Australian folklore on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Australian folklore refers to the
 *
*
 * Gippsland phantom cat – An urban legend centred on the idea that when United States soldiers were based in
* Gippsland phantom cat – An urban legend centred on the idea that when United States soldiers were based in
folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
and urban legends
An urban legend (sometimes contemporary legend, modern legend, urban myth, or urban tale) is a genre of folklore comprising stories or fallacious claims circulated as true, especially as having happened to a "friend of a friend" or a family m ...
that have evolved in Australia from Aboriginal Australian
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Isl ...
myths to colonial and contemporary
Contemporary history, in English-language historiography, is a subset of modern history that describes the historical period from approximately 1945 to the present. Contemporary history is either a subset of the late modern period, or it is o ...
folklore including people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
, places and events, that have played part in shaping the culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
, image and traditions that are seen in contemporary Old Australia.
Australian Aboriginal mythology
* Baijini – Unknown race mentioned in Yolngu folklore. * Bora – Sacred Aboriginal initiation ceremony. Many sites still exist throughout Australia. *Bunyip
The bunyip is a creature from the aboriginal mythology of southeastern Australia, said to lurk in swamps, billabongs, creeks, riverbeds, and waterholes.
Name
The origin of the word ''bunyip'' has been traced to the Wemba-Wemba or Wergaia ...
– According to legend, they are said to lurk in swamps, billabongs, creeks, riverbeds, and waterholes.
*Dreamtime
The Dreaming, also referred to as Dreamtime, is a term devised by early anthropologists to refer to a religio-cultural worldview attributed to Australian Aboriginal beliefs. It was originally used by Francis Gillen, quickly adopted by his co ...
– The Dreamtime to Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Isl ...
is the beginning of time, the creation of knowledge from which their culture began more than 60,000 years ago.
 *
*Kata Tjuta
Kata Tjuṯa / The Olgas (Pitjantjatjara: , lit. 'many heads'; ) is a group of large, domed rock formations or bornhardts located about southwest of Alice Springs, in the southern part of the Northern Territory, central Australia. Uluṟu / Aye ...
– Many Dreamtime stories are told by the Pitjantjatjara
The Pitjantjatjara (; or ) are an Aboriginal people of the Central Australian desert near Uluru. They are closely related to the Yankunytjatjara and Ngaanyatjarra and their languages are, to a large extent, mutually intelligible (all are va ...
people, including a mythical creature that lurks the summit.
*Lake Mungo remains
The Lake Mungo remains are three prominent sets of human remains that are possibly Aboriginal Australian: Lake Mungo 1 (also called Mungo Woman, LM1, and ANU-618), Lake Mungo 3 (also called Mungo Man, Lake Mungo III, and LM3), and Lake Mungo 2 ...
– Human skeletons found in 1969, believed to have lived between 40,000 and 68,000 years ago are the oldest human remains found in Australia.
*Rainbow Serpent
The Rainbow Serpent or Rainbow Snake is a common deity often seen as the creator God, known by numerous names in different Australian Aboriginal languages by the many different Aboriginal peoples. It is a common motif in the art and religion ...
– It is the sometimes unpredictable Rainbow Serpent, who vies with the ever-reliable Sun, that replenishes the stores of water, forming gullies and deep channels as he slithered across the landscape, allowing for the collection and distribution of water.
*Yara-ma-yha-who
The Yara-ma-yha-who is a legendary creature found in Australian Aboriginal mythology. The legend is recounted by David Unaipon. According to legend, the creature resembles a little red frog-like man with a very big head, a large mouth with no tee ...
– According to Myth, the creature resembles a red frog-like creature that hides in trees waiting for an unsuspecting victim to consume.
Animals and creatures
* Bob the Railway Dog – A Dog that was remembered for traveling along the South Australian Railway. * Booie Monster – Reports of a monster lurking in a cave first reported in the 1950s * Drop bear – Stories of drop bears are frequently related to visiting tourists as a joke. (see also the Queensland tiger) * Gippsland phantom cat – An urban legend centred on the idea that when United States soldiers were based in
* Gippsland phantom cat – An urban legend centred on the idea that when United States soldiers were based in Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
during WWII
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, they released cougars into the wild. Consequently, many sightings of big cats have been reported across Gippsland
Gippsland is a rural region that makes up the southeastern part of Victoria, Australia, mostly comprising the coastal plains to the rainward (southern) side of the Victorian Alps (the southernmost section of the Great Dividing Range). It cove ...
and even in other parts of Australia.
* Hook Island Sea Monster – Gigantic, tadpole-like sea monster
Sea monsters are beings from folklore believed to dwell in the sea and often imagined to be of immense size. Marine monsters can take many forms, including sea dragons, sea serpents, or tentacled beasts. They can be slimy and scaly and are of ...
, Photographed in Stonehaven Bay, Hook Island, Queensland.
*Megalania
Megalania (''Varanus priscus'') is an extinct species of giant monitor lizard, part of the megafaunal assemblage that inhabited Australia during the Pleistocene. It is the largest terrestrial lizard known to have existed, reaching an estimated ...
– A giant goanna
A goanna is any one of several species of lizards of the genus '' Varanus'' found in Australia and Southeast Asia.
Around 70 species of ''Varanus'' are known, 25 of which are found in Australia. This varied group of carnivorous reptiles ranges ...
(lizard), generally believed to be extinct. However, there have been numerous reports and rumors of living Megalania in Australia, and occasionally New Guinea, but the only physical evidence that Megalania might still be alive today are plaster casts of possible Megalania footprints made in 1979.
*Platypus
The platypus (''Ornithorhynchus anatinus''), sometimes referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic, egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. The platypus is the sole living representative or mono ...
– Native Australian animal which is one of only two mammals that lay eggs (the other being the echidna
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the family Tachyglossidae . The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the ...
), and one of the few species that is venomous. Due to its unique features the scientist who initially discovered and examined the creature thought it was made of several animals sewn together and deemed it to be a hoax.
* Red Dog – A dog that was known for his long travels through Western Australia's Pilbara region.
*Tasmanian tiger
The thylacine ( , or , also ) (''Thylacinus cynocephalus'') is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The last known live animal was captured in 1930 in Tasma ...
– Despite the widely held view that the thylacine (or Tasmanian tiger) became extinct during the 1930s, accounts of alleged sightings in eastern Victoria and parts of Tasmania have persisted to the present day.
* Yowie (cryptid) – In the modern context, the Yowie is the generic (and somewhat affectionate) term for an unidentified hominid reputed to lurk in the Australian wilderness, analogous to the Himalayan Yeti
The Yeti ()"Yeti"
''
''
Bigfoot.
*The Dog on the Tuckerbox – an allegorical bullock driver's dog that loyally guarded the man's tuckerbox until its death. It has been immortalized in both a poem and a statue at
 *
*
 *
*
, – Meacham, Steve, ''
 * Don Bradman – Perhaps the greatest cricketer ever, the fact that he needed only 4 runs in his last innings in order to retire with a test average of 100 but was uncharacteristically bowled for a duck (leaving him stranded on an average of 99.94) has become a part of Australian folklore and added greatly to his mystique. (there are rumours that he has made the 4 runs in another match that was miscounted)
* William Buckley – Australian convict who escaped and became famous for living in an Aboriginal community for more than thirty years. Believed by many Australians to be the source of the saying "You've got Buckley's Chance".
* Azaria Chamberlain – the name of two-month-old Australian baby who disappeared on the night of 17 August 1980 on a camping trip with her family. Her parents, Lindy Chamberlain and
* Don Bradman – Perhaps the greatest cricketer ever, the fact that he needed only 4 runs in his last innings in order to retire with a test average of 100 but was uncharacteristically bowled for a duck (leaving him stranded on an average of 99.94) has become a part of Australian folklore and added greatly to his mystique. (there are rumours that he has made the 4 runs in another match that was miscounted)
* William Buckley – Australian convict who escaped and became famous for living in an Aboriginal community for more than thirty years. Believed by many Australians to be the source of the saying "You've got Buckley's Chance".
* Azaria Chamberlain – the name of two-month-old Australian baby who disappeared on the night of 17 August 1980 on a camping trip with her family. Her parents, Lindy Chamberlain and  *
* *
*
 * Franklin House – Historic house in Launceston that has had reports of ghost sightings.
* Gallipoli – the name of a peninsula in
* Franklin House – Historic house in Launceston that has had reports of ghost sightings.
* Gallipoli – the name of a peninsula in  *
* *
*
 *
*
 * Colliwobbles – The "colliwobbles" refers to the Collingwood Football Club's apparent penchant for losing grand finals over a 32-year period between 1958 and 1990. During this premiership drought, fans endured nine fruitless grand finals (1960, 1964, 1966, 1970, 1977 (drawn, then lost in a replay the following week), 1979, 1980, 1981). The term "Colliwobbles" was to enter the Victorian vocabulary to signify a choking phenomenon.
* The Invincibles – First
* Colliwobbles – The "colliwobbles" refers to the Collingwood Football Club's apparent penchant for losing grand finals over a 32-year period between 1958 and 1990. During this premiership drought, fans endured nine fruitless grand finals (1960, 1964, 1966, 1970, 1977 (drawn, then lost in a replay the following week), 1979, 1980, 1981). The term "Colliwobbles" was to enter the Victorian vocabulary to signify a choking phenomenon.
* The Invincibles – First
 * 5 o'clock wave – Supposedly a large wave, several metres in height and created by the daily release of dam overflow, that is said to travel downriver at high speed, and to reach the location at which the tale is being told at 5 o'clock each afternoon.
*
* 5 o'clock wave – Supposedly a large wave, several metres in height and created by the daily release of dam overflow, that is said to travel downriver at high speed, and to reach the location at which the tale is being told at 5 o'clock each afternoon.
* *Kariong, New South Wales#Gosford glyphs, Gosford glyphs – Egyptian hieroglyphs that are carved into two parallel sandstone walls. Found in 1975 by a local surveyor, it is debated whether they are authentic or not.
*Frederick Bailey Deeming#Jack the Ripper theory, Jack the Ripper in Australia – Frederick Bailey Deeming an English born Australian man was once thought to have been the infamous Jack the Ripper living in Melbourne.
*Lasseter's Reef – A fabulously rich gold deposit said to have been discovered – and then subsequently lost – by bushman Lewis Hubert (Harold Bell) Lasseter, Harold Bell Lasseter in a remote and desolate corner of central Australia towards the end of the 19th century.
*Kariong, New South Wales#Gosford glyphs, Gosford glyphs – Egyptian hieroglyphs that are carved into two parallel sandstone walls. Found in 1975 by a local surveyor, it is debated whether they are authentic or not.
*Frederick Bailey Deeming#Jack the Ripper theory, Jack the Ripper in Australia – Frederick Bailey Deeming an English born Australian man was once thought to have been the infamous Jack the Ripper living in Melbourne.
*Lasseter's Reef – A fabulously rich gold deposit said to have been discovered – and then subsequently lost – by bushman Lewis Hubert (Harold Bell) Lasseter, Harold Bell Lasseter in a remote and desolate corner of central Australia towards the end of the 19th century.
 *Mahogany Ship – A supposed wrecked Portuguese caravel which is purported to lie beneath the sand approximately six miles west of Warrnambool in southwest Victoria, Australia.
*Marree Man – A large modern geoglyph, created using an agricultural plough, first noted by air in 1998 near Marree, South Australia, Marree in South Australia. The Marree Hotel publican and other locals restored the outline using a plough in August 2016 after it had all but disappeared into the sand.
*Min Min light – An unexplained light seen in central Australia.
*Mullumbimby#Stone arrangement, Mullumbimby Stonehenge – Ancient stone arrangement, which dates back to the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age. The location remains unknown to the Australian public due to fears of theft and further destruction.
*Nullarbor Nymph – A hoax and legend in 1971 and 1972 in Australia which grew from the supposed sighting of a half naked woman on the Nullarbor Plain living amongst some kangaroos.
*Rex Gilroy – One of Australia's most famous Cryptozoologists.
*The Speewah – A mythical Australian station that is the subject of many tall tales told by Australian bushmen.
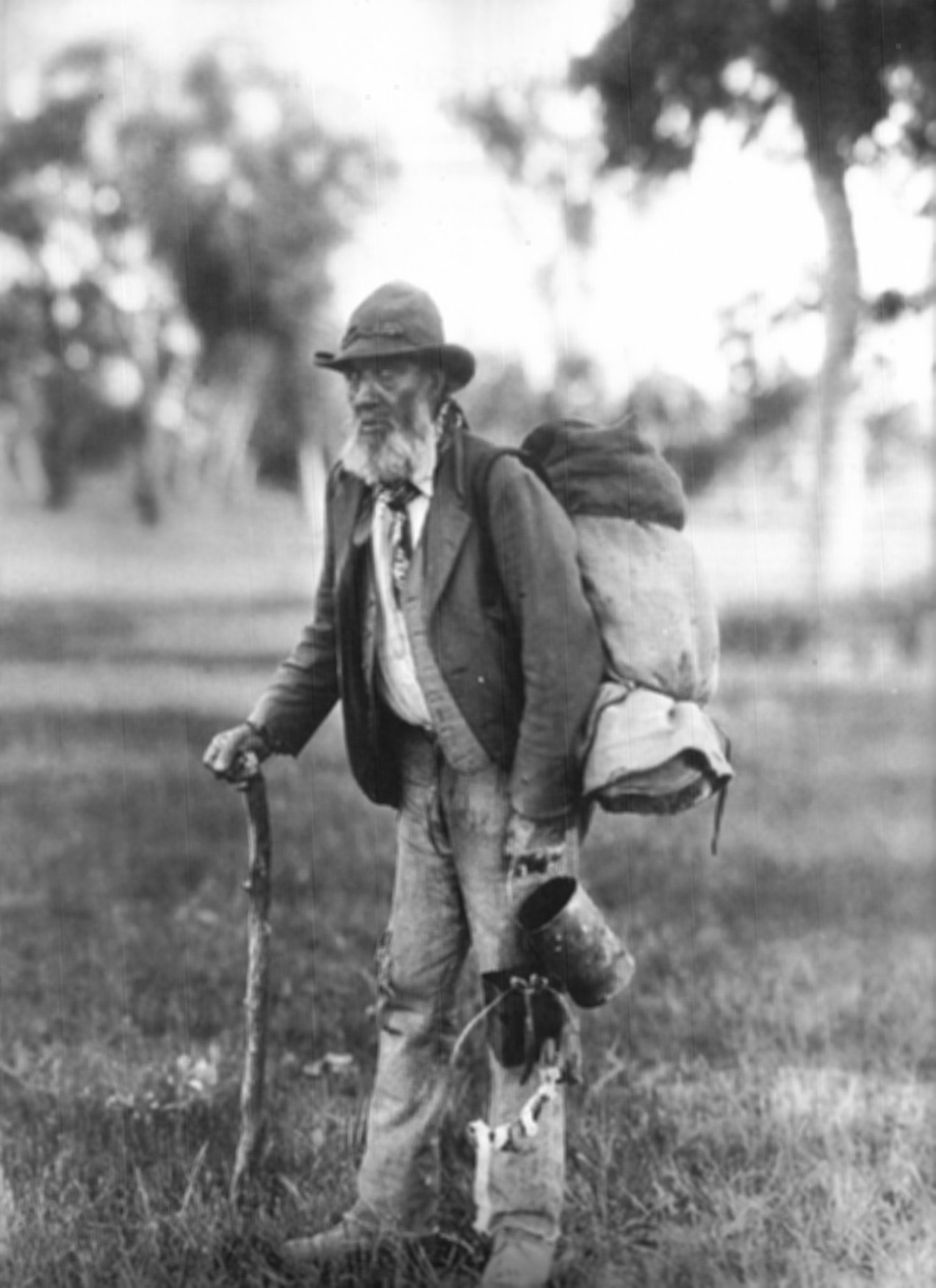
*Swagman – Vagabond who travelled by foot to different locations looking for work carrying his belongings, seen as a folk hero in 19th-century Australia.
*Tamam Shud case – In 1948 an unidentified man was found dead at a Glenelg, South Australia, beach in Adelaide, South Australia. The case involves an encrypted message and is considered "one of Australia's most profound mysteries". The Cold case, case is unsolved and remains open to this day.
*Toyota Land Cruiser – 4WD Vehicle that was originally used to help build the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Scheme. Often considered to be Australia's Greatest off-road vehicle. Especially the 80 Series of the 1990s.
*Thomas Welsby Clark – Body of a Deceased man that was found at sea near the shores of Christmas Island, which is 1,550 kilometres from Australia's closest point, who was a sailor from only body found from sinking of ship with all hands on deck.
*Mahogany Ship – A supposed wrecked Portuguese caravel which is purported to lie beneath the sand approximately six miles west of Warrnambool in southwest Victoria, Australia.
*Marree Man – A large modern geoglyph, created using an agricultural plough, first noted by air in 1998 near Marree, South Australia, Marree in South Australia. The Marree Hotel publican and other locals restored the outline using a plough in August 2016 after it had all but disappeared into the sand.
*Min Min light – An unexplained light seen in central Australia.
*Mullumbimby#Stone arrangement, Mullumbimby Stonehenge – Ancient stone arrangement, which dates back to the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age. The location remains unknown to the Australian public due to fears of theft and further destruction.
*Nullarbor Nymph – A hoax and legend in 1971 and 1972 in Australia which grew from the supposed sighting of a half naked woman on the Nullarbor Plain living amongst some kangaroos.
*Rex Gilroy – One of Australia's most famous Cryptozoologists.
*The Speewah – A mythical Australian station that is the subject of many tall tales told by Australian bushmen.
*Swagman – Vagabond who travelled by foot to different locations looking for work carrying his belongings, seen as a folk hero in 19th-century Australia.
*Tamam Shud case – In 1948 an unidentified man was found dead at a Glenelg, South Australia, beach in Adelaide, South Australia. The case involves an encrypted message and is considered "one of Australia's most profound mysteries". The Cold case, case is unsolved and remains open to this day.
*Toyota Land Cruiser – 4WD Vehicle that was originally used to help build the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Scheme. Often considered to be Australia's Greatest off-road vehicle. Especially the 80 Series of the 1990s.
*Thomas Welsby Clark – Body of a Deceased man that was found at sea near the shores of Christmas Island, which is 1,550 kilometres from Australia's closest point, who was a sailor from only body found from sinking of ship with all hands on deck.
Gundagai
Gundagai is a town in New South Wales, Australia. Although a small town, Gundagai is a popular topic for writers and has become a representative icon of a typical Australian country town. Located along the Murrumbidgee River and Muniong, Hon ...
in southern NSW. By way of explanation – tucker means food – so a tuckerbox is a lunch box
A lunch box (alt. spelling lunchbox) refers to a hand-held container used to transport food, usually to work or to school. It is commonly made of metal or plastic, is reasonably airtight and often has a handle for carrying.
In the United ...
.
Historical events
 *
*Eureka Stockade
The Eureka Rebellion was a series of events involving gold miners who revolted against the British administration of the colony of Victoria, Australia during the Victorian gold rush. It culminated in the Battle of the Eureka Stockade, which ...
– A rebellion that took place in Ballarat on 3 December 1854.
* Ancient Coins Marchinbar Island – Nine coins found, some believing they could have come from the Kilwa Sultanate of east Africa which dates back to the 10th century.
* Frontier wars – A much less talked about event in Australian history, a war that spanned 146 years which was fought between mostly British settlers and Aboriginal tribes.
* First Fleet – Name given to the 11 ships that departed England in 1787, with convicts, officers and free settlers to found what became the first European settlement in Australia, Sydney.
* Frederick escape – A ship hijacked by Australian convicts and used to sail to Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
in 1834.
* Lachlan Gold Escort robbery – One of the largest ever gold robberies in Australian history. Led by outlaw Ben Hall & Frank Gardiner
Frank Gardiner (1830 – c. 1882) was an Australian bushranger who gained infamy for his lead role in the a robbery of a gold escort at Eugowra, New South Wales in June 1862. It is considered the largest gold heist in Australian history. Gard ...
, Most of the gold was recovered, but some still search the area for treasure. Would equate to about A$13 million in today's value.
* Nelson robbery - One of the biggest robberies during the Victorian gold rush
The Victorian gold rush was a period in the history of Victoria, Australia approximately between 1851 and the late 1860s. It led to a period of extreme prosperity for the Australian colony, and an influx of population growth and financial capit ...
, in which 8,183 ounces of gold were taken at Gunpoint.
*Kokoda Track campaign
The Kokoda Track campaign or Kokoda Trail campaign was part of the Pacific War of World War II. The campaign consisted of a series of battles fought between July and November 1942 in what was then the Australian Territory of Papua. It was primar ...
- Battles fought in 1942 in what was then the Australian Territory of Papua
The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the a ...
with Australian and United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
forces defeating the Japanese who directly threatened the security of Australia and is considered part of the ANZAC legend
The Anzac spirit or Anzac legend is a concept which suggests that Australian and New Zealand soldiers possess shared characteristics, specifically the qualities those soldiers allegedly exemplified on the battlefields of World War I. These p ...
.
* Portuguese discovery of Australia – A much disputed theory that claims early Portuguese navigators were the first Europeans to sight Australia between 1521 and 1524, well before the arrival of Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon
Willem Janszoon (; ), sometimes abbreviated to Willem Jansz., was a Dutch navigator and colonial governor. Janszoon served in the Dutch East Indies in the periods 16031611 and 16121616, including as governor of Fort Henricus on the island of S ...
in 1606.
Art, film, music and literature
*Bush ballad
The bush ballad, bush song or bush poem is a style of poetry and folk music that depicts the life, character and scenery of the Australian bush. The typical bush ballad employs a straightforward rhyme structure to narrate a story, often one of ...
– Poems that usually depict Australian life in the outback or bush.
* Clancy of the Overflow – A poem by Banjo Paterson
Andrew Barton "Banjo" Paterson, (17 February 18645 February 1941) was an Australian bush poet, journalist and author. He wrote many ballads and poems about Australian life, focusing particularly on the rural and outback areas, including the ...
which admires the Outback.
*Eternity
Eternity, in common parlance, means infinite time that never ends or the quality, condition, or fact of being everlasting or eternal. Classical philosophy, however, defines eternity as what is timeless or exists outside time, whereas sempit ...
– A Graffiti tag done more than 500,000 times by Arthur Stace
Arthur Malcolm Stace (9 February 1885 – 30 July 1967), known as Mr Eternity, was an Australian soldier. He was an alcoholic from his teenage years until the early 1930s, when he converted to Christianity and began to spread his message by ...
over a 35-year period, in which only 2 original tags remain.
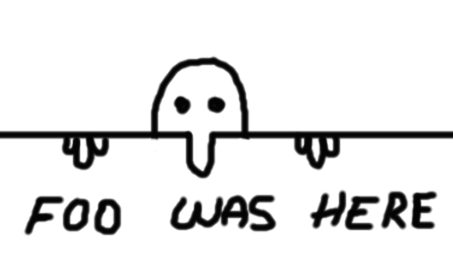
* Foo was here – Popular Graffiti signature during WW1
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
that was later adopted by Americans during WW2 and called Kilroy was here. Is said to have Influenced modern Street art.
 *
*My Country
"My Country" is a poem about Australia, written by Dorothea Mackellar (1885–1968) at the age of 19 while homesick in the United Kingdom. After travelling through Europe extensively with her father during her teenage years, she started ...
– More commonly known as "I Love a Sunburnt Country" is a patriotic poem about Australia published in 1908 written by Dorothea Mackellar
Isobel Marion Dorothea Mackellar, (1 July 1885 – 14 January 1968) was an Australian poet and fiction writer. Her poem ''My Country'' is widely known in Australia, especially its second stanza, which begins: "''I love a sunburnt country/ ...
when she was 19 and homesick living in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
.
*The Lucky Country
''The Lucky Country'' is a 1964 book by Donald Horne. The title has become a nickname for Australia and is generally used favourably, although the origin of the phrase was negative in the context of the book. Among other things, it has been use ...
– Is a book by Donald Horne
Donald Richmond Horne (26 December 1921 – 8 September 2005) was an Australian journalist, writer, social critic, and academic who became one of Australia's best known public intellectuals, from the 1960s until his death.
Horne was a prol ...
in which the phrase itself was used as sarcasm within the context of the book but has taken place in Australian culture as a true and meaningful title.
*The Story of the Kelly Gang
''The Story of the Kelly Gang'' is a 1906 Australian bushranger film that traces the exploits of 19th-century bushranger and outlaw Ned Kelly and his gang. It was directed by Charles Tait and shot in and around the city of Melbourne. The origin ...
– The world's first full-length film. Made in 1906, it ran for more than an hour; it is, however, considered a Lost film
A lost film is a feature
Feature may refer to:
Computing
* Feature (CAD), could be a hole, pocket, or notch
* Feature (computer vision), could be an edge, corner or blob
* Feature (software design) is an intentional distinguishing char ...
, as only 20 minutes of the original film still exist.
*Rod Ansell
Rodney William Ansell (1 October 1954 – 3 August 1999) was an Australian cattle Pastoral farming, grazier and a buffalo hunter. Described to be from "the bush", Ansell became famous in 1977 after he was stranded in extremely remote country in t ...
– Outback Australian who became the inspiration for the famous film Crocodile Dundee
''Crocodile Dundee'' (stylized as ''"Crocodile" Dundee'' in the U.S.) is a 1986 action comedy film set in the Australian Outback and in New York City. It stars Paul Hogan as the weathered Mick Dundee, and American actress Linda Kozlowski as ...
.
*Streets of Forbes
"Streets of Forbes" is an Australian folksong about the death of bushranger Ben Hall. The song is one of the best-known elements of the Australian folk repertoire. It has been recorded by many folk and popular artists and groups including Martin ...
– Folk song about iconic Bushranger Ben Hall.
*Waltzing Matilda
"Waltzing Matilda" is a song developed in the Australian style of poetry and folk music called a bush ballad. It has been described as the country's "unofficial national anthem".
The title was Australian slang for travelling on foot (waltzing) ...
– Extensive folklore surrounds the song and the process of its creation, to the extent that the song has its own museum in Winton, Queensland
Winton is a town and locality in the Shire of Winton in Central West Queensland, Australia. It is northwest of Longreach. The main industries of the area are sheep and cattle raising. The town was named in 1876 by postmaster Robert Allen, aft ...
People
* John Batman – 19th century pioneer, controversial with how he dealt withIndigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
, but nevertheless signed a peaceful agreement with the Wurundjeri known as Batman's Treaty which would eventuality lead to the Foundation of Melbourne
The city of Melbourne was founded in 1835. The exact circumstances of ''the foundation of Melbourne'', and the question of who should take credit, have long been matters of dispute.
Exploration
A series of colonisers, mostly operating from Syd ...
* Ben Hall - an Australian bushranger and leading member of the Gardiner–Hall gang. He and his associates carried out many raids across New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, from Bathurst to Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also r ...
, south to Gundagai
Gundagai is a town in New South Wales, Australia. Although a small town, Gundagai is a popular topic for writers and has become a representative icon of a typical Australian country town. Located along the Murrumbidgee River and Muniong, Hon ...
and east to Goulburn
Goulburn ( ) is a regional city in the Southern Tablelands of the Australian state of New South Wales, approximately south-west of Sydney, and north-east of Canberra. It was proclaimed as Australia's first inland city through letters pate ...
. Unlike many bushrangers of the era, Hall was not directly responsible for any deaths, although several of his associates were. He was shot dead by police in May 1865 at Goobang Creek. The police claimed that they were acting under the protection of the ''Felons Apprehension Act 1865'' which allowed any bushranger who had been specifically named under the terms of the Act to be shot and killed by any person at any time without warning. At the time of Hall's death, the Act had not yet come into force, resulting in considerable controversy over the legality of his killing."Family seeks justice for Bold Ben's demise", – Meacham, Steve, ''
The Age
''The Age'' is a daily newspaper in Melbourne, Australia, that has been published since 1854. Owned and published by Nine Entertainment, ''The Age'' primarily serves Victoria, but copies also sell in Tasmania, the Australian Capital Territory ...
'', 31 March 2007 Hall is a prominent figure in Australian folklore, inspiring many bush ballad
The bush ballad, bush song or bush poem is a style of poetry and folk music that depicts the life, character and scenery of the Australian bush. The typical bush ballad employs a straightforward rhyme structure to narrate a story, often one of ...
s, books and screen works, including the 1975 television series '' Ben Hall'' and the 2016 feature film '' The Legend of Ben Hall''.
 * Don Bradman – Perhaps the greatest cricketer ever, the fact that he needed only 4 runs in his last innings in order to retire with a test average of 100 but was uncharacteristically bowled for a duck (leaving him stranded on an average of 99.94) has become a part of Australian folklore and added greatly to his mystique. (there are rumours that he has made the 4 runs in another match that was miscounted)
* William Buckley – Australian convict who escaped and became famous for living in an Aboriginal community for more than thirty years. Believed by many Australians to be the source of the saying "You've got Buckley's Chance".
* Azaria Chamberlain – the name of two-month-old Australian baby who disappeared on the night of 17 August 1980 on a camping trip with her family. Her parents, Lindy Chamberlain and
* Don Bradman – Perhaps the greatest cricketer ever, the fact that he needed only 4 runs in his last innings in order to retire with a test average of 100 but was uncharacteristically bowled for a duck (leaving him stranded on an average of 99.94) has become a part of Australian folklore and added greatly to his mystique. (there are rumours that he has made the 4 runs in another match that was miscounted)
* William Buckley – Australian convict who escaped and became famous for living in an Aboriginal community for more than thirty years. Believed by many Australians to be the source of the saying "You've got Buckley's Chance".
* Azaria Chamberlain – the name of two-month-old Australian baby who disappeared on the night of 17 August 1980 on a camping trip with her family. Her parents, Lindy Chamberlain and Michael Chamberlain
Michael Leigh Chamberlain (27 February 1944 – 9 January 2017) was a New Zealand-Australian writer, teacher and pastor falsely implicated in the August 1980 death of his missing daughter Azaria, which was later demonstrated to be the result ...
, reported that she had been taken from their tent by a dingo, but they were arrested, tried, and convicted of her murder in 1982. Both were later cleared, and thus the case is best remembered for what was an injustice. The Chamberlains were Seventh-day Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and i ...
and an urban myth had developed that they were required to sacrifice a child as part of their religious beliefs and that the name Azaria meant "sacrifice". These statements are false.
*John Curtin
John Curtin (8 January 1885 – 5 July 1945) was an Australian politician who served as the 14th prime minister of Australia from 1941 until his death in 1945. He led the country for the majority of World War II, including all but the last few ...
– 14th Prime Minister of Australia. Led Australia through WW2 when the country was threatened by Japanese invasion and was successful but died in office towards the end of the war. He is considered Australia's greatest Prime Minister.
*Errol Flynn
Errol Leslie Thomson Flynn (20 June 1909 – 14 October 1959) was an Australian-American actor who achieved worldwide fame during the Golden Age of Hollywood. He was known for his romantic swashbuckler roles, frequent partnerships with Olivia ...
– first Australian born actor to achieve significant fame in Hollywood.
*Dawn Fraser
Dawn Fraser (born 4 September 1937) is an Australian freestyle champion swimmer and former politician. She is one of only four swimmers to have won the same Olympic individual event three times – in her case the women's 100-metre freestyle. ...
– perhaps the greatest Australian female swimmer of all time. Known for her politically incorrect
''Political correctness'' (adjectivally: ''politically correct''; commonly abbreviated ''PC'') is a term used to describe language, policies, or measures that are intended to avoid offense or disadvantage to members of particular groups in socie ...
behaviour or larrikin
Larrikin is an Australian English term meaning "a mischievous young person, an uncultivated, rowdy but good hearted person", or "a person who acts with apparent disregard for social or political conventions".
In the 19th and early 20th centurie ...
character as much as her athletic ability, Fraser won eight Olympic medals, including four golds, and six Commonwealth Games
The Commonwealth Games, often referred to as the Friendly Games or simply the Comm Games, are a quadrennial international multi-sport event among athletes from the Commonwealth of Nations. The event was first held in 1930, and, with the exce ...
gold medals. It was alleged that she took the flag from Emperor Hirohito's palace, while this was proved false, the incident became part of the folklore.
* Harold Holt – a prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
who disappeared while swimming in 1967. Conspiracy theories include Holt being picked up by a Chinese submarine, faking his own death, suicide, and CIA involvement. Formal investigations determined that he drowned accidentally.The expression "Like leaving the (porch) light on for Harold Holt" means to have an misplaced hope for an event to happen when the reality is that the event (Holt's having actually survived and being discovered still alive) is never likely to ever happen.
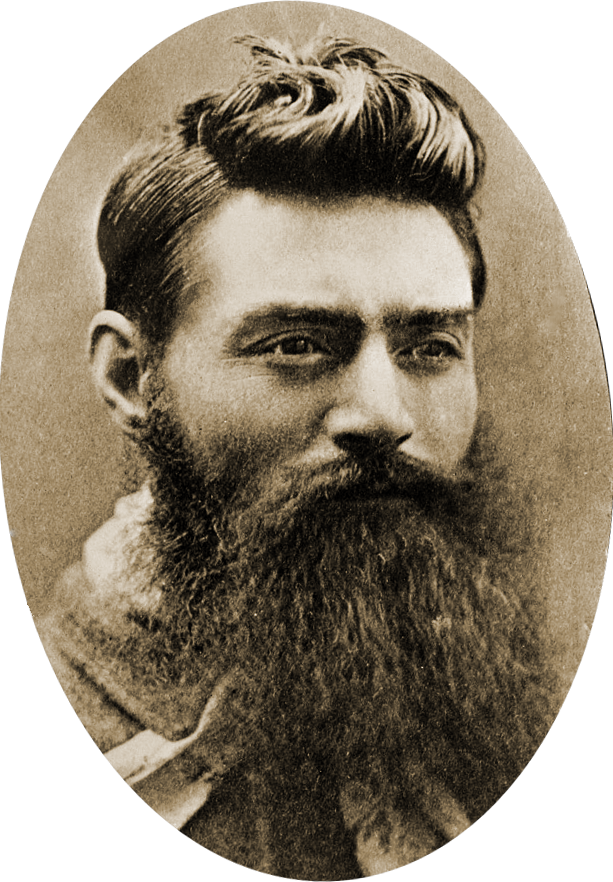
*Ned Kelly
Edward Kelly (December 1854 – 11 November 1880) was an Australian bushranger, outlaw, gang leader and convicted police-murderer. One of the last bushrangers, he is known for wearing a suit of bulletproof armour during his final shootout wi ...
– Australian 19th-century bushranger, many films, books and artworks have been made about him, possibly his exploits have been exaggerated in the public eye and become something of folklore. It especially surrounds his capture at Glenrowan where the Kelly gang tried to derail a train of Victorian police which were arriving, and were surrounded in the hotel. Kelly had made armour from stolen iron mould boards of ploughs, and came out shooting, whereupon he was shot in the legs. Some consider him as Australia's Robin Hood
Robin Hood is a legendary heroic outlaw originally depicted in English folklore and subsequently featured in literature and film. According to legend, he was a highly skilled archer and swordsman. In some versions of the legend, he is dep ...
whiles others would disagree.
 *
*Peter Lalor
Peter Fintan Lalor (; 5 February 1827 – 9 February 1889) was an Irish-Australian rebel and, later, politician who rose to fame for his leading role in the Eureka Rebellion, an event identified with the "birth of democracy" in Australia. ...
– An Irish-Australian rebel in the Eureka Stockade
The Eureka Rebellion was a series of events involving gold miners who revolted against the British administration of the colony of Victoria, Australia during the Victorian gold rush. It culminated in the Battle of the Eureka Stockade, which ...
who later became the only outlaw to make it to parliament.
*Eddie Mabo
Edward Koiki Mabo (''né'' Sambo; 29 June 1936 – 21 January 1992) was an Indigenous Australian man from the Torres Strait Islands known for his role in campaigning for Indigenous land rights in Australia, in particular the landmark decision o ...
– challenged the Australian Government as to who owned the island of Mer where he was born and lived. He believed the land belonged to the Indigenous peoples of the Torres Strait Islands. He challenged the first court case to win in the High Court on 3 June 1992 – but sadly did not live to see his victory.
*Wally Lewis
Walter James Lewis AM (born 1 December 1959) is an Australian former professional rugby league footballer who played in the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s, and coached in the 1980s and 1990s. He became a commentator for television coverage of the sp ...
– legendary rugby league player, captained the Queensland rugby league team in The State of Origin series
The State of Origin series is an annual best-of-three rugby league series between two Australian state representative sides, the New South Wales Blues and the Queensland Maroons.
Referred to as “Australian sport's greatest rivalry”, the ...
a record 30 times.
*Dancing Man
''Dancing Man'' is the name given to a photograph of a man who was filmed dancing on the street in Sydney, Australia, after the end of World War II. On 15 August 1945, a cameraman, Jim Pearson, took note of a man's joyful expression and dance ...
– Unknown man dancing in the street in Sydney, Australia, after the end of World War II.
*Mary MacKillop
Mary Helen MacKillop RSJ (15 January 1842 – 8 August 1909) was an Australian religious sister who has been declared a saint by the Catholic Church, as St Mary of the Cross. Of Scottish descent, she was born in Melbourne but is best known f ...
– Australia's first saint, responsible for miracles such as curing a woman of leukemia after her family prayed for it.
 *
*Dame Nellie Melba
Dame Nellie Melba (born Helen Porter Mitchell; 19 May 186123 February 1931) was an Australian operatic dramatic coloratura soprano (three octaves). She became one of the most famous singers of the late Victorian era and the early 20th centur ...
– an Australian opera soprano, the first Australian to achieve international recognition in the form. The French dessert peach Melba is named after her. Many old theatre halls in regional Australia persist with rumours that she once graced their stage, most notably, that of the gold mining town of Gulgong, New South Wales
Gulgong is a 19th-century gold rush town in the Central Tablelands and the wider Central West regions of the Australian state of New South Wales. The town is situated within the Mid-Western Regional Council local government area. It is locate ...
. She is also remembered in the vernacular Australian expression "more comebacks than Nellie Melba", which satirised her seemingly endless series of "retirement" tours in the 1920s.
*Bert Newton
Albert Watson Newton (23 July 1938 – 30 October 2021) was an Australian media personality. He was a Logie Hall of Fame inductee, quadruple Gold Logie award-winning entertainer and radio, theatre and television personality and presenter. Newt ...
– Looked upon as the most influential man in the history of Australian television.
* Lennie Gwyther – 9-year-old boy famous for traveling more than 1000 km on horseback from his home in Leongatha
Leongatha is a town in the foothills of the Strzelecki Ranges, South Gippsland Shire, Victoria, Australia, located south-east of Melbourne. At the , Leongatha had a population of 5,869.
Canadian dairy company Saputo which trades in Australia ...
to see the opening of the Sydney Harbour Bridge in 1932.
*Pintupi Nine
The Pintupi are an Australian Aboriginal group who are part of the Western Desert cultural group and whose traditional land is in the area west of Lake Macdonald and Lake Mackay in Western Australia. These people moved (or were moved) into ...
– Last indigenous Australian tribe who lived a traditional hunter-gatherer life in the Gibson Desert until they were discovered in 1984, almost 200 years since first colonization.
*Johnny O'Keefe
John Michael O'Keefe (19 January 1935 – 6 October 1978) was an Australian rock and roll singer whose career began in the 1950s. Some of his hits include " Wild One" (1958), " Shout!" and "She's My Baby". In his twenty-year career, O'Keefe rel ...
– Australia's most successful chart performer, with twenty-nine Top 40 hits to his credit in Australia between 1959 and 1974.
*Banjo Paterson
Andrew Barton "Banjo" Paterson, (17 February 18645 February 1941) was an Australian bush poet, journalist and author. He wrote many ballads and poems about Australian life, focusing particularly on the rural and outback areas, including the ...
– Was A bush poet who wrote many ballads and poems about Australian life, focusing mainly on the rural and outback areas of the country. Is widely considered Australia's greatest writer.
*Pemulwuy
Pemulwuy (also rendered as Pimbloy, Pemulvoy, Pemulwoy, Pemulwy or Pemulwye, or sometimes by contemporary Europeans as Bimblewove, Bumbleway or Bembulwoyan) (c. 1750 – 2 June 1802) was a Bidjigal man of the Eora nation, born around 1750 in t ...
– an Aboriginal rebel who fought against the British during the 18th and early 19th centuries, believed to have impossibly escaped from capture on countless occasions.
* Simpson and his Donkey – Soldier who is part of the ANZAC legend. During the Gallipoli Campaign at ANZAC Cove Simpson would help rescue Australian Soldiers and take them to safety.
*Squizzy Taylor
Joseph Theodore Leslie "Squizzy" Taylor (29 June 1888 – 27 October 1927) was an Australian gangster from Melbourne. He appeared repeatedly and sometimes prominently in Melbourne news media because of suspicions, formal accusations and some co ...
– A petty criminal turned gangster from Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
. He is believed to have constructed a series of tunnels throughout the inner suburbs of Fitzroy and Collingwood.
*Yagan
Yagan (; – 11 July 1833) was an Aboriginal Australian warrior from the Noongar people. Yagan was pursued by the local authorities after he killed Erin Entwhistle, a servant of farmer Archibald Butler. It was an act of retaliation after ...
– Aboriginal warrior who fought against British settlement but was captured, in what is now Perth, Western Australia
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth i ...
.
*White woman of Gippsland
The white woman of Gippsland, or the captive woman of Gippsland, was supposedly a European woman rumoured to have been held against her will by Aboriginal Kurnai people in the Gippsland region of Australia in the 1840s. Her supposed plight exci ...
– A European woman who was allegedly held captive by Aboriginals against her will in the 1840s, although her existence has been debated.
Places and structures
* Finke River – "Oldest river in the world", a claim that has been attributed to "scientists" by a generation of central Australian bus drivers and tour brochure writers. Parts of the Finke River are likely the oldest major river known in the world or among the oldest, as shown in scientific literature, but this does not apply to the southern part of the river. Neighboring, smaller rivers are just as old. * Franklin House – Historic house in Launceston that has had reports of ghost sightings.
* Gallipoli – the name of a peninsula in
* Franklin House – Historic house in Launceston that has had reports of ghost sightings.
* Gallipoli – the name of a peninsula in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, but also the name given to the Allied campaign
Campaign or The Campaign may refer to:
Types of campaigns
* Campaign, in agriculture, the period during which sugar beets are harvested and processed
*Advertising campaign, a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme
* Bl ...
on that peninsula during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. There were around 180,000 Allied casualties and 220,000 Turkish casualties. This campaign has become a "founding myth
An origin myth is a myth that describes the origin of some feature of the natural or social world. One type of origin myth is the creation or cosmogonic myth, a story that describes the creation of the world. However, many cultures have sto ...
" for both Australia and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, and ANZAC Day is still commemorated as a holiday in both countries. The idea that Australian soldiers were mowed down by Turkish gunfire following stupid decisions of the British commanding officers is part of the folklore, as is the escape from Gallipoli, where the ANZAC
The Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) was a First World War army corps of the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force. It was formed in Egypt in December 1914, and operated during the Gallipoli campaign. General William Birdwood comm ...
s used rifles rigged to fire by water dripped into a pan attached to the trigger to make it seem like there were still soldiers in the trenches as they were leaving. Another aspect of the ANZAC spirit
The Anzac spirit or Anzac legend is a concept which suggests that Australian and New Zealand soldiers possess shared characteristics, specifically the qualities those soldiers allegedly exemplified on the battlefields of World War I. These p ...
is the story of Simpson and his donkey.
* Gentle Annie – Name for selected especially steep sections of bush roads, difficult to climb in wet weather. The folk term may have arisen as early as in bullock team days, whether drawing wagons or timber jinkers.
* Gympie Pyramid – A small pyramid like structure in Gympie
Gympie ( ) is a city and a locality in the Gympie Region, Queensland, Australia. In the Wide Bay-Burnett District, Gympie is about north of the state capital, Brisbane. The city lies on the Mary River, which floods Gympie occasionally. The ...
, Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
(That has been mostly destroyed) that many believe to be a construction made by Chinese or Incan origin. Although researchers would more likely argue that it is a hoax.
*Monte Cristo Homestead
Monte Cristo Homestead is a historic homestead located in the town of Junee, New South Wales, Australia. Constructed by local pioneer Christopher William Crawley in 1885, it is a double-storey late- Victorian-style manor standing on a hill ov ...
– Historic estate in Junee, New South Wales
Junee () is a medium-sized town in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia. The town's prosperity and mixed services economy is based on a combination of agriculture, rail transport, light industry and government services, and in pa ...
, said to be the most Haunted property in Australia.
*Parkes Observatory
Parkes Observatory is a radio astronomy observatory, located north of the town of Parkes, New South Wales, Australia. It hosts Murriyang, the 64 m CSIRO Parkes Radio Telescope also known as "The Dish", along with two smaller radio telescopes. ...
– Landmark in New South Wales, responsible for helping NASA broadcast the moon landing
A Moon landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon. This includes both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was the Soviet Union's Luna 2, on 13 September 1959.
The United S ...
s to the world.
 *
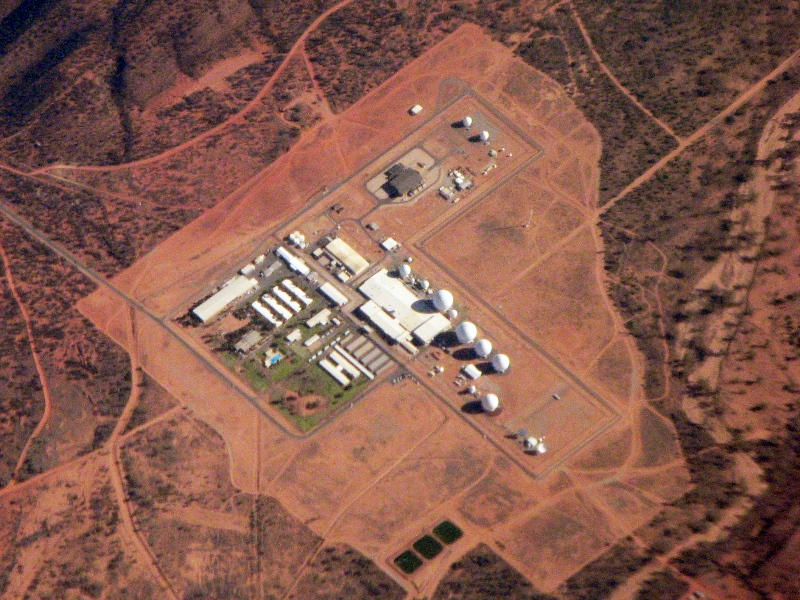
*Pine Gap
Pine Gap is a satellite surveillance base and Australian Earth station approximately south-west of the town of Alice Springs, Northern Territory in the center of Australia. It is jointly operated by Australia and the United States, and sinc ...
– A Government base in Central Australia run by both Australia and the United States. Similar to Area 51
Area 51 is the common name of a highly classified United States Air Force (USAF) facility within the Nevada Test and Training Range. A remote detachment administered by Edwards Air Force Base, the facility is officially called Homey Airport ...
.
*Port Arthur, Tasmania
Port Arthur is a town and former convict settlement on the Tasman Peninsula, in Tasmania, Australia. It is located approximately southeast of the state capital, Hobart.
The site forms part of the Australian Convict Sites, a World Heritag ...
– Former convict site, Has a complex and negative past, is said to haunted; But still a tourist attraction in Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, the site of Australia's biggest and most well known mass shootings, the Port Arthur Massacre (Australia)
The Port Arthur massacre was a mass shooting that occurred on 28 April 1996 at Port Arthur, a tourist town in the Australian state of Tasmania. The perpetrator, Martin Bryant, killed 35 people and wounded 23 others, the worst massacre in mod ...
.
* Princess Theatre Ghost sightings – One of the oldest theatres in Australia, it is said to be haunted after the death of a Frederick Federici.
*Shrine of Remembrance
The Shrine of Remembrance (commonly referred to as The Shrine) is a war memorial in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, located in Kings Domain on St Kilda Road. It was built to honour the men and women of Victoria who served in World War I, but ...
– War memorial in Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
built to honour the men and women of Victoria who served in World War I but later dedicated to all Australians who gave their lives in war.
* Sydney–Melbourne rivalry – there has been a long-standing rivalry, usually friendly yet sometimes heated, between the cities of Melbourne and Sydney, the two largest cities in Australia. It was this very rivalry that ultimately acted as the catalyst for the eventual founding of Canberra as the capital city of Australia.
 *
*Snowy River
The Snowy River is a major river in south-eastern Australia. It originates on the slopes of Mount Kosciuszko, Australia's highest mainland peak, draining the eastern slopes of the Snowy Mountains in New South Wales, before flowing through the ...
– immortalised in another Banjo Paterson poem, "The Man from Snowy River The Man from Snowy River may refer to:
* "The Man from Snowy River" (poem), an 1890 Australian poem by Banjo Paterson.
* '' The Man from Snowy River and Other Verses'' an 1895 poetry collection by Banjo Paterson (including the above)
* ''The Man ...
". The river has received much attention of late for now being nothing more than a trickle, and in fact has become a symbol for wider Australian interest in the health of its great rivers, particularly those in the Murray-Darling basin.
*Sovereign Hill
Sovereign Hill is an open-air museum in Golden Point, a suburb of Ballarat, Victoria, Australia. Sovereign Hill depicts Ballarat's first ten years after the discovery of gold there in 1851. It was officially opened on 29 November 1970 and has ...
– An Open-Air Museum
An open-air museum (or open air museum) is a museum that exhibits collections of buildings and artifacts out-of-doors. It is also frequently known as a museum of buildings or a folk museum.
Definition
Open air is “the unconfined atmosphere� ...
in Ballarat depicting an 1850s gold rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New ...
town.
* St James station tunnels – The tunnel is home to many urban legends including being a secret military bunker during World War II and a large bell that sounds like Big Ben.
*Sydney Harbour Bridge
The Sydney Harbour Bridge is a steel through arch bridge in Sydney, spanning Port Jackson, Sydney Harbour from the Sydney central business district, central business district (CBD) to the North Shore (Sydney), North Shore. The view of the bridg ...
& Sydney Opera House – Two of Australia's most famous national landmarks. Know to people worldwide and cementing Sydney as Australia's global city.
* The Great Barrier Reef – the only landmark in Australia (or Oceania) to be one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
*Uluru
Uluru (; pjt, Uluṟu ), also known as Ayers Rock ( ) and officially gazetted as UluruAyers Rock, is a large sandstone formation in the centre of Australia. It is in the southern part of the Northern Territory, southwest of Alice Spring ...
– Large sandstone rock formation in central Australia. Has great cultural significance to Aboriginal Australians and is one of Australia's most famous landmarks.
* Westall – biggest UFO sighting in Australian history, what actually was sighted remains a mystery to this day.
*Wiebbe Hayes Stone Fort
The Wiebbe Hayes Stone Fort on West Wallabi Island (also known as Wiebbe Hayes Island) is the oldest surviving European building in Australia and was built in 1629 by survivors of the shipwreck and massacre. West Wallabi Island is from the co ...
– Oldest European building in Australia, built in 1629 by survivors of the Batavia shipwreck in which a mutiny took place.
Socio-political events
*Australian constitutional crisis of 1975
The 1975 Australian constitutional crisis, also known simply as the Dismissal, culminated on 11 November 1975 with the dismissal from office of the prime minister, Gough Whitlam of the Australian Labor Party (ALP), by Governor-General Sir ...
– a real political crisis that has since taken on mythic proportions and elevated the protagonists to legendary status (depending on which side of the debate one takes). A visiting American politician at the time wryly observed that he was sure he had only heard the tip of the ice cube. Gough Whitlam
Edward Gough Whitlam (11 July 191621 October 2014) was the 21st prime minister of Australia, serving from 1972 to 1975. The longest-serving federal leader of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) from 1967 to 1977, he was notable for being the ...
's speech "Well may we say God save the Queen
"God Save the King" is the national and/or royal anthem of the United Kingdom, most of the Commonwealth realms, their territories, and the British Crown Dependencies. The author of the tune is unknown and it may originate in plainchant, bu ...
, because nothing will save the Governor General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy ...
" is replayed frequently.
 *
* Eureka stockade
The Eureka Rebellion was a series of events involving gold miners who revolted against the British administration of the colony of Victoria, Australia during the Victorian gold rush. It culminated in the Battle of the Eureka Stockade, which ...
– A miners' revolt in 1854 in Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
, Australia against the officials supervising the gold-mining region of Ballarat, in particular, the high prices of digging licenses. It is often regarded as the "Birth of Australian Democracy" and an event of equal significance to Australian history
The history of Australia is the story of the land and peoples of the continent of Australia.
Aboriginal Australians, People first arrived on the Australian mainland by sea from Maritime Southeast Asia between 50,000 and 65,000 years ago, and ...
as the storming of the Bastille
The Storming of the Bastille (french: Prise de la Bastille ) occurred in Paris, France, on 14 July 1789, when revolutionary insurgents stormed and seized control of the medieval armoury, fortress, and political prison known as the Bastille. At ...
was to French history
The first written records for the history of France appeared in the Iron Age. What is now France made up the bulk of the region known to the Romans as Gaul. The first writings on indigenous populations mainly start in the first century BC. Greek ...
, but almost equally often dismissed as being of little or no consequence.
* The Stolen Generation – From the late 1800s to the early 1970s, young Aboriginal people were forcibly removed from their families as children between the 1900s and the 1960s, to be brought up by white foster families or in institutions. In 1999 then-prime minister John Howard
John Winston Howard (born 26 July 1939) is an Australian former politician who served as the 25th prime minister of Australia from 1996 to 2007, holding office as leader of the Liberal Party. His eleven-year tenure as prime minister is the ...
avoided using the word "sorry", to the families. In 2008 Kevin Rudd
Kevin Michael Rudd (born 21 September 1957) is an Australian former politician and diplomat who served as the 26th prime minister of Australia from 2007 to 2010 and again from June 2013 to September 2013, holding office as the leader of the ...
made an official apology to the stolen generation and their families, on behalf of the Australian government.
* Tenterfield Oration – Speech given by Sir Henry Parkes
Sir Henry Parkes, (27 May 1815 – 27 April 1896) was a colonial Australian politician and longest non-consecutive Premier of the Colony of New South Wales, the present-day state of New South Wales in the Commonwealth of Australia. He has be ...
in 1889 calling for the six Australian colonies to be Federated, which would eventually lead to the Commonwealth of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
.
Sport
*2000 Sydney Olympics
The 2000 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXVII Olympiad and also known as Sydney 2000 (Dharug: ''Gadigal 2000''), the Millennium Olympic Games or the Games of the New Millennium, was an international multi-sport event held from ...
– Hailed as one of, if not the greatest Olympic games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a vari ...
of all time, It captured the imagination of an entire country and gave birth to many Australian sporting moments and icons including Cathy Freeman
Catherine Astrid Salome Freeman (born 16 February 1973) is an Aboriginal Australian former sprinter, who specialised in the 400 metres event. Her personal best of 48.63 seconds currently ranks her as the ninth-fastest woman of all time, set ...
, Grant Hackett
Grant George Hackett OAM (born 9 May 1980) is an Australian swimmer, most famous for winning the men's 1500 metres freestyle race at both the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney and the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens. This achievement has led him to ...
, Susie O'Neill & Ian Thorpe
Ian James Thorpe, (born 13 October 1982) is an Australian retired swimmer who specialised in freestyle, but also competed in backstroke and the individual medley. He has won five Olympic gold medals, the most won by any Australian along wit ...
.
*'' Australia II'' – A 12-metre class
The 12 Metre class is a rating class for racing sailboats that are designed to the International rule. It enables fair competition between boats that rate in the class whilst retaining the freedom to experiment with the details of their designs. ...
yacht
A yacht is a sailing or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, though the term generally applies to vessels with a cabin intended for overnight use. To be termed a , as opposed to a , such a pleasu ...
that was the first successful challenger for the America's Cup after 132 years. On the morning of the victory (Australian time) the then Australian Prime Minister, Bob Hawke, famously said that any employer who sacked any of their employees for not coming in that day was a "bum". The challenge also resulted in the popularisation of the boxing kangaroo
The boxing kangaroo is a national symbol of Australia, frequently seen in pop culture. The symbol is often displayed prominently by Australian spectators at sporting events, such as at cricket, tennis, basketball and football matches, and at t ...
representation.
 * Colliwobbles – The "colliwobbles" refers to the Collingwood Football Club's apparent penchant for losing grand finals over a 32-year period between 1958 and 1990. During this premiership drought, fans endured nine fruitless grand finals (1960, 1964, 1966, 1970, 1977 (drawn, then lost in a replay the following week), 1979, 1980, 1981). The term "Colliwobbles" was to enter the Victorian vocabulary to signify a choking phenomenon.
* The Invincibles – First
* Colliwobbles – The "colliwobbles" refers to the Collingwood Football Club's apparent penchant for losing grand finals over a 32-year period between 1958 and 1990. During this premiership drought, fans endured nine fruitless grand finals (1960, 1964, 1966, 1970, 1977 (drawn, then lost in a replay the following week), 1979, 1980, 1981). The term "Colliwobbles" was to enter the Victorian vocabulary to signify a choking phenomenon.
* The Invincibles – First Test match Test match in some sports refers to a sporting contest between national representative teams and may refer to:
* Test cricket
* Test match (indoor cricket)
* Test match (rugby union)
* Test match (rugby league)
* Test match (association football)
...
side to play an entire tour of England without losing, and is often considered to be one of the greatest cricket teams of all time.
* Kennett curse – A 5-year winning streak Geelong had over Hawthorn over comments made by then Hawthorn club President Jeff Kennett saying that Geelong does not have the mental drive to defeat Hawthorn. Most games were decided by ten points or less and are considered some of the best in recent memory.
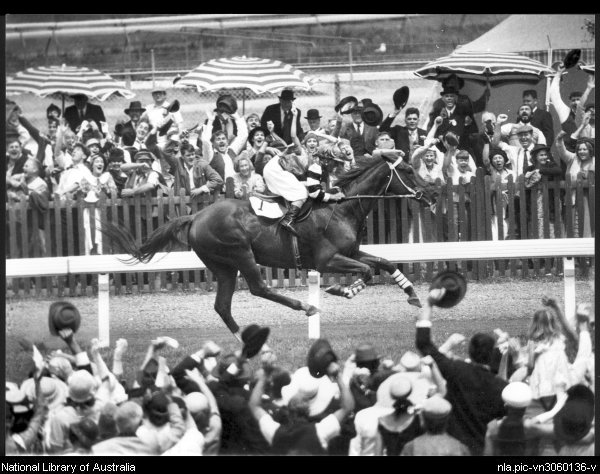
*Phar Lap
Phar Lap (4 October 1926 – 5 April 1932) was a champion New Zealand–bred Thoroughbred racehorse who is widely regarded as New Zealand's greatest racehorse ever. Achieving incredible success during his distinguished career, his initial u ...
– A thoroughbred
The Thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. Although the word ''thoroughbred'' is sometimes used to refer to any breed of purebred horse, it technically refers only to the Thoroughbred breed. Thoroughbreds are ...
horse who is considered by many to be the world's greatest racehorse, and is probably subject to more conspiracy theories than any other racehorse (in relation to the cause of his death). His name entered the Australian lexicon in the expression "to have a heart bigger than Phar Lap's", referring to someone's tenacity and courage. It is part of Australian folklore that Phar Lap's heart was physically twice the size of the average horse's heart.
*Super League war
The Super League war was a commercial competition between the Australian Rugby League (ARL) and the Australian Super League to establish pre-eminence in professional rugby league competition in Australia and New Zealand in the mid-1990s.
Super ...
– A dispute between the Packer and Murdoch families over control of the top-level Rugby League
Rugby league football, commonly known as just rugby league and sometimes football, footy, rugby or league, is a full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular field measuring 68 metres (75 yards) wide and 11 ...
competition in Australia in the mid-1990s.
* Steven Bradbury – An Australian short track speed skater who memorably won gold at the 2002 Winter Olympics at the 1,000 m short track, going from last to first after all other skaters were involved in a pile-up during the final metres. This led to the phrase 'doing a Bradbury', meaning to achieve something with the odds stacked against you.
Other
 * 5 o'clock wave – Supposedly a large wave, several metres in height and created by the daily release of dam overflow, that is said to travel downriver at high speed, and to reach the location at which the tale is being told at 5 o'clock each afternoon.
*
* 5 o'clock wave – Supposedly a large wave, several metres in height and created by the daily release of dam overflow, that is said to travel downriver at high speed, and to reach the location at which the tale is being told at 5 o'clock each afternoon.
*ANZAC spirit
The Anzac spirit or Anzac legend is a concept which suggests that Australian and New Zealand soldiers possess shared characteristics, specifically the qualities those soldiers allegedly exemplified on the battlefields of World War I. These p ...
– Idea shared by Australian & New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
soldiers during WW1
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
which has contributed to the "National Character" of both countries, and embodies the cultural idiom of Mateship
Mateship is an Australian cultural idiom that embodies equality, loyalty and friendship. Russel Ward, in ''The Australian Legend'' (1958), once saw the concept as central to the Australian people. ''Mateship'' derives from '' mate'', meaning ...
.
*Akubra
Akubra is an Australian hat manufacturer. The company is associated with bush hats made of rabbit fur felt with wide brims that are worn in rural Australia. The term "Akubra" is sometimes used to refer to any hat of this kind, however the compa ...
– Wide-brimmed hat made famous by outlaws and soldiers.
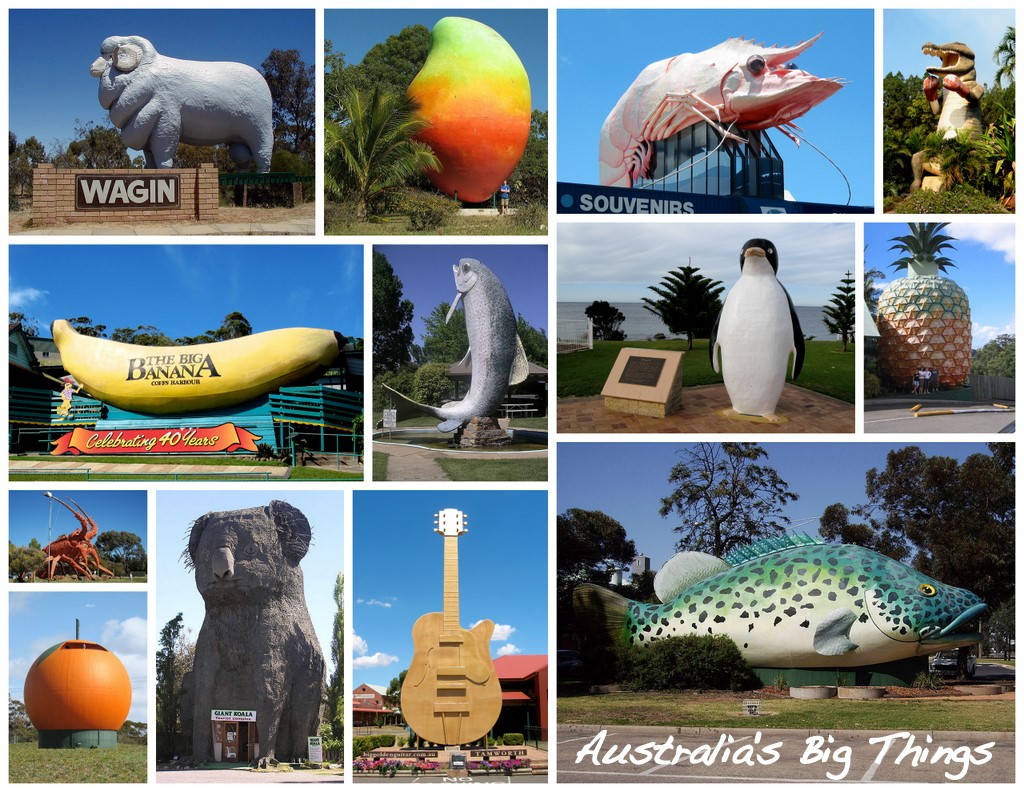
*Australia's Big Things, Big Things – Many Australian towns are known for their large and sometimes unusual structures or sculptures.
*Bass Strait Triangle – Similar to the Bermuda Triangle, the Bass Strait Triangle which lies between the states of Victoria, Australia, Victoria and Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
has been known to cause mysterious aviation and marine incidents, most notably the Disappearance of Frederick Valentich, Valentich Disappearance.
*Sinking of HMAS Sydney, Battle between HMAS Sydney and Kormoran – Suspicion, and even a cover-up, has been discussed regarding how the HMAS Sydney, warship was defeated by a modified merchant vessel like Kormoran.
*Drover (Australian), Drover – Australian livestock movers known for their hard work in the outback of Australia.
*Fisher's ghost – Popular early 19th century ghost story about a man who suddenly disappeared in Campbelltown, New South Wales, but his ghost can be seen sitting on a fence.
*Geelong Keys – A set of keys discovered in 1845 or 1846 by Governor Charles La Trobe at Corio Bay in Victoria, Australia which have led some people to believe they may have belonged to Theory of the Portuguese discovery of Australia, the Portuguese.
 *Kariong, New South Wales#Gosford glyphs, Gosford glyphs – Egyptian hieroglyphs that are carved into two parallel sandstone walls. Found in 1975 by a local surveyor, it is debated whether they are authentic or not.
*Frederick Bailey Deeming#Jack the Ripper theory, Jack the Ripper in Australia – Frederick Bailey Deeming an English born Australian man was once thought to have been the infamous Jack the Ripper living in Melbourne.
*Lasseter's Reef – A fabulously rich gold deposit said to have been discovered – and then subsequently lost – by bushman Lewis Hubert (Harold Bell) Lasseter, Harold Bell Lasseter in a remote and desolate corner of central Australia towards the end of the 19th century.
*Kariong, New South Wales#Gosford glyphs, Gosford glyphs – Egyptian hieroglyphs that are carved into two parallel sandstone walls. Found in 1975 by a local surveyor, it is debated whether they are authentic or not.
*Frederick Bailey Deeming#Jack the Ripper theory, Jack the Ripper in Australia – Frederick Bailey Deeming an English born Australian man was once thought to have been the infamous Jack the Ripper living in Melbourne.
*Lasseter's Reef – A fabulously rich gold deposit said to have been discovered – and then subsequently lost – by bushman Lewis Hubert (Harold Bell) Lasseter, Harold Bell Lasseter in a remote and desolate corner of central Australia towards the end of the 19th century.
 *Mahogany Ship – A supposed wrecked Portuguese caravel which is purported to lie beneath the sand approximately six miles west of Warrnambool in southwest Victoria, Australia.
*Marree Man – A large modern geoglyph, created using an agricultural plough, first noted by air in 1998 near Marree, South Australia, Marree in South Australia. The Marree Hotel publican and other locals restored the outline using a plough in August 2016 after it had all but disappeared into the sand.
*Min Min light – An unexplained light seen in central Australia.
*Mullumbimby#Stone arrangement, Mullumbimby Stonehenge – Ancient stone arrangement, which dates back to the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age. The location remains unknown to the Australian public due to fears of theft and further destruction.
*Nullarbor Nymph – A hoax and legend in 1971 and 1972 in Australia which grew from the supposed sighting of a half naked woman on the Nullarbor Plain living amongst some kangaroos.
*Rex Gilroy – One of Australia's most famous Cryptozoologists.
*The Speewah – A mythical Australian station that is the subject of many tall tales told by Australian bushmen.
*Swagman – Vagabond who travelled by foot to different locations looking for work carrying his belongings, seen as a folk hero in 19th-century Australia.
*Tamam Shud case – In 1948 an unidentified man was found dead at a Glenelg, South Australia, beach in Adelaide, South Australia. The case involves an encrypted message and is considered "one of Australia's most profound mysteries". The Cold case, case is unsolved and remains open to this day.
*Toyota Land Cruiser – 4WD Vehicle that was originally used to help build the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Scheme. Often considered to be Australia's Greatest off-road vehicle. Especially the 80 Series of the 1990s.
*Thomas Welsby Clark – Body of a Deceased man that was found at sea near the shores of Christmas Island, which is 1,550 kilometres from Australia's closest point, who was a sailor from only body found from sinking of ship with all hands on deck.
*Mahogany Ship – A supposed wrecked Portuguese caravel which is purported to lie beneath the sand approximately six miles west of Warrnambool in southwest Victoria, Australia.
*Marree Man – A large modern geoglyph, created using an agricultural plough, first noted by air in 1998 near Marree, South Australia, Marree in South Australia. The Marree Hotel publican and other locals restored the outline using a plough in August 2016 after it had all but disappeared into the sand.
*Min Min light – An unexplained light seen in central Australia.
*Mullumbimby#Stone arrangement, Mullumbimby Stonehenge – Ancient stone arrangement, which dates back to the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age. The location remains unknown to the Australian public due to fears of theft and further destruction.
*Nullarbor Nymph – A hoax and legend in 1971 and 1972 in Australia which grew from the supposed sighting of a half naked woman on the Nullarbor Plain living amongst some kangaroos.
*Rex Gilroy – One of Australia's most famous Cryptozoologists.
*The Speewah – A mythical Australian station that is the subject of many tall tales told by Australian bushmen.
*Swagman – Vagabond who travelled by foot to different locations looking for work carrying his belongings, seen as a folk hero in 19th-century Australia.
*Tamam Shud case – In 1948 an unidentified man was found dead at a Glenelg, South Australia, beach in Adelaide, South Australia. The case involves an encrypted message and is considered "one of Australia's most profound mysteries". The Cold case, case is unsolved and remains open to this day.
*Toyota Land Cruiser – 4WD Vehicle that was originally used to help build the Snowy Mountains Hydro-Electric Scheme. Often considered to be Australia's Greatest off-road vehicle. Especially the 80 Series of the 1990s.
*Thomas Welsby Clark – Body of a Deceased man that was found at sea near the shores of Christmas Island, which is 1,550 kilometres from Australia's closest point, who was a sailor from only body found from sinking of ship with all hands on deck.
See also
*Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology *Culture of Australia *History of Australia *Honest historyReferences
External links
{{Oceania topic, Folklore of Australian folklore, Folklore by country