Battle of Badr on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Badr ( ar, غَزْوَةُ بَدِرْ ), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ) in the
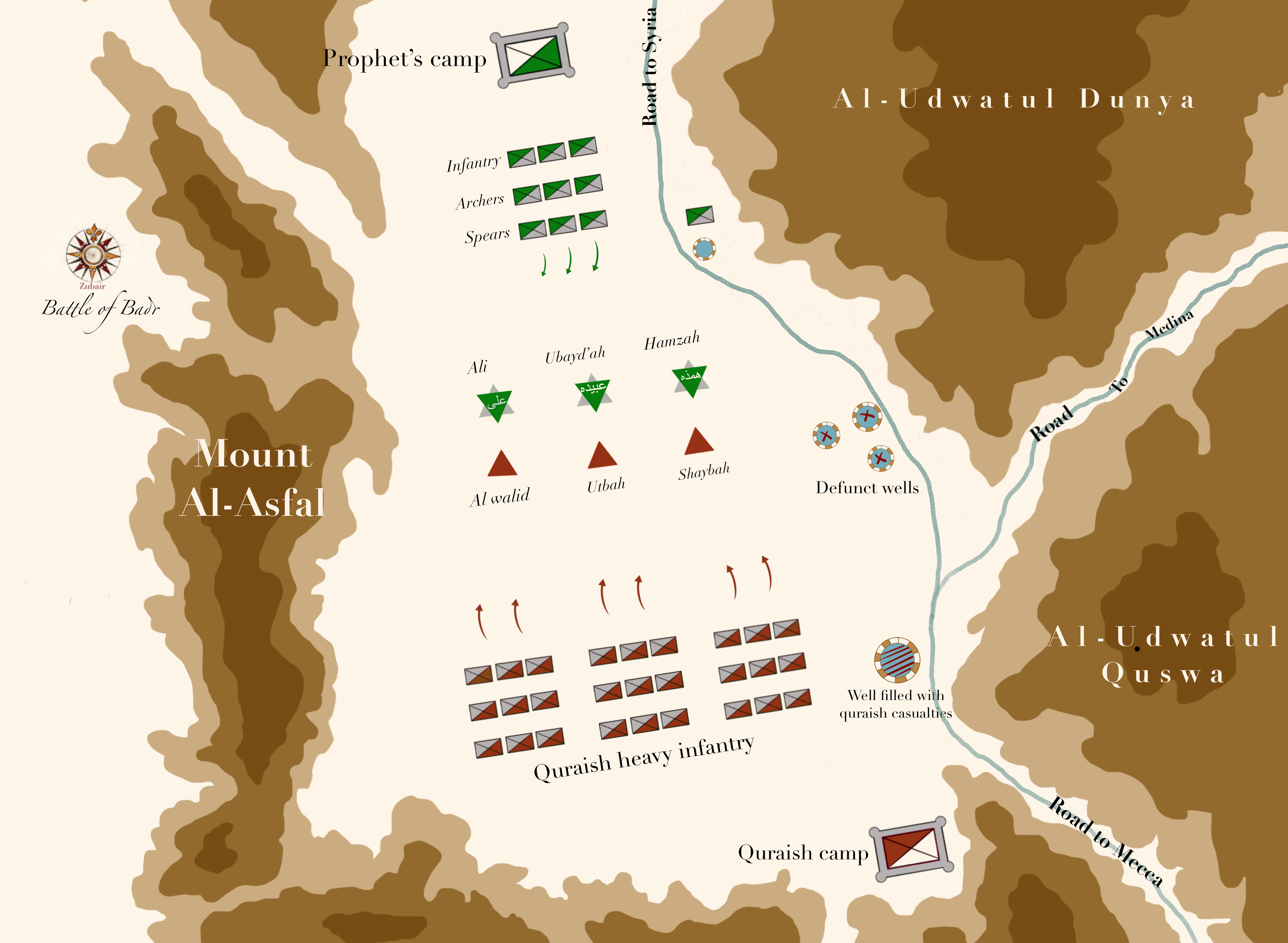 The valley of Badr is surrounded by two large sand dunes to the east, called ''al-'Udwatud Dunya'' (the near side of the valley) and ''al-'Udwatul Quswa'' (the far side of the valley). The Qur'an speaks of these two in Surah 8, verse 42. The west of the valley was covered by the al-Asfal Mountain (''Jabal Al-Asfal'') with an opening between it and another hill in the northwest.
Between al-'Udwatud Dunya and al-'Udwatul Quswa was an opening, which was the primary route to
The valley of Badr is surrounded by two large sand dunes to the east, called ''al-'Udwatud Dunya'' (the near side of the valley) and ''al-'Udwatul Quswa'' (the far side of the valley). The Qur'an speaks of these two in Surah 8, verse 42. The west of the valley was covered by the al-Asfal Mountain (''Jabal Al-Asfal'') with an opening between it and another hill in the northwest.
Between al-'Udwatud Dunya and al-'Udwatul Quswa was an opening, which was the primary route to
 Muhammad was able to gather an army of 313-317 men. Sources vary upon the exact number, but the generally accepted number is 313. This army consisted of 82 Muhajirun, 61 men from the 'Aws and 170 men from the Khazraj. They were not well-equipped for a major conflict nor prepared. They only had two horses, and those belonged to
Muhammad was able to gather an army of 313-317 men. Sources vary upon the exact number, but the generally accepted number is 313. This army consisted of 82 Muhajirun, 61 men from the 'Aws and 170 men from the Khazraj. They were not well-equipped for a major conflict nor prepared. They only had two horses, and those belonged to
 Muhammad held a
Muhammad held a

"Libyan Rebels Say They Are Closing In on Tripoli"
Battle of Badr, 17th Ramadan 624 A.D
Badr
at IslamAnswers.Net
The first battle of Islam at Badr
Islamic Occasions Network
Analysis of Qur'anic verses by Irshaad Hussain. {{Authority control Badr Campaigns led by Muhammad Angelic apparitions Muhammad in Medina
Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan, 2 AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
. Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
, commanding an army of his Sahaba
The Companions of the Prophet ( ar, اَلصَّحَابَةُ; ''aṣ-ṣaḥāba'' meaning "the companions", from the verb meaning "accompany", "keep company with", "associate with") were the disciples and followers of Muhammad who saw or m ...
, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām
ʿAmr ibn Hishām al-Makhzūmī ( ar, عمرو بن هشام المخزومي), (570 – 13 March 624), also known as Abu Jahl (lit. 'Father of Ignorance'), was one of the Meccan polytheist pagan leaders from the Quraysh known for his opposition ...
, better known as Abu Jahl. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
and his tribe. Prior to the battle, the Muslims and the Meccans had fought several smaller skirmishes in late 623 and early 624.
Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans after his migration to Medina, seeing it as repayment for his people, the Muhajirun. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya ibn Abd Shams ( ar, صخر بن حرب بن أمية بن عبد شمس, Ṣakhr ibn Ḥarb ibn Umayya ibn ʿAbd Shams; ), better known by his '' kunya'' Abu Sufyan ( ar, أبو سفيان, Abū Sufyān), was a prominent ...
, Muhammad gathered a small expeditionary force to capture it. Abu Sufyan, learning of the Muslim plan to ambush his caravan, changed course and took a longer route away from Muhammad's base at Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
and sent a messenger to Mecca, asking for help. Abu Jahl commanded an army nearly one-thousand strong, approaching Badr and encamping at the sand dune al-'Udwatul Quswa.
Badr was the first large-scale engagement between the Muslims and Quraysh Meccans. Advancing from the north, the Muslims faced the Meccans. The battle began with duels between the warriors on both sides, following which the Meccans charged upon the Muslims under a cover of arrows. The Muslims countered their charge and broke the Meccan lines, killing several important Quraishi leaders including Abu Jahl
ʿAmr ibn Hishām al-Makhzūmī ( ar, عمرو بن هشام المخزومي), (570 – 13 March 624), also known as Abu Jahl (lit. 'Father of Ignorance'), was one of the Meccan polytheist pagan leaders from the Quraysh known for his opposition ...
and Umayyah ibn Khalaf
Umayya ibn Khalaf () (died 13 March 624) was an Arab slave master and the chieftain of the Banu Jumah of the Quraysh in the seventh century. He was one of the chief opponents against the Muslims led by Muhammad. Umayya is best known as the master ...
.
The Muslim victory strengthened Muhammad's position; The Medinese eagerly joined his future expeditions and tribes outside Medina openly allied with Muhammad. The battle has been passed down in Islamic history as a decisive victory attributable to divine intervention
Divine intervention is an event that occurs when a deity (i.e. God or a god) becomes actively involved in changing some situation in human affairs. In contrast to other kinds of divine action, the expression "divine ''intervention''" implies that ...
, and by other sources to the strategic prowess of Muhammad.
Background
After theHijra
Hijra, Hijrah, Hegira, Hejira, Hijrat or Hijri may refer to:
Islam
* Hijrah (often written as ''Hejira'' in older texts), the migration of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE
* Migration to Abyssinia or First Hegira, of Muhammad's followers ...
(migration to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
) in 622 CE, the population of Medina chose Muhammad to be the leader of the community. Muhammad's followers decided to raid the caravans of the Meccans as they passed by Medina. This decision was taken in response to the Meccans persecution of the Muslims and their forceful seizing of Muslim land and property following the Hijra.John Esposito, ''Islam'', Expanded edition, Oxford University Press, p.4-5 In early 624, a caravan of the Quraysh led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya ibn Abd Shams ( ar, صخر بن حرب بن أمية بن عبد شمس, Ṣakhr ibn Ḥarb ibn Umayya ibn ʿAbd Shams; ), better known by his '' kunya'' Abu Sufyan ( ar, أبو سفيان, Abū Sufyān), was a prominent ...
carrying wealth and goods
In economics, goods are items that satisfy human wants
and provide utility, for example, to a consumer making a purchase of a satisfying product. A common distinction is made between goods which are transferable, and services, which are not t ...
from the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
was returning to Mecca. Knowing of the threat of Muhammad's growing influence in the region, Abu Sufyan routinely sent spies to check on Muhammad and warn him of any Muslim movement in the area.
Muhammad had gathered a small expeditionary force of around 300 men to intercept the caravan. Abu Sufyan's spies informed him of the Muslims' plot to ambush his caravan. Fearing the loss of wealth that was imminent, Abu Sufyan sent the messenger Damdam bin 'Amr al-Ghifari to the Quraish. Damdam, upon his arrival at the Ka'bah
The Kaaba (, ), also spelled Ka'bah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah ( ar, ٱلْكَعْبَة ٱلْمُشَرَّفَة, lit=Honored Ka'bah, links=no, translit=al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah), is a building at the c ...
, cut off the nose and ears of his camel, turned its saddle upside down, tore off his shirt and cried:"O Quraish! Your merchandise! It is with Abu Sufyan. The caravan is being intercepted by Muhammad and his companions. I cannot say what would have happened to them. Help! Help!"Abu Sufyan had rerouted his caravan toward the
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
and escaped the Muslim threat by Damdam's arrival at Mecca.
Battlefield
 The valley of Badr is surrounded by two large sand dunes to the east, called ''al-'Udwatud Dunya'' (the near side of the valley) and ''al-'Udwatul Quswa'' (the far side of the valley). The Qur'an speaks of these two in Surah 8, verse 42. The west of the valley was covered by the al-Asfal Mountain (''Jabal Al-Asfal'') with an opening between it and another hill in the northwest.
Between al-'Udwatud Dunya and al-'Udwatul Quswa was an opening, which was the primary route to
The valley of Badr is surrounded by two large sand dunes to the east, called ''al-'Udwatud Dunya'' (the near side of the valley) and ''al-'Udwatul Quswa'' (the far side of the valley). The Qur'an speaks of these two in Surah 8, verse 42. The west of the valley was covered by the al-Asfal Mountain (''Jabal Al-Asfal'') with an opening between it and another hill in the northwest.
Between al-'Udwatud Dunya and al-'Udwatul Quswa was an opening, which was the primary route to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
. Muhammad and his army did not approach the battlefield from here, they came from the north, as they were originally planning to target the caravan, which was moving from the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
in the north, to Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
in the south. Between al-'Udwatul Quswa and the hill covering the southern part of the battlefield was another opening, which was the primary route from Mecca.
The Quraish had encamped in the south-eastern portion of the valley near the road to Mecca, while Muhammad and his army had encamped in some date-palms in the north. They had taken a well near the center of the western margin of al-'Udwatul Dunya and destroyed the other wells near the road to Medina to prevent the Makkans from getting any water. Another well situated at the end of the road to Mecca was later filled with the dead bodies of the dead Makkans.
Rainfall
On the night of 11 March (15 Ramadan), it had rained over the battlefield and the surrounding region. Muslims believe this was a blessing from Allah for the believers and a curse for the disbelievers, who suffered hardship in trying to climb the muddy slope.Battle
Muslim march to Badr
Zubayr ibn al-Awwam
Az Zubayr ( ar, الزبير) is a city in and the capital of Al-Zubair District, part of the Basra Governorate of Iraq. The city is just south of Basra. The name can also refer to the old Emirate of Zubair.
The name is also sometimes written ...
and al-Miqdad ibn 'Amr. The entire army had 70 camels, meaning that they had one camel for two to three men to ride alternatively.Lings, pp. 138–39 Muhammad shared a camel with 'Ali ibn Abu Talib and Marthad ibn Abi Marthad al-Ghanawi. The guardianship and administration of Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
was entrusted with Ibn Umm Maktum, but later with Abu Lubaba ibn 'Abd al-Mundhir. Muhammad handed a white standard to Mus‘ab ibn 'Umair al-Qurashi al-'Abdari. The army was divided into two battalions: one of the 82 Muhajirun and the other of the 231 Ansar. The flag of the Muhajirun was carried by 'Ali ibn Abu Talib, while that of the Ansar was carried by Sa'd ibn Mu'adh
Saʿd ibn Muʿādh ( ar, سعد ابن معاذ) () was the chief of the Aws tribe in Medina and one of the prominent companions of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon Him). He died shortly after the Battle of the Trench.
Family
Sa'd wa ...
. az-Zubayr commanded the right flank, while al-Miqdad commanded the left. And the rear of the army was commanded by Qays bin Abi Sa'sa'ah.
With Muhammad in the lead, the army marched out along the main road to Mecca, from the north. At Safra', he dispatched Basbas al-Juhani and 'Adi al-Juhani to scout for the Quraish. The future Caliph Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic prop ...
stayed behind to care of his sick wife Ruqayyah Ruqayya ( ar, رقيّة) is an Arabic female given name meaning "spell, enchantment, or incantation.”
It is not to be confused with a separate Arabic term "Ruqia" from Arabic رقى (ruqia) meaning “to rise” or “ascend.”
Ruqayya bint M ...
, the daughter of Muhammad, who later died from illness. Salman al-Farsi
Salman the Persian or Salmān al-Fārsī ( ar, سَلْمَان ٱلْفَارِسِيّ), born Rūzbeh Khoshnūdān ( fa, ), was a Persian companion (Sahaba) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was raised as a Zoroastrian in Sasanian Persia, t ...
also could not join the battle, as he was still not a free man.
Qurayshi advance toward Badr
All of the clans of the Quraish except the Banu 'Adi quickly assembled an excited army of around 1300 men, 100 horses and a large number of camels. Moving swiftly towards Badr, they passed the valleys of 'Usfan, Qadid and al-Juhfah. At al-Juhfah, another messenger from Abu Sufyan informed them of the safety of their merchandise and wealth. Upon receiving this message, the Makkan army expressed delight and showed a desire to return home.Abu Jahl
ʿAmr ibn Hishām al-Makhzūmī ( ar, عمرو بن هشام المخزومي), (570 – 13 March 624), also known as Abu Jahl (lit. 'Father of Ignorance'), was one of the Meccan polytheist pagan leaders from the Quraysh known for his opposition ...
was not interested in returning and insisted on proceeding to Badr, and holding a feast
A banquet (; ) is a formal large meal where a number of people consume food together. Banquets are traditionally held to enhance the prestige of a host, or reinforce social bonds among joint contributors. Modern examples of these purposes i ...
there to show the Muslims and the surrounding tribes that they were superior. Despite Abu Jahl's threat and insistence, the Banu Zahrah, numbering around 300, broke away from the army and returned to Mecca, on the advice of Al-Akhnas ibn Shurayq. Muhammad's clan, the Banu Hashim, also attempted to break away but were threatened by Abu Jahl to stay. Many of the Qurayshi nobles, including Abu Jahl
ʿAmr ibn Hishām al-Makhzūmī ( ar, عمرو بن هشام المخزومي), (570 – 13 March 624), also known as Abu Jahl (lit. 'Father of Ignorance'), was one of the Meccan polytheist pagan leaders from the Quraysh known for his opposition ...
, al-Walid ibn 'Utbah, ' Utbah ibn Rabi'ah, and Umayyah ibn Khalaf
Umayya ibn Khalaf () (died 13 March 624) was an Arab slave master and the chieftain of the Banu Jumah of the Quraysh in the seventh century. He was one of the chief opponents against the Muslims led by Muhammad. Umayya is best known as the master ...
, joined the Meccan army. Their reasons varied: some were out to protect their financial interests in the caravan; others wanted to avenge Ibn al-Hadrami, a guard killed in one of the caravan ambushes at Nakhlah; finally, a few must have wanted to take part in what was expected to be an easy victory against the Muslims. Amr ibn Hishām is described as shaming Umayyah ibn Khalaf into joining the expedition.
Plans of action
Muslim council near Badr
 Muhammad held a
Muhammad held a council of war
A council of war is a term in military science that describes a meeting held to decide on a course of action, usually in the midst of a battle. Under normal circumstances, decisions are made by a commanding officer, optionally communicated ...
to review the situation and decide on a plan-of-action. According to some Muslim scholars, the following verses of Al Anfal, Q8:5-6, were revealed in lieu of some Muslims fearing the encounter. Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
was the first to speak at the meeting and he reassured Muhammad. 'Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
was next. Then, al-Miqdad ibn 'Amr got up and said:"O Messenger of Allah! Proceed where Allah directs you to, for we are with you. We will not say as the Children of Israel said to Musa: "Go you and your Lord and fight and we will stay here;" rather we shall say: "Go you and your Lord and fight and we will fight along with you." By Allah! If you were to take us to Birk al-Ghimad, we will still fight resolutely with you against its defenders until you gained it."Muhammad then praised him and supplicated for him, but the three who had spoken were of the Muhajirun, who only constituted around one-third of the Muslim men in
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
. Muhammad wanted the opinion of the Ansar, who were not committed to fighting beyond their territories in the Pledges of 'Aqabah. Muhammad then indirectly asked the Ansar to speak, which Sa'd ibn Mu'adh
Saʿd ibn Muʿādh ( ar, سعد ابن معاذ) () was the chief of the Aws tribe in Medina and one of the prominent companions of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon Him). He died shortly after the Battle of the Trench.
Family
Sa'd wa ...
understood and asked for permission to speak. Muhammad immediately gave him permission to speak and Sa'd said:"O Prophet of Allah! We believe in you and we bear witness to what you have brought is the Truth. We give you our firm pledge of obedience and sacrifice. We will obey you most willingly in whatever you command us, and by Allah, Who has sent you with the Truth, if you were to ask us to throw ourselves into the sea, we will do that most readily and not a man of us will stay behind. We do not deny the idea of encounter with the enemy. We are experienced in war and we are trustworthy in control. We hope that Allah will show you through our hands those deeds of bravery which will please your eyes. Kindly lead us to the battlefield in the Name of Allah."Muhammad, impressed with his loyalty and spirit of sacrifice, ordered the march towards Badr to continue.
Muslim plan of action
By Sunday, 11 March (15 Ramadan), both armies were about a day's march from Badr. Muhammad and Abu Bakr had conducted a scouting operation and managed to locate the camp of the Quraish. They came across an old bedouin nearby from whom they managed to find out the exact strength of their army and their location. In the evening, Muhammad dispatched 'Ali, az-Zubayr andSa'd ibn Abi Waqqas
, image = File:Saad ibn Abi Waqqas Masjid an-Nabawi Calligraphy.png
, alt =
, caption = His name in Arabic calligraphy
, birth_date =
, death_date =
, birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia
, death_place ...
to scout for the Makkans. They captured two Meccan water-bearers at the wells of Badr. Expecting them to say they were with the caravan, the Muslims were horrified to hear them say they were with the main Quraishi army. Unsatisfied with their answer, while Muhammad was praying, some of the Muslims beat the two boys into lying and Muhammad strictly condemned this action later. Muhammad then extracted the details of the Makkans from the boys. The next day Muhammad ordered a march to Badr and arrived before the Meccans.
When the Muslim army arrived from the east, Muhammad initially chose to encamp at the first well he encountered. al-Hubab ibn al-Mundhir, however, asked him if this choice was from divine instruction or Muhammad's own opinion. When Muhammad responded in the latter, Hubab suggested that the Muslims occupy the well closest to the Quraishi army, and block off or destroy the other ones. Muhammad accepted this decision and the plan was carried out at midnight. Muhammad had also given strict orders to not begin an attack without his sole permission.
Muhammad spent the whole night of 12 March (16 Ramadan) praying near a tree. The Muslim army enjoyed a refreshing night of sleep, again believed by Muslims, to be a blessing from Allah.
Meccan plan of action
While little is known about the progress of the Quraishi army from the time it left Mecca until its arrival just outside Badr, several things are worth noting: although many Arab armies brought their women and children along on campaigns both to motivate and care for the men, the Meccan army did not. The Quraish apparently made little or no effort to contact the many allies they had scattered throughout the Hejaz. Both facts suggest the Quraish lacked the time to prepare for a proper campaign in their haste to protect the caravan. Besides, it is believed they expected an easy victory. Since Muhammad's army had either destroyed or taken all the wells in the city, a few Makkans approached the well controlled by Muslims to draw out water. All were shot except Hakim ibn Hizam, who later accepted Islam. At midnight on 13 March (17 Ramadan), the Quraish broke camp and marched into the valley of Badr. 'Umayr ibn Wahb al-Jumahi made a survey of the Muslim position and reported 300 men keen on fighting to the last man.Lings, pp. 143–44. After another scouting mission, he reported that neither were the Muslims going to be reinforced, nor were they planning any ambushes. This further demoralized the Quraish, as Arab battles were traditionally low-casualty affairs, and set off another round of bickering among the Quraishi leadership. However, according to Arab traditions Amr ibn Hishām quashed the remaining dissent by appealing to the Quraishis' sense of honor and demanding that they fulfill their blood vengeance.The Duels
The battle began with al-Aswad bin 'Abdul-Asad al-Makhzumi, one of the men from Abu Jahl's clan, theBanu Makhzum
The Banu Makhzum () was one of the wealthy clans of the Quraysh. They are regarded as being among the three most powerful and influential clans in Mecca before the advent of Islam, the other two being the Banu Hashim (the tribe of the Islamic proph ...
, swearing that he would drink from the well of the Muslims or otherwise destroy it or die for it. In response to his cries, Hamza ibn 'Abdul-Muttalib, one of Muhammad's uncles, came out and they began fighting in a duel. Hamza struck al-Aswad's leg before dealing him another blow that killed him. Seeing this, three men protected by armor and shields, Utbah ibn Rabi'ah, alongside his brother, Shaybah ibn Rabi'ah Shaybah ibn Rabīʿah (Arabic language, Arabic: شيبة بن ربيعة) (c.560–624) was the brother of Utba ibn Rabi'ah, Utbah ibn Rabi'ah belonging to the clan of Banu Abd Shams (parent clan of Banu Umayyah) from the tribe of Quraysh tribe, Qur ...
and son, al-Walid ibn 'Utbah, emerged from the Makkan ranks. Three of the Madani Ansar emerged from the Muslim ranks, only to be shouted back by the Meccans, who were nervous about starting any unnecessary feuds and only wanted to fight the Muhajirun, keeping the dispute within the tribe. So Hamza approached and called on Ubaydah ibn al-Harith
ʿUbayda ibn al-Ḥārith ( ar, عبيدة بن الحارث) () was a relative and companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He is known for commanding the expedition in which Islam’s first arrow was shot and for being the first Muslim to b ...
and 'Ali ibn Abu Talib to join him. The first two duels between 'Ali and al-Walid and Hamza and Shaybah were quick with both managing to kill their opponents swiftly. After the fight between Ali and Walid, Hamza looked at 'Ubaydah to find him seriously wounded. He then fell upon and killed Shaybah. Ali and Hamza then carried Ubaydah back into the Muslim lines. He died later due to a disease. A shower of arrows from both sides followed these duels and this was followed by several other duels, most of which were won by the Muslims. The Makkans now took the offensive and charged upon the Muslim lines.
The Makkan charge and Muslim counter-attack
As the Makkans charged upon the Muslims, Muhammad kept asking Allah, stretching his hands toward the Qibla:"O Allah! Should this group (of Muslims) be defeated today, You will no longer be worshipped."Muhammad kept reciting his prayer until his cloak fell off his shoulders, at which point Abu Bakr picked it up and put it back on his shoulders and said:
"O Prophet of Allah, you have cried out enough to your Lord. He will surely fulfil what He has promised you."Muhammad gave the order to carry out a counterattack against the enemy now, throwing a handful of pebbles at the Makkans in what was probably a traditional Arabian gesture while yelling "Defaced be those faces!"Armstrong, p. 176.Lings, p. 148. or "Confusion seize their faces." The Muslim army yelled in reply, ''"Yā manṣūr amit!"'' meaning "O thou whom God hath made victorious, slay!" and rushed the Qurayshi lines. The Makkans, understrength and unenthusiastic about fighting, promptly broke and ran. Muslims attribute their fear of fighting and fleeing from the battlefield to divine intervention, with the Qur'an stating in Chapter 8, verse 12, that Allah sent thousands of angels (''
mala'ikah
In Islam, angels ( ar, , malāk; plural: ar, , malāʾik/malāʾikah, label=none) are believed to be heavenly beings, created from a luminous origin by God. They have different roles, including their praise of God, interacting with humans in ordi ...
'') to strengthen the ranks of Muslims. The battle itself only lasted a few hours and was over by early afternoon. The Qur'an describes the force of the Muslim attack in many verses, which refer to thousands of angels descending from Heaven at Badr to terrify the Quraish. It also describes how Iblis, the Leader of the Jinn, mentioned to have taken the form of Suraqa ibn Malik, fled the battlefield upon seeing the angels. Muslim sources take this account literally, and there are several ahadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
where Muhammad discusses the Angel Jibreel and the role he played in the battle. Modern non-Muslim historians, such as Richard A. Gabriel, attribute the victory and the subsequent triumph over the Quraysh to Muhammad's strategic and military prowess.

Aftermath
Imprisonment of captives and their ransom
Three days after the battle,William Muir wrote of this period:Muhammad Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...left Badr forMedina Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the .... As far as the treatment of prisoners was concerned,Abu Bakr Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...was of the opinion that they should be ransomed, since they were all of their own kin. 'Umar ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...argued against this, saying that there is no notion of blood relationships as far as Islam is concerned, and that all the prisoners should be executed, and that everyone should execute him who is closest to him by blood. ' Ali should kill his brother 'Aqeel ibn Abu Talib, Hamza ibn 'Abdul-Muttalib should behead his brother 'Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib ( ar, ٱلْعَبَّاسُبْنُ عَبْدِ ٱلْمُطَّلِبِ, al-ʿAbbās ibn ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib; CE) was a paternal uncle and Sahabi (companion) of Muhammad, just three years older than his ..., and that he himself would kill someone close to him. Muhammad accepted Abu Bakr's suggestion to ransom the captives. Some 70 prisoners were taken captive and are noted to have been treated humanely, including a number of Quraysh leaders. Most of the prisoners were released upon payment of ransom and those who were literate were released on the condition that they teach ten persons how to read and write and this teaching was to count as their ransom.
The Throwing of the Pagan Corpses
After the battle had subsided, Muhammad had ordered that the corpses of the 24 leaders of the Quraysh should be tossed into one of the dirty dry wells of Badr. A few days later Muhammad went back to these wells and spoke to the corpses therein, addressing each of them by name"Would it have pleased you had you obeyed Allah and His Apostle? We have found true what our Lord promised us. Have you too found true what your Lord promised you?"
Casualties
Despite scholars estimating Meccan casualties at around 70, only the names of the more prominent ones are known. However, the names of the 14 Muslims who were killed during the course of the war or later (due to injuries sustained during the war) are all known.Meccan casualties
Well-known Meccans who were killed during the battle includedAmr ibn Hishām
ʿAmr ibn Hishām al-Makhzūmī ( ar, عمرو بن هشام المخزومي), (570 – 13 March 624), also known as Abu Jahl (lit. 'Father of Ignorance'), was one of the Meccan polytheist pagan leaders from the Quraysh known for his opposition ...
, Umayyah ibn Khalaf
Umayya ibn Khalaf () (died 13 March 624) was an Arab slave master and the chieftain of the Banu Jumah of the Quraysh in the seventh century. He was one of the chief opponents against the Muslims led by Muhammad. Umayya is best known as the master ...
, ' Utbah ibn Rabi'ah, Shaybah ibn Rabi'ah Shaybah ibn Rabīʿah (Arabic language, Arabic: شيبة بن ربيعة) (c.560–624) was the brother of Utba ibn Rabi'ah, Utbah ibn Rabi'ah belonging to the clan of Banu Abd Shams (parent clan of Banu Umayyah) from the tribe of Quraysh tribe, Qur ...
, al-Walid ibn 'Utbah, al-Aswad bin and 'Abdul-Asad al-Makhzumi. Nadr ibn al-Harith and 'Uqbah ibn Abū Mu‘ayṭ were also killed, though the circumstances of their deaths are unclear. According to some sources the last two were killed during fighting in the field of battle at Badr and subsequently buried in a pit, while Safiur Rahman al-Mubarakpuri writes that these two were taken as prisoners and subsequently executed by Ali. Sahih Bukhari: Volume 1, Book 4, Number 241
Muslim casualties
Implications
The Battle of Badr was extremely influential in the rise of two men who determined the course of Arabian history in the next century. The first wasMuhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
, who was transformed overnight from a Meccan outcast into the leader of a new community and city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
at Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
. Marshall Hodgson adds that Badr forced the other Arabs to "regard the Muslims as challengers and potential inheritors to the prestige and the political role of the uraish" Shortly thereafter he expelled the Banu Qaynuqa
The Banu Qaynuqa ( ar, بنو قينقاع; he, בני קינוקאע; also spelled Banu Kainuka, Banu Kaynuka, Banu Qainuqa, Banu Qaynuqa) was one of the three main Jewish tribes living in the 7th century of Medina, now in Saudi Arabia. The grea ...
, one of the Jewish tribes in Medina for assaulting a Muslim woman which led to their expulsion for breaking the peace treaty. The tribe is also known for having threatened Muhammad's political position. At the same time 'Abd Allah ibn Ubayy, Muhammad's chief opponent in Medina, found his own position seriously weakened. He was only able to mount limited challenges to Muhammad.
The other major beneficiary of the Battle of Badr was Abu Sufyan ibn Harb
Sakhr ibn Harb ibn Umayya ibn Abd Shams ( ar, صخر بن حرب بن أمية بن عبد شمس, Ṣakhr ibn Ḥarb ibn Umayya ibn ʿAbd Shams; ), better known by his '' kunya'' Abu Sufyan ( ar, أبو سفيان, Abū Sufyān), was a prominent ...
, safely away from the battle leading the caravan. The death of Amr ibn Hisham
ʿAmr ibn Hishām al-Makhzūmī ( ar, عمرو بن هشام المخزومي), (570 – 13 March 624), also known as Abu Jahl (lit. 'Father of Ignorance'), was one of the Meccan polytheist pagan leaders from the Quraysh known for his opposition t ...
, as well as many other Quraishi nobles, gave Abu Sufyan the opportunity, almost by default, to become chief of the Quraish
The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Qu ...
. As a result, when Muhammad marched into Mecca six years later, it was Abu Sufyan who helped negotiate its peaceful surrender. Abu Sufyan subsequently became a high-ranking official in the Muslim Empire, and his son Mu'awiya
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
later went on to found the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
.
In later days, the battle of Badr became so significant that Ibn Ishaq included a complete name-by-name roster of the Muslim army in his biography of Muhammad. In many hadiths, veterans who fought at Badr are identified as such as a formality, and they may have even received a stipend in later years. The death of the last of the Badr veterans occurred during the First Fitna.
Legacy
In theQuran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
, the battle is referred to as Yawm al-Furqan (; ). The story of the Battle of Badr has been passed down in Islamic history throughout the centuries, before being combined in the multiple biographies of Muhammad
This is a chronological listing of biographies of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, ranging from the earliest traditional writers to modern times.
Earliest biographers
The following is a list of the earliest known Hadith collectors who speciali ...
that exist today. It is mentioned in the Quran, and all knowledge of the battle comes from traditional Islamic accounts, recorded and compiled sometime after the battle. There is little evidence beside these and there are no written descriptions of the battle prior to the 9th century, and as such, the historicity and authenticity of the battle are debated by contemporary historians.
"Badr" has become popular among Muslim armies and paramilitary organizations. " Operation Badr" was used to describe Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
's offensive in the 1973 Yom Kippur War as well as Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
's actions in the 1999 Kargil War. Iranian offensive operations against Iraq in the late 1980s were also named after Badr. During the 2011 Libyan civil war, the rebel leadership stated that they selected the date of the assault on Tripoli to be the 20th of Ramadan, marking the anniversary of the Battle of Badr.Laub, Karin (21 August 2011)"Libyan Rebels Say They Are Closing In on Tripoli"
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
(via '' The Atlanta Journal-Constitution''). Retrieved 21 August 2011.
The Battle of Badr was featured in the 1976 film '' The Message'', the 2004 animated movie '' Muhammad: The Last Prophet'', the 2012 TV series '' Omar'' and the 2015 animated movie '' Bilal: A New Breed of Hero.''
Further reading
* Al Mubarakpuri, Safiur Rahman (2002). ''The Sealed Nectar: Biography of the Noble Prophet ﷺ.'' Riyadh:Darussalam Publishers
Darussalam International Publishing & Distribution (also known as Dar-us-Salam in U.S) is a Saudi-based multilingual international publishing house operates in 35 countries. It's the second-largest publisher of translations of the Islamic script ...
.
* Najeebabadi, Akbar Shah (2000). ''The History of Islam''. Riyadh: Darussalam Publishers
Darussalam International Publishing & Distribution (also known as Dar-us-Salam in U.S) is a Saudi-based multilingual international publishing house operates in 35 countries. It's the second-largest publisher of translations of the Islamic script ...
.
* Abu Khalil, Shauqi (2003). ''Atlas of the Qur'an: Places. Nations. Landmarks.'' Riyadh: Darussalam Publishers
Darussalam International Publishing & Distribution (also known as Dar-us-Salam in U.S) is a Saudi-based multilingual international publishing house operates in 35 countries. It's the second-largest publisher of translations of the Islamic script ...
See also
* Islamic military jurisprudence *Muslim–Quraysh War
The Muslim–Quraysh War was the six-year-long military and religious conflict in the Arabian Peninsula between the early Muslims led by Muhammad, and the Arab pagan Quraysh tribe. The conflict started in March 623 with the Battle of Badr, and c ...
* Military career of Muhammad
* Pre-Islamic Arabia
* List of expeditions of Muhammad
Footnotes
References
Books and articles
* * * * * * * * * *Online references
* * * *External links
Battle of Badr, 17th Ramadan 624 A.D
Badr
at IslamAnswers.Net
The first battle of Islam at Badr
Islamic Occasions Network
Analysis of Qur'anic verses by Irshaad Hussain. {{Authority control Badr Campaigns led by Muhammad Angelic apparitions Muhammad in Medina