Austin Chalk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
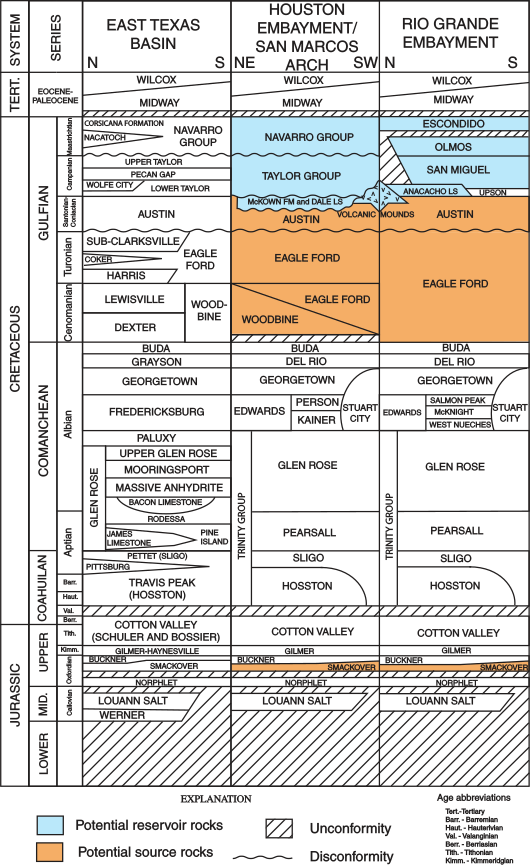 The Austin Chalk is an upper
The Austin Chalk is an upper
 The Austin Chalk is an upper
The Austin Chalk is an upper Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
geologic formation
Formation may refer to:
Linguistics
* Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes
* Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes
Mathematics and science
* Cave formation or speleothem, a secondar ...
in the Gulf Coast region of the United States. It is named after type section outcrops near Austin, Texas
Austin is the capital city of the U.S. state of Texas, as well as the seat and largest city of Travis County, with portions extending into Hays and Williamson counties. Incorporated on December 27, 1839, it is the 11th-most-populous city ...
. The formation is made up of chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
and marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part ...
.
Fossils
The putative galloanseran bird ''Austinornis lentus
''Austinornis'' is a genus of prehistoric birds related to Galliformes. It is known from a fossil partial tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed ...
'' has been found in the Austin Chalk.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. The general absence of dinosaurs is a reflection of the Austin limestone being marine in origin, primarily composed of microscopic shell fragments from floating sea organisms known as "coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the king ...
s" (the same organisms that contributed to the White Cliffs of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, depos ...
, on the south coast of England). Nevertheless, the Austin Chalk will occasionally produce fossils of larger creatures, such as ''Inoceramus
''Inoceramus'' (Greek: translation "strong pot") is an extinct genus of fossil marine pteriomorphian bivalves that superficially resembled the related winged pearly oysters of the extant genus '' Pteria''. They lived from the Early Jurassic to l ...
'' clams, ammonite cephalopods, and large marine vertebrates such as '' Xiphactinus'', a predaceous fish.
Geology
The rocks of the Austin Chalk consist of recrystallized, fossiliferous,interbedded
In geology, interbedding occurs when beds (layers of rock) of a particular lithology lie between or alternate with beds of a different lithology. For example, sedimentary rocks may be interbedded if there were sea level variations in their sedi ...
chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
s and marls
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part o ...
. Exposures of Austin Chalk are mainly seen in quarries, roadcuts, and stream beds where water eroded the soil. Austin Chalk outcrops can be seen throughout Dallas
Dallas () is the third largest city in Texas and the largest city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 million people. It is the largest city in and seat of Dallas County ...
, and extend south underneath I-35 down into Austin and San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_ ...
. Volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
layers are present in the Austin chalk, and dates obtained from radioactive minerals in these ash layers indicate they were deposited by wind from distant erupting volcanoes around 86 mya. These eruptions occurred along a 250-mile long by 50 mile wide belt of submarine volcanoes
Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ri ...
, which are located in present-day south-central Texas. This belt of volcanoes coincides with the trend of the Balcones Fault zone and is known as the Balcones volcanic province. Evidence of these ancient volcanoes is only visible in a few places as most were buried by the Austin and Taylor Group, and now are in the subsurface. The presence of this volcanism during deposition of the Austin Chalk is correlated with the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the ...
. Sea level rose for conditions to be right for the deposition of the Austin Chalk, which also coincides with the maximum extent of the Cretaceous Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea, ...
. The depths of the deposition of the Austin Chalk occurred in ~250 m or 820 ft of water, well-suited to the deposition of coccoliths.
See also
* Geology of the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex *List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations
This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils have been documented.
Containing body fossils
* List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils
** List of stratigraphic units with ...
* Orr Branch
Footnotes
References
* Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp. .External links
Cretaceous Arkansas Cretaceous geology of Texas Chalk Austin, Texas Limestone formations of the United States {{Texas-geologic-formation-stub