Barbier reaction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Barbier reaction is an organometallic reaction between an alkyl halide (chloride, bromide, iodide), a carbonyl group and a metal. The reaction can be performed using
Website
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
, aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts ...
, tin, samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samar ...
, barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
or their salts. The reaction product is a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
. The reaction is similar to the Grignard reaction but the crucial difference is that the organometallic species in the Barbier reaction is generated '' in situ'', whereas a Grignard reagent is prepared separately before addition of the carbonyl compound. Unlike many Grignard reagents, the organometallic species generated in a Barbier reaction are unstable and thus cannot be stored or sold commercially. Barbier reactions are nucleophilic addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions d ...
reactions that involve relatively inexpensive, water insensitive metals (e.g zinc powder) or metal compounds. For this reason it is possible in many cases to run the reaction in water, making the procedure part of green chemistry. In contrast, Grignard reagents and organolithium reagents are highly moisture sensitive and must be used under an inert atmosphere without the presence of water. The Barbier reaction is named after Victor Grignard's teacher Philippe Barbier.
Scope
Examples of Barbier reactions are the reaction of propargylic bromide with butanal with zinc metal (the reaction is carried out in THF, the saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution added later to quench the reaction): the intramolecular Barbier reaction with samarium(II) iodide: the reaction of anallyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, ...
bromide with formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) ( systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section ...
in THF with indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts ...
powder:
The reaction of 3-Bromocyclohexene with benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful.
It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-like odor. ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
powder in water:
Asymmetric Variants
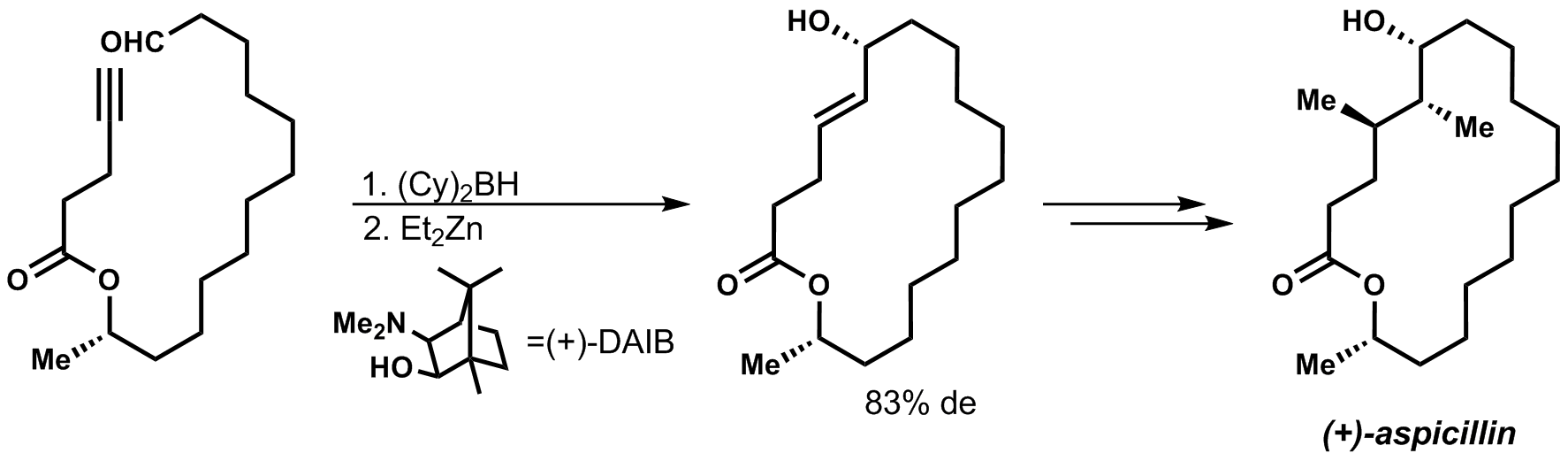
The synthesis of (+)-aspicillin, starts first with a hydroboration, then transmetallation to zinc which can then do an addition into the aldehyde substituent.
See also
* Grignard reaction * Nozaki-Hiyama-Kishi reaction * Indium mediated allylationExternal links
* Barbier reaction @ University of ConnecticuWebsite
References
{{Organic reactions Addition reactions Free radical reactions Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions Name reactions