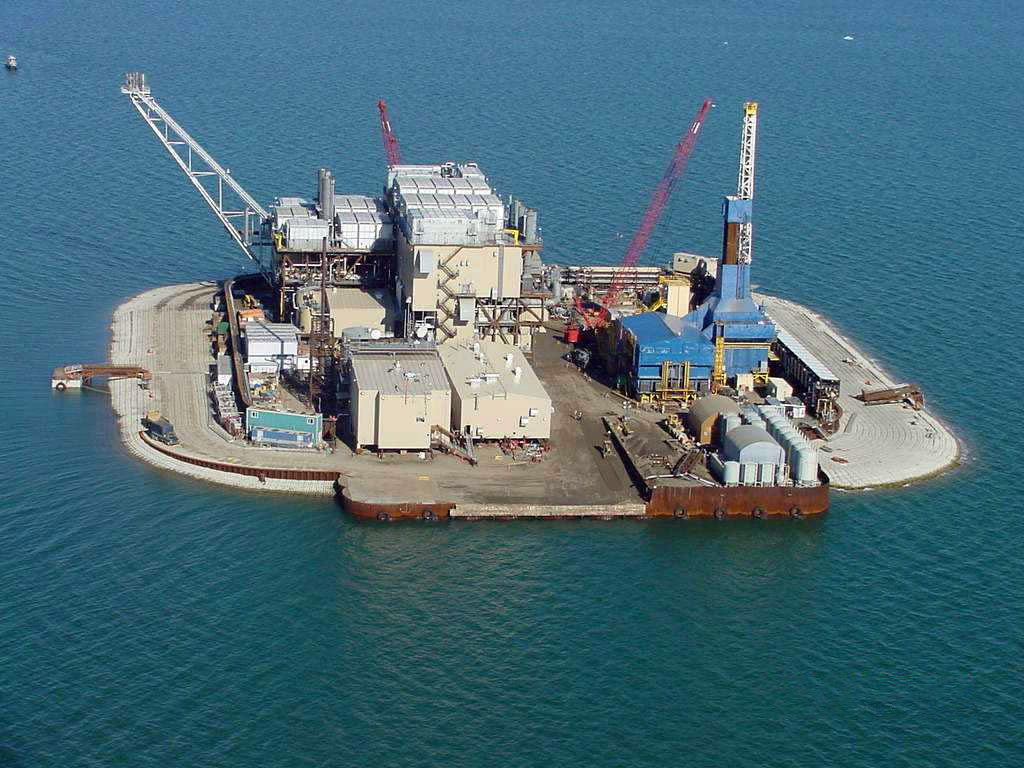  Bowhead whales were hunted in the sea between 1888 and 1914. This practice stopped, first because of the decline in whale population and then because of government regulations, but resumed in the 1990s.
The major settlements along the Beaufort Sea are
Bowhead whales were hunted in the sea between 1888 and 1914. This practice stopped, first because of the decline in whale population and then because of government regulations, but resumed in the 1990s.
The major settlements along the Beaufort Sea are
stats.gov.nt.ca) in Canada and
Petroleum provinces of the twenty-first century
AAPG, 2001 , p. 125 These activities resulted in dredging of about 46.5 million m3 of sea bottom soil, as well as discharge of drilling muds which contained barite, clay,
Perspectives on Canadian marine fisheries management
NRC Research Press, 1993
Sea Ice in the Beaufort Sea
from ''
CAC (Civil Applications Committee)/USGS Global Fiducials Program web page containing scientific description and interactive map viewer featuring declassified high-resolution time-series imagery
{{Authority control Canada–United States border disputes Disputed waters Geography of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region Bodies of water of North Slope Borough, Alaska Seas of the Arctic Ocean Seas of the United States Bodies of water of Alaska Arctic Watershed of North America Bodies of water of Yukon Bodies of water of the Northwest Territories Seas of Canada
marginal sea
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Terminology
* Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Ocea ...
of the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
, and Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk
Tuktoyaktuk , or ''Tuktuyaaqtuuq'' (Inuvialuktun: ''it looks like a caribou''), is an Inuvialuit hamlet located in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada, at the northern terminus of the Inuvik–Tuktoyaktuk Highway.Montgomer ...
, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores.
The sea, characterized by severe climate, is frozen over most of the year. Historically, only a narrow pass up to opened in August–September near its shores, but recently due to climate change in the Arctic
Major environmental issues caused by contemporary climate change in the Arctic region range from the well-known, such as the loss of sea ice or melting of the Greenland ice sheet, to more obscure, but deeply significant issues, such as permaf ...
the ice-free area in late summer has greatly enlarged. Until recently, the Beaufort Sea was known as an important reservoir for the replenishment of Arctic sea ice. Sea ice would often rotate for several years in the Beaufort Gyre
The Beaufort Gyre is one of the two major ocean currents in the Arctic Ocean. It is roughly located north of the Alaskan and Canadian coast. In the past, Arctic sea-ice would circulate in the Beaufort gyre up to several years, leading to the forma ...
, the dominant ocean current of the Beaufort Sea, growing into sturdy and thick multi-year ice.
Claims that the seacoast was populated about 30,000 years ago have been largely discredited (see below); present population density is very low. The sea contains significant resources of petroleum and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
under its shelf, such as the Amauligak field. They were discovered in the period between the 1950s and 1980s, and since the latter part of that period their exploration has become the major human activity in the area. The traditional occupations of fishery and whale and seal hunting are practiced only locally, and have no commercial significance. As a result, the sea hosts one of the largest colonies of beluga whale
The beluga whale () (''Delphinapterus leucas'') is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus ''Delphinapterus''. It is also known as the ...
s, and there is no sign of overfishing. To prevent overfishing in its waters, the US adopted precautionary commercial fisheries management plan in August 2009. In April 2011 the Canadian government signed a memorandum of understanding with the Inuvialuit
The Inuvialuit (sing. Inuvialuk; ''the real people'') or Western Canadian Inuit are Inuit who live in the western Canadian Arctic region. They, like all other Inuit, are descendants of the Thule who migrated eastward from Alaska. Their homelan ...
as a first step in developing a larger ocean management plan. The Canadian government announced in October 2014 that no new commercial fisheries in the Beaufort Sea will be considered until research has shown sustainable stocks that would be made available to Inuvialuit first.
The Canadian government designated blocks of the Beaufort Sea as Marine Protected Areas
Marine protected areas (MPA) are protected areas of seas, oceans, estuaries or in the US, the Great Lakes. These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity for a conserv ...
(MPAs). The Anguniaqvia niqiqyuam MPA surrounds the Parry Peninsula in the Amundsen Gulf
Amundsen Gulf is a gulf located mainly in the Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada with a small section in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut. It lies between Banks Island and Victoria Island and the mainland. It is approximately in leng ...
, and the Tarium Niryutait MPA is located at the Mackenzie River delta and estuary. The protected areas are set to protect species and habitats for the Inuvialuit
The Inuvialuit (sing. Inuvialuk; ''the real people'') or Western Canadian Inuit are Inuit who live in the western Canadian Arctic region. They, like all other Inuit, are descendants of the Thule who migrated eastward from Alaska. Their homelan ...
community.


Extent
TheInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organisation representing hydrography. , the IHO comprised 98 Member States.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ensure that the world's seas, oceans and navigable waters a ...
defines the limits of the Beaufort Sea as follows:
''On the North.'' A line fromPoint Barrow Point Barrow or Nuvuk is a headland on the Arctic coast in the U.S. state of Alaska, northeast of Utqiaġvik (formerly Barrow). It is the northernmost point of all the territory of the United States, at , south of the North Pole. (The nor ..., Alaska, to Lands End,Prince Patrick Island A member of the Arctic Archipelago, Prince Patrick Island is the westernmost of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in the Northwest Territories of Canada, lying northwest of Melville Island. The area of Prince Patrick Island is , making it the 55th la ...(). ''On the East.'' From Lands End through the Southwest coast of Prince Patrick Island to Griffiths Point, thence a line to Cape Prince Alfred, the Northwestern extreme ofBanks Island Banks Island is one of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago. Situated in the Inuvik Region, and part of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, of the Northwest Territories, it is separated from Victoria Island to its east by the Prince of Wa ..., through its West coast to Cape Kellet, the Southwestern point, and thence a line toCape Bathurst Cape Bathurst (Inuit: ''Awaq'') is a cape and a peninsula located on the northern coast of the Northwest Territories in Canada. Cape Bathurst is the northernmost point of mainland Northwest Territories and one of the few peninsulas in mainland Nor ...on the mainland ().
Border dispute
 There is an unresolved dispute involving a wedge-shaped slice on the International Boundary in the Beaufort Sea, between the Canadian
There is an unresolved dispute involving a wedge-shaped slice on the International Boundary in the Beaufort Sea, between the Canadian territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
of Yukon and the U.S. state of Alaska. Canada claims the maritime boundary
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Boun ...
to be along the 141st meridian west out to a distance of , following the Alaska–Yukon land border. The position of the United States is that the boundary line is perpendicular to the coast out to a distance of , following a line of equidistance from the coast. This difference creates a wedge with an area of about that is claimed by both nations.
Canada's position has its roots in the Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1825)
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg of 1825 or the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825, officially the Convention Concerning the Limits of Their Respective Possessions on the Northwest Coast of America and the Navigation of the Pacific Ocean, defined th ...
between the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
that set the boundary between the two. Canada is the successor state
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th- ...
to Great Britain in relation to this treaty, which stipulates:
Canada maintains that this treaty is extensible from the land into the Beaufort Sea along the meridian. The United States rejects this extension and instead asserts a boundary line based upon equidistance, although its position is somewhat undermined by its acceptance in 1867 of similar treaty wording and a similar interpretation under the treaty whereby it acquired Alaska. Both the U.S. and Canada agree that they are bound by the 1958 Convention on the Continental Shelf
The Convention on the Continental Shelf was an international treaty created to codify the rules of international law relating to continental shelves. The treaty, after entering into force 10 June 1964, established the rights of a sovereign stat ...
; and they both agree that the boundary should be "equitable", as determined by the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordanc ...
. They differ on what should be deemed "equitable". The U.S. contends that "equidistance is an appropriate principle for determining a maritime boundary where there are no special circumstances in the area and when equidistance results in a boundary in accordance with equitable principles". Canada contends that an equidistance principle
The equidistance principle, or principle of equidistance, is a legal concept in maritime boundary claims that a nation's maritime boundaries should conform to a median line that is equidistant from the shores of neighboring nations. The concept was ...
does not result in an equitable boundary, because distortion would occur. The coast of Yukon is concave, whereas the coast of Alaska is convex; and thus an equidistance principle would result in a significant extension of the U.S. possession. This dispute has taken on increased significance due to the possible presence of natural reserves within the wedge, which according to Canada's National Energy Board
The National Energy Board was an independent economic regulatory agency created in 1959 by the Government of Canada to oversee "international and inter-provincial aspects of the oil, gas and electric utility industries". Its head office was located ...
may contain of gas, which would cover the national consumption for 20 years, and more than of oil.US-Canada Arctic border dispute key to maritime richesBBC News, 2 August 2010 Because of this, Canada argues that "special circumstances" apply to this border, a position that the U.S. rejects. This dispute is in this respect a mirror image of the dispute between the U.S. and Canada over the
Gulf of Maine
, image =
, alt =
, caption =
, image_bathymetry = GulfofMaine2.jpg
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry = Major features of the Gulf of Maine
, location = Northeast coast of the ...
, where the U.S. argued for "special circumstances" and Canada argued for the equidistance principle. (In that latter dispute, both of those arguments were rejected, and the border was drawn based upon geometric principles taking into account geographic factors.) Neither the U.S. nor Canada has pressed for a swift resolution for the matter, or arbitration at the International Court of Justice, however; and the two have in the meantime cooperated in several measures aimed at preserving the maritime environment.
Before the end of 2004, the US leased eight plots of land below the water for oil exploration and exploitation, provoking a diplomatic protest from Canada.Sea ChangesInstitute of the North On 20 August 2009,
United States Secretary of Commerce
The United States secretary of commerce (SecCom) is the head of the United States Department of Commerce. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to commerce. The secretary rep ...
Gary Locke announced a moratorium on commercial fishing of the Beaufort Sea north of Alaska, including the disputed waters. In July 2010, US–Canada negotiations have started in Ottawa with the next meeting planned in 2011. A joint geological survey of the area has been initiated, and the issue was marked as settled by the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
,Disputes – international: CIA – The World Factbook. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 2013-03-21. though no official document has been released by September 2010.
Moratorium on commercial fishing
On August 20, 2009United States Secretary of Commerce
The United States secretary of commerce (SecCom) is the head of the United States Department of Commerce. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to commerce. The secretary rep ...
Gary Locke announced a moratorium on fishing the Beaufort Sea north of Alaska. According to Locke:
There is no widespread commercial fisheries in those waters now.
The moratorium was imposed in anticipation that global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
would make those waters accessible to commercial fisheries.
The moratorium stirred controversy in Canada because the region where the USA announced the moratorium included a large wedge-shaped region of disputed waters. Randy Boswell, of '' Canada.com'' wrote that the disputed area covered a section of the Beaufort Sea.
He wrote that Canada had filed a "diplomatic note
Diplomatic correspondence is correspondence between one state and another and is usually of a formal character. It follows several widely observed customs and style in composition, substance, presentation, and delivery and can generally be categor ...
" with the US in April when the USA first announced plans for the moratorium. Jack Layton
John Gilbert Layton (July 18, 1950 – August 22, 2011) was a Canadian academic and politician who served as the leader of the New Democratic Party (NDP) from 2003 to 2011 and leader of the Official Opposition in 2011. He previously sat on To ...
, leader of the New Democratic Party of Canada, called the U.S. moratorium over the disputed waters in the Beaufort Sea the "largest encroachment on Canadian territory in our history."
Geography
 Several rivers such as the Kongakut River in Alaska and the Firth River in Yukon empty into the Beaufort. The major river to flow into the sea is the Mackenzie, Canada's longest, which empties into the Canadian part of the sea, west of Tuktoyaktuk. The
Several rivers such as the Kongakut River in Alaska and the Firth River in Yukon empty into the Beaufort. The major river to flow into the sea is the Mackenzie, Canada's longest, which empties into the Canadian part of the sea, west of Tuktoyaktuk. The coastal shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
area is rather narrow, especially near and east of Point Barrow in the Alaskan part of the sea, and contains numerous submarine valleys. It becomes wider near the delta of the Mackenzie River but nowhere exceeds . Near the coast, the depths are shallower than but they rapidly increase northwards up to a few kilometers, transforming into a massive platform which is geologically similar to that of the oceans. There are many small islands in the sea and in the delta of the Mackenzie River. A few larger ones lie west of the Mackenzie River, such as Herschel Island
Herschel Island (french: Île d'Herschel; Inuit languages: ''Qikiqtaruk'') is an island in the Beaufort Sea (part of the Arctic Ocean), which lies off the coast of Yukon in Canada, of which it is administratively a part. It is Yukon's only ...
( off the shore, area ) and Barter Island ( from the coast, area ). The coasts are low, with the maximum elevations between . The soil is frozen all year around at the depth below about or less, forming permafrost, and only the top few tens of centimeters thaws in summer. Consequently, buildings have to be elevated above ground on wooden piles that are immersed into the permafrost.

Hydrology and climate
 The Beaufort Sea is frozen over through the year, except for August and September when the ice breaks near the coast and opens what was once a wide strip of open water. During the 2000s, due to
The Beaufort Sea is frozen over through the year, except for August and September when the ice breaks near the coast and opens what was once a wide strip of open water. During the 2000s, due to climate change in the Arctic
Major environmental issues caused by contemporary climate change in the Arctic region range from the well-known, such as the loss of sea ice or melting of the Greenland ice sheet, to more obscure, but deeply significant issues, such as permaf ...
, the ice-free area in late summer greatly enlarged. During the record minimum extent of Arctic sea ice in September, 2012, the sea ice boundary had retreated northward much farther than normal from the coast.
The channels of the Mackenzie River thaw earlier, in late May–early June. This thawing increases the average water discharge from about .Mackenzie RiverEncyclopædia Britannica on-line Hidden changes in the ice cover of the Beaufort Sea were discovered in 2009. Whereas the ice area remain stable, as detected by the observation satellites, so as the associated water temperature and salinity, the ice structure has changed recently. The new ice, called
rotten ice
Rotten ice is a loose term for ice that is melting or structurally disintegrating due to being honeycombed by liquid water, air, or contaminants trapped between the initial growth of ice crystals. It may appear transparent or splotchy grey, and it ...
, is thinner and much weaker structurally.
The sea water has a stable temperature and is separated into four distinct layers as follows. The top are surface water which has a temperature of in summer and in winter. The next layer is formed by the inflows from the Pacific Ocean and Bering Sea coming through the Bering Strait; it extends up to the North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
. The warmest, deep Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
layer has the temperatures between 0 and 1 °C (32 to 34 °F), and water at the bottom is a bit colder at −0.4 to −0.8 °C (31.3 to 30.6 °F). The average salinity varies between 28‰ and 32‰ (parts per thousand) from south to north. Typical air temperatures (at Tuktoyaktuk) are in January and in July.
The water currents form the clockwise-directed Beaufort Gyre
The Beaufort Gyre is one of the two major ocean currents in the Arctic Ocean. It is roughly located north of the Alaskan and Canadian coast. In the past, Arctic sea-ice would circulate in the Beaufort gyre up to several years, leading to the forma ...
, that results in south-westerly and westerly currents near the shores. The Mackenzie River partly affects this circulation inducing minor eastwards streams near its mouth. The river annually brings about 15 million tonnes of sediments which are rich in dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
and calcium carbonate. Those deposits are spread over the sea and mixed with mud and gravel.
Flora and fauna
The shoreline of the Beaufort Sea is covered withtundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
and marks the northern limit of the terrestrial range of the polar bear in North America. The Mackenzie River is an important habitat for whales and seabirds and is still relatively untouched by commercial traffic. The delta of Mackenzie River contains numerous lakes and ponds which are inhabited by muskrat.
 The sea hosts about 80 species of
The sea hosts about 80 species of zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
, more than 70 species of phytoplankton, and nearly 700 species of polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made ...
s, bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a ...
ns, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s and mollusks, but their total volume is relatively small owing to the cold climate. Major fish species include polar cod
''Boreogadus saida'', known as the polar cod or as the Arctic cod, is a fish of the cod family Gadidae, related to the true cod (genus ''Gadus''). Another fish species for which both the common names Arctic cod and polar cod are used is ''Arct ...
(''Boreogadus saida''), Arctic cod
''Arctogadus glacialis'', known also with ambiguous common names Arctic cod and polar cod, is an Arctic species of fish in the cod family Gadidae, related to the true cod (genus ''Gadus''). ''Arctogadus glacialis'' is found in icy water. They ...
(''Arctogadus glacialis''), saffron cod
The saffron cod ''(Eleginus gracilis)'' is a commercially harvested fish closely related to true cods (genus '' Gadus''). It is dark grey-green to brown, with spots on its sides and pale towards the belly. It may grow to 55 cm and weigh up t ...
(''Eleginus gracilis''), Arctic char
The Arctic char or Arctic charr (''Salvelinus alpinus'') is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes and arctic and subarctic coastal waters. Its distribution is Circumpolar North. It spawns in freshwater and populat ...
(''Salvelinus alpinus''), chum salmon (''Oncorhynchus keta''), Arctic cisco
Arctic cisco (''Coregonus autumnalis''), also known as omul russian: Омуль, is an anadromous species of freshwater whitefish that inhabits the Arctic parts of Siberia, Alaska and Canada. It has a close freshwater relative in several lakes of ...
(''Coregonus autumnalis''), least cisco
''Coregonus sardinella'', known as the least cisco or the sardine cisco, is a fresh- and brackishwater salmonid fish that inhabits rivers, estuaries and coastal waters of the marginal seas of the Arctic Basin, as well as some large lakes of tho ...
(''Coregonus sardinella''), lake whitefish
The lake whitefish (''Coregonus clupeaformis'') is a species of freshwater whitefish from North America. Lake whitefish are found throughout much of Canada and parts of the northern United States, including all of the Great Lakes. The lake white ...
(''Coregonus clupeaformis''), broad whitefish
The broad whitefish (''Coregonus nasus'') is a freshwater whitefish species. Dark silvery in colour, and like a herring in its shape, its distinctive features include a convex head, short gill rakers, and a mild overbite. It is found in the Arcti ...
(''Coregonus nasus''), Pacific herring
The Pacific herring (''Clupea pallasii'') is a species of the herring family associated with the Pacific Ocean environment of North America and northeast Asia. It is a silvery fish with unspined fins and a deeply forked caudal fin. The distribut ...
(''Clupea pallasii''), fourhorn sculpin
The fourhorn sculpin (''Myoxocephalus quadricornis'') is a species of fish in the family Cottidae. It is a demersal fish distributed mainly in brackish arctic coastal waters in Canada, Greenland, Russia, and Alaska, and also as a relict in the bo ...
(''Myoxocephalus quadricornis''), inconnu (''Stenodus leucichthys'') and flatfish.
 The eastern part of the sea is a major habitat of beluga whales with an estimated population of 39,000. This population is stable and might even be increasing; it is not affected by the offshore oil exploration in the area. Belugas spend summer in the coastal area and Mackenzie River delta, which are free of ice then, and in winter migrate long distances to the polynyas of the deep sea. Genetic analyses have confirmed that belugas of the Beaufort Sea are clearly distinct from those of other Canadian and Alaskan waters, despite often sharing a common wintering habitat.
The food chain of the Beaufort Sea is relatively simple: It starts with phytoplankton and epontic algae (single-cell algae associated with the lower interface of sea ice), which provide energy to zooplankton, and epontic and coastal amphipods. The latter serve as a food for seabirds and fish, primarily as polar cod and Arctic char. Polar cod is a major food of Arctic char, beluga, narwhal, seabirds and seals, which are dominated by the bearded seal (''Erignatus barbatus'') and
The eastern part of the sea is a major habitat of beluga whales with an estimated population of 39,000. This population is stable and might even be increasing; it is not affected by the offshore oil exploration in the area. Belugas spend summer in the coastal area and Mackenzie River delta, which are free of ice then, and in winter migrate long distances to the polynyas of the deep sea. Genetic analyses have confirmed that belugas of the Beaufort Sea are clearly distinct from those of other Canadian and Alaskan waters, despite often sharing a common wintering habitat.
The food chain of the Beaufort Sea is relatively simple: It starts with phytoplankton and epontic algae (single-cell algae associated with the lower interface of sea ice), which provide energy to zooplankton, and epontic and coastal amphipods. The latter serve as a food for seabirds and fish, primarily as polar cod and Arctic char. Polar cod is a major food of Arctic char, beluga, narwhal, seabirds and seals, which are dominated by the bearded seal (''Erignatus barbatus'') and ringed seal
The ringed seal (''Pusa hispida'') is an earless seal inhabiting the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. The ringed seal is a relatively small seal, rarely greater than 1.5 m in length, with a distinctive patterning of dark spots surrounded by light ...
(''Pusa hispida''). Bearded seal and walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
also feed on benthic invertebrates. On top of the food pyramid stands the polar bear, which feeds primarily on seals, but also on any large marine mammals when it has a chance, such as carcasses and whales trapped in ice fields.Parsons, pp. 215–217
Human activities
 "There is only one proposed Early-Entry site in eastern Beringia that still has proponents, Bluefish Caves in the Porcupine River Basin, Yukon Territory, Canada. Claims of great antiquity in the area .g., 30kyahave a convoluted history. A caribou tibia flesher, the most diagnostic human implement from the Old Crow basin, had been dated at near 28 kya. When redated using accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) of small amounts of remnant collagen the bone produced a 1.8 kya date (Yesner 1996b:255)". There is no evidence for anomalous occupation of Beaufort coasts in the context of Arctic cultures generally, including the arrival about 4,000 years ago by
"There is only one proposed Early-Entry site in eastern Beringia that still has proponents, Bluefish Caves in the Porcupine River Basin, Yukon Territory, Canada. Claims of great antiquity in the area .g., 30kyahave a convoluted history. A caribou tibia flesher, the most diagnostic human implement from the Old Crow basin, had been dated at near 28 kya. When redated using accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) of small amounts of remnant collagen the bone produced a 1.8 kya date (Yesner 1996b:255)". There is no evidence for anomalous occupation of Beaufort coasts in the context of Arctic cultures generally, including the arrival about 4,000 years ago by Paleo-Eskimo
The Paleo-Eskimo (also pre-Thule or pre-Inuit) were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka (e.g., Chertov Ovrag) in present-day Russia across North America to Greenland prior to the arrival of the modern Inuit (Eskimo) and rel ...
s such as the Dorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
, around 1,000 years ago by the Thule
Thule ( grc-gre, Θούλη, Thoúlē; la, Thūlē) is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. Modern interpretations have included Orkney, Shetland, northern Scotland, the island of Saar ...
and finally by the modern Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
. From early ages, they practiced fishing – bones of Arctic char were found at the 4,000 years old settlements. While originally they lived nomadic life, later, they started to form permanent settlements. Their population is increasing, but the unemployment rate is relatively high. Bowhead whales were hunted in the sea between 1888 and 1914. This practice stopped, first because of the decline in whale population and then because of government regulations, but resumed in the 1990s.
The major settlements along the Beaufort Sea are
Bowhead whales were hunted in the sea between 1888 and 1914. This practice stopped, first because of the decline in whale population and then because of government regulations, but resumed in the 1990s.
The major settlements along the Beaufort Sea are Tuktoyaktuk
Tuktoyaktuk , or ''Tuktuyaaqtuuq'' (Inuvialuktun: ''it looks like a caribou''), is an Inuvialuit hamlet located in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada, at the northern terminus of the Inuvik–Tuktoyaktuk Highway.Montgomer ...
(population 930 in 2009Tuktoyaktuk – Statistical Profilestats.gov.nt.ca) in Canada and
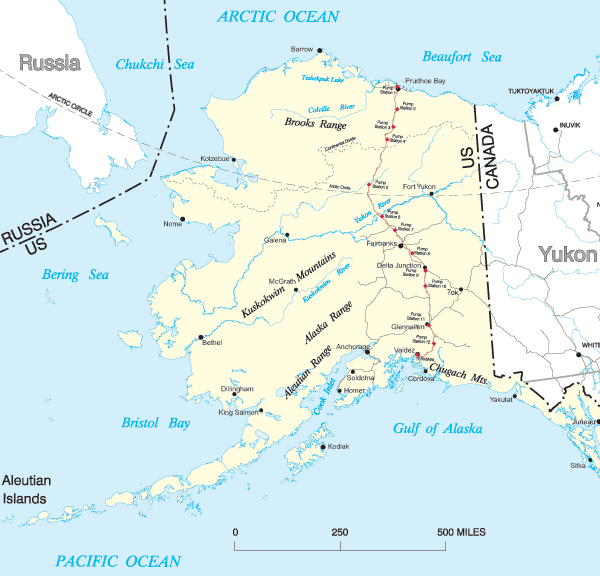
Prudhoe Bay, Alaska
Prudhoe Bay is a census-designated place (CDP) located in North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2010 census, the population of the CDP was 2,174 people, up from just five residents in the 2000 census; however, at any give ...
. Although Prudhoe Bay is permanently populated by only a few people, there are thousands of contract workers in the area employed on petroleum production at the Prudhoe Bay Oil Field
Prudhoe Bay Oil Field is a large oil field on Alaska's North Slope. It is the largest oil field in North America, covering and originally containing approximately of oil.
, which is on the coastal lowland known as the North Slope. Artificial island
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those th ...
s, such as Endicott and Northstar Northstar may refer to:
* Polaris, a star
Arts and entertainment
* Northstar (band), an emo band from Alabama
* Northstar (rap group), a rap group affiliated with the Wu-Tang Clan
* "Northstar", a 2019 song by XXXTentacion from the album ''Bad Vi ...
, have been raised near the shores in 1987 and 2001, respectively. The crude oil is transported through the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) is an oil transportation system spanning Alaska, including the trans-Alaska crude-oil pipeline, 11 pump stations, several hundred miles of feeder pipelines, and the Valdez Marine Terminal. TAPS is one o ...
to the southern port of Valdez.
Fishing and sea hunting are practised by the local inhabitants and have no commercial value, especially after a US moratorium on commercial fishing of the Beaufort Sea, adopted in 2009. Trapping of muskrat at the Mackenzie River delta was the main source of income for the Athabaskan First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
peoples and Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
during 1920–1960, but has since declined.
Oil and gas exploration
The Beaufort Sea contains major gas and petroleum reserves beneath the seabed, a continuation of proven reserves in the nearby Mackenzie River and North Slope. The Beaufort Sea was first explored for sub-shelf hydrocarbons in the 1950s and estimated to contain about of oil and of natural gas under its coastal shelf. Offshore drilling began in 1972; about 70 wells were set up by the 1980s and 200 wells by 2000.Marlan W. Downey, William Andrew Morgan, Jack C. Threet, American Association of Petroleum GeologistPetroleum provinces of the twenty-first century
AAPG, 2001 , p. 125 These activities resulted in dredging of about 46.5 million m3 of sea bottom soil, as well as discharge of drilling muds which contained barite, clay,
caustic soda
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
, and heavy metals zinc, copper, lead, chromium, cobalt, nickel, cadmium and mercury. About of oil was produced in 1986.Parsons, p. 233
A major gas field, named Taglu Gas Field, was discovered in the Mackenzie River delta in 1971, followed by the Parson Lake field and Niglintgak field. The estimated gas reserves of these fields are , and , respectively. Moreover, further into the sea from the Mackenzie delta lies the Amauligak field. This, the largest known oil deposit of the Beaufort Sea, was discovered in 1984, and is estimated to contain of oil and of gas. The development of these fields is hindered by their remote location. This problem was alleviated for Prudhoe Bay by constructing the Trans-Alaska Pipeline, but is limiting regular commercial production at Mackenzie River deposits. For example, the Amauligak Project was started soon after the discovery of the field. In September 1985, the tanker ''Gulf Beaufort'' has transported of crude oil to Japan, which was the first shipment of oil from the Arctic deposits. However, the project has stalled after that.
In July 2017, the U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management
The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior, established in 2010 by Secretarial Order.
The Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act (OCSLA) states: "...the outer Continental Shelf is a v ...
approved a plan to allow Eni, an Italian multinational oil and gas company, to drill four oil exploration wells on Spy Island, one of four artificial islands
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those th ...
in the Beaufort Sea.
In popular culture
Stan Rogers references the Beaufort Sea in his popular Canadian Folk Song "Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
".
See also
* Arctic policy of the United States *Canadian Internal Waters Canadian Internal Waters is a Canadian term for the waters "on the landward side of the baselines of the territorial sea of Canada."
Definition
The baselines are defined as "the low-water line along the coast or on a low-tide elevation that is situ ...
* List of areas disputed by Canada and the United States
Canada and the United States have one land dispute over Machias Seal Island (off the coast of Maine), and four other maritime disputes in the Arctic and Pacific. Although they share the longest international border in the world, the two countri ...
* List of seas
* Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
* Petroleum exploration in the Arctic
The exploration of the Arctic for petroleum is considered to be quite technically challenging. However, recent technological developments, the melting of Arctic permafrost, as well as relatively high oil prices, have allowed for exploration. As a ...
References
Bibliography
* L. S. Parsons, William Henry Lear, National Research Council of CanadPerspectives on Canadian marine fisheries management
NRC Research Press, 1993
Further reading
* * * *External links
Sea Ice in the Beaufort Sea
from ''
NASA Earth Observatory
NASA Earth Observatory is an online publishing outlet for NASA which was created in 1999. It is the principal source of satellite imagery and other scientific information pertaining to the climate and the environment which are being provided by NA ...
''
CAC (Civil Applications Committee)/USGS Global Fiducials Program web page containing scientific description and interactive map viewer featuring declassified high-resolution time-series imagery
{{Authority control Canada–United States border disputes Disputed waters Geography of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region Bodies of water of North Slope Borough, Alaska Seas of the Arctic Ocean Seas of the United States Bodies of water of Alaska Arctic Watershed of North America Bodies of water of Yukon Bodies of water of the Northwest Territories Seas of Canada