Bacteriophage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a
 It has been suggested that members of '' Picobirnaviridae'' infect bacteria, but not mammals.
There are also many unassigned genera of the class ''
It has been suggested that members of '' Picobirnaviridae'' infect bacteria, but not mammals.
There are also many unassigned genera of the class ''
 In 1896, Ernest Hanbury Hankin reported that something in the waters of the
In 1896, Ernest Hanbury Hankin reported that something in the waters of the
 Phages were discovered to be antibacterial agents and were used in the former
Phages were discovered to be antibacterial agents and were used in the former
 The life cycle of bacteriophages tends to be either a
The life cycle of bacteriophages tends to be either a
 Bacterial cells are protected by a cell wall of polysaccharides, which are important virulence factors protecting bacterial cells against both immune host defenses and antibiotics.
Host growth conditions also influence the ability of the phage to attach and invade them. As phage virions do not move independently, they must rely on random encounters with the correct receptors when in solution, such as blood, lymphatic circulation, irrigation, soil water, etc.
Myovirus bacteriophages use a
Bacterial cells are protected by a cell wall of polysaccharides, which are important virulence factors protecting bacterial cells against both immune host defenses and antibiotics.
Host growth conditions also influence the ability of the phage to attach and invade them. As phage virions do not move independently, they must rely on random encounters with the correct receptors when in solution, such as blood, lymphatic circulation, irrigation, soil water, etc.
Myovirus bacteriophages use a
 Bacteriophage genomes can be highly
Bacteriophage genomes can be highly

 A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria
''Duplodnaviria'' is a realm of viruses that includes all double-stranded DNA viruses that encode the HK97 fold major capsid protein. The HK97 fold major capsid protein (HK97 MCP) is the primary component of the viral capsid, which stores the v ...
virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
that infects and replicates within bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
.
Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass after prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Conne ...
s, where up to 9x108 virions
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
per millilitre have been found in microbial mats
A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet of microorganisms, mainly bacteria and archaea, or bacteria alone. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few survive in deserts. ...
at the surface, and up to 70% of marine bacteria
Marine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. All cellular ...
may be infected by phages.
Phages have been used since the late 20th century as an alternative to antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
in the former Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Central Europe, as well as in France. – Documentary about the history of phage medicine in Russia and the West They are seen as a possible therapy against multi-drug-resistant
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ...
strains of many bacteria (see phage therapy
Phage therapy, viral phage therapy, or phagotherapy is the therapeutic use of bacteriophages for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. This therapeutic approach emerged at the beginning of the 20th century but was progressively re ...
).
Phages are known to interact with the immune system both indirectly via bacterial expression of phage-encoded proteins and directly by influencing innate immunity and bacterial clearance. Phage–host interactions are becoming increasingly important areas of research.
Classification
Bacteriophages occur abundantly in the biosphere, with different genomes and lifestyles. Phages are classified by theInternational Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to ap ...
(ICTV) according to morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
and nucleic acid.

 It has been suggested that members of '' Picobirnaviridae'' infect bacteria, but not mammals.
There are also many unassigned genera of the class ''
It has been suggested that members of '' Picobirnaviridae'' infect bacteria, but not mammals.
There are also many unassigned genera of the class ''Leviviricetes
''Leviviricetes'' is a class of viruses, which infect prokaryotes. Most of these bacteriophages were discovered by metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a ...
'': '' Chimpavirus'', '' Hohglivirus'', '' Mahrahvirus'', '' Meihzavirus'', '' Nicedsevirus'', '' Sculuvirus'', '' Skrubnovirus'', '' Tetipavirus'' and '' Winunavirus'' containing linear ssRNA genomes and the unassigned genus '' Lilyvirus'' of the order ''Caudovirales
''Caudovirales'' is an order of viruses known as the tailed bacteriophages (''cauda'' is Latin for "tail"). Under the Baltimore classification scheme, the ''Caudovirales'' are group I viruses as they have double stranded DNA (dsDNA) genomes ...
'' containing a linear dsDNA genome.
History
 In 1896, Ernest Hanbury Hankin reported that something in the waters of the
In 1896, Ernest Hanbury Hankin reported that something in the waters of the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
and Yamuna
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of B ...
rivers in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
had a marked antibacterial action against cholera and it could pass through a very fine porcelain filter. In 1915, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
bacteriologist
A bacteriologist is a microbiologist, or similarly trained professional, in bacteriology -- a subdivision of microbiology that studies bacteria, typically pathogenic ones. Bacteriologists are interested in studying and learning about bacteria, ...
Frederick Twort
Frederick William Twort FRS (22 October 1877 – 20 March 1950) was an English bacteriologist and was the original discoverer in 1915 of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria). He studied medicine at St Thomas's Hospital, London, was super ...
, superintendent of the Brown Institution of London, discovered a small agent that infected and killed bacteria. He believed the agent must be one of the following:
# a stage in the life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
*Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
* Life-cycle hypothesis ...
of the bacteria
# an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
produced by the bacteria themselves, or
# a virus that grew on and destroyed the bacteria
Twort's research was interrupted by the onset of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, as well as a shortage of funding and the discoveries of antibiotics.
Independently, French-Canadian microbiologist Félix d'Hérelle
Félix d'Hérelle (25 April 1873 – 22 February 1949) was a French microbiologist. He was co-discoverer of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) and experimented with the possibility of phage therapy. D'Herelle has also been credited ...
, working at the Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute (french: Institut Pasteur) is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who invented pasteurization and vaccines ...
in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
, announced on 3 September 1917 that he had discovered "an invisible, antagonistic microbe of the dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
bacillus". For d'Hérelle, there was no question as to the nature of his discovery: "In a flash I had understood: what caused my clear spots was in fact an invisible microbe... a virus parasitic on bacteria." D'Hérelle called the virus a bacteriophage, a bacteria-eater (from the Greek ', meaning "to devour"). He also recorded a dramatic account of a man suffering from dysentery who was restored to good health by the bacteriophages. It was d'Hérelle who conducted much research into bacteriophages and introduced the concept of phage therapy
Phage therapy, viral phage therapy, or phagotherapy is the therapeutic use of bacteriophages for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. This therapeutic approach emerged at the beginning of the 20th century but was progressively re ...
.
Nobel prizes awarded for phage research
In 1969,Max Delbrück
Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück (; September 4, 1906 – March 9, 1981) was a German–American biophysicist who participated in launching the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s. He stimulated physical scientists' interest int ...
, Alfred Hershey, and Salvador Luria
Salvador Edward Luria (August 13, 1912 – February 6, 1991) was an Italian microbiologist, later a Naturalized citizen of the United States#Naturalization, naturalized U.S. citizen. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1969, with ...
were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
for their discoveries of the replication of viruses and their genetic structure. Specifically the work of Hershey, as contributor to the Hershey–Chase experiment in 1952 provided convincing evidence that DNA, not protein, was the genetic material of life. Delbrück and Luria carried out the Luria–Delbrück experiment which demonstrated statistically that mutations in bacteria occur randomly and thus follow Darwinian
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
rather than Lamarckian
Lamarckism, also known as Lamarckian inheritance or neo-Lamarckism, is the notion that an organism can pass on to its offspring physical characteristics that the parent organism acquired through use or disuse during its lifetime. It is also calle ...
principles.
Uses
Phage therapy
 Phages were discovered to be antibacterial agents and were used in the former
Phages were discovered to be antibacterial agents and were used in the former Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
Republic of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
(pioneered there by Giorgi Eliava with help from the co-discoverer of bacteriophages, Félix d'Hérelle
Félix d'Hérelle (25 April 1873 – 22 February 1949) was a French microbiologist. He was co-discoverer of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) and experimented with the possibility of phage therapy. D'Herelle has also been credited ...
) during the 1920s and 1930s for treating bacterial infections. They had widespread use, including treatment of soldiers in the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
. However, they were abandoned for general use in the West for several reasons:
* Antibiotics were discovered and marketed widely. They were easier to make, store, and prescribe.
* Medical trials of phages were carried out, but a basic lack of understanding of phages raised questions about the validity of these trials.
* Publication of research in the Soviet Union was mainly in the Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
or Georgian languages and for many years, was not followed internationally.
The use of phages has continued since the end of the Cold War in Russia, Georgia, and elsewhere in Central and Eastern Europe. The first regulated, randomized, double-blind clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
was reported in the ''Journal of Wound Care'' in June 2009, which evaluated the safety and efficacy of a bacteriophage cocktail to treat infected venous ulcers of the leg in human patients. The FDA approved the study as a Phase I clinical trial. The study's results demonstrated the safety of therapeutic application of bacteriophages, but did not show efficacy. The authors explained that the use of certain chemicals that are part of standard wound care (e.g. lactoferrin
Lactoferrin (LF), also known as lactotransferrin (LTF), is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, s ...
or silver) may have interfered with bacteriophage viability. Shortly after that, another controlled clinical trial in Western Europe (treatment of ear infections caused by ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'') was reported in the journal ''Clinical Otolaryngology
''Clinical Otolaryngology'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering the field of otorhinolaryngology. It was established in 1976 as ''Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences'', obtaining its current title in 2005. It is publish ...
'' in August 2009. The study concludes that bacteriophage preparations were safe and effective for treatment of chronic ear infections in humans. Additionally, there have been numerous animal and other experimental clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of bacteriophages for various diseases, such as infected burns and wounds, and cystic fibrosis-associated lung infections, among others. On the other hand, phages of ''Inoviridae
Filamentous bacteriophage is a family of viruses (''Inoviridae'') that infect bacteria. The phages are named for their filamentous shape, a worm-like chain (long, thin and flexible, reminiscent of a length of cooked spaghetti), about 6 nm ...
'' have been shown to complicate biofilms
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
involved in pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
and cystic fibrosis and to shelter the bacteria from drugs meant to eradicate disease, thus promoting persistent infection.
Meanwhile, bacteriophage researchers have been developing engineered viruses to overcome antibiotic resistance, and engineering the phage genes responsible for coding enzymes that degrade the biofilm matrix, phage structural proteins, and the enzymes responsible for lysis of the bacterial cell wall. There have been results showing that T4 phages that are small in size and short-tailed, can be helpful in detecting ''E. coli'' in the human body.
Therapeutic efficacy of a phage cocktail was evaluated in a mice model with nasal infection of multidrug-resistant (MDR) '' A. baumannii''. Mice treated with the phage cocktail showed a 2.3-fold higher survival rate compared to those untreated at seven days post-infection. In 2017, a patient with a pancreas compromised by MDR ''A. baumannii'' was put on several antibiotics; despite this, the patient's health continued to deteriorate during a four-month period. Without effective antibiotics, the patient was subjected to phage therapy using a phage cocktail containing nine different phages that had been demonstrated to be effective against MDR ''A. baumannii''. Once on this therapy the patient's downward clinical trajectory reversed, and returned to health.
D'Herelle "quickly learned that bacteriophages are found wherever bacteria thrive: in sewers, in rivers that catch waste runoff from pipes, and in the stools of convalescent patients." This includes rivers traditionally thought to have healing powers, including India's Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
River.
Other
Food industry – Phages have increasingly been used to safen food products and to forestall spoilage bacteria. Since 2006, theUnited States Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
(FDA) and United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
(USDA) have approved several bacteriophage products. LMP-102 (Intralytix) was approved for treating ready-to-eat (RTE) poultry and meat products. In that same year, the FDA approved LISTEX (developed and produced by Micreos) using bacteriophages on cheese to kill ''Listeria monocytogenes
''Listeria monocytogenes'' is the species of pathogenic bacteria that causes the infection listeriosis. It is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, capable of surviving in the presence or absence of oxygen. It can grow and reproduce inside the host ...
'' bacteria, in order to give them generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status. In July 2007, the same bacteriophage were approved for use on all food products. In 2011 USDA confirmed that LISTEX is a clean label processing aid and is included in USDA. Research in the field of food safety is continuing to see if lytic phages are a viable option to control other food-borne pathogens in various food products.
Diagnostics – In 2011, the FDA cleared the first bacteriophage-based product for in vitro diagnostic use. The KeyPath MRSA/MSSA Blood Culture Test uses a cocktail of bacteriophage to detect '' Staphylococcus aureus'' in positive blood cultures and determine methicillin
Methicillin ( USAN), also known as meticillin ( INN), is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.
Methicillin was discovered in 1960.
Medical uses
Compared to other penicillins that face antimicrobial resistance ...
resistance or susceptibility. The test returns results in about five hours, compared to two to three days for standard microbial identification and susceptibility test methods. It was the first accelerated antibiotic-susceptibility test approved by the FDA.
Counteracting bioweapons and toxins – Government agencies in the West have for several years been looking to Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
and the former Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
for help with exploiting phages for counteracting bioweapons and toxins, such as anthrax and botulism
Botulism is a rare and potentially fatal illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum''. The disease begins with weakness, blurred vision, feeling tired, and trouble speaking. This may then be followed by weakne ...
. Developments are continuing among research groups in the U.S. Other uses include spray application in horticulture for protecting plants and vegetable produce from decay and the spread of bacterial disease. Other applications for bacteriophages are as biocides for environmental surfaces, e.g., in hospitals, and as preventative treatments for catheters and medical devices before use in clinical settings. The technology for phages to be applied to dry surfaces, e.g., uniforms, curtains, or even sutures for surgery now exists. Clinical trials reported in ''Clinical Otolaryngology'' show success in veterinary treatment of pet dogs with otitis.
The SEPTIC bacterium sensing and identification method uses the ion emission and its dynamics during phage infection and offers high specificity and speed for detection.
Phage display is a different use of phages involving a library of phages with a variable peptide linked to a surface protein. Each phage genome encodes the variant of the protein displayed on its surface (hence the name), providing a link between the peptide variant and its encoding gene. Variant phages from the library may be selected through their binding affinity to an immobilized molecule (e.g., botulism toxin) to neutralize it. The bound, selected phages can be multiplied by reinfecting a susceptible bacterial strain, thus allowing them to retrieve the peptides encoded in them for further study.
Antimicrobial drug discovery – Phage proteins often have antimicrobial activity and may serve as leads for peptidomimetic
A peptidomimetic is a small protein-like chain designed to mimic a peptide. They typically arise either from modification of an existing peptide, or by designing similar systems that mimic peptides, such as peptoids and β-peptides. Irrespective ...
s, i.e. drugs that mimic peptides. Phage-ligand technology makes use of phage proteins for various applications, such as binding of bacteria and bacterial components (e.g. endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer m ...
) and lysis of bacteria.
Basic research – Bacteriophages are important model organisms
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the working ...
for studying principles of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
and ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
.
Detriments
Dairy industry
Bacteriophages present in the environment can cause cheese to not ferment. In order to avoid this, mixed-strain starter cultures and culture rotation regimes can be used. Genetic engineering of culture microbes – especially ''Lactococcus lactis
''Lactococcus lactis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium used extensively in the production of buttermilk and cheese, but has also become famous as the first genetically modified organism to be used alive for the treatment of human disease. ''L. lact ...
'' and ''Streptococcus thermophilus
''Streptococcus thermophilus'' also known as ''Streptococcus salivarius ''subsp.'' thermophilus'' is a gram-positive bacterium, and a fermentative facultative anaerobe, of the '' viridans'' group. It tests negative for cytochrome, oxidase, an ...
'' – have been studied for genetic analysis and modification to improve phage resistance. This has especially focused on plasmid and recombinant chromosomal modifications.
Some research has focused on the potential of bacteriophages as antimicrobial against foodborne pathogens and biofilm formation within the dairy industry. As the spread of antibiotic resistance is a main concern within the dairy industry, phages can serve as a promising alternative.
Replication
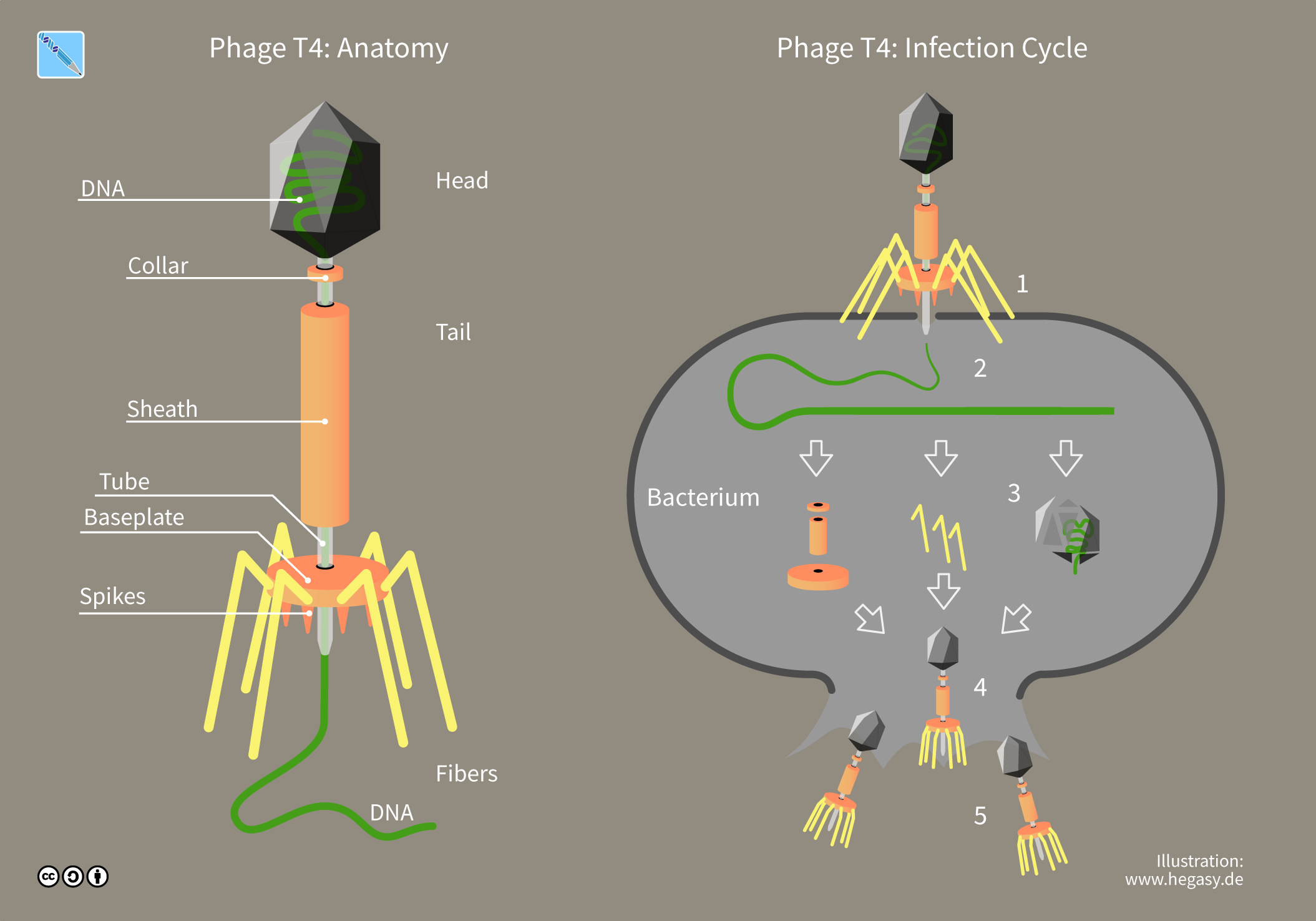
 The life cycle of bacteriophages tends to be either a
The life cycle of bacteriophages tends to be either a lytic cycle
The lytic cycle ( ) is one of the two cycles of viral reproduction (referring to bacterial viruses or bacteriophages), the other being the lysogenic cycle. The lytic cycle results in the destruction of the infected cell and its membrane. Bacteri ...
or a lysogenic cycle
Lysogeny, or the lysogenic cycle, is one of two cycles of viral reproduction (the lytic cycle being the other). Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacterium's genome or formation of a circu ...
. In addition, some phages display pseudolysogenic behaviors.
With ''lytic phages'' such as the T4 phage, bacterial cells are broken open (lysed) and destroyed after immediate replication of the virion. As soon as the cell is destroyed, the phage progeny can find new hosts to infect. Lytic phages are more suitable for phage therapy
Phage therapy, viral phage therapy, or phagotherapy is the therapeutic use of bacteriophages for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. This therapeutic approach emerged at the beginning of the 20th century but was progressively re ...
. Some lytic phages undergo a phenomenon known as lysis inhibition, where completed phage progeny will not immediately lyse out of the cell if extracellular phage concentrations are high. This mechanism is not identical to that of the temperate phage In virology, temperate refers to the ability of some bacteriophages (notably coliphage λ) to display a lysogenic life cycle. Many (but not all) temperate phages can integrate their genomes into their host bacterium's chromosome, together becoming ...
going dormant and usually is temporary.
In contrast, the ''lysogenic cycle
Lysogeny, or the lysogenic cycle, is one of two cycles of viral reproduction (the lytic cycle being the other). Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacterium's genome or formation of a circu ...
'' does not result in immediate lysing of the host cell. Those phages able to undergo lysogeny are known as temperate phage In virology, temperate refers to the ability of some bacteriophages (notably coliphage λ) to display a lysogenic life cycle. Many (but not all) temperate phages can integrate their genomes into their host bacterium's chromosome, together becoming ...
s. Their viral genome will integrate with host DNA and replicate along with it, relatively harmlessly, or may even become established as a plasmid. The virus remains dormant until host conditions deteriorate, perhaps due to depletion of nutrients, then, the endogenous phages (known as prophages) become active. At this point they initiate the reproductive cycle, resulting in lysis of the host cell. As the lysogenic cycle allows the host cell to continue to survive and reproduce, the virus is replicated in all offspring of the cell. An example of a bacteriophage known to follow the lysogenic cycle and the lytic cycle is the phage lambda of ''E. coli.''
Sometimes prophages may provide benefits to the host bacterium while they are dormant by adding new functions to the bacterial genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
, in a phenomenon called lysogenic conversion
Lysogeny, or the lysogenic cycle, is one of two cycles of viral reproduction (the lytic cycle being the other). Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacterium's genome or formation of a circu ...
. Examples are the conversion of harmless strains of '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' or ''Vibrio cholerae
''Vibrio cholerae'' is a species of Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe and comma-shaped bacteria. The bacteria naturally live in brackish or saltwater where they attach themselves easily to the chitin-containing shells of crabs, shrimps, and oth ...
'' by bacteriophages, to highly virulent ones that cause diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
or cholera, respectively. Strategies to combat certain bacterial infections by targeting these toxin-encoding prophages have been proposed.
Attachment and penetration
 Bacterial cells are protected by a cell wall of polysaccharides, which are important virulence factors protecting bacterial cells against both immune host defenses and antibiotics.
Host growth conditions also influence the ability of the phage to attach and invade them. As phage virions do not move independently, they must rely on random encounters with the correct receptors when in solution, such as blood, lymphatic circulation, irrigation, soil water, etc.
Myovirus bacteriophages use a
Bacterial cells are protected by a cell wall of polysaccharides, which are important virulence factors protecting bacterial cells against both immune host defenses and antibiotics.
Host growth conditions also influence the ability of the phage to attach and invade them. As phage virions do not move independently, they must rely on random encounters with the correct receptors when in solution, such as blood, lymphatic circulation, irrigation, soil water, etc.
Myovirus bacteriophages use a hypodermic syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside o ...
-like motion to inject their genetic material into the cell. After contacting the appropriate receptor, the tail fibers flex to bring the base plate closer to the surface of the cell. This is known as reversible binding. Once attached completely, irreversible binding is initiated and the tail contracts, possibly with the help of ATP present in the tail, injecting genetic material through the bacterial membrane. The injection is accomplished through a sort of bending motion in the shaft by going to the side, contracting closer to the cell and pushing back up. Podoviruses lack an elongated tail sheath like that of a myovirus, so instead, they use their small, tooth-like tail fibers enzymatically to degrade a portion of the cell membrane before inserting their genetic material.
Synthesis of proteins and nucleic acid
Within minutes, bacterial ribosomes start translating viral mRNA into protein. For RNA-based phages,RNA replicase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to ...
is synthesized early in the process. Proteins modify the bacterial RNA polymerase so it preferentially transcribes viral mRNA. The host's normal synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids is disrupted, and it is forced to manufacture viral products instead. These products go on to become part of new virions within the cell, helper proteins that contribute to the assemblage of new virions, or proteins involved in cell lysis. In 1972, Walter Fiers
Walter Fiers (31 January 1931 in Ypres, West Flanders – 28 July 2019 in Destelbergen) was a Belgian molecular biologist.
He obtained a degree of Engineer for Chemistry and Agricultural Industries at the University of Ghent in 1954, and started ...
(University of Ghent
Ghent University ( nl, Universiteit Gent, abbreviated as UGent) is a public research university located in Ghent, Belgium.
Established before the state of Belgium itself, the university was founded by the Dutch King William I in 1817, when the ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
) was the first to establish the complete nucleotide sequence of a gene and in 1976, of the viral genome of bacteriophage MS2. Some dsDNA bacteriophages encode ribosomal proteins, which are thought to modulate protein translation during phage infection.
Virion assembly
In the case of the T4 phage, the construction of new virus particles involves the assistance of helper proteins that act catalytically during phagemorphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
. The base plates are assembled first, with the tails being built upon them afterward. The head capsids, constructed separately, will spontaneously assemble with the tails. During assembly of the phage T4 virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
, the morphogenetic proteins encoded by the phage gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s interact with each other in a characteristic sequence. Maintaining an appropriate balance in the amounts of each of these proteins produced during viral infection appears to be critical for normal phage T4 morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
. The DNA is packed efficiently within the heads. The whole process takes about 15 minutes.
Release of virions
Phages may be released via cell lysis, by extrusion, or, in a few cases, by budding. Lysis, by tailed phages, is achieved by an enzyme calledendolysin
Lysins, also known as endolysins or murein hydrolases, are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages in order to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. Lysins are highly evolved enzymes that are able to target ...
, which attacks and breaks down the cell wall peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ba ...
. An altogether different phage type, the filamentous phage, make the host cell continually secrete new virus particles. Released virions are described as free, and, unless defective, are capable of infecting a new bacterium. Budding is associated with certain '' Mycoplasma'' phages. In contrast to virion release, phages displaying a lysogenic
Lysogeny, or the lysogenic cycle, is one of two cycles of viral reproduction (the lytic cycle being the other). Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacterium's genome or formation of a circu ...
cycle do not kill the host and instead become long-term residents as prophages.
Communication
Research in 2017 revealed that the bacteriophage Φ3T makes a short viral protein that signals other bacteriophages to lie dormant instead of killing the host bacterium.Arbitrium
Arbitrium is a viral peptide produced by bacteriophages to communicate with each other. It is six amino acids long, and is produced when a phage infects a bacterial host. It signals to other phages that a host has been infected.
Discovery
Arbitr ...
is the name given to this protein by the researchers who discovered it.
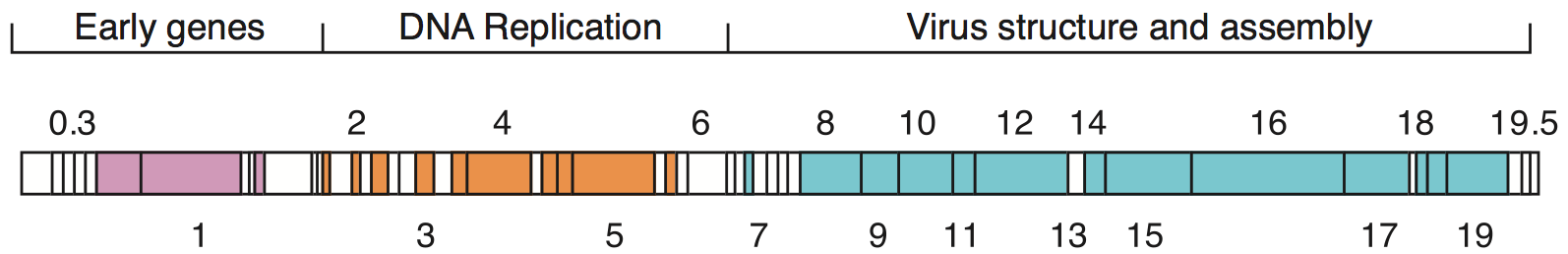
Genome structure
Given the millions of different phages in the environment, phage genomes come in a variety of forms and sizes. RNA phages such as MS2 have the smallest genomes, with only a few kilobases. However, some DNA phages such as T4 may have large genomes with hundreds of genes; the size and shape of thecapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
varies along with the size of the genome. The largest bacteriophage genomes reach a size of 735 kb. Bacteriophage genomes can be highly
Bacteriophage genomes can be highly mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
, i.e. the genome of many phage species appear to be composed of numerous individual modules. These modules may be found in other phage species in different arrangements. Mycobacteriophages, bacteriophages with mycobacterial hosts, have provided excellent examples of this mosaicism. In these mycobacteriophages, genetic assortment may be the result of repeated instances of site-specific recombination Site-specific recombination, also known as conservative site-specific recombination, is a type of genetic recombination in which DNA strand exchange takes place between segments possessing at least a certain degree of sequence homology. Enzymes kno ...
and illegitimate recombination
Illegitimate recombination, or nonhomologous recombination, is the process by which two unrelated double stranded segments of DNA are joined. This insertion of genetic material which is not meant to be adjacent tends to lead to genes being broken ...
(the result of phage genome acquisition of bacterial host genetic sequences). Evolutionary mechanisms shaping the genomes of bacterial viruses vary between different families and depend upon the type of the nucleic acid, characteristics of the virion structure, as well as the mode of the viral life cycle.
Some marine roseobacter phages contain deoxyuridine (dU) instead of deoxythymidine
Thymidine (symbol dT or dThd), also known as deoxythymidine, deoxyribosylthymine, or thymine deoxyriboside, is a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine (A) in double-stranded DNA. ...
(dT) in their genomic DNA. There is some evidence that this unusual component is a mechanism to evade bacterial defense mechanisms such as restriction endonucleases
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class o ...
and CRISPR/Cas systems which evolved to recognize and cleave sequences within invading phages, thereby inactivating them. Other phages have long been known to use unusual nucleotides. In 1963, Takahashi and Marmur identified a ''Bacillus
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum '' Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacill ...
'' phage that has dU substituting dT in its genome, and in 1977, Kirnos et al. identified a cyanophage
Cyanophages are viruses that infect cyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta or blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through the process of photosynthesis. Although cyanobacteria metabolize photoautotro ...
containing 2-aminoadenine (Z) instead of adenine (A).
Systems biology
The field of systems biology investigates the complex networks of interactions within an organism, usually using computational tools and modeling. For example, a phage genome that enters into a bacterial host cell may express hundreds of phage proteins which will affect the expression of numerous host gene or the host'smetabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
. All of these complex interactions can be described and simulated in computer models.
For instance, infection of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerug ...
'' by the temperate phage PaP3 changed the expression of 38% (2160/5633) of its host's genes. Many of these effects are probably indirect, hence the challenge becomes to identify the direct interactions among bacteria and phage.
Several attempts have been made to map protein–protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events steered by interactions that include electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding and th ...
s among phage and their host. For instance, bacteriophage lambda was found to interact with its host, ''E. coli'', by dozens of interactions. Again, the significance of many of these interactions remains unclear, but these studies suggest that there most likely are several key interactions and many indirect interactions whose role remains uncharacterized.
Host resistance
Bacteriophages are a major threat to bacteria and prokaryotes have evolved numerous mechanisms to block infection or to block the replication of bacteriophages within host cells. The CRISPR system is one such mechanism as areretron
A retron is a distinct DNA sequence found in the genome of many bacteria species that codes for reverse transcriptase and a unique single-stranded DNA/RNA hybrid called multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA). Retron msr RNA is the non-coding RN ...
s and the anti-toxin system encoded by them. The Thoeris defense system is known to deploy a unique strategy for bacterial antiphage resistance via NAD+ degradation.
Bacteriophage–host symbiosis
Temperate phages are bacteriophages that integrate their genetic material into the host as extrachromosomal episomes or as a prophage during alysogenic cycle
Lysogeny, or the lysogenic cycle, is one of two cycles of viral reproduction (the lytic cycle being the other). Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacterium's genome or formation of a circu ...
. Some temperate phages can confer fitness advantages to their host in numerous ways, including giving antibiotic resistance through the transfer or introduction of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), protecting hosts from phagocytosis, protecting hosts from secondary infection through superinfection exclusion, enhancing host pathogenicity, or enhancing bacterial metabolism or growth. Bacteriophage–host symbiosis may benefit bacteria by providing selective advantages while passively replicating the phage genome.
In the environment
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microb ...
has allowed the in-water detection of bacteriophages that was not possible previously.
Also, bacteriophages have been used in hydrological
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
tracing and modelling in river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of w ...
systems, especially where surface water and groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
interactions occur. The use of phages is preferred to the more conventional dye marker because they are significantly less absorbed when passing through ground waters and they are readily detected at very low concentrations. Non-polluted water may contain approximately 2×108 bacteriophages per ml.
Bacteriophages are thought to contribute extensively to horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). H ...
in natural environments, principally via transduction, but also via transformation
Transformation may refer to:
Science and mathematics
In biology and medicine
* Metamorphosis, the biological process of changing physical form after birth or hatching
* Malignant transformation, the process of cells becoming cancerous
* Tran ...
. Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microb ...
-based studies also have revealed that virome
Virome refers to the assemblage of viruses that is often investigated and described by metagenomic sequencing of viral nucleic acids that are found associated with a particular ecosystem, organism or holobiont. The word is frequently used to de ...
s from a variety of environments harbor antibiotic-resistance genes, including those that could confer multidrug resistance
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ...
.
In humans
Although phages do not infect humans, there are countless phage particles in the human body, given our extensivemicrobiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
. Our phage population has been called the human phageome, including the "healthy gut phageome" (HGP) and the "diseased human phageome" (DHP). The active phageome of a healthy human (i.e., actively replicating as opposed to nonreplicating, integrated prophage) has been estimated to comprise dozens to thousands of different viruses.
There is evidence that bacteriophages and bacteria interact in the human gut microbiome
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut mi ...
both antagonistically and beneficially.
Preliminary studies have indicated that common bacteriophages are found in 62% of healthy individuals on average, while their prevalence was reduced by 42% and 54% on average in patients with ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and ...
(UC) and Crohn's disease (CD). Abundance of phages may also decline in the elderly.
The most common phages in the human intestine, found worldwide, are crAssphages. CrAssphages are transmitted from mother to child soon after birth, and there is some evidence suggesting that they may be transmitted locally. Each person develops their own unique crAssphage clusters. CrAss-like phages also may be present in primates besides humans.
Commonly studied bacteriophage
Among the countless phage, only a few have been studied in detail, including some historically important phage that were discovered in the early days of microbial genetics. These, especially the T-phage, helped to discover important principles of gene structure and function. * 186 phage *λ phage
''Enterobacteria phage λ'' (lambda phage, coliphage λ, officially ''Escherichia virus Lambda'') is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species ''Escherichia coli'' (''E. coli''). It was discovered by Esther Leder ...
* Φ6 phage
* Φ29 phage
* ΦX174
The phi X 174 (or ΦX174) bacteriophage is a single-stranded DNA ( ssDNA) virus that infects ''Escherichia coli'', and the first DNA-based genome to be sequenced. This work was completed by Fred Sanger and his team in 1977. In 1962, Walter Fie ...
* Bacteriophage φCb5
* G4 phage
Escherichia virus G4 is a bacteriophage that infects '' E. coli''. First isolated in 1973, the phage was originally isolated from samples of raw sewage and has 5,577 nucleotides. Its isometric capsid contains a single-stranded circular genome ...
* M13 phage
M13 is one of the Ff phages (fd and f1 are others), a member of the family filamentous bacteriophage ( inovirus). Ff phages are composed of circular single-stranded DNA ( ssDNA), which in the case of the m13 phage is 6407 nucleotides long and ...
* MS2 phage (23–28 nm in size)
* N4 phage
* P1 phage
P1 is a temperate bacteriophage that infects ''Escherichia coli'' and some other bacteria. When undergoing a lysogenic cycle the phage genome exists as a plasmid in the bacterium unlike other phages (e.g. the lambda phage) that integrate into t ...
* P2 phage
* P4 phage
* R17 phage
* T2 phage
* T4 phage (169 kbp genome, 200 nm long)
* T7 phage
Bacteriophage T7 (or the T7 phage) is a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. It infects most strains of ''Escherichia coli'' and relies on these hosts to propagate. Bacteriophage T7 has a lytic life cycle, meaning that it destroys th ...
* T12 phage
See also
*Bacterivore A bacterivore is an organism which obtains energy and nutrients primarily or entirely from the consumption of bacteria. The term is most commonly used to describe free-living, heterotrophic, microscopic organisms such as nematodes as well as many s ...
* CrAssphage
* CRISPR
* DNA viruses
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and ...
* Macrophage
* Phage ecology
* Phage monographs (a comprehensive listing of phage and phage-associated monographs, 1921–present)
* Phagemid
A phagemid or phasmid is a DNA-based cloning vector, which has both bacteriophage and plasmid properties. These vectors carry, in addition to the origin of plasmid replication, an origin of replication derived from bacteriophage. Unlike commonly u ...
* Polyphage
* RNA viruses
* Transduction
* Viriome
* Virophage, viruses that infect other viruses
References
Bibliography
* *External links
* * * * * * * * {{Authority control Biology