Aztec Triple Alliance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance ( nci, ńíxcńĀn TlahtŇćlŇćyńĀn, ąj√©ňź ÉkaňźnŐ• tÕ°…¨a Ētoňźňąl√≥ňźjaňźnŐ• was an alliance of three Nahua city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the

 Shortly after the formation of the Triple Alliance, Itzcoatl and Tlacopan instigated sweeping reforms on the Aztec state and
Shortly after the formation of the Triple Alliance, Itzcoatl and Tlacopan instigated sweeping reforms on the Aztec state and
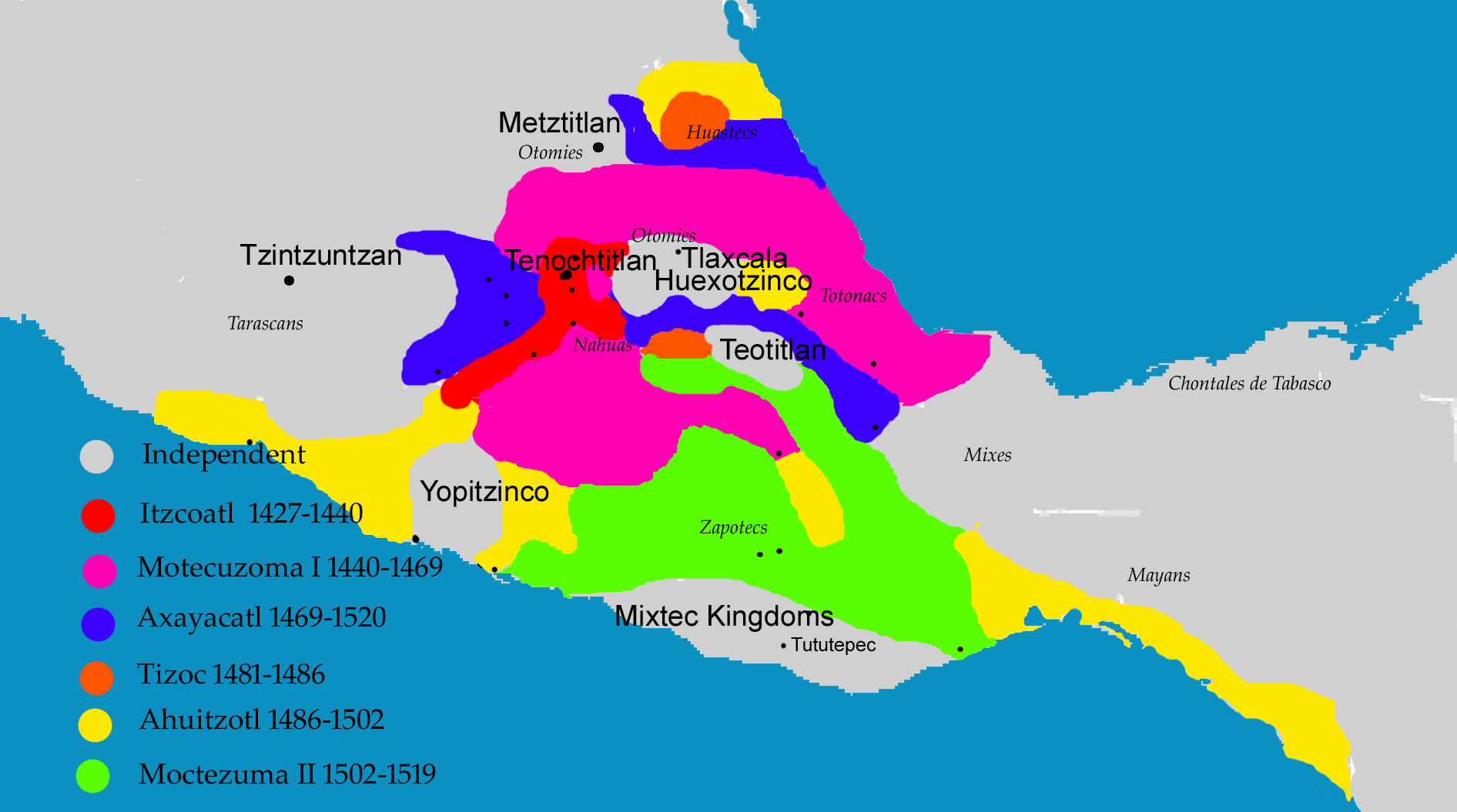 After the defeat of the Tepanecs, Itzcoatl and Nezahualcoyotl consolidated power in the Basin of Mexico and began to expand beyond its borders. The first targets for imperial expansion were Coyoacan in the Basin of Mexico and Cuauhnahuac and Huaxtepec in the modern Mexican state of
After the defeat of the Tepanecs, Itzcoatl and Nezahualcoyotl consolidated power in the Basin of Mexico and began to expand beyond its borders. The first targets for imperial expansion were Coyoacan in the Basin of Mexico and Cuauhnahuac and Huaxtepec in the modern Mexican state of
 Tizoc was succeeded by his brother
Tizoc was succeeded by his brother
 The Spanish expedition leader
The Spanish expedition leader 
 The Spanish-led Totonac army crossed into
The Spanish-led Totonac army crossed into  The Spaniards and their allies attempted to retreat without detection in what is known as the "Sad Night" or La Noche Triste, realizing that they were vulnerable to the hostile Mexica in Tenochtitlan following Moctezuma's death. Spaniards and their Indigenous allies were discovered clandestinely retreating and were then forced to fight their way out of the city with heavy loss of life. Some Spaniards lost their lives by drowning, loaded down with gold. They retreated to Tlacopan (now Tacuba) and made their way to
The Spaniards and their allies attempted to retreat without detection in what is known as the "Sad Night" or La Noche Triste, realizing that they were vulnerable to the hostile Mexica in Tenochtitlan following Moctezuma's death. Spaniards and their Indigenous allies were discovered clandestinely retreating and were then forced to fight their way out of the city with heavy loss of life. Some Spaniards lost their lives by drowning, loaded down with gold. They retreated to Tlacopan (now Tacuba) and made their way to
 Before the reign of
Before the reign of
 Nahua metaphysics centers around , "a single, dynamic, vivifying, eternally self-generating and self-regenerating sacred power, energy or force." This is conceptualized in a kind of monistic pantheism as manifest in the supreme god , as well as a large pantheon of lesser gods and idealizations of natural phenomena such as stars and fire. Priests and educated upper classes held more monistic views, while the popular religion of the uneducated tended to embrace the polytheistic and mythological aspects.
The Aztec empire's state-sanctioned religion meanwhile had to fulfill the spiritual obligations of the upper classes while maintaining their control over the lower classes and conquered populations. This was executed in grand public religious ceremonies, sponsorship of the most popular cults, and a relative degree of religious freedom.
Rulers, if they are local or , or central Huetlatoani, were seen as representatives of the gods and therefore ruled by divine right. , or the principle of rulership, established that descent inherited this divine right. Political order was, therefore, also a cosmic order, and to kill a was to transgress that order. For this reason, whenever the Nahuas killed or otherwise removed a tlatoani from their station, their stead typically placed a relative and member of the same bloodline. The establishment of the office of Huetlatoani understood through the creation of another level of rulership, , standing in superior contrast to the lesser principle.
A militaristic interpretation of Nahua religion, specifically a devout veneration of the sun god, Huitzilopochtli, guided expansion of the empire. Militaristic state rituals were performed throughout the year according to a ceremonial calendar of events, rites, and mock battles. The time period they lived in was understood as the , or Sun of Movement, which was believed to have been the final age after which humanity would be destroyed. It was under Tlacaelel that Huitzilopochtli assumed his elevated role in the state pantheon and who argued that it was through blood sacrifice that the Sun would be maintained and thereby stave off the end of the world. It was under this new, militaristic interpretation of Huitzilopochtli that Aztec soldiers were encouraged to fight wars and capture enemy soldiers for sacrifice. Though blood sacrifice was common in Mesoamerica, the scale of
Nahua metaphysics centers around , "a single, dynamic, vivifying, eternally self-generating and self-regenerating sacred power, energy or force." This is conceptualized in a kind of monistic pantheism as manifest in the supreme god , as well as a large pantheon of lesser gods and idealizations of natural phenomena such as stars and fire. Priests and educated upper classes held more monistic views, while the popular religion of the uneducated tended to embrace the polytheistic and mythological aspects.
The Aztec empire's state-sanctioned religion meanwhile had to fulfill the spiritual obligations of the upper classes while maintaining their control over the lower classes and conquered populations. This was executed in grand public religious ceremonies, sponsorship of the most popular cults, and a relative degree of religious freedom.
Rulers, if they are local or , or central Huetlatoani, were seen as representatives of the gods and therefore ruled by divine right. , or the principle of rulership, established that descent inherited this divine right. Political order was, therefore, also a cosmic order, and to kill a was to transgress that order. For this reason, whenever the Nahuas killed or otherwise removed a tlatoani from their station, their stead typically placed a relative and member of the same bloodline. The establishment of the office of Huetlatoani understood through the creation of another level of rulership, , standing in superior contrast to the lesser principle.
A militaristic interpretation of Nahua religion, specifically a devout veneration of the sun god, Huitzilopochtli, guided expansion of the empire. Militaristic state rituals were performed throughout the year according to a ceremonial calendar of events, rites, and mock battles. The time period they lived in was understood as the , or Sun of Movement, which was believed to have been the final age after which humanity would be destroyed. It was under Tlacaelel that Huitzilopochtli assumed his elevated role in the state pantheon and who argued that it was through blood sacrifice that the Sun would be maintained and thereby stave off the end of the world. It was under this new, militaristic interpretation of Huitzilopochtli that Aztec soldiers were encouraged to fight wars and capture enemy soldiers for sacrifice. Though blood sacrifice was common in Mesoamerica, the scale of
 Originally, the Aztec empire was a loose alliance between three cities: Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and the most junior partner, Tlacopan. As such, they were known as the 'Triple Alliance.' This political form was very common in Mesoamerica, where alliances of city-states were ever fluctuating. However, over time, Tenochtitlan assumed paramount authority in the alliance, and although each partner city shared spoils of war and rights to regular tribute from the provinces and were governed by their own Huetlatoani, Tenochtitlan became the largest, most powerful, and most influential of the three cities. It was the de facto and acknowledged center of empire.
Though the Aztecs did not describe them this way, there were essentially two types of provinces: Tributary and Strategic. Strategic provinces were essentially subordinate client states which provided tribute or aid to the Aztec state under "mutual consent." Tributary provinces, on the other hand, provided regular tribute to the empire; obligations on the part of Tributary provinces were mandatory rather than consensual.
Originally, the Aztec empire was a loose alliance between three cities: Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and the most junior partner, Tlacopan. As such, they were known as the 'Triple Alliance.' This political form was very common in Mesoamerica, where alliances of city-states were ever fluctuating. However, over time, Tenochtitlan assumed paramount authority in the alliance, and although each partner city shared spoils of war and rights to regular tribute from the provinces and were governed by their own Huetlatoani, Tenochtitlan became the largest, most powerful, and most influential of the three cities. It was the de facto and acknowledged center of empire.
Though the Aztecs did not describe them this way, there were essentially two types of provinces: Tributary and Strategic. Strategic provinces were essentially subordinate client states which provided tribute or aid to the Aztec state under "mutual consent." Tributary provinces, on the other hand, provided regular tribute to the empire; obligations on the part of Tributary provinces were mandatory rather than consensual.
 * Centeotl, god of maize associated with the Tianquiztli (goddesses of the Pleiades). Centeotl's name is also spelt as Cinteotl and was like a goddess.
* Chalchiuhtotolin, the god of cleanse and contamination, absolve human of guilt, and overcoming god of fate.
* Xochipilli, god of flowers, pleasure, feasting, frivolity and artistic creativity.
* Huehuecoyotl, god of old-age, origin, and deception. He is also the patron of wisdom, followed by his tricks and foolings. His name is similar to the god of happiness, Ueuecoyotl.
* Huitzilopochtli, god of will and the war, patron god of force, ruler of the
* Centeotl, god of maize associated with the Tianquiztli (goddesses of the Pleiades). Centeotl's name is also spelt as Cinteotl and was like a goddess.
* Chalchiuhtotolin, the god of cleanse and contamination, absolve human of guilt, and overcoming god of fate.
* Xochipilli, god of flowers, pleasure, feasting, frivolity and artistic creativity.
* Huehuecoyotl, god of old-age, origin, and deception. He is also the patron of wisdom, followed by his tricks and foolings. His name is similar to the god of happiness, Ueuecoyotl.
* Huitzilopochtli, god of will and the war, patron god of force, ruler of the
 * Chalchiuhtlicue, goddess of running water, lakes, rivers, oceans, streams, horizontal waters, storms and baptism.
* Chantico, goddess of fire, homes and
* Chalchiuhtlicue, goddess of running water, lakes, rivers, oceans, streams, horizontal waters, storms and baptism.
* Chantico, goddess of fire, homes and
 *
*
Valley of Mexico
The Valley of Mexico ( es, Valle de México) is a highlands plateau in central Mexico roughly coterminous with present-day Mexico City and the eastern half of the State of Mexico. Surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, the Valley of Mexico w ...
from 1428 until the combined forces of the Spanish and their native allies who ruled under defeated them in 1521.
The alliance was formed from the victorious factions of a civil war fought between the city of and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, the capital became dominant militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1519, the lands of the alliance were effectively ruled from , while other partners of the alliance had taken subsidiary roles.
The alliance waged wars of conquest and expanded after its formation. The alliance controlled most of central Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
at its height, as well as some more distant territories within Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
, such as the Xoconochco province, an Aztec exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
near the present-day Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, Rep√ļblica de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
n border. Aztec rule has been described by scholars as " hegemonic" or "indirect". The Aztecs left rulers of conquered cities in power so long as they agreed to pay semi-annual tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conq ...
to the alliance, as well as supply military forces when needed for the Aztec war efforts. In return, the imperial authority offered protection and political stability and facilitated an integrated economic network of diverse lands and peoples who had significant local autonomy.
Aztec religion was a monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of teotl
Teotl () is a Nahuatl term for sacredness or divinity that is sometimes translated as "god". For the Aztecs was the metaphysical omnipresence upon which their religious philosophy was based.
As described by James Maffie, "is essentially power: ...
was construed as the supreme god Ometeotl, as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion tended to embrace the mythological and polytheistic aspects, and the empire's state religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a t ...
sponsored both the monism of the upper classes and the popular heterodoxies. The empire even officially recognized the largest cults such that the deity was represented in the central temple precinct of the capital . The imperial cult was specifically that of the distinctive warlike patron god of the Mexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: , ;''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1990). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frolink/ref> singular ) were a Nahuatl-speaking indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of ...
. Peoples were allowed to retain and freely continue their own religious traditions in conquered provinces so long as they added the imperial god to their local pantheons.
Etymology and definitions
The word "Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
" in modern usage would not have been used by the people themselves. It has variously been used to refer to the Aztecs or Triple Alliance, the Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
-speaking people of central Mexico prior to the Spanish conquest, or specifically the Mexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: , ;''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1990). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frolink/ref> singular ) were a Nahuatl-speaking indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of ...
ethnicity of the Nahuatl-speaking tribes (from ). The name comes from the singular Nahuatl word () that means " eoplefrom Aztlan", reflecting the mythical place of origin for Nahua peoples.
History

Before the Aztec Empire
Nahua peoples descended from Chichimec peoples, who migrated to central Mexico from the north (mainly centered sparsely around present-day states of Zacatecas,San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí), is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and i ...
, and Guanajuato
Guanajuato (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato), is one of the 32 states that make up the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 46 municipalities and its capital city i ...
) in the early 13th century. The migration story of the Mexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: , ;''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1990). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frolink/ref> singular ) were a Nahuatl-speaking indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of ...
is similar to those of other polities in central Mexico, with supernatural sites, individuals, and events, joining earthly and divine history, as they sought political legitimacy. Pictographic codices in which the Aztecs recorded their history say that the empire's place of origin was called Aztl√°n
Aztl√°n (from nah, Astlan, ) is the ancestral home of the Aztec peoples. '' Astekah'' is the Nahuatl word for "people from Aztlan". Aztlan is mentioned in several ethnohistorical sources dating from the colonial period, and while they each cite ...
. Early migrants settled the Basin of Mexico and surrounding lands by establishing a series of independent city-states. These early Nahua city-states or were ruled by dynastic heads called (singularly ). Most of the existing settlements had been established by other indigenous peoples before the Mexica migration.
These early city-states fought various small-scale wars with each other but no individual city gained dominance due to shifting alliances. The Mexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: , ;''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1990). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frolink/ref> singular ) were a Nahuatl-speaking indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of ...
were the last of the Nahua migrants to arrive in Central Mexico. They entered the Basin of Mexico around the year 1250, and, by then, most of the good agricultural land had already been claimed. The Mexica persuaded the king of Culhuacan, a small city-state but important historically as a refuge of the Toltecs
The Toltec culture () was a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, reaching prominence from 950 to 1150 CE ...
to make them settle in a relatively infertile patch of land called Chapultepec (''Chapoltepńďc,'' "in the hill of grasshoppers"). The Mexica served as mercenaries for Culhuacan.
After the Mexica served Culhuacan in battle, the ruler appointed one of his daughters to rule over the Mexica. Mythological native accounts say that the Mexica instead sacrificed her by flaying her skin on the command of their god Xipe Totec
In Aztec mythology and religion, Xipe Totec (; nci-IPA, Xńępe Totńďc, ňą Éiňźpe ňątoteňźk( ∑)) or Xipetotec ("Our Lord the Flayed One") was a life-death-rebirth deity, god of agriculture, vegetation, the east, spring, goldsmiths, silversmith ...
. The ruler of Culhuacan attacked and used his army to drive the Mexica from Tizaapan by force when he learned of this. The Mexica moved to an island in the middle of Lake Texcoco where an eagle nested on a nopal cactus. The Mexica interpreted this as a sign from their gods and founded their new city Tenochtitlan on this island in the year (or "Two House", 1325 AD).
Aztec warfare
The Mexica rose to prominence as fierce warriors and were able to establish themselves as a military power. The importance of warriors and the integral nature of warfare in Mexica political and religious life helped propel them to emerge as the dominant military power, prior to the arrival of the Spanish in 1519. The new Mexica city-state allied with the city ofAzcapotzalco
Azcapotzalco ( nci, ńÄzcapŇćtzalco , , from '' ńĀzcapŇćtzalli'' ‚Äúanthill‚ÄĚ + '' -co'' ‚Äúplace‚ÄĚ; literally, ‚ÄúIn the place of the anthills‚ÄĚ) is a borough (''demarcaci√≥n territorial'') in Mexico City. Azcapotzalco is in the northwestern ...
and paid tribute to its ruler Tezozomoc. Azcapotzalco began to expand into a small tributary empire with Mexica assistance. The Mexica ruler was not recognized as a legitimate king until this point. Mexica leaders successfully petitioned one of the kings of Culhuacan to provide a daughter to marry into the Mexica line. Their son Acamapichtli was enthroned as the first of Tenochtitlan in 1372.
The Tepanecs of Azcapotzalco expanded their rule with help from the Mexica, while the Acolhua
The Acolhua are a Mesoamerican people who arrived in the Valley of Mexico in or around the year 1200 CE. The Acolhua were a sister culture of the Aztecs (or Mexica) as well as the Tepanec, Chalca, Xochimilca and others.
The most important poli ...
city of Texcoco grew in power in the eastern portion of the lake basin. Eventually, war erupted between the two states, and the Mexica played a vital role in the conquest of Texcoco. By then, Tenochtitlan had grown into a major city and was rewarded for its loyalty to the Tepanecs by receiving Texcoco as a tributary province.
Mexica warfare was marked by a focus on capturing enemies rather than killing them from its tactics to arms. Capturing enemies was important for religious ritual and provided a means by which soldiers could distinguish themselves during campaigns.
Tepanec War
In 1426, the Tepanec king Tezozomoc died, and the resulting succession crisis precipitated a civil war between potential successors. The Mexica supported Tezozomoc's preferred heir Tayahauh, who was initially enthroned as king. But his son Maxtla soon usurped the throne and turned against factions that opposed him, including the Mexica ruler Chimalpopoca. The latter died shortly thereafter, possibly assassinated by Maxtla. The new Mexica ruler Itzcoatl continued to defy Maxtla, and he blockaded Tenochtitlan and demanded increased tribute payments. Maxtla similarly turned against theAcolhua
The Acolhua are a Mesoamerican people who arrived in the Valley of Mexico in or around the year 1200 CE. The Acolhua were a sister culture of the Aztecs (or Mexica) as well as the Tepanec, Chalca, Xochimilca and others.
The most important poli ...
, and the king of Texcoco Nezahualcoyotl Nezahualcoyotl may refer to:
* Nezahualcoyotl (tlatoani), the ruler of Texcoco
* Ciudad Nezahualcóyotl, a city in the State of Mexico
* Nezahualcóyotl metro station, in Mexico City
* The Nezahualcóyotl Award, a literary prize in Mexico
* Neza ...
fled into exile. Nezahualcoyotl recruited military help from the king of Huexotzinco, and the Mexica gained the support of a dissident Tepanec city called Tlacopan. In 1427, Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, Tlacopan, and Huexotzinco went to war against Azcapotzalco, emerging victorious in 1428.
After the war, Huexotzinco withdrew, and, in 1430, the three remaining cities formed a treaty now known as the Triple Alliance. The Tepanec lands were carved up among the three cities, whose leaders agreed to cooperate in future wars of conquest. Land acquired from these conquests was to be held by the three cities together. A tribute was divided so that two kings of the alliance would go to Tenochtitlan and Texcoco and one would go to Tlacopan. The three kings assumed the title "huetlatoani" ("Elder Speaker", often translated as "Emperor") in turn. Each temporarily held a position above the rulers of other city-states ("tlatoani") in this role.
In the following 100 years, the Triple Alliance of Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan dominated the Valley of Mexico and extended its power to the shores of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
and the Pacific. Tenochtitlan gradually became the dominant power in the alliance. Two of the primary architects of this alliance were the half-brothers and nephews of Itzcoatl Tlacaelel and Moctezuma. Moctezuma eventually succeeded Itzcoatl as the Mexica in 1440. Tlacaelel occupied the newly created " Cihuacoatl" title, equivalent to something between "Prime Minister" and "Viceroy".
Imperial reforms
religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
. It has been alleged that Tlacaelel ordered the burning of some or most of the extant Aztec books, claiming that they contained lies and that it was "not wise that all the people should know the paintings". If he ordered book-burnings, it would have been primarily limited to documents containing political propaganda from previous regimes. He rewrote the history of the Aztecs thereafter, naturally placing the Mexica in a more central role.
After Moctezuma I
Moctezuma I (‚Äď1469), also known as Moteuczomatzin Ilhuicamina (), Huehuemoteuczoma or Montezuma I ( nci, MotńďuczŇćma Ilhuicamńęna , nci, HuńďhuemotńďuczŇćma ), was the second Aztec emperor and fifth king of Tenochtitlan. During his reign, t ...
succeeded Itzcoatl as the Mexica emperor, more reforms were instigated to maintain control over conquered cities. Uncooperative kings were replaced with puppet rulers loyal to the Mexica. A new imperial tribute system established Mexica tribute collectors that taxed the population directly, bypassing the authority of local dynasties. Nezahualcoyotl also instituted a policy in the Acolhua lands of granting subject kings tributary holdings in lands far from their capitals. This was done to create an incentive for cooperation with the empire; if a city's king rebelled, he lost the tribute he received from foreign land. Some rebellious kings were replaced by or appointed governors rather than dynastic rulers.
Moctezuma issued new laws that separated nobles from commoners and instituted the death penalty for adultery and other offenses. A religiously supervised school was built in every neighborhood by royal decree. Commoner neighborhoods had a school called a "" where they received basic religious instruction and military training. A second, more prestigious type of school called a "" served to teach the nobility, as well as commoners of high standing seeking to become priests or artisans. Moctezuma also created a new title called "" that could be conferred on commoners. This title was a form of non-hereditary lesser nobility awarded for outstanding military or civil service (similar to the English knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the Christian denomination, church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood ...
). Commoners who received this title rarely married into royal families and became kings.
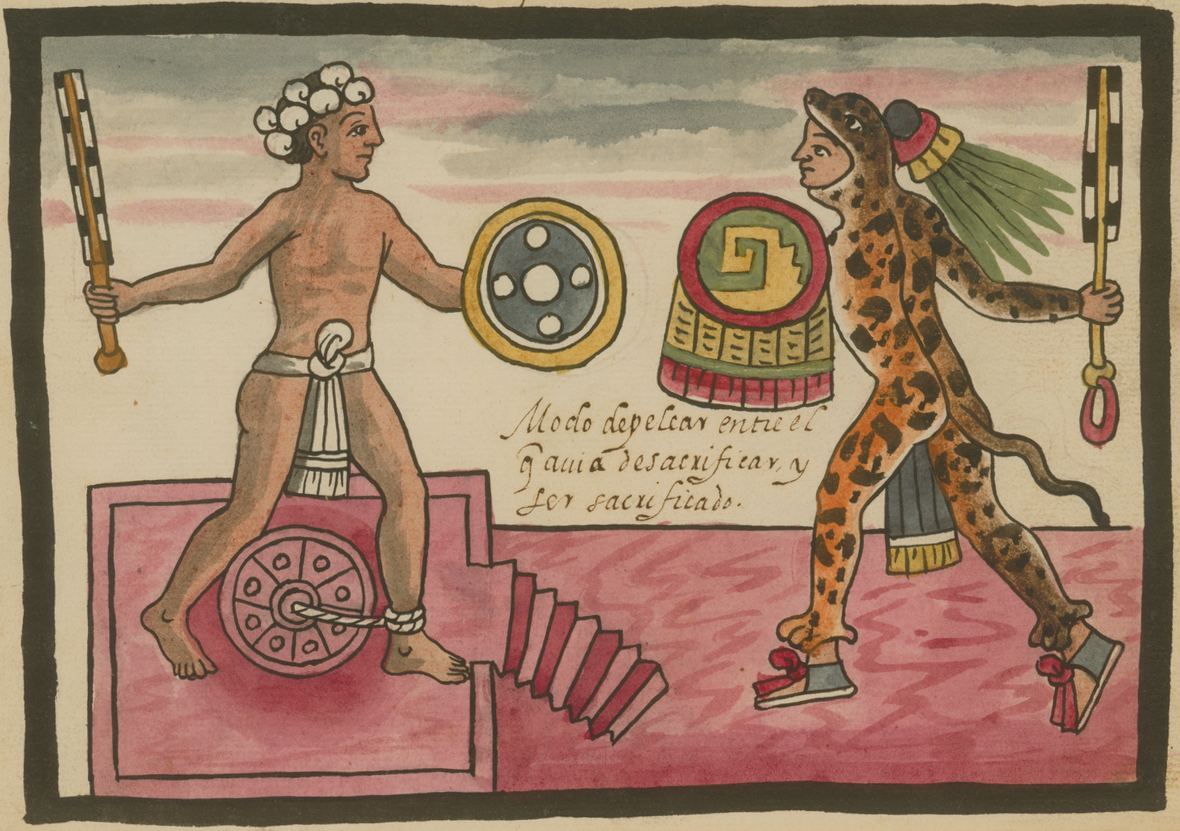
One component of this reform was the creation of an institution of regulated warfare called the Flower Wars. Mesoamerican warfare overall is characterized by a strong preference for capturing live prisoners as opposed to slaughtering the enemy on the battlefield, which was considered sloppy and gratuitous. The Flower Wars are a potent manifestation of this approach to warfare. These highly ritualized wars ensured a steady, healthy supply of experienced Aztec warriors as well as a steady, healthy supply of captured enemy warriors for sacrifice
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly exis ...
to the gods. Flower wars were pre-arranged by officials on both sides and conducted specifically for the purpose of each polity collecting prisoners for sacrifice. Native historical accounts say that these wars were instigated by Tlacaelel as a means of appeasing the gods in response to a massive drought that gripped the Basin of Mexico from 1450 to 1454. The flower wars were mostly waged between the Aztec Empire and the neighboring cities of their arch-enemy Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala (; , ; from nah, TlaxcallńĀn ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is ...
.
Early years of expansion
 After the defeat of the Tepanecs, Itzcoatl and Nezahualcoyotl consolidated power in the Basin of Mexico and began to expand beyond its borders. The first targets for imperial expansion were Coyoacan in the Basin of Mexico and Cuauhnahuac and Huaxtepec in the modern Mexican state of
After the defeat of the Tepanecs, Itzcoatl and Nezahualcoyotl consolidated power in the Basin of Mexico and began to expand beyond its borders. The first targets for imperial expansion were Coyoacan in the Basin of Mexico and Cuauhnahuac and Huaxtepec in the modern Mexican state of Morelos
Morelos (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Morelos ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Morelos), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 36 municipalities and its capital city is Cue ...
. These conquests provided the new empire with a large influx of tribute, especially agricultural goods.
Itzcoatl died, and Moctezuma I was enthroned as the new Mexica emperor. The expansion of the empire was briefly halted by a major four-year drought that hit the Basin of Mexico in 1450, and several cities in Morelos had to be re-conquered after the drought subsided. Moctezuma and Nezahualcoyotl continued to expand the empire east towards the Gulf of Mexico and south into Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, HuńĀxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipaliti ...
. In 1468, Moctezuma I died and was succeeded by his son Axayacatl. Most of Axayacatl's thirteen-year reign was spent consolidating the territory acquired under his predecessor. Motecuzoma and Nezahualcoyotl had expanded rapidly and many provinces rebelled.
Also, as the Aztec Empire was expanding and consolidating power, the Purépecha Empire in West Mexico was similarly expanding. In 1455, the Purépecha under their king Tzitzipandaquare had invaded the Toluca Valley, claiming lands previously conquered by Motecuzoma and Itzcoatl. In 1472, Axayacatl re-conquered the region and successfully defended it from Purépecha's attempts to take it back. In 1479, Axayacatl launched a major invasion of the Purépecha Empire with 32,000 Aztec soldiers. Purépecha met them just across the border with 50,000 soldiers and scored a resounding victory, killing or capturing over 90% of the Aztec army. Axayacatl himself was wounded in the battle, retreated to Tenochtitlan, and never engaged the Purépecha in battle again.
In 1472, Nezahualcoyotl died, and his son Nezahualpilli
Nezahualpilli (Nahuatl for "fasting prince"; 1464‚Äď1515, ) was king (''tlatoani'') of the Mesoamerican city-state of Texcoco, elected by the city's nobility after the death of his father, Nezahualcoyotl, in 1472. Nezahuapilli's mother was Azcal ...
was enthroned as the new huetlatoani of Texcoco. This was followed by the death of Axayacatl in 1481. Axayacatl was replaced by his brother Tizoc
Tizocic or Tizocicatzin usually known in English as Tizoc, was the seventh ''tlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan. His name means, "He who makes sacrifices" or "He who does penance." Either Tizoc or his successor Ahuitzotl was the first ''tlatoani'' of ...
. Tizoc's reign was notoriously brief. He proved to be ineffectual and did not significantly expand the empire. Tizoc was likely assassinated by his own nobles five years into his rule, apparently due to his incompetence.
Later years of expansion
Ahuitzotl
Ahuitzotl ( nah, ńĀhuitzotl, ) was the eighth Aztec ruler, the ''Huey Tlatoani'' of the city of Tenochtitlan, son of princess Atotoztli II. His name literally means "Water Thorny" and was also applied to the otter. It is also theorized that m ...
in 1486. Like his predecessors, the first part of Ahuitzotl's reign was spent suppressing rebellions that were commonplace due to the indirect nature of Aztec rule. Ahuitzotl then began a new wave of conquests including the Oaxaca Valley
The Central Valleys ( es, Valles Centrales) of Oaxaca, also simply known as the Oaxaca Valley, is a geographic region located within the modern-day state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico. In an administrative context, it has been defined as comprisin ...
and the Soconusco Coast. Ahuitzotl conquered the border city of Otzoma and turned the city into a military outpost due to increased border skirmishes with the Purépecha. The population of Otzoma was either killed or dispersed in the process. The Purépecha subsequently established fortresses nearby to protect against Aztec expansion. Ahuitzotl responded by expanding further west to the Pacific Coast of Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
.
By the reign of Ahuitzotl, the Mexica were the largest and most powerful faction in the Aztec Triple Alliance. Building on the prestige the Mexica had acquired over the course of the conquests, Ahuitzotl began to use the title "huehuetlatoani" ("Eldest Speaker") to distinguish himself from the rulers of Texcoco and Tlacopan. The alliance still technically ran the empire. But the Mexica Emperor now assumed nominal if not actual seniority.
Ahuitzotl was succeeded by his nephew Moctezuma II
Moctezuma Xocoyotzin ( ‚Äď 29 June 1520; oteňźkňąsoňźmaŠłĀ ÉoňźkoňąjoňźtÕ°sń©nŐ•), nci-IPA, MotńďuczŇćmah XŇćcoyŇćtzin, moteňźk ∑ňąsoňźma Éoňźkoňąjoňźtsin variant spellings include Motewksomah, Motecuhzomatzin, Montezuma, Moteuczoma, Motecu ...
in 1502. Moctezuma II spent most of his reign consolidating power in lands conquered by his predecessors. In 1515, Aztec armies commanded by the Tlaxcalan general Tlahuicole invaded the Purépecha Empire once again. The Aztec army failed to take any territory and was mostly restricted to raiding. The Purépecha defeated them and the army withdrew.
Moctezuma II instituted more imperial reforms. The death of Nezahualcoyotl caused the Mexica Emperors to become the rulers of the alliance. Moctezuma II used his reign to attempt to consolidate power more closely with the Mexica Emperor. He removed many of Ahuitzotl's advisors and had several of them executed. He also abolished the class, destroying the chance for commoners to advance to the nobility. His reform efforts were cut short by the Spanish Conquest in 1519.
Spanish conquest
Hernán Cortés
Hern√°n Cort√©s de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 ‚Äď December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
landed in Yucatán in 1519 with approximately 630 men (most armed with only a sword and shield). Cortés had actually been removed as the expedition's commander by the governor of Cuba Diego Velásquez but had stolen the boats and left without permission. At the island of Cozumel, Cortés encountered a shipwrecked Spaniard named Gerónimo de Aguilar
Jer√≥nimo de Aguilar O.F.M. (1489‚Äď1531) was a Franciscan friar born in √Čcija, Spain. Aguilar was sent to Panama to serve as a missionary. He was later shipwrecked on the Yucat√°n Peninsula in 1511 and captured by the Maya. In 1519 Hern√°n ...
who joined the expedition and translated between Spanish and Mayan. The expedition then sailed west to Campeche, where, after a brief battle with the local army, Cortés was able to negotiate peace through his interpreter Aguilar. The King of Campeche gave Cortés a second translator, a bilingual Nahua-Maya slave woman named La Malinche
Marina or Malintzin ( 1500 ‚Äď 1529), more popularly known as La Malinche , a Nahua woman from the Mexican Gulf Coast, became known for contributing to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire (1519‚Äď1521), by acting as an interpreter, ad ...
(she was known also as Malinalli aliňąnalňźi Malintzin aňąlintsinor Do√Īa Marina ądo…≤a maňą…ĺina. Aguilar translated from Spanish to Mayan, and La Malinche translated from Mayan to Nahuatl. Malinche became Cort√©s' translator for both language and culture once she learned Spanish, and she was a key figure in interactions with Nahua rulers.
Cortés then sailed from Campeche to Cempoala, a tributary province of the Aztec Triple Alliance. Nearby, he founded the town of Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
where he met with ambassadors from the reigning Mexica emperor Motecuzoma II. When the ambassadors returned to Tenochtitlan, Cortés went to Cempoala to meet with the local Totonac leaders. The Totonac ruler told Cortés of his various grievances against the Mexica, and Cortés convinced the Totonacs to imprison an imperial tribute collector. Cortés subsequently released the tribute collector after persuading him that the move was entirely the Totonac's idea and that he had no knowledge of it. The Totonacs provided Cortés with 20 companies of soldiers for his march to Tlaxcala, having effectively declared war on the Aztecs. At this time, several of Cortés' soldiers attempted to mutiny. When Cortés discovered the plot, he had his ships scuttled and sank them in the harbor to remove any possibility of escaping to Cuba.

 The Spanish-led Totonac army crossed into
The Spanish-led Totonac army crossed into Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala (; , ; from nah, TlaxcallńĀn ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is ...
to seek the latter's alliance against the Aztecs. However, the Tlaxcalan general Xicotencatl the Younger believed them to be hostile and attacked. After fighting several close battles, Cortés eventually convinced the leaders of Tlaxcala to order their general to stand down. Cortés then secured an alliance with the people of Tlaxcala and traveled from there to the Basin of Mexico with a smaller company of 5,000-6,000 Tlaxcalans and 400 Totonacs in addition to the Spanish soldiers. During his stay in the city of Cholula, Cortés claims he received word of a planned ambush against the Spanish. In a pre-emptive response, Cortés directed his troops to attack and kill a large amount of unarmed Cholulans gathered in the main square of the city.
Following the massacre at Cholula, Cortés and the other Spaniards entered Tenochtitlan, where they were greeted as guests and given quarters in the palace of former emperor Axayacatl. After staying in the city for six weeks, two Spaniards from the group left behind in Veracruz were killed in an altercation with an Aztec lord named Quetzalpopoca. Cortés claims that he used this incident as an excuse to take Motecuzoma prisoner under threat of force. Motecuzoma continued to run the kingdom as a prisoner of Cortés for several months. A second, larger Spanish expedition then arrived in 1520 under the command of Pánfilo de Narváez
P√°nfilo de Narv√°ez (; 147?‚Äď1528) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' and soldier in the Americas. Born in Spain, he first embarked to Jamaica in 1510 as a soldier. He came to participate in the conquest of Cuba and led an expedition to Camag√ ...
sent by Diego Velásquez with the goal of arresting Cortés for treason. Before confronting Narváez, Cortés secretly persuaded Narváez's lieutenants to betray him and join Cortés.
Cortés was away from Tenochtitlan dealing with Narváez, while his second-in-command Pedro de Alvarado
Pedro de Alvarado (; c. 1485 ‚Äď 4 July 1541) was a Spanish conquistador and governor of Guatemala.Lovell, Lutz and Swezey 1984, p. 461. He participated in the conquest of Cuba, in Juan de Grijalva's exploration of the coasts of the Yucat ...
massacred a group of Aztec nobility, in response to a ritual of human sacrifice honoring Huitzilopochtli. The Aztecs retaliated by attacking the palace where the Spanish were quartered. Cortés returned to Tenochtitlan and fought his way to the palace. He then took Motecuzoma up to the roof of the palace to ask his subjects to stand down. However, by this point, the ruling council of Tenochtitlan had voted to depose Motecuzoma and had elected his brother Cuitlahuac as the new emperor. One of the Aztec soldiers struck Motecuzoma in the head with a sling stone, and he died several days later, though the exact circumstances of his death are unclear.
 The Spaniards and their allies attempted to retreat without detection in what is known as the "Sad Night" or La Noche Triste, realizing that they were vulnerable to the hostile Mexica in Tenochtitlan following Moctezuma's death. Spaniards and their Indigenous allies were discovered clandestinely retreating and were then forced to fight their way out of the city with heavy loss of life. Some Spaniards lost their lives by drowning, loaded down with gold. They retreated to Tlacopan (now Tacuba) and made their way to
The Spaniards and their allies attempted to retreat without detection in what is known as the "Sad Night" or La Noche Triste, realizing that they were vulnerable to the hostile Mexica in Tenochtitlan following Moctezuma's death. Spaniards and their Indigenous allies were discovered clandestinely retreating and were then forced to fight their way out of the city with heavy loss of life. Some Spaniards lost their lives by drowning, loaded down with gold. They retreated to Tlacopan (now Tacuba) and made their way to Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala (; , ; from nah, TlaxcallńĀn ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is ...
where they recovered and prepared for the second, successful assault on Tenochtitlan. After this incident, a smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
outbreak
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
hit Tenochtitlan. The outbreak alone killed more than 50% of the region's population, including the emperor Cuitl√°huac
Cuitl√°huac (, ) (c. 1476 – 1520) or Cuitl√°huac (in Spanish orthography; nah, CuitlńĀhuac, , honorific form: Cuitlahuatzin) was the 10th ''Huey Tlatoani'' (emperor) of the Aztec city of Tenochtitlan for 80 days during the year Two Flin ...
, as the indigenous of the New World had no previous exposure to smallpox. The new emperor Cuauhtémoc dealt with the smallpox outbreak, while Cortés raised an army of Tlaxcalans, Texcocans, Totonacs, and others discontent with Aztec rule. Cortés marched back to the Basin of Mexico with a combined army of up to 100,000 warriors. The overwhelming majority of warriors were indigenous rather than Spanish. Cortés captured various indigenous city-states or altepetl
The (, plural ''altepeme'' or ''altepemeh'') was the local, ethnically-based political entity, usually translated into English as "city-state," of pre-Columbian Nahuatl-speaking societiesSmith 1997 p. 37 in the Americas. The ''altepetl'' was ...
around the lake shore and surrounding mountains through numerous subsequent battles and skirmishes, including the other capitals of the Triple Alliance, Tlacopan and Texcoco. Texcoco, in fact, had already become firm allies of the Spaniards and the city-state and subsequently petitioned the Spanish crown for recognition of their services in the conquest similar to Tlaxcala.
Cortés used boats constructed in Texcoco from parts salvaged from the scuttled ships to blockade and lay siege to Tenochtitlan for a period of several months. Eventually, the Spanish-led army assaulted the city both by boat and using the elevated causeways connecting it to the mainland. The attackers took heavy casualties, although the Aztecs were ultimately defeated. The city of Tenochtitlan was thoroughly destroyed in the process. Cuauhtémoc was captured as he attempted to flee the city. Cortés kept him prisoner and tortured him for a period of several years before finally executing him in 1525.
Government
The Aztec Empire was an example of anempire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
that ruled by indirect means. It was ethnically very diverse like most European empires but was more a system of tributes than a single unitary form of government unlike them. In the theoretical framework of imperial systems posited by American historian Alexander J. Motyl
Alexander John Motyl ( uk, –ě–Ľ–Ķ–ļ—Ā–į–Ĺ–ī—Ä –ú–ĺ—ā–ł–Ľ—Ć; born October 21, 1953) is an American historian, political scientist, poet, writer, translator and artist-painter. He is a resident of New York City. He is professor of political science ...
, the Aztec empire was an informal type of empire in that the Alliance did not claim supreme authority over its tributary provinces. It merely expected to pay tributes. The empire was also territorially discontinuous, i.e. land did not connect all of its dominated territories. For example, the southern peripheral zones of Xoconochco were not in immediate contact with the central part of the empire. The hegemonic nature of the Aztec empire can be seen in the fact that generally local rulers were restored to their positions once they conquered their city-state, and the Aztecs did not interfere in local affairs as long as the tribute payments were made.
The form of government is often referred to as an empire, yet most areas within the empire were, in fact, organized as city-states (individually known as in Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
, the language of the Aztecs). These were small polities ruled by a king or (literally "speaker", plurally ) from an aristocratic dynasty. The Early Aztec period was a time of growth and competition among altepeme. After the Nahuas formed the empire in 1428 and the empire began its program of expansion through conquest, the altepetl remained the dominant form of organization at the local level. The efficient role of the altepetl as a regional political unit was largely responsible for the success of the empire's hegemonic form of control.
The term "Aztec empire" is actually modern and not one used by the Aztecs themselves. The Aztec realm was at its core composed of three Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
-speaking city-states in the densely populated Valley of Mexico. Asymmetries of power elevated one of those city states Tenochtitlan above the other two over time. The "Triple Alliance" came to establish hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC ‚Äď AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
over much of central Mesoamerica, including areas of great linguistic and cultural diversity. The Nahuas performed administration of the empire through largely traditional, indirect means. Something of a nascent bureaucracy
The term bureaucracy () refers to a body of non-elected governing officials as well as to an administrative policy-making group. Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected offi ...
, however, may have been beginning to form over time, insofar as the state organization became increasingly centralized.
Central administration

 Before the reign of
Before the reign of Nezahualcoyotl Nezahualcoyotl may refer to:
* Nezahualcoyotl (tlatoani), the ruler of Texcoco
* Ciudad Nezahualcóyotl, a city in the State of Mexico
* Nezahualcóyotl metro station, in Mexico City
* The Nezahualcóyotl Award, a literary prize in Mexico
* Neza ...
(1429‚Äď1472), the Aztec empire operated as a confederation along traditional Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
n lines. Independent altepetl were led by (lit., "speakers"), who supervised village headmen, who in turn supervised groups of households. A typical Mesoamerican confederation placed a (lit., "great speaker") at the head of several tlatoani. Following Nezahualcoyotl, the Aztec empire followed a somewhat divergent path, with some tlatoani of recently conquered or otherwise subordinated altepetl becoming replaced with stewards charged with collecting tribute on behalf of the Huetlatoani rather than simply replacing an old tlatoque with new ones from the same set of local nobility.
Yet the Huey tlatoani was not the sole executive. It was the responsibility of the Huey tlatoani to deal with the ''external'' issues of empire; the management of tribute, war, diplomacy, and expansion were all under the purview of the Huey tlatoani. It was the role of the to govern a given city itself. The Cihuacoatl was always a close relative of the Huey tlatoani; Tlacaelel, for example, was the brother of Moctezuma I. Both the title "Cihuacoatl", which means "female snake" (it is the name of a Nahua deity), and the role of the position, somewhat analogous to a European Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
or Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
, reflect the dualistic nature of Nahua cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher ...
. Neither the position of Cihuacoatl nor the position of Huetlatoani were priestly, yet both did have important ritual tasks. Those of the former were associated with the "female" wet season, those of the latter with the "male" dry season. While the position of Cihuacoatl is best attested in Tenochtitlan, it is known that the position also existed the nearby altepetl of Azcapotzalco
Azcapotzalco ( nci, ńÄzcapŇćtzalco , , from '' ńĀzcapŇćtzalli'' ‚Äúanthill‚ÄĚ + '' -co'' ‚Äúplace‚ÄĚ; literally, ‚ÄúIn the place of the anthills‚ÄĚ) is a borough (''demarcaci√≥n territorial'') in Mexico City. Azcapotzalco is in the northwestern ...
, Culhuacan, and Tenochtitlan's ally Texcoco. Despite the apparent lesser status of the position, a Cihuacoatl could prove both influential and powerful, as in the case of Tlacaelel.
Early in the history of the empire, Tenochtitlan developed a four-member military and advisory Council which assisted the Huey tlatoani in his decision-making: the ; the ; the ; and the . This design not only provided advise for the ruler, it also served to contain ambition on the part of the nobility, as henceforth Huey Tlatoani
''Tlatoani'' ( , "one who speaks, ruler"; plural ' or tlatoque) is the Classical Nahuatl term for the ruler of an , a pre-Hispanic state. It is the noun form of the verb "tlahtoa" meaning "speak, command, rule". As a result, it has been various ...
could only be selected from the council. Moreover, the actions of any one member of the council could easily be blocked by the other three, providing a simple system of checks on the ambition higher officials. These four Council members were also generals, members of various military societies. The ranks of the members were not equal, with the and having a higher status than the others. These two Councillors were members of the two most prestigious military societies, the ("shorn ones") and the (" Otomies"). The , the relatives of the former Huey tlatoani, will choose the next Huey tlatoani from the four council members.
Provincial administration
Traditionally, provinces and altepetl were governed by hereditary tlatoani. As the empire grew, the system evolved further and some tlatoani were replaced by other officials. The other officials had similar authority to tlatoani. As has already been mentioned, directly appointed stewards (singular , plural ) were sometimes imposed on altepetl instead of the selection of provincial nobility to the same position of tlatoani. At the height of empire, the organization of the state into tributary and strategic provinces saw an elaboration of this system. The 38 tributary provinces fell under the supervision of high stewards, or , whose authority extended over the lower-ranking calpixque. These calpixque and huecalpixque were essentially managers of the provincial tribute system which was overseen and coordinated in the paramount capital of Tenochtitlan not by the , but rather by a separate position altogether: the . On the occasion that a recently conquered altepetl was seen as particularly restive, the Nahuas placed a military governor, or , at the head of provincial supervision. During his reign, Moctezuma I elaborated the calpixque system, with two calpixque assigned per tributary province. The province itself stationed one, perhaps for supervising the collection of tribute, and the other in Tenochtitlan, perhaps for supervising storage of tribute. Commoners drew the tribute, the , and distributed to the nobility, be they 'kings' (), lesser rulers (), or provincial nobility (). The Nahuas supervised the tribute collection by the above officials and relied upon the coercive power of the Aztec military, but also upon the cooperation of the (the local nobility who were themselves exempt from and recipient to tribute) and the hereditary class of merchants known as . These pochteca had various gradations of ranks which granted them certain trading rights and so were not necessarily pipiltin themselves, yet they played an important role in both the growth and administration of the Aztec tributary system nonetheless. The pochteca strongly tied their power, political and economic, to the political and military power of the Aztec nobility and state. In addition to serving as diplomats (, or "travelers of the lord") and spies in the prelude to conquest, higher-ranking pochteca also served as judges in market plazas and were to certain degree autonomouscorporate groups
A corporate group or group of companies is a collection of parent and subsidiary corporations that function as a single economic entity through a common source of control. These types of groups are often managed by an account manager. The concept ...
, having administrative duties within their own estate.
Ideology and state
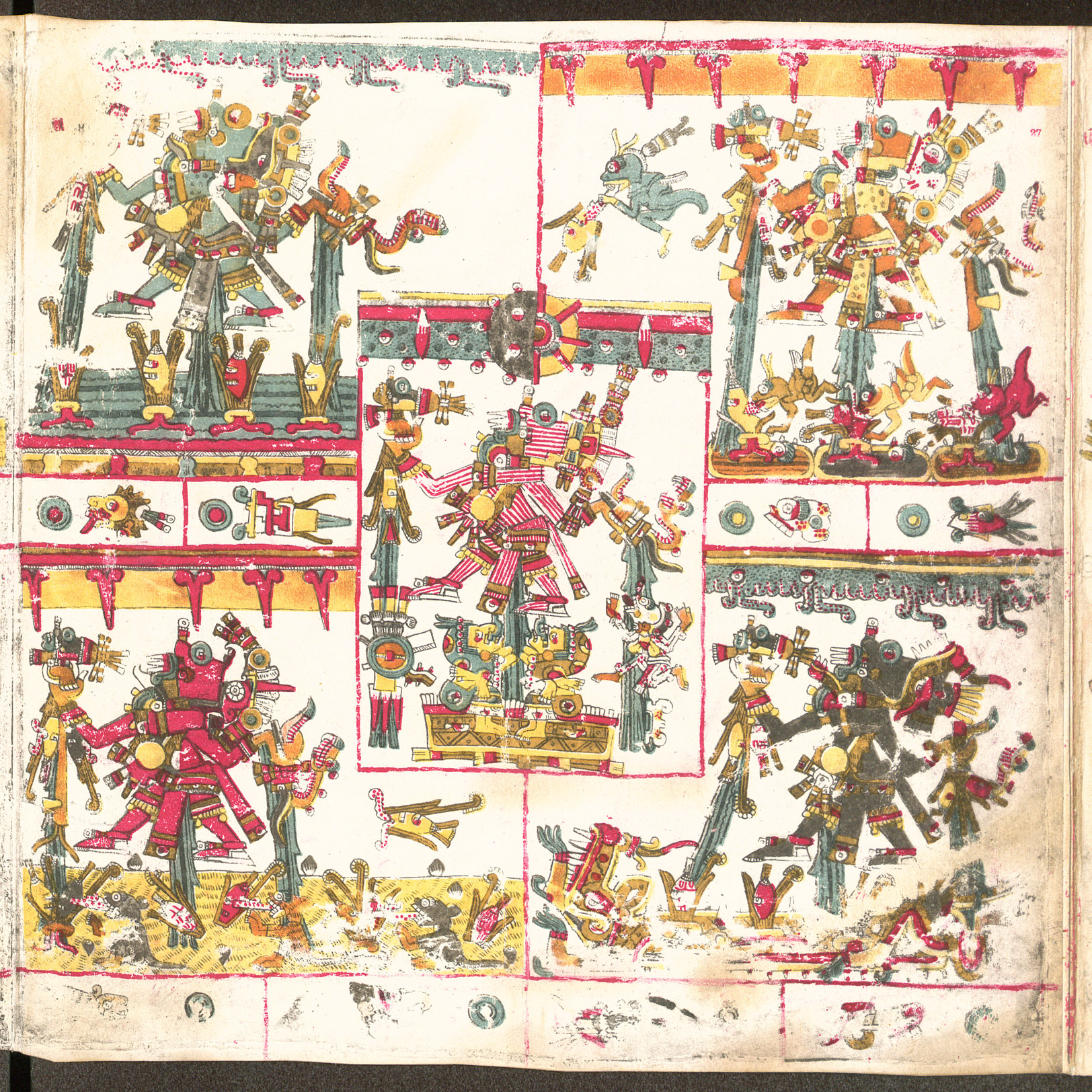
 Nahua metaphysics centers around , "a single, dynamic, vivifying, eternally self-generating and self-regenerating sacred power, energy or force." This is conceptualized in a kind of monistic pantheism as manifest in the supreme god , as well as a large pantheon of lesser gods and idealizations of natural phenomena such as stars and fire. Priests and educated upper classes held more monistic views, while the popular religion of the uneducated tended to embrace the polytheistic and mythological aspects.
The Aztec empire's state-sanctioned religion meanwhile had to fulfill the spiritual obligations of the upper classes while maintaining their control over the lower classes and conquered populations. This was executed in grand public religious ceremonies, sponsorship of the most popular cults, and a relative degree of religious freedom.
Rulers, if they are local or , or central Huetlatoani, were seen as representatives of the gods and therefore ruled by divine right. , or the principle of rulership, established that descent inherited this divine right. Political order was, therefore, also a cosmic order, and to kill a was to transgress that order. For this reason, whenever the Nahuas killed or otherwise removed a tlatoani from their station, their stead typically placed a relative and member of the same bloodline. The establishment of the office of Huetlatoani understood through the creation of another level of rulership, , standing in superior contrast to the lesser principle.
A militaristic interpretation of Nahua religion, specifically a devout veneration of the sun god, Huitzilopochtli, guided expansion of the empire. Militaristic state rituals were performed throughout the year according to a ceremonial calendar of events, rites, and mock battles. The time period they lived in was understood as the , or Sun of Movement, which was believed to have been the final age after which humanity would be destroyed. It was under Tlacaelel that Huitzilopochtli assumed his elevated role in the state pantheon and who argued that it was through blood sacrifice that the Sun would be maintained and thereby stave off the end of the world. It was under this new, militaristic interpretation of Huitzilopochtli that Aztec soldiers were encouraged to fight wars and capture enemy soldiers for sacrifice. Though blood sacrifice was common in Mesoamerica, the scale of
Nahua metaphysics centers around , "a single, dynamic, vivifying, eternally self-generating and self-regenerating sacred power, energy or force." This is conceptualized in a kind of monistic pantheism as manifest in the supreme god , as well as a large pantheon of lesser gods and idealizations of natural phenomena such as stars and fire. Priests and educated upper classes held more monistic views, while the popular religion of the uneducated tended to embrace the polytheistic and mythological aspects.
The Aztec empire's state-sanctioned religion meanwhile had to fulfill the spiritual obligations of the upper classes while maintaining their control over the lower classes and conquered populations. This was executed in grand public religious ceremonies, sponsorship of the most popular cults, and a relative degree of religious freedom.
Rulers, if they are local or , or central Huetlatoani, were seen as representatives of the gods and therefore ruled by divine right. , or the principle of rulership, established that descent inherited this divine right. Political order was, therefore, also a cosmic order, and to kill a was to transgress that order. For this reason, whenever the Nahuas killed or otherwise removed a tlatoani from their station, their stead typically placed a relative and member of the same bloodline. The establishment of the office of Huetlatoani understood through the creation of another level of rulership, , standing in superior contrast to the lesser principle.
A militaristic interpretation of Nahua religion, specifically a devout veneration of the sun god, Huitzilopochtli, guided expansion of the empire. Militaristic state rituals were performed throughout the year according to a ceremonial calendar of events, rites, and mock battles. The time period they lived in was understood as the , or Sun of Movement, which was believed to have been the final age after which humanity would be destroyed. It was under Tlacaelel that Huitzilopochtli assumed his elevated role in the state pantheon and who argued that it was through blood sacrifice that the Sun would be maintained and thereby stave off the end of the world. It was under this new, militaristic interpretation of Huitzilopochtli that Aztec soldiers were encouraged to fight wars and capture enemy soldiers for sacrifice. Though blood sacrifice was common in Mesoamerica, the scale of human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherei ...
under the Aztecs was likely unprecedented in the region.
Schematic of hierarchy
Provincial structure
 Originally, the Aztec empire was a loose alliance between three cities: Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and the most junior partner, Tlacopan. As such, they were known as the 'Triple Alliance.' This political form was very common in Mesoamerica, where alliances of city-states were ever fluctuating. However, over time, Tenochtitlan assumed paramount authority in the alliance, and although each partner city shared spoils of war and rights to regular tribute from the provinces and were governed by their own Huetlatoani, Tenochtitlan became the largest, most powerful, and most influential of the three cities. It was the de facto and acknowledged center of empire.
Though the Aztecs did not describe them this way, there were essentially two types of provinces: Tributary and Strategic. Strategic provinces were essentially subordinate client states which provided tribute or aid to the Aztec state under "mutual consent." Tributary provinces, on the other hand, provided regular tribute to the empire; obligations on the part of Tributary provinces were mandatory rather than consensual.
Originally, the Aztec empire was a loose alliance between three cities: Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and the most junior partner, Tlacopan. As such, they were known as the 'Triple Alliance.' This political form was very common in Mesoamerica, where alliances of city-states were ever fluctuating. However, over time, Tenochtitlan assumed paramount authority in the alliance, and although each partner city shared spoils of war and rights to regular tribute from the provinces and were governed by their own Huetlatoani, Tenochtitlan became the largest, most powerful, and most influential of the three cities. It was the de facto and acknowledged center of empire.
Though the Aztecs did not describe them this way, there were essentially two types of provinces: Tributary and Strategic. Strategic provinces were essentially subordinate client states which provided tribute or aid to the Aztec state under "mutual consent." Tributary provinces, on the other hand, provided regular tribute to the empire; obligations on the part of Tributary provinces were mandatory rather than consensual.
List of rulers
Mythological nature rulers
These are Aztec gods and goddesses, who were also part of the Thirteen Heavens, as well as the ''Aztec Empire''.Gods
 * Centeotl, god of maize associated with the Tianquiztli (goddesses of the Pleiades). Centeotl's name is also spelt as Cinteotl and was like a goddess.
* Chalchiuhtotolin, the god of cleanse and contamination, absolve human of guilt, and overcoming god of fate.
* Xochipilli, god of flowers, pleasure, feasting, frivolity and artistic creativity.
* Huehuecoyotl, god of old-age, origin, and deception. He is also the patron of wisdom, followed by his tricks and foolings. His name is similar to the god of happiness, Ueuecoyotl.
* Huitzilopochtli, god of will and the war, patron god of force, ruler of the
* Centeotl, god of maize associated with the Tianquiztli (goddesses of the Pleiades). Centeotl's name is also spelt as Cinteotl and was like a goddess.
* Chalchiuhtotolin, the god of cleanse and contamination, absolve human of guilt, and overcoming god of fate.
* Xochipilli, god of flowers, pleasure, feasting, frivolity and artistic creativity.
* Huehuecoyotl, god of old-age, origin, and deception. He is also the patron of wisdom, followed by his tricks and foolings. His name is similar to the god of happiness, Ueuecoyotl.
* Huitzilopochtli, god of will and the war, patron god of force, ruler of the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sŇę√ĺ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sun√ĺa ...
.
* Itztlacoliuhqui-Ixquimilli, god of frost, ice, cold, winter, sin, punishment and human misery. He is also the god of blindfolded justice.
* Ometecuhtli, god of duality and substance.
* Itztli, god of stone who is a variant of Tezcatlipoca.
* Mictlantecuhtli, god of the Underworld (Mictlan). He is extremely skeleton with bonus horror bits; particularly his exposed liver which dangles cheekily from his chest cavity.
* Patecatl, god of healing and patron god of doctors and peyote. He is the Centzontotochtin's father.
* Piltzintecuhtli
In Aztec mythology, Piltzintecuhtli was a god of the rising sun, healing, and visions, associated with TŇćnatiuh. The name means "the Young Prince". It may have been another name for TŇćnatiuh, but he is also mentioned as a possibly unique indiv ...
, god of the visions and the sun. In Aztec mythology Piltzintecuhtli is associated with Mercury and also healing.
* Quetzalcoatl
Quetzalcoatl (, ; Spanish: ''Quetzalc√≥atl'' ; nci-IPA, QuetzalcŇćńĀtl, ketÕ°sa…¨ňąkoňźaňźtÕ°…¨ (Modern Nahuatl pronunciation), in honorific form: ''QuetzalcŇćńĀtzin'') is a deity in Aztec culture and literature whose name comes from the Nah ...
, god of life, the light and wisdom, lord of the winds and the day, ruler of the West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
.
* Tecciztecatl, god of the moon. Tecciztecatl is Tlaloc and Chalchiuhtlicue's son.
* Tepeyollotl, god of the animals, darkened caves, echoes and earthquakes. Tepeyollotl is a variant of Tezcatlipoca and is associated with mountains.
* Tezcatlipoca, god of providence, the darkness and the invisible, lord of the night, ruler of the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
. Tezcatlipoca had overthrew Quetzalcoatl
Quetzalcoatl (, ; Spanish: ''Quetzalc√≥atl'' ; nci-IPA, QuetzalcŇćńĀtl, ketÕ°sa…¨ňąkoňźaňźtÕ°…¨ (Modern Nahuatl pronunciation), in honorific form: ''QuetzalcŇćńĀtzin'') is a deity in Aztec culture and literature whose name comes from the Nah ...
, who overthrew him in return.
* Tlahuizcalpantecuhtli, god of dawn (Venus) and aspect of Quetzalcoatl.
* Tlaloc, god of rain, lightning and thunder. He is associated with fertility and agriculture.
* Tonacatecuhtli, god of sustenance associated with Ometecuhtli.
* Tonatiuh, god of the sun.
* Xipe Totec
In Aztec mythology and religion, Xipe Totec (; nci-IPA, Xńępe Totńďc, ňą Éiňźpe ňątoteňźk( ∑)) or Xipetotec ("Our Lord the Flayed One") was a life-death-rebirth deity, god of agriculture, vegetation, the east, spring, goldsmiths, silversmith ...
, god of rejuvenation, vegetation and spring, lord of the seasons, ruler of the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
.
* Xiuhtecuhtli, god of fire and time.
* Ehecatl
Ehecatl ( nci-IPA, Ehńďcatl, e Ēňąeňźkat…¨, ) is a pre-Columbian deity associated with the wind, who features in Aztec mythology and the mythologies of other cultures from the central Mexico region of Mesoamerica. He is most usually interpreted ...
, god of wind.
* Tzontemoc, god who resided in one of the nine layers of the Underworld.
* Xolotl, god of death, associated with Venus as the Evening Star. He is the twin god, and a double of Quetzalcoatl.
* Mixcoatl, aztec god of fishing and hunting and old god of hurricanes and storms who is associated with the Milky Way.
* Nanahuatzin, god sun. Nanahuatzin sacrificed himself in a burning fire so that the sun should continue to shine all over the world, so the god Tonatiuh took his place.
* Atlahua, god of water and protector of archers and fishermen. The Aztecs prayed to him when there were deaths in water.
* Opochtli
In Aztec mythology, Opochtli was a god of hunting and fishing.
He is said to have invented the atlatl, the net, the canoe pole, and the bird snare
SNARE proteins ‚Äď " SNAP REceptor" ‚Äď are a large protein family consisting of at least ...
, god of fishing and birdcatchers. Apparently, he is the discoverer of the harpoon and net.
* Painal, Huitzilopochtli's messenger.
* Techlotl, god who resided in one of the nine layers of the Underworld. This deity was associated with owls.
* Ometochtli, god of pulque and leader of the Centzontotochtin.
Goddesses
volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates ...
es.
* Cihuacoatl, goddess of childbirth and picker of souls.
* Citlalicue, goddess of female stars in the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
.
* Itzpapalotl, goddess of death. She was the leader of the Tzitzimitl. Stone knives pop out from her eyes.
* Mayahuel
Mayahuel () is the female deity associated with the maguey plant among cultures of central Mexico in the Postclassic era of pre-Columbian Mesoamerican chronology, and in particular of the Aztec cultures. As the personification of the maguey plant ...
, goddess of agave and maguey Maguey may refer to various American plants:
* Genus '' Agave'', especially
** Species ''Agave americana'', the century plant
** Species ''Agave salmiana
''Agave salmiana'' (also known as ''maguey pulquero'' and green maguey) is a species of the ...
. She was the Centzontotochtin's mother.
* Mictecacihuatl, goddess of the Underworld (Mictlan).
* Tlaltecuhtli, old goddess of earth (changed in the Earth's landscape and atmosphere).
* Tlazolteotl, goddess of lust, passions, carnality, and sexual misdeeds.
* Xochiquetzal, goddess of flowers, love, pleasure and beauty. She protects young mothers. She also is ever young and pretty.
* Atlatoman, patron goddess of those who are born with physical deformities or those unfortunate Mexica who have suffered from open sores. Some codexes have also thought this deity as the cause of these ailments.
* Huixtocihuatl, goddess of salt and patron of cultivated foods (including people in the salt trade).
* Chalmecacihuatl, goddess who resided in one of the nine layers of the Underworld. She was Tzontemoc's wife.
* Chicomecoatl, goddess of agriculture.
* Coyolxauhqui, goddess or leader of the Centzonhuitznahua, associated with the moon.
Mythological nature groups of rulers
 *
* Cihuateteo
In Aztec mythology, the Cihuateteo (; nci, CihuńĀtńďteoh, in singular ) or "Divine Women", were the malevolent spirits of women who died in childbirth. They were likened to the spirits of male warriors who died in violent conflict, because ch ...
, ( Cihuacoatl) the malevolent spirits of women who died in childbirth. Their name comes from the goddess Cihuacoatl. Their name is also spelt as "Ciuateteo". (Goddesses)
* Ahuiateteo
Ahuiateteo () or Macuiltonaleque () were a group of five Aztec gods of excess and pleasure. They also represented the dangers that come along with these. These five gods were also invoked by diviners and mystics.Miller and Taube 1993, 2003, p. 40 ...
, gods of excess and pleasure, the gods who are known as Macuilcozcacuauhtli, Macuilcuetzpalin, Macuilmalinalli, Macuiltochtli, and Macuilxochitl. (Gods)
* Ixcuiname, goddesses of the carnality. (Goddesses)
* Cinteteo, gods of the maizes. (Gods)
* Centzontotochtin, ( Ometochtli) gods of pulque. (Gods)
* Xiuhtotontli, the gods of fire (alternative manifestations or states of Xiuhtecuhtli). (Gods)
* Ehecatotontli, (Ehecatl
Ehecatl ( nci-IPA, Ehńďcatl, e Ēňąeňźkat…¨, ) is a pre-Columbian deity associated with the wind, who features in Aztec mythology and the mythologies of other cultures from the central Mexico region of Mesoamerica. He is most usually interpreted ...
) breath-holding gods of the breezes ‚ÄĒ who are just like Ehecatl
Ehecatl ( nci-IPA, Ehńďcatl, e Ēňąeňźkat…¨, ) is a pre-Columbian deity associated with the wind, who features in Aztec mythology and the mythologies of other cultures from the central Mexico region of Mesoamerica. He is most usually interpreted ...
. (Gods)
* Civateteo, (Cihuacoatl) goddesses who are vampires. Civateteo are similar to Cihuateteo, who are not as bad as Civateteo are. Civateteo mostly live in regular Mexico, and Civateteo come from somewhere vampire-esque. (Goddesses)
* Tzitzimitl
In Aztec mythology, a Tzitzimitl (plural Tzitzimimeh ) is a monstrous deity associated with stars. They were depicted as skeletal female figures wearing skirts often with skull and crossbones designs. In postconquest descriptions they are often de ...
, ( Itzpapalotl) goddesses of the stars. Tzitzimitl mostly live in regular Mexico, and Tzitzimitl come from Tamoanchan. (Goddesses)
* Centzonmimixcoa, ( Cuahuitlicac) 400 gods of the northern stars and "The 400 Northerners." (gods)
* Centzonhuitznahua, ( Coyolxauhqui) 400 gods of the southern stars. (Gods)
* Tlaloque, gods of rain, weather and mountains. Tlaloc had also been considered the ruler of this motley group. (Gods)
* Tianquizli, ( Citlalicue) these are goddesses of the Pleiades. (Goddesses)
* Ometeotl, gods of the duality. (Gods)
* Tezcatlipocas
In Aztec mythology, Creator-gods are the only four Tezcatlipocas, the children of the creator couple Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl "Lord and Lady of Duality", "Lord and Lady of the Near and the Close", "Father and Mother of the Gods", "Father and M ...
, creator god's. (Gods)
* Tonalleque, embodied spirits who died during the Battle (Gods)
Mythological sacred places
* Tamoanchan, a place where Itzpapalotl usually rules over. The gods created the first of the present human race out of sacrificed blood and ground human bones. Tamoanchan may mean "We go down to our home." * Mictlan, the place where Mictlantecuhtli and Mictecacihuatl rule over in aztec mythology. This is literally theUnderworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwo ...
.
Law
RulerNezahualcoyotl Nezahualcoyotl may refer to:
* Nezahualcoyotl (tlatoani), the ruler of Texcoco
* Ciudad Nezahualcóyotl, a city in the State of Mexico
* Nezahualcóyotl metro station, in Mexico City
* The Nezahualcóyotl Award, a literary prize in Mexico
* Neza ...
developed the most developed code of law in the city-state of Texcoco under him. It was a formal written code, not merely a collection of customary practices. The sources for knowing about the legal code are colonial-era writings by Franciscan Toribio de Benavente Motolinia, Franciscan Fray Juan de Torquemada, and Texcocan historians Juan Bautista Pomar Juan Bautista (de) Pomar (c. 1535 Рafter 1601) was a mestizo descendant of the rulers of prehispanic Texcoco, a historian and writer on prehispanic Aztec history. He is the author of two major works. His ''Relación de Texcoco'' was written ...
, and Fernando de Alva Cortés Ixtlilxochitl
Fernando is a Spanish and Portuguese given name and a surname common in Spain, Portugal, Italy, France, Switzerland, former Spanish or Portuguese colonies in Latin America, Africa, the Philippines, India, and Sri Lanka. It is equivalent to the G ...
. The law code in Texcoco under Nezahualcoyotl was legalistic, as many tried cases by particular types of evidence and many disregarded the social status of the litigants, and consisted of 80 written laws. These laws called for severe, publicly administered punishments, creating a legal framework of social control.
Much less is known about the legal system in Tenochtitlan, which might be less legalistic or sophisticated as those of Texcoco for this period. Those under the reign of Moctezuma I
Moctezuma I (‚Äď1469), also known as Moteuczomatzin Ilhuicamina (), Huehuemoteuczoma or Montezuma I ( nci, MotńďuczŇćma Ilhuicamńęna , nci, HuńďhuemotńďuczŇćma ), was the second Aztec emperor and fifth king of Tenochtitlan. During his reign, t ...
established it. These laws served to establish and govern relations between the state, classes, and individuals. State authorities meted out punishments solely. The Nahuas enshrined Nahua mores in these laws, criminalizing public acts of homosexuality, drunkenness, and nudity, not to mention more universal proscriptions against theft, murder, and property damage. As stated before, could serve as judges, often exercising judicial oversight of their own members. Likewise, military courts
Military justice (also military law) is the legal system (bodies of law and procedure) that governs the conduct of the active-duty personnel of the armed forces of a country. In some nation-states, civil law and military law are distinct bodi ...
dealt with both cases within the military and without during wartime. There was an appeal
In law, an appeal is the process in which cases are reviewed by a higher authority, where parties request a formal change to an official decision. Appeals function both as a process for error correction as well as a process of clarifying and ...
process, with appellate courts standing between local, typically market-place courts, on the provincial level and a supreme court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
and two special higher appellate courts at Tenochtitlan. One of those two special courts dealt with cases arising within Tenochtitlan, the other with cases originating from outside the capital. The ultimate judicial authority laid in hands of the , who had the right to appoint lesser judges.
See also
*Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
*Aztec mythology
Aztec mythology is the body or collection of myths of the Aztec civilization of Central Mexico. The Aztecs were Nahuatl-speaking groups living in central Mexico and much of their mythology is similar to that of other Mesoamerican cultures. Accor ...
*Aztec philosophy
Aztec philosophy was a school of philosophy that developed out of Aztec culture. The Aztecs had a well-developed school of philosophy, perhaps the most developed in the Americas and in many ways comparable to Ancient Greek philosophy, even amassi ...
* Aztec religion
* Aztec society
*Crónica Mexicayotl
The ''Crónica Mexicayotl'' is a chronicle of the history of the Aztec Empire from the early Nahua migrations to the colonial period, which was written in the Nahuatl language around the 16th century. Its authorship is debated because the earliest ...
*Flower war
A flower war or flowery war ( nah, xŇćchiyńĀŇćyŇćtl, es, guerra florida) was a ritual war fought intermittently between the Aztec Triple Alliance and its enemies from the "mid-1450s to the arrival of the Spaniards in 1519." Enemies included t ...
* List of Aztec gods and supernatural beings
* List of rulers of Texcoco
* List of Tenochtitlan rulers
*List of Tlatelolco rulers
This is a list of the '' tlatoque'' of the pre-Columbian era ''altepetl'' of Tlatelolco.
Pre-Hispanic rulers
Colonial rulers
See also
* List of rulers of Tenochtitlan
* List of rulers of Tetzcoco
* Family tree of Aztec monarchs
*Aztec Empire ...
*Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
* Nahuas
References
Bibliography
Primary sources
* * * *Secondary sources
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*https://www.azteccalendar.com/god/ *https://www.godchecker.com/aztec-mythology/ {{Authority control * * Mesoamerica Indigenous culture of the Americas Former empires in the Americas 1521 in Mexico Former confederations Former monarchies of North America History of Mesoamerica Political systems 15th-century establishments in Mexico States and territories established in 1428 States and territories disestablished in 1521 1428 establishments in North America 15th-century establishments in the Aztec civilization 16th-century disestablishments in the Aztec civilization 1521 disestablishments in North America