Avars (Caucasus) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Avars, also known as ''Maharuls'' ( Avar: , , "mountaineers") are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group. The Avars are the largest of several ethnic groups living in the Russian republic of Dagestan. The Avars reside in the
Кавказская война в отдельных очерках, эпизодах, легендах и биографиях
в 5 т. – СПб.: Тип. Е. Евдокимова, 1887–1889. Potto claimed that members of Avarian tribe also often referred to themselves by the alternate endonym , also meaning "mountaineer". Most of those known as Tavlins trace their lineage to the upper parts of two tributaries of the
/ref>
 The Russians instituted heavy taxes, expropriated estates, and constructed fortresses in the Avar region. The Avar population revolted under the flag of the Muslim Imamate of Dagestan. Ghazi Mohammed (1828–1832), Gamzat-bek (1832–1834), and
The Russians instituted heavy taxes, expropriated estates, and constructed fortresses in the Avar region. The Avar population revolted under the flag of the Muslim Imamate of Dagestan. Ghazi Mohammed (1828–1832), Gamzat-bek (1832–1834), and
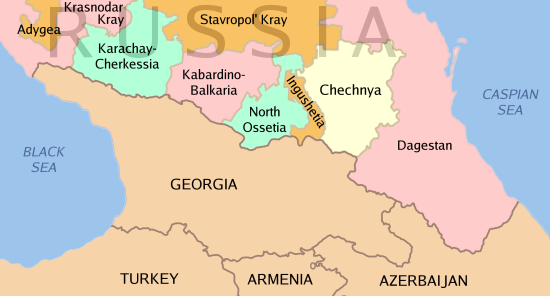 The Avarians are a Northeast Caucasian people who speak Avar, a Northeast Caucasian language. According to ''
The Avarians are a Northeast Caucasian people who speak Avar, a Northeast Caucasian language. According to ''
Azərbaycan Milli Elmlər Akademiyası İqtisadiyyat İnstitutu
/ref> In 2002, 1,996 Kvareli Avars lived in Georgia. In
In
 Avarian is a collective term; among the Avarians there are around 15 sub-ethnic groups, including the Avar, Andi, and Tsez (Dido) peoples.
Avarian is a collective term; among the Avarians there are around 15 sub-ethnic groups, including the Avar, Andi, and Tsez (Dido) peoples.
 *Khabib Nurmagomedov, mixed martial artist, two-time Combat Sambo World Champion, and an undefeated former List of UFC champions, UFC Lightweight (MMA), lightweight champion
*Ramazan Emeev, mixed martial artist currently competing in the Welterweight (MMA), welterweight division of the Ultimate Fighting Championship. He is a former M-1 Global Middleweight (MMA), middleweight champion.
*Zagalav Abdulbekov, first Avar Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Abdulrashid Sadulaev, wrestler who won a gold medal in freestyle wrestling for Russia during the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro. He also won a gold medal at the Wrestling at the 2020 Summer Olympics, 2020 Summer Olympics in the 97 kg category.
*Mavlet Batirov, two-time Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Khadzhimurad Magomedov, Khadzimurad Magomedov, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Sagid Murtazaliev, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Makhach Murtazaliev, Olympic bronze medalist and two-time world champion in freestyle wrestling
*Alisa Ganieva, author who writes in Russian but identifies herself as an Avar
*Gadzhimurat Kamalov, investigative journalist who reported on corruption in the Dagestan area
*Ali Shabanau, freestyle wrestler representing Belarus
*Magomed Tolboyev, Soviet-era test pilot for the Buran space shuttle, also a Hero of Russia
*Shaykh Jemaladdin Kumuki, a sufi tariqa shaykh from Kumukh and relative of Imam Shamil
*Khabib Nurmagomedov, mixed martial artist, two-time Combat Sambo World Champion, and an undefeated former List of UFC champions, UFC Lightweight (MMA), lightweight champion
*Ramazan Emeev, mixed martial artist currently competing in the Welterweight (MMA), welterweight division of the Ultimate Fighting Championship. He is a former M-1 Global Middleweight (MMA), middleweight champion.
*Zagalav Abdulbekov, first Avar Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Abdulrashid Sadulaev, wrestler who won a gold medal in freestyle wrestling for Russia during the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro. He also won a gold medal at the Wrestling at the 2020 Summer Olympics, 2020 Summer Olympics in the 97 kg category.
*Mavlet Batirov, two-time Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Khadzhimurad Magomedov, Khadzimurad Magomedov, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Sagid Murtazaliev, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Makhach Murtazaliev, Olympic bronze medalist and two-time world champion in freestyle wrestling
*Alisa Ganieva, author who writes in Russian but identifies herself as an Avar
*Gadzhimurat Kamalov, investigative journalist who reported on corruption in the Dagestan area
*Ali Shabanau, freestyle wrestler representing Belarus
*Magomed Tolboyev, Soviet-era test pilot for the Buran space shuttle, also a Hero of Russia
*Shaykh Jemaladdin Kumuki, a sufi tariqa shaykh from Kumukh and relative of Imam ShamilŞeyh Cemaleddin Kumuki Hz. (Turkish)
Evliyalar.net
*Abdullah Daghestani, spiritual guide of Shaykh Nazim; buried on Mount Qasioun, Damascus
File:Murad Magomedov about Old Bulgars N-Caucasus.ogg, Avarian archeologist Dr. Murad Magomedov speaks about ancient migration of Iranians, Turks and Proto-Mongols to the Caspian-Dagestan area.
File:Adallo interview Sound 1a.ogg, Famous in Dagestan and the Dagestani diaspora in Turkey, the Avarian poet Adallo Ali (also known as Adallo Aliev) speaks about the Avar language and Avar poetry and literature. Part 1.
File:Adallo interview Sound 1b.ogg, The Avarian poet Adallo Ali (also known as Adallo Aliev) speaks about the Avar language and Avar poetry and literature. Part 2.
North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
between the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
and the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
. Alongside other ethnic groups in the North Caucasus region, the Avars live in ancient villages located approximately 2,000 m above sea level. The Avar language spoken by the Caucasian Avars belongs to the family of Northeast Caucasian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages, also called East Caucasian, Nakh-Daghestani or ''Vainakh-Daghestani'', is a family of languages spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya and Ingushetia and in Northern Azerbaijan as well as in ...
. Sunni Islam has been the prevailing religion of the Avars since the 13th century.
Ethnonyms
According to 19th-century Russian historians, the Avars' neighbors usually referred to them as Tavlins (''tavlintsy''). This is anexonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
. Vasily Potto
Vasily Aleksandrovich Potto (russian: Василий Александрович Потто; 1 January 1836 – 29 November 1911) was a Russian lieutenant-general (1907) and military historian, known for his landmark works on the history of the Ca ...
wrote that those to the south usually knew them as Tavlins (''tavlintsy''). Potto wrote, "The words in different languages have the same meaning... fmountain dwellers rhighlanders."''В. А. Потто.'Кавказская война в отдельных очерках, эпизодах, легендах и биографиях
в 5 т. – СПб.: Тип. Е. Евдокимова, 1887–1889. Potto claimed that members of Avarian tribe also often referred to themselves by the alternate endonym , also meaning "mountaineer". Most of those known as Tavlins trace their lineage to the upper parts of two tributaries of the
Sulak River
The Sulak (russian: Сула́к, kum, Сулак (Sulak)/Къой-сув (Qoysuw), ce, ĠoysuLepiev A.S., Lepiev İ.A., Türkçe-Çeçençe sözlük, Turkoyŋ-noxçiyŋ doşam, Ankara, 2003) drains most of the mountainous interior of Dagesta ...
: the Andiyskoe Koisu and Avarskoye Koisu.:''Том I. Книга 1. Дубровин Николай Федорович.''/ref>
History
Between the 5th and 12th centuries, GeorgianOrthodox Christianity
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Chur ...
was introduced to the Avar valleys. At the time, the Christian kingdom of Sarir
Sarir or Serir was a medieval Christian state lasting from the 6th or 7th century to the 12th century in the mountainous regions of modern-day Dagestan. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for "throne" and refers to a golden throne that wa ...
governed much of modern-day Dagestan. The neighboring Kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ...
was also Christian. However, when Sarir fell in the early 12th century and Mongol invasions led by Subutai and Jebe
Jebe (or Jebei, mn, Зэв, ''Zev''; birth name: Jirqo'adai (Modern Mongolian: Zurgadai), mn, Зургаадай, ) (death: approximately 1224) was one of the most prominent Noyans (generals) of Genghis Khan. He belonged to the Besud clan, ...
weakened Georgia, Christian influence in the area ended. The Avar Khanate
The Avar Khanate, the Avar Nutsaldom ( av, Avar Nutsallhi; russian: Аварское ханство), also known as Khundzia or Avaria, was a long-lived Avar state, which controlled mountainous parts of Dagestan (in the North Caucasus) from the ...
, a predominantly Muslim polity, succeeded Sarir.''An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires'', by James Stuart Olson, Lee Brigance Pappas, Nicholas Charles Pappas, p. 58 The only extant monument of Sarir architecture is the 10th-century Datuna Church
Datuna Church ( av, Датуна гьатӀан; ka, დათუნას ეკლესია; russian: Датунский храм) is the only medieval church that survives in modern Dagestan (where most of the population is Muslim). It is ...
in the village of Datuna. The Mongol invasions seem not to have affected the Avar territory, and the alliance with the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
enabled the Avar khans to increase their prosperity. In the 15th century the Horde declined, and the Shamkhalate of Kazi-Kumukh
"Gazikumukh Shamkhalate" is a term introduced in Russian-Dagestan historiography starting from the 1950s–60s to denote the Kumyk state that existed on the territory of present-day Dagestan in the period of the 8th to 17th centuries with the capi ...
rose to power. The Shamkhalate absorbed the Avar Khanate.
From the 16th century onwards, the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
and Ottomans began expanding their territory in the Caucasus. By the mid-16th century, what is now Dagestan, eastern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
, and Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
were under Safavid Persian rule. The area that is now western Georgia fell under Ottoman Turkish control. Although the Ottoman Turks briefly gained Dagestan during the Ottoman-Safavid War of 1578–1590, Dagestan and many of its Avar inhabitants stayed under Persian suzerainty for many centuries. Despite Persian rule, many ethnic groups in Dagestan, including many Avars, retained relatively high amounts of freedom and self-governance.
After the Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723, Russia briefly took Dagestan from the Persians. The Persians reestablished full control over the Caucasus again in the early 18th century under Nader Shah's Caucasus campaign
The Caucasus campaign comprised armed conflicts between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, later including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus, the German Empire, the Central Caspian Dict ...
and Dagestan campaign. During that same time, the Avars routed one of Nader Shah's armies at Andalal during the later stages of his Dagestan campaign. In the wake of this triumph, Umma Khan of the Avars (reigned 1774–1801) managed to extract tribute from most states of the Caucasus, including Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
and Georgia.
Umma Khan died in 1801. Two years later, the khanate voluntarily submitted to Russian authority following the Russian annexation of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
and the Treaty of Georgievsk
The Treaty of Georgievsk (russian: Георгиевский трактат, Georgievskiy traktat; ka, გეორგიევსკის ტრაქტატი, tr) was a bilateral treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and the east Ge ...
. This was only confirmed after considerable Russian successes and the victory in the Russo-Persian War of 1804–1813, after which Persia lost southern Dagestan and many of its other Caucasian territories to Russia. The 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second ...
indefinitely consolidated Russian control over Dagestan and other areas where the Avars lived.
 The Russians instituted heavy taxes, expropriated estates, and constructed fortresses in the Avar region. The Avar population revolted under the flag of the Muslim Imamate of Dagestan. Ghazi Mohammed (1828–1832), Gamzat-bek (1832–1834), and
The Russians instituted heavy taxes, expropriated estates, and constructed fortresses in the Avar region. The Avar population revolted under the flag of the Muslim Imamate of Dagestan. Ghazi Mohammed (1828–1832), Gamzat-bek (1832–1834), and Shamil Shamil (Arabic: شَامِل ''shāmil'') is a lesser common masculine Arabic name. The name is usually from the adjective which have several correlated meanings from the Arabic "complete, comprehensive, universal" but could also mean "embodying, pr ...
(1834–1859) led the revolts.
This Caucasian War
The Caucasian War (russian: Кавказская война; ''Kavkazskaya vojna'') or Caucasus War was a 19th century military conflict between the Russian Empire and various peoples of the North Caucasus who resisted subjugation during the ...
raged until 1864, when the Avarian Khanate was abolished and replaced by the Avarian District. Some Avars refused to collaborate with Russians and migrated to Turkey, where their descendants live to this day. Despite war and emigration, the Avars retained their position as the dominant ethnic group in Dagestan during the Soviet period. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, many Avars left the barren highlands for the fertile plains closer to the shores of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
.
Description
 The Avarians are a Northeast Caucasian people who speak Avar, a Northeast Caucasian language. According to ''
The Avarians are a Northeast Caucasian people who speak Avar, a Northeast Caucasian language. According to ''Encyclopedia Britannica
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articl ...
'', the Turanian nomads also share the name Avar. The Encyclopedia Britannica describes the Turanian nomads as "a people of undetermined origin and language."
As of 2002, the Avarians numbered about 1.04 million. 912,020 Avarians lived in Russia during the 2010 census; 850,011 of them lived in Dagestan. Only 32% lived in cities. Avarians inhabit most of the mountainous part of Dagestan as well the plains (Buynaksk
Buynaksk (russian: Буйна́кск; kum, Шура / Темирхан-Шура, ''Şura / Temirxan-Şura'') is a town in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia, located at the foothills of the Greater Caucasus on the Shura-Ozen River, southwest of ...
, Khasavyurt
Khasavyurt (russian: Хасавю́рт; av, Хасаюрт; ce, Хаси-Эвл, ''Xasi-Evl''; kum, Хасав-ю́рт, ''Xasav-yurt'') is a city in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia. Population:
History
It was founded in 1846 and granted ...
, Kizilyurt and other regions). Outside of Dagestan, Russian Avars also live in Chechnya and Kalmykia.
As of 1999, 50,900 Avarians lived in the Balakan and Zakatala rayons of Azerbaijan. The Avarian population of Azerbaijan had decreased to 49,800 by 2009.Devlet İstatistik KomitesiAzərbaycan Milli Elmlər Akademiyası İqtisadiyyat İnstitutu
/ref> In 2002, 1,996 Kvareli Avars lived in Georgia.
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, Avarians are considered "ethnic Turks", and so aren't counted as their own ethnic group on the census. This makes it difficult to know exactly how many Avarians live in Turkey. According to Ataev B.M., who referenced A.M. Magomeddadaev's research, the Avarian population there should have been around 53,000 in 2005.
Ethnic groups
Avarians as highlanders and armed people
, transliterated as means "inhabitants of the top grounds, mountaineers." Another group of Avarians is described as belonging to a different category, ( (with a soft "χ"). This term means "inhabitants of plains (warm valleys) and gardeners". The name "Avarians" has a narrower meaning; it has a national meaning connected with former statehood. "Avar" is a significant part of the word "Avaria," which refers to theKhunzakh
Khunzakh ( av, Хунзахъ, , russian: Хунзах) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') and the administrative center of Khunzakhsky District in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia, located in the North Caucasus mountains above sea level. Populati ...
Khanate. The Khanate formed in the 12th century after the disintegration of Sаrir. From the middle of the 19th century, this territory was the Avarian District of the Daghestan area. This area is now referred to as Khunzakhsky District of Dagestan. Khunzakhsky District is referred to as in literary Avarian and in a local dialect.
The modern literary language of Avarias (), both in the past and today, is known among Avarians as the language of (). The Avarian word means "army, armed people." According to reconstructions, this word descends from in the proto-Avarian language ("ʔ" represents a glottal stop).
Names for the Avars
In modern Avarian, three words retain the ancient basis of . They include , meaning "envoy, prophet, messiah"; , meaning "pommel of a saddle"; and , meaning "obstacle, opposition". means "to make an obstacle, to resist." There is also an Avarian river called in Avarian and in Russian. All three listed words are found in ancient lexicons of theIranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
. The Parthian word and the Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
word both mean "up, on, over" and "higher, superior." The Middle Persian word means "acclivity," or uphill slope. Similar Middle Persian words include , meaning "superior"; , meaning "god, divinity"; , meaning "noble"; , meaning "to surpass", and , meaning "to attack".
At the same time, according to the morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
of the Middle Persian language, the word , meaning "superior" can also be translated as "Aβarian", "Khurasanian", and "Parthian" as seen, for example, in a Middle Persian word, , meaning "Iranian".
The first known use of the term "Avar" was in the 10th century. According to Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
author Ibn Rustah
Ahmad ibn Rustah Isfahani ( fa, احمد ابن رسته اصفهانی ''Aḥmad ibn Rusta Iṣfahānī''), more commonly known as Ibn Rustah (, also spelled ''Ibn Rusta'' and ''Ibn Ruste''), was a tenth-century Persian explorer and geographer ...
, a so-called governor of Sarir
Sarir or Serir was a medieval Christian state lasting from the 6th or 7th century to the 12th century in the mountainous regions of modern-day Dagestan. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for "throne" and refers to a golden throne that wa ...
, Johannes de Galonifontibus was the first person to write about Avars under the name "Avar." He wrote in 1404 that "Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
, Leks
A lek is an aggregation of male animals gathered to engage in competitive displays and courtship rituals, known as lekking, to entice visiting females which are surveying prospective partners with which to mate. A lek can also indicate an avail ...
, Yasses, Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
, Avars, ndKazikumukhs" live in the Caucasus. According to Vladimir Minorsky, one account from 1424 called the Daghestanian Avars the Auhar.
Azerbaijani writer Abbasgulu Bakikhanov
Abbasgulu agha Bakikhanov ( az, Abbasqulu ağa Bakıxanov) (21 June 1794, Amirjan – 31 May 1847, Wadi Fatima, near Jeddah), Abbas Qoli Bakikhanov, or Abbas-Qoli ibn Mirza Mohammad (Taghi) Khan Badkubi was an Azerbaijani writer, historian, journa ...
wrote that the "inhabitants of vicinities of Agran have been moved here from Khurasan. A residence of this emir also was Agran". The editor of this book, an academician of the Academy of Sciences of Azerbaijan, Z.M. Buniyatov, confirms that this "Agran" corresponds to the Avar Khanate
The Avar Khanate, the Avar Nutsaldom ( av, Avar Nutsallhi; russian: Аварское ханство), also known as Khundzia or Avaria, was a long-lived Avar state, which controlled mountainous parts of Dagestan (in the North Caucasus) from the ...
.
The word "Agran" is unknown to modern Avars. According to the ''Altiranisches Wörterbuch,'' written by Christian Bartholomae, "agra" means in his language, German. This corresponds to "first, upper, beginning, tip" in English. He also wrote that "agra'va" meant in German, which translates to "from the top, coming from the upper side."
Nöldeke, Hübschmann, Frye, Christensen and Enoki identify Aparshahr/Abarshahr/Abharshahr/Abrashahr with Khurasan, a historical region of Iran, or with Nishapur, an Iranian city. The Khurasan () in Iranian studies is known as "rise of Sun." The Parthian word (Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
, meaning "up, on, over") and Parthian/Middle Persian are cognate with Old Iranian
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are grouped ...
, which means "empire, power, the sovereign house.") In summary, Aparšahr/Aβaršahr is very similar to the German word . According to historian H.W. Haussig, Aβaršahr means ("Kingdom of the Abar") and should be sought in the south-western territory of the Western Turkic Khaganate
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
.
A Dahae
The Dahae, also known as the Daae, Dahas or Dahaeans (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: , , , ; Latin: ; Chinese: ; Persian: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian nomadic tribal confederation, who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia.
Ident ...
tribe, the Aparnak (Parni
The Parni (; grc, Πάρνοι, ''Parnoi'') or Aparni (; Ἄπαρνοι, ''Aparnoi'') were an East Iranian people who lived around the Ochus ( grc, Ὧχος ''Okhos'') ( Tejen) River, southeast of the Caspian Sea. It is believed that their o ...
) moved from the south-eastern shore of the Caspian Sea (part of modern Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
), into the territory of Khurasan, where they founded a confederation of Dahae tribes that Avestani texts referred to as "barbarians" and "enemies of Aryans," according to Christian Bartholomae.
On the border of Khurasan, the Sassanid Persians built a strong wall, named the "Great Wall of Gorgan
The Great Wall of Gorgan is a Sasanian-era defense system located near modern Gorgan in the Golestān Province of northeastern Iran, at the southeastern corner of the Caspian Sea. The western, Caspian Sea, end of the wall is near the remains ...
" or "The Red Snake." The wall was built to protect Iran from invasion by the White Huns (Hepthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
; called Khionites, X'iiaona and Xyôn in Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ...
texts). Later another wave of White Huns conquered Khurasan and occupied it for a long time. According to Richard Helli: "By such reasoning, the Ephthalites are thought to have originated at Hsi-mo-ta-lo (southwest of Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic Ba ...
and near the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
), which tantalizingly, stands for Himtala, 'snow plain', which may be the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
ized form of Hephthal." In 484, the Hephthalite chief Akhshunwar led his army to attack the Sassanian King Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after ...
, who was defeated and killed in Khurasan. After the victory, the Hephthalite empire extended to Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
and Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
. Some of the White Huns drew up a peace treaty with Iran and the two became allies, both fighting against the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. Thus, Hephthalites lived in the Khurasan/Khorasan area. According to the Chinese classic Liang chih-kung-t'u
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering'' () were tributary documentative paintings (with illustration on each of the portrait) produced by various Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese dynasties and later as well in other East Asian dynasties, su ...
, (pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally writte ...
: ) was the name the Hephthalites used for themselves, and that is probably a Chinese transfer of a similar-sounding word, war/Uar.
Mehmed Tezcan writes that according to a Chinese record, the Hephthalites descended from a Ruan Ruan tribe called Hua in the Qeshi region (near Turpan). This tribe came to Tokharistan and soon settled also in eastern regions of Khorasan at the beginning of the 5th century. About the same time, the name Avars/Awards appears in the sources. Again, in his well-known Atlas of China, A. Herrmann shows the eastern regions of Khorasan, Tokharistan, etc. as the dominions of Afu/Hua/Awards/Hephthalites between ca. 440 and 500 A.D., relying on the identification Hua = Uar = Awar.
The German researcher Karl Heinrich Menges considered Eurasian Avars to be one of the ancient Mongol peoples, who "were the first to use the title ga gan (later qān, ḵān) for their supreme ruler." He describes the "traces of a Mongol residue in Daghestan". Supporters of the so-called old Turanian nomad horde "infiltrate" point of view (with various clauses) include the following scientists: Josef Markwart, Omeljan Pritsak, Vladimir Minorsky, Vladimir Baileys, Harald Haarmann, Murad Gadjievich Magomedov, Alikber Alikberov, and Timur Aytberov.
Language
The Avar language belongs to the Avar-Andi-Tsez subgroup of the Northeast Caucasian (or Nakh–Dagestanian) language family. The writing is based on the Cyrillic script, which replaced the Arabic script used before 1927 and the Latin script used between 1927 and 1938. More than 60% of the Avars living in Dagestan speak Russian language, Russian as their second language.Notable Avars
* Imam Shamil, resistance leader during theCaucasian War
The Caucasian War (russian: Кавказская война; ''Kavkazskaya vojna'') or Caucasus War was a 19th century military conflict between the Russian Empire and various peoples of the North Caucasus who resisted subjugation during the ...
* Ghazi Muhammad, Islamic scholar
* Gamzat-bek, imam
* Rasul Gamzatov, poet
* Hadji Murad, military leader during the Caucasian War
The Caucasian War (russian: Кавказская война; ''Kavkazskaya vojna'') or Caucasus War was a 19th century military conflict between the Russian Empire and various peoples of the North Caucasus who resisted subjugation during the ...
, waged by of the peoples of Dagestan and Chechnya from 1811–1864 against the Russian Empire. He was also a rival to Imam Shamil.
*Magomet Gadzhiyev, World War II submarine commander and hero of the Soviet Union
*Kadi Abakarov, a Red Army sergeant who fought during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Abakarov was awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union for his actions in the Battle of the Seelow Heights.
*Ali Aliyev (wrestler), Ali Aliyev, a Freestyle wrestling, freestyle wrestler who won five world titles and was the first wrestler from Dagestan to win a world title in freestyle wrestling.
*Murad Gaidarov, freestyle wrestler representing Belarus.
*Magomedkhan Gamzatkhanov, martial artist
*Mustafa Dağıstanlı, Turkish freestyle wrestler of Avar descent
*Sultan Ibragimov, retired boxer who was a former WBO heavyweight champion
*Mansur Isaev, judoka from Russia. He won gold in the finals at the 2012 Summer Olympics in the class 73 kg.
*Tagir Khaybulaev, judoka from Russia. He won gold in the finals at the 2012 Summer Olympics in the class 100 kg. *Khabib Nurmagomedov, mixed martial artist, two-time Combat Sambo World Champion, and an undefeated former List of UFC champions, UFC Lightweight (MMA), lightweight champion
*Ramazan Emeev, mixed martial artist currently competing in the Welterweight (MMA), welterweight division of the Ultimate Fighting Championship. He is a former M-1 Global Middleweight (MMA), middleweight champion.
*Zagalav Abdulbekov, first Avar Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Abdulrashid Sadulaev, wrestler who won a gold medal in freestyle wrestling for Russia during the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro. He also won a gold medal at the Wrestling at the 2020 Summer Olympics, 2020 Summer Olympics in the 97 kg category.
*Mavlet Batirov, two-time Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Khadzhimurad Magomedov, Khadzimurad Magomedov, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Sagid Murtazaliev, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Makhach Murtazaliev, Olympic bronze medalist and two-time world champion in freestyle wrestling
*Alisa Ganieva, author who writes in Russian but identifies herself as an Avar
*Gadzhimurat Kamalov, investigative journalist who reported on corruption in the Dagestan area
*Ali Shabanau, freestyle wrestler representing Belarus
*Magomed Tolboyev, Soviet-era test pilot for the Buran space shuttle, also a Hero of Russia
*Shaykh Jemaladdin Kumuki, a sufi tariqa shaykh from Kumukh and relative of Imam Shamil
*Khabib Nurmagomedov, mixed martial artist, two-time Combat Sambo World Champion, and an undefeated former List of UFC champions, UFC Lightweight (MMA), lightweight champion
*Ramazan Emeev, mixed martial artist currently competing in the Welterweight (MMA), welterweight division of the Ultimate Fighting Championship. He is a former M-1 Global Middleweight (MMA), middleweight champion.
*Zagalav Abdulbekov, first Avar Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Abdulrashid Sadulaev, wrestler who won a gold medal in freestyle wrestling for Russia during the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro. He also won a gold medal at the Wrestling at the 2020 Summer Olympics, 2020 Summer Olympics in the 97 kg category.
*Mavlet Batirov, two-time Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Khadzhimurad Magomedov, Khadzimurad Magomedov, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Sagid Murtazaliev, Olympic gold medalist in freestyle wrestling
*Makhach Murtazaliev, Olympic bronze medalist and two-time world champion in freestyle wrestling
*Alisa Ganieva, author who writes in Russian but identifies herself as an Avar
*Gadzhimurat Kamalov, investigative journalist who reported on corruption in the Dagestan area
*Ali Shabanau, freestyle wrestler representing Belarus
*Magomed Tolboyev, Soviet-era test pilot for the Buran space shuttle, also a Hero of Russia
*Shaykh Jemaladdin Kumuki, a sufi tariqa shaykh from Kumukh and relative of Imam ShamilEvliyalar.net
Media files
See also
* Pannonian Avars * Vainakh * Peoples of the CaucasusReferences
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Avars Avar people, Ethnic groups in Dagestan Ethnic groups in Azerbaijan Ethnic groups in Georgia (country) Muslim communities of Russia Peoples of the Caucasus