Augustus III on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was
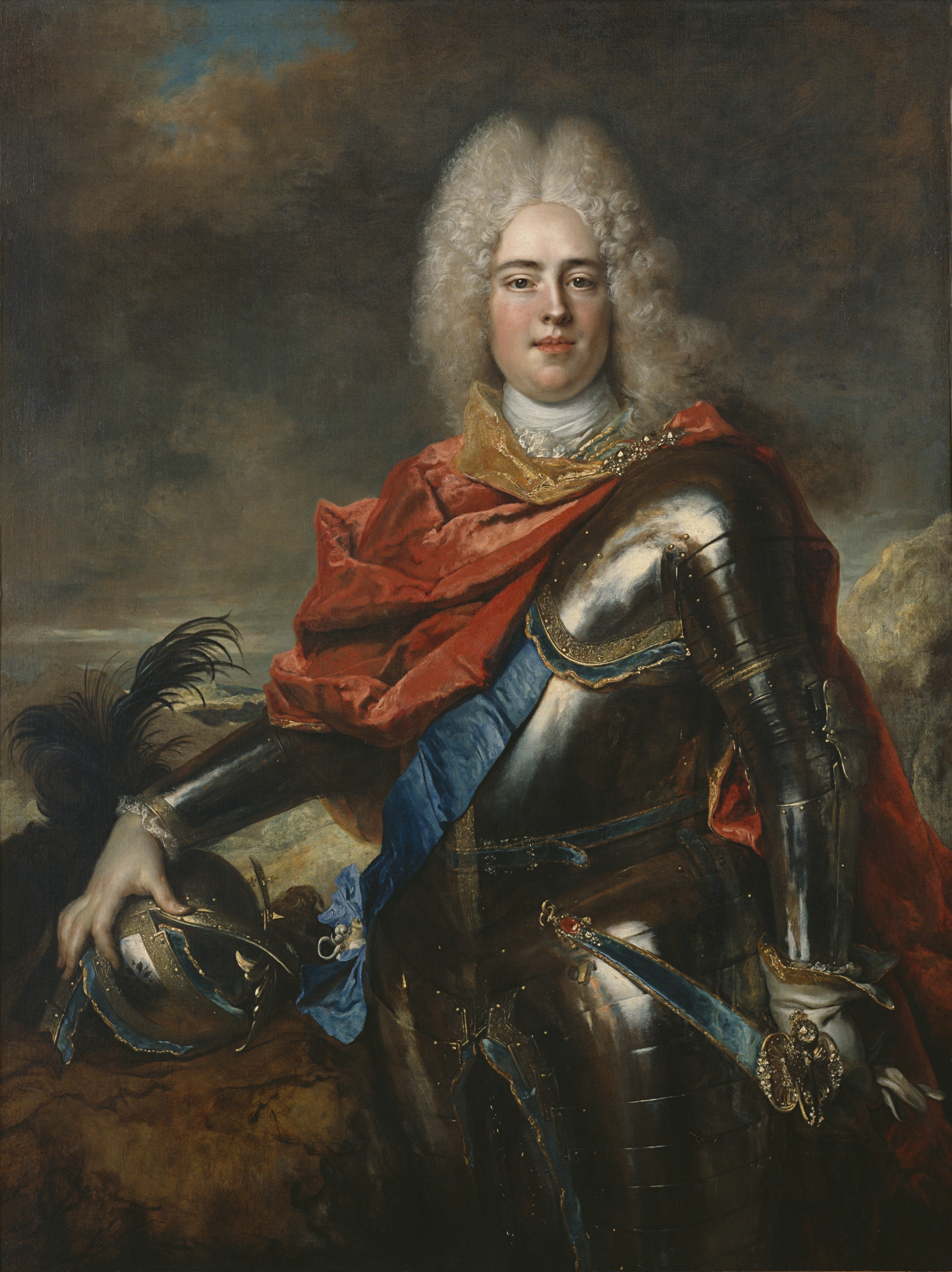

 From his early years, Augustus was groomed to succeed as king of Poland-Lithuania; best tutors were hired from across the continent and the prince studied Polish, German, French and Latin. He was taught Russian, but was unable to speak it fluently,Staszewski, '' Op. cit.'', p. 28 as well as
From his early years, Augustus was groomed to succeed as king of Poland-Lithuania; best tutors were hired from across the continent and the prince studied Polish, German, French and Latin. He was taught Russian, but was unable to speak it fluently,Staszewski, '' Op. cit.'', p. 28 as well as  On 26 September 1714, Augustus was warmly welcomed by
On 26 September 1714, Augustus was warmly welcomed by
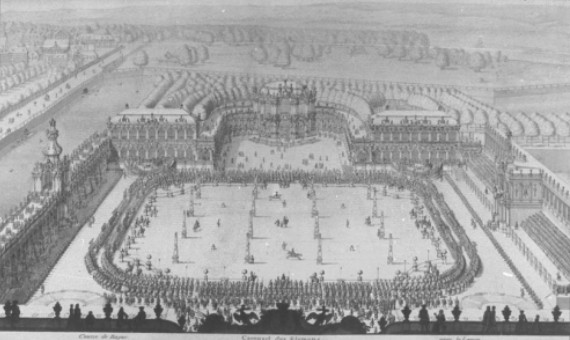 On 20 August 1719, Augustus married Maria Josepha of Austria in
On 20 August 1719, Augustus married Maria Josepha of Austria in  The wedding celebration in Dresden was one of the most splendorous and expensive of the Baroque era in Europe. Over 800 guests were invited for a 2-week celebration. The main banquet was held in a chamber that was transformed into an artificial silver mine to astound the invitees. Apart from exotic dishes, over 500 deer were brought in from the
The wedding celebration in Dresden was one of the most splendorous and expensive of the Baroque era in Europe. Over 800 guests were invited for a 2-week celebration. The main banquet was held in a chamber that was transformed into an artificial silver mine to astound the invitees. Apart from exotic dishes, over 500 deer were brought in from the
page 32–33
Austria received a promise that as king, Augustus would both renounce any claim to the Austrian succession and continue respecting the
page 286–288
 Augustus on his candidacy to the Polish throne was opposed by Stanisław I Leszczyński (Stanislaus I), who had usurped the throne with Swedish support during the
Augustus on his candidacy to the Polish throne was opposed by Stanisław I Leszczyński (Stanislaus I), who had usurped the throne with Swedish support during the
 As King, Augustus was uninterested in the affairs of his Polish–Lithuanian dominion, focusing instead on hunting, the opera, and the collection of artwork at the
As King, Augustus was uninterested in the affairs of his Polish–Lithuanian dominion, focusing instead on hunting, the opera, and the collection of artwork at the
 With the marriage to the Austrian princess Maria Josepha, Augustus was bound to accept the succession of her cousin,
With the marriage to the Austrian princess Maria Josepha, Augustus was bound to accept the succession of her cousin,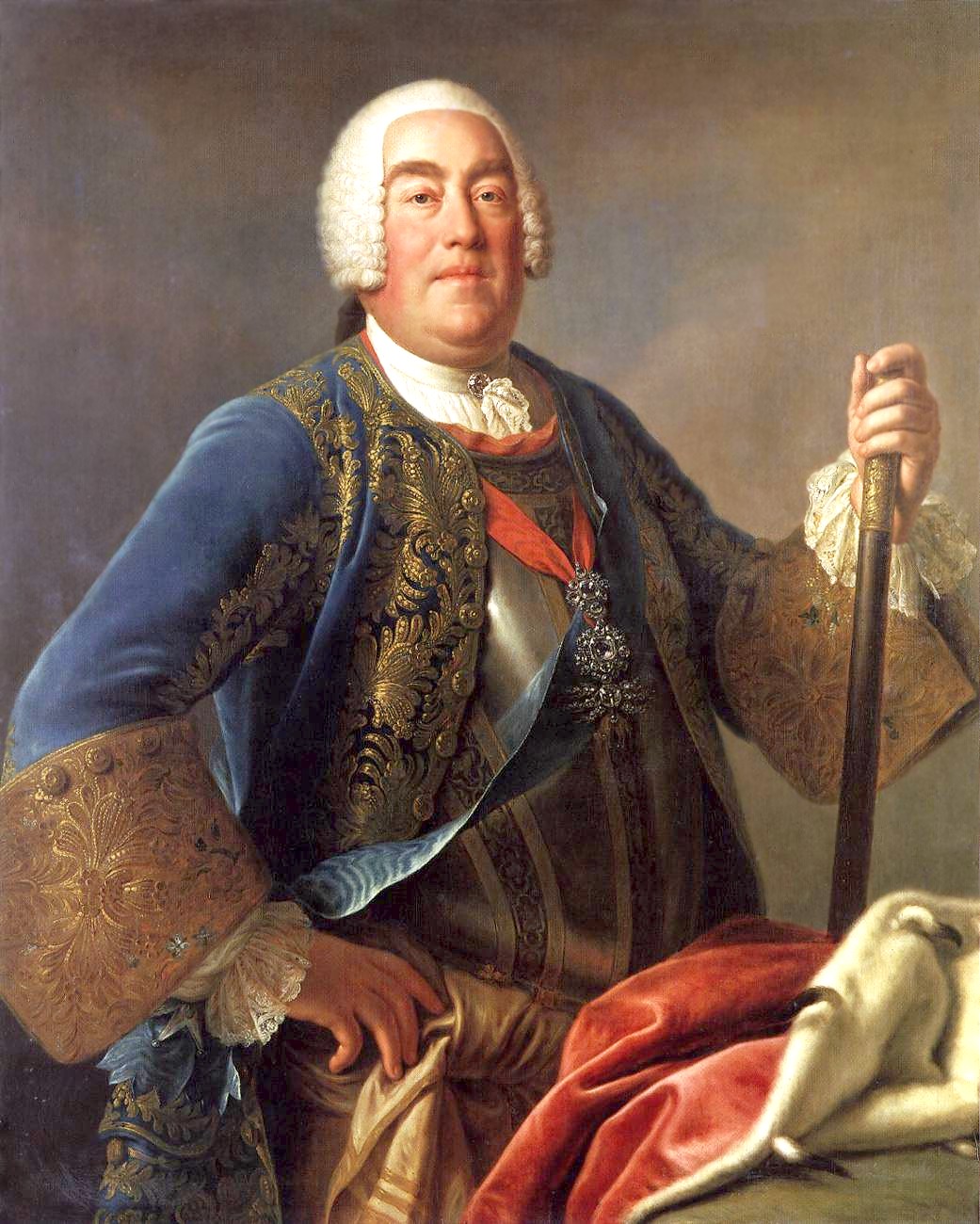  Saxony joined Austria in the Second Silesian War, which erupted after Prussia proclaimed to keep Charles VII as Holy Roman Emperor and invaded
Saxony joined Austria in the Second Silesian War, which erupted after Prussia proclaimed to keep Charles VII as Holy Roman Emperor and invaded
 Augustus III was a great patron of the arts and architecture. During his reign the
Augustus III was a great patron of the arts and architecture. During his reign the
 In 1732, a French priest named Gabriel Piotr Baudouin founded the first
In 1732, a French priest named Gabriel Piotr Baudouin founded the first
File:August III.jpg, Portrait of Crown Prince Augustus
File:August III the Saxon in Polish costume.PNG, Augustus III in Sarmatian costume, by Louis de Silvestre, ''c.''1737
File:Coat of arms of Augustus III of Poland as vicar of the Holy Roman Empire.svg, Coat of arms of Augustus III of Poland as vicar of the Holy Roman Empire
File:Polish Royal Banner of The House of Wettin.svg, Banner of Poland during the reign of Augustus III of Poland
File:POL JS Mock Wjazd Augusta III do Warszawy.jpg, ''Entry of Augustus III into Warsaw'' by Johann Samuel Mock
File:Köler Regalia of Augustus III and Maria Josepha.jpg, Crown Regalia of King Augustus and Maria Josepha
File:POLAND, DANZIG (GDANSK), AUGUSTUS III 1763 -6 GROSCHEN a - Flickr - woody1778a.jpg, 6 groschen, 1763
King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th ...
and Grand Duke of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Lithuania, which was established as an absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three ducal dynasties that managed to stay in power— Ho ...
from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
where he was known as Frederick Augustus II (german: link=no, Friedrich August II).
He was the only legitimate son of Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II; german: August der Starke; lt, Augustas II; in Saxony also known as Frederick Augustus I – Friedrich August I (12 May 16701 February 1733), most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as K ...
, and converted to Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
in 1712 to secure his candidacy for the Polish throne. In 1719 he married Maria Josepha, daughter of Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor, and became Elector of Saxony following his father's death in 1733. Augustus was able to gain the support of Charles VI by agreeing to the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713
The Pragmatic Sanction ( la, Sanctio Pragmatica, german: Pragmatische Sanktion) was an edict issued by Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, on 19 April 1713 to ensure that the Habsburg hereditary possessions, which included the Archduchy of Austria ...
and also gained recognition from Russian Empress Anna
Anna may refer to:
People Surname and given name
* Anna (name)
Mononym
* Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke
* Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773)
* Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century)
* Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 1221) ...
by supporting Russia's claim to the region of Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia ...
. He was elected king of Poland by a small minority on 5 October 1733 and subsequently banished the former Polish king Stanisław I. He was crowned in Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
on 17 January 1734.
Augustus was supportive of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
against Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
in the War of the Austrian Succession (1742) and again in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
(1756), both of which resulted in Saxony being defeated and occupied by Prussia. In Poland, his rule was marked by the increasing influence of the Czartoryski and Poniatowski families, and by the intervention of Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anha ...
in Polish affairs. His rule deepened the social anarchy in Poland and increased the country's dependence on its neighbours, notably Prussia, Austria, and Russia. The Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
prevented him from installing his family on the Polish throne, supporting instead the aristocrat Stanisław August Poniatowski
Stanisław II August (born Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski; 17 January 1732 – 12 February 1798), known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarc ...
, the lover of Catherine the Great. Throughout his reign, Augustus was known to be more interested in ease and pleasure than in the affairs of state; this notable patron of the arts left the administration of Saxony and Poland to his chief adviser, Heinrich von Brühl
Heinrich, count von Brühl ( pl, Henryk Brühl, 13 August 170028 October 1763), was a Polish-Saxon statesman at the court of Saxony and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and a member of the powerful German von Brühl family. The incumbency ...
, who in turn left Polish administration chiefly to the powerful Czartoryski family.
Royal titles
Royal titles in la , Augustus tertius, Dei gratia rex Poloniae, magnus dux Lithuaniæ, Russiæ, Prussiæ, Masoviæ, Samogitiæ, Kijoviæ, Volhiniæ, Podoliæ, Podlachiæ, Livoniæ, Smolensciæ, Severiæ, Czerniechoviæque, nec non-hæreditarius dux Saxoniæ et princeps elector etc. English translation: ''August III, by the grace of God, King ofPoland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Grand Duke of Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Ruthenia
Ruthenia or , uk, Рутенія, translit=Rutenia or uk, Русь, translit=Rus, label=none, pl, Ruś, be, Рутэнія, Русь, russian: Рутения, Русь is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin as one of several terms ...
, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
, Masovia, Samogitia, Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
, Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
, Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-centra ...
, Podlachia, Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
, Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ...
, Severia
Severia or Siveria ( orv, Сѣверія, russian: Северщина, translit=Severshchina, uk, Сіверія or , translit. ''Siveria'' or ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, eastern ...
, Chernihiv
Chernihiv ( uk, Черні́гів, , russian: Черни́гов, ; pl, Czernihów, ; la, Czernihovia), is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within ...
, and also hereditary Duke of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a ...
and Prince-Elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the princ ...
, etc.''
Biography

Early life and education
Augustus was born 17 October 1696 inDresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
, the only legitimate son of Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II; german: August der Starke; lt, Augustas II; in Saxony also known as Frederick Augustus I – Friedrich August I (12 May 16701 February 1733), most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as K ...
, Prince-Elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the princ ...
of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a ...
and ruler of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
who belonged to the Albertine line of the House of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its ori ...
. His mother was Christiane Eberhardine of Brandenburg-Bayreuth
Christiane Eberhardine of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (19 December 1671 – 4 September 1727) was Electress of Saxony from 1694 to 1727 (her death) and Queen Consort of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1697 to 1727 by marriage to Augustus I ...
, daughter of Christian Ernst, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth. Unlike his father, Christiane remained a fervent Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
throughout her life and never set foot in Catholic Poland during her 30-year service as queen consort. Despite the pressure from Augustus II, she was never crowned at Wawel in Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
and purely held a titular title of queen.Clarissa Campbell Orr: Queenship in Europe 1660–1815: The Role of the Consort. Cambridge University Press (2004) This move was viewed by the Polish nobility as a provocation and from the beginning the prince was treated with prejudice
Prejudice can be an affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classification of another person based on that person's per ...
in Poland.
 From his early years, Augustus was groomed to succeed as king of Poland-Lithuania; best tutors were hired from across the continent and the prince studied Polish, German, French and Latin. He was taught Russian, but was unable to speak it fluently,Staszewski, '' Op. cit.'', p. 28 as well as
From his early years, Augustus was groomed to succeed as king of Poland-Lithuania; best tutors were hired from across the continent and the prince studied Polish, German, French and Latin. He was taught Russian, but was unable to speak it fluently,Staszewski, '' Op. cit.'', p. 28 as well as exact sciences
The exact sciences, sometimes called the exact mathematical sciences, are those sciences "which admit of absolute precision in their results"; especially the mathematical sciences. Examples of the exact sciences are mathematics, optics, astron ...
including mathematics, chemistry and geography. He also practiced equestrianism
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, driving, and vaulting. This broad description includes the ...
in his youth. While his father spent time in Poland, the young Augustus was left in the care of his grandmother, Princess Anna Sophie of Denmark, who initially raised him Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
. This was particularly unfavourable for the Poles, who wouldn't accept or tolerate a Protestant monarch. As a consequence, troubled Augustus II organized a tour of Catholic countries in Europe for his son which he hoped would bring him closer to Catholicism and break the bond between him and his controlling grandmother. In Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, the Polish entourage thwarted a kidnapping attempt organized by British agents of Queen Anne in order to prevent him from converting. He also witnessed the coronation of Charles VI in 1711 after the death of his brother and predecessor, Joseph I.
Augustus eventually converted to Roman Catholicism in November 1712 while extensively touring Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and its cultural and religious heritage. He was then under the supervision of the Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
, who certainly contributed to the cause. The public announcement of conversion in 1717 triggered discontent among the Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
Saxon aristocracy... Faced with a hereditary Catholic succession for Saxony, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
and Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
attempted to oust Saxony from the directorship of the Protestant body in the Reichstag of the Holy Roman Empire, but Saxony managed to retain the directorship.
 On 26 September 1714, Augustus was warmly welcomed by
On 26 September 1714, Augustus was warmly welcomed by Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of ...
at Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
. Louis rejoiced when he heard that Augustus converted to Catholicism and permitted him to stay at the royal court and in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
. The young prince participated in balls, masquerades and private parties that were hosted by the Sun King himself. During this time, Augustus improved his knowledge of the French language and learnt how to approach politics and diplomacy. In June 1715, he departed Versailles and travelled across France, visiting Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectu ...
, Moissac, Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and fr ...
, Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the Aud ...
, Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Fra ...
and Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of ...
. Apart from sightseeing, the purpose of this trip was to understand how cities and villages function. Being brought up in great wealth, Augustus was not entirely aware of how extensive poverty and poor living conditions can be in the countryside.
Marriage and wedding
 On 20 August 1719, Augustus married Maria Josepha of Austria in
On 20 August 1719, Augustus married Maria Josepha of Austria in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
. She was the daughter of the deceased Emperor Joseph I and niece of Charles VI of the Holy Roman Empire, whose coronation young Augustus attended. This marriage wasn't coincidental; Augustus II the Strong orchestrated it to maintain the might of the Saxons within the Holy Roman Empire. The alliance with Catholic Charles would prove fruitful in case of hostile or armed opposition from the Protestant states within the Empire. Ten days earlier, on 10 August 1719, Maria Josepha was forced to renounce her claim to the throne of Austria in favour of her uncle's daughter, Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position '' suo jure'' (in her own right) ...
. In accordance with the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713
The Pragmatic Sanction ( la, Sanctio Pragmatica, german: Pragmatische Sanktion) was an edict issued by Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, on 19 April 1713 to ensure that the Habsburg hereditary possessions, which included the Archduchy of Austria ...
issued by Charles, a female heir or the eldest daughter would be permitted to inherit the throne of Austria. Augustus II also hoped to place Saxony in a better position should there arise a war of succession to the Austrian territories.
Białowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest; lt, Baltvyžių giria; pl, Puszcza Białowieska ; russian: Беловежская пуща, Belovezhskaya Pushcha is a forest on the border between Belarus and Poland. It is one of the last and largest remaining pa ...
for the feast. Approximately 4 million thaler
A thaler (; also taler, from german: Taler) is one of the large silver coins minted in the states and territories of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy during the Early Modern period. A ''thaler'' size silver coin has a diameter o ...
s were spent for this occasion.
Succession
Augustus II died suddenly on 1 February 1733, following aSejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
(Polish parliament) session in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
. Augustus III inherited the Saxon electorate without any problems, but his election to the Polish throne was much more complicated. Shortly before the ailing king died, Prussia, Austria and Russia signed a pact known as the Treaty of the Three Black Eagles, which would prevent Augustus III and Stanisław Leszczyński from inheriting the Polish throne. The royal elections in Poland
Royal elections in Poland ( Polish: ''wolna elekcja'', lit. ''free election'') were the elections of individual kings, rather than dynasties, to the Polish throne. Based on traditions dating to the very beginning of the Polish statehood, strengt ...
and the elective monarchy, in general, weakened the country and allowed other powers to meddle in Polish affairs. The neighbouring countries that signed the treaty preferred a neutral monarch like Infante Manuel, Count of Ourém, brother of John V of Portugal
Dom John V ( pt, João Francisco António José Bento Bernardo; 22 October 1689 – 31 July 1750), known as the Magnanimous (''o Magnânimo'') and the Portuguese Sun King (''o Rei-Sol Português''), was King of Portugal from 9 December 17 ...
, or any living relative of the Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branch ...
. The agreement had provisions for all three powers to agree that it was in their best interest that their common neighbour, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, did not undertake any reforms that might strengthen it and trigger expansionism. The new king would also have to maintain friendly relations with these countries.
The treaty quickly became ineffective as Prussia began to support Leszczyński and allowed him safe passage from France to Poland through German lands. As a result, Austria and Russia signed on 19 August 1733 the Löwenwolde's Treaty, named after Karl Gustav von Löwenwolde. The terms of Löwenwolde's Treaty were direct; Russia opted for a ''quid pro quo
Quid pro quo ('what for what' in Latin) is a Latin phrase used in English to mean an exchange of goods or services, in which one transfer is contingent upon the other; "a favor for a favor". Phrases with similar meanings include: "give and take", ...
'' – they would provide troops to ensure Augustus III is elected king and in turn, Augustus would recognise Anna Ivanovna as Empress of Russia
The emperor or empress of all the Russias or All Russia, ''Imperator Vserossiyskiy'', ''Imperatritsa Vserossiyskaya'' (often titled Tsar or Tsarina/Tsaritsa) was the monarch of the Russian Empire.
The title originated in connection with Russia' ...
, thus relinquishing Polish claims to Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
and Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia ...
.Ragsdale, Hugh (1993) ''Imperial Russian foreign policy'' Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Englandpage 32–33
Austria received a promise that as king, Augustus would both renounce any claim to the Austrian succession and continue respecting the
Pragmatic Sanction of 1713
The Pragmatic Sanction ( la, Sanctio Pragmatica, german: Pragmatische Sanktion) was an edict issued by Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, on 19 April 1713 to ensure that the Habsburg hereditary possessions, which included the Archduchy of Austria ...
.Corwin, Edward Henry Lewinski (1917) ''The political History of Poland'' Polish Book Importing Company, New Yorkpage 286–288
War of the Polish Succession
 Augustus on his candidacy to the Polish throne was opposed by Stanisław I Leszczyński (Stanislaus I), who had usurped the throne with Swedish support during the
Augustus on his candidacy to the Polish throne was opposed by Stanisław I Leszczyński (Stanislaus I), who had usurped the throne with Swedish support during the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swe ...
. Reigning from 1706 until 1709, Stanisław was overthrown after the Swedish defeat at Poltava. Returning from exile in 1733 with the support of Louis XV of France
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
and Spain, Stanisław sparked the War of the Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession ( pl, Wojna o sukcesję polską; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of thei ...
.
Throughout the spring and summer of 1733, France began mobilizing and stationing forces along its northern and eastern borders, while Austria massed troops on the Polish frontier, reducing garrisons in the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
for the purpose. Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene Francis of Savoy–Carignano, (18 October 1663 – 21 April 1736) better known as Prince Eugene, was a field marshal in the army of the Holy Roman Empire and of the Austrian Habsburg dynasty during the 17th and 18th centuries. He ...
recommended to the emperor a more warlike posture against its longtime rival, France. He suggested that the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
valley and northern Italy should be strengthened with more troops, however only minimal steps were taken to improve imperial defences on the Rhine. In July 1733, Augustus agreed to Austria's and Russia's terms per Löwenwolde's Treaty. During the election sejm
Royal elections in Poland (Polish: ''wolna elekcja'', lit. ''free election'') were the elections of individual kings, rather than dynasties, to the Polish throne. Based on traditions dating to the very beginning of the Polish statehood, strengthe ...
in August, Russian troops counting 30,000 men under the command of Peter Lacy entered Poland to secure Augustus' succession. The election was ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legall ...
'' won by Stanisław, with 12,000 votes. Augustus received 3,000, however, he had the support of Poland's influential, wealthiest and most corrupt magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s, such as Michael Servacy Wiśniowiecki.
The Franco-Spanish coalition declared war on Austria and Saxony on 10 October. The Italian states of Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Sa ...
-Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
and Parma
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second m ...
also joined the struggle against Austrian rule in northern Italy. Most of the battles took place outside of Poland and the main focus of the war was personal interests and demonstration of superiority. The Russian-Saxon forces chased Stanisław until he was besieged at Gdańsk (Danzig) on 22 February 1734. In June, when the garrisons at Gdańsk surrendered, Stanisław fled to Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was ...
and then back to France. The Pacification Sejm in 1736 ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' confirmed Augustus III as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania.
To this day, the aphorism and phrase ''od Sasa do Lasa'' (lit. from the Saxon to Leszczyński) exists in the Polish language and is used when describing two completely opposite things in everyday life.
Reign and diplomacy
Poland
 As King, Augustus was uninterested in the affairs of his Polish–Lithuanian dominion, focusing instead on hunting, the opera, and the collection of artwork at the
As King, Augustus was uninterested in the affairs of his Polish–Lithuanian dominion, focusing instead on hunting, the opera, and the collection of artwork at the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister
The Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister (, ''Old Masters Gallery'') in Dresden, Germany, displays around 750 paintings from the 15th to the 18th centuries. It includes major Italian Renaissance works as well as Dutch and Flemish paintings. Outstand ...
. He spent less than three years of his thirty-year reign in Poland, where political feuding between the House of Czartoryski and the Potocki
The House of Potocki (; plural: Potoccy, male: Potocki, feminine: Potocka) was a prominent Polish noble family in the Kingdom of Poland and magnates of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, forma ...
paralyzed the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
( Liberum veto), fostering internal political anarchy and weakening the Commonwealth. Augustus delegated most of his powers and responsibilities in the Commonwealth to Heinrich von Brühl
Heinrich, count von Brühl ( pl, Henryk Brühl, 13 August 170028 October 1763), was a Polish-Saxon statesman at the court of Saxony and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and a member of the powerful German von Brühl family. The incumbency ...
, who served in effect as the viceroy of Poland. Brühl in turn left the politics in Poland to the most powerful magnates and nobles, which resulted in widespread corruption. Under Augustus, Poland was not involved in any major conflicts which further lessened its position in Europe and allowed the neighbouring countries to take advantage of the disorder. Any opposition was violently crushed by Brühl, who used either Saxon or Russian forces that permanently stationed in the country.
Brühl was a skillful diplomat and strategist; Augustus could only be reached through him if an important political feud arose. He was also the head of the Saxon court in Dresden and was fond of collectibles, such as gadgets, jewellery and Meissen porcelain, the most famous being the Swan Service
The Swan Service ( German: ''Schwanenservice'', pl, Serwis łabędzi) is a large service of baroque Meissen porcelain which was made for the First Minister of the Electorate of Saxony and favourite of king Augustus III of Poland, Heinrich von Br� ...
composed of 2,200 individual pieces made between 1737 and 1741. It has been described as possibly "the finest table service ever produced" and part of it are exhibited at the National Museum in Warsaw. He also owned the largest collections of watches, vests, wigs and hats in Europe, though this cannot be accurately assessed. Brühl was depicted by his rivals as a nouveau-riche
''Nouveau riche'' (; ) is a term used, usually in a derogatory way, to describe those whose wealth has been acquired within their own generation, rather than by familial inheritance. The equivalent English term is the "new rich" or "new money" ( ...
materialist, who used his wealth to gain support. His lavish spending was immortalized by Augustus' reported question to the viceroy "Brühl, do I have money?"
By 1748 Augustus III completed extending the Saxon Palace in Warsaw and made significant contributions in remodelling the Royal Castle. In 1750, von Brühl purchased a residence adjacent to the larger Saxon Palace and transformed it into a rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
masterpiece, which later became known as the Brühl Palace. Both buildings were completely destroyed by the Nazis during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
War of the Austrian Succession
 With the marriage to the Austrian princess Maria Josepha, Augustus was bound to accept the succession of her cousin,
With the marriage to the Austrian princess Maria Josepha, Augustus was bound to accept the succession of her cousin, Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position '' suo jure'' (in her own right) ...
, as Holy Roman Empress. Saxony mediated between the friendly French faction and the Habsburg faction of Maria Theresa. Between 1741 and 1742 Saxony was allied with France, but changed sides with the help of Austrian diplomats.
In the first days of December 1740, the Prussians assembled along the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river and on 16 December, Frederick invaded Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
without a formal declaration of war. The Austrian troops which then stationed in Silesia were poorly supplied and outnumbered as the Habsburgs concentrated their supreme force on Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
and Italy. They held onto the fortresses of Glogau, Breslau, and Brieg, but abandoned the rest of the region and withdrew into Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The ...
. This campaign gave Prussia control of most of the richest provinces in the Habsburg Empire, with the commercial centre of Breslau as well as mining, weaving and dyeing industries. Silesia was also rich in natural resources such as coal, chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
and gold.
 Saxony joined Austria in the Second Silesian War, which erupted after Prussia proclaimed to keep Charles VII as Holy Roman Emperor and invaded
Saxony joined Austria in the Second Silesian War, which erupted after Prussia proclaimed to keep Charles VII as Holy Roman Emperor and invaded Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
on 15 August 1744. The true cause behind the invasion was Frederick's personal expansionist
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who ...
ideas and goals. On 8 January 1745, the Treaty of Warsaw united Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
, the Habsburg Monarchy, the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
and Saxony into what became known as the "Quadruple Alliance", which was aimed at securing the Austrian throne for Maria Theresa. Soon-after Charles VII died of gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intens ...
in Munich, which weakened the Prussians. However, Prussia still maintained military superiority; the successful battles of Hennersdorf and Kesselsdorf
Kesselsdorf is a village in Saxony, Germany, part of the town of Wilsdruff. It is located close to the Saxon capital city of Dresden.
The village is known for the decisive Battle of Kesseldorf between Austrians and Prussians on December 15, 17 ...
opened the way to Dresden, which Frederick occupied on 18 December. The Treaty of Dresden was eventually completed on Christmas Day (25 December) and Saxony was obliged to pay one million rixdollar Rixdollar is the English term for silver coinage used throughout the European continent (german: Reichsthaler, nl, rijksdaalder, da, rigsdaler, sv, riksdaler).
The same term was also used of currency in Cape Colony and Ceylon. However, the R ...
s in reparations to the Prussian state. The treaty ended the Second Silesian War with a ''status quo ante bellum
The term ''status quo ante bellum'' is a Latin phrase meaning "the situation as it existed before the war".
The term was originally used in treaties to refer to the withdrawal of enemy troops and the restoration of prewar leadership. When use ...
''.
Maria Theresa was finally recognized as Empress with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748, which proved a Pyrrhic victory
A Pyrrhic victory ( ) is a victory that inflicts such a devastating toll on the victor that it is tantamount to defeat. Such a victory negates any true sense of achievement or damages long-term progress.
The phrase originates from a quote from ...
for Augustus III, however, the conflict nearly bankrupted Saxony. Meanwhile, the affairs in Poland remained highly neglected.
Seven Years' War
TheElectorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.
In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charle ...
was involved in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754 ...
from 1756 to 1763. The Saxons were allied with Austria and Russia against Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
of Prussia, who saw Saxony as another potential field for expansion. Saxony was then merely a buffer zone between Prussia and Austrian Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
as well as Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
, which Frederick attempted to annex in their entirety. Moreover, Saxony and Poland were separated by a strip of land in Silesia and Lusatia
Lusatia (german: Lausitz, pl, Łużyce, hsb, Łužica, dsb, Łužyca, cs, Lužice, la, Lusatia, rarely also referred to as Sorbia) is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr ...
which made the movement of troops even more difficult. Frederick's plans also entailed annexing Duchy of Hanover, but joining France would trigger an Austro-Russian attack and occupation. On 29 August 1756, the Prussian army preemptively invaded Saxony, beginning the Third Silesian War
The Third Silesian War () was a war between Prussia and Austria (together with its allies) that lasted from 1756 to 1763 and confirmed Prussia's control of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland). The war was fought mainly in Silesi ...
, a theatre of the Seven Years' War. Saxony was bled dry and exploited at the maximum extent to support Prussia's war effort. The Treaty of Hubertusburg signed on 15 February 1763 ended the conflict with Frederick's victory and Saxony renounced its claim to Silesia.
Death
In April 1763, Augustus returned ill and frail from Poland to Dresden with his closest advisors, leaving PrimateWładysław Aleksander Łubieński
Władysław Aleksander Łubieński (1703–1767) was archbishop of Lwów (1758–59) and primate of Poland (1759–1767). He was an ally of the Czartoryski Familia and of the Russian Empire and an opponent of religious tolerance. He acted as Int ...
behind to take care of the affairs in the Commonwealth. He died suddenly on 5 October 1763 in Dresden from apoplexy
Apoplexy () is rupture of an internal organ and the accompanying symptoms. The term formerly referred to what is now called a stroke. Nowadays, health care professionals do not use the term, but instead specify the anatomic location of the bleedi ...
(stroke). Unlike his father who rests at Wawel in Kraków, Augustus III was buried at Dresden Cathedral and remains one of the few Polish monarchs who were buried outside of Poland.
Augustus's eldest surviving son, Frederick Christian of Saxony
Frederick Christian (german: Friedrich Christian; 5 September 1722 – 17 December 1763) was the Prince-Elector of Saxony for fewer than three months in 1763. He was a member of the House of Wettin. He was the third but eldest surviving son of ...
, succeeded his father as Elector but died two and a half months later.
In the Commonwealth, on September 7, 1764, with the small participation of the szlachta initiated by the Czartoryski's and the strong support of Russia, Stanisław August Poniatowski
Stanisław II August (born Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski; 17 January 1732 – 12 February 1798), known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarc ...
was elected king of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. Reigning under the name Stanisław II Augustus, Poniatowski was the son of the elder Stanisław Poniatowski, a powerful Polish noble and a onetime agent of Stanisław I; in youth he was a lover of Catherine II of Russia
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anha ...
and as such enjoyed strong support from that Empress's court.
Legacy
Patron of arts
 Augustus III was a great patron of the arts and architecture. During his reign the
Augustus III was a great patron of the arts and architecture. During his reign the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
Catholic Church of the Royal Court in Dresden (present-day Dresden Cathedral) was built, in which he was later buried as one of the few Polish kings buried outside the Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral ( pl, Katedra Wawelska), formally titled the Royal Archcathedral Basilica of Saints Stanislaus and Wenceslaus, is a Roman Catholic cathedral situated on Wawel Hill in Kraków, Poland. Nearly 1000 years old, it is part of the ...
in Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
. He greatly expanded the Dresden art gallery, to the extent that in 1747 it was placed in a new location at the present-day Johanneum, where it remained until 1855 when it was moved to the newly built Semper Gallery. In 1748 he founded the Opera House (''Operalnia'') in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
and the ''Collegium medico-chirurgicum'', the first medical school in Dresden. During his reign, the extension of the Saxon Palace in Warsaw, begun by his father Augustus II, was completed, and the reconstruction of the eastern façade of the Royal Castle was ordered, thus creating the so-called Saxon Facade, an iconic part of the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
panorama of the Warsaw Old Town
Warsaw Old Town ( pl, Stare Miasto, italic=yes and colloquially as ''Starówka'') is the oldest part of Warsaw, the capital city of Poland. It is bounded by the ''Wybrzeże Gdańskie'' (Gdańsk Boulevards), along with the bank of the Vistula riv ...
.
In 1733, the composer Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the '' Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard wo ...
dedicated the Kyrie–Gloria Mass in B minor, (early version), to Augustus in honor of his succession to the Saxon electorate, with the hope of appointment as Court Composer, a title Bach received three years later. Bach's title of ''Koeniglicher Pohlnischer Hoff Compositeur'' (''Royal Polish Court Composer'', and court composer to the Elector of Saxony) is engraved on the title page of Bach's famous Goldberg Variations. Augustus III was also the patron of composer Johann Adolph Hasse
Johann Adolph Hasse (baptised 25 March 1699 – 16 December 1783) was an 18th-century German composer, singer and teacher of music. Immensely popular in his time, Hasse was best known for his prolific operatic output, though he also composed a co ...
, who was granted the title of the Royal-Polish and Electoral-Saxon Kapellmeister
(, also , ) from German ''Kapelle'' (chapel) and ''Meister'' (master)'','' literally "master of the chapel choir" designates the leader of an ensemble of musicians. Originally used to refer to somebody in charge of music in a chapel, the term ha ...
by his father, Augustus II, in 1731, and thanks to Augustus III the same title was obtained in 1716 by composer Johann David Heinichen
Johann David Heinichen (17 April 1683 – 16 July 1729) was a German Baroque composer and music theorist who brought the musical genius of Venice to the court of Augustus II the Strong in Dresden. After he died, Heinichen's music attracted little ...
.
Personal life and criticism
 In 1732, a French priest named Gabriel Piotr Baudouin founded the first
In 1732, a French priest named Gabriel Piotr Baudouin founded the first orphanage
An orphanage is a residential institution, total institution or group home, devoted to the care of orphans and children who, for various reasons, cannot be cared for by their biological families. The parents may be deceased, absent, or a ...
in Poland, situated in Warsaw's Old Town. The facility was later moved to the nearby Warecki Square (now Warsaw Uprising Square
Warsaw Uprising Square (Polish: ''Plac Powstańców Warszawy''), still popularly known by its former name Napoleon Square (Polish: ''Plac Napoleona''), is a square in the central Warsaw district of Śródmieście.
Located at the junction of '' ...
), and in 1758 Augustus III decreed that the new institution be called ''Szpital Generalny Dzieciątka Jezus'' (The General Hospital of Infant Jesus). The newly established hospital expanded its operations into treating not only orphans but also the sick and the poor. Augustus remained a charitable man throughout his life and donated to the hospital. His successor, Stanisław Augustus, also contributed to the cause.
Despite his charitable manner, Augustus was viewed in Poland as an impotent monarch, obese, plump, ugly and lazy sybarite
Sybarite may refer to:
* Sybarite, a native of Sybaris, an ancient Greek city in southern Italy
* Sybarite (musician) Sybarite is the solo project of musician Xian Hawkins, who played with the Silver Apples for a number of years in the 1990s. Sybar ...
with no interest in the affairs of the state. Such harsh critique and opinion continues to this day. On the other hand, historian Jacek Staszewski was able to find a description of Augustus' character in the Dresden archives in the late 1980s; he was considered an honest and affectionate man, who was widely respected during his reign by both the Saxons and the Poles. In his personal life, Augustus was a devoted husband to Maria Josepha, with whom he had sixteen children. Unlike his father who was a notorious womanizer, he was never unfaithful and enjoyed spending time with his spouse, uncommon among the royalty in those days. He also favoured hunting.
Depictions
Augustus III was portrayed by Ernst Dernburg in the 1941 film '' Friedemann Bach''.Issue
On 20 August 1719, Augustus married Archduchess Maria Josepha of Austria, the eldest child of Joseph I, the Holy Roman Emperor. They had sixteen children, but only fourteen or fifteen are recognized by historians: * Frederick Augustus Franz Xavier (born Dresden, 18 November 1720 – died Dresden, 22 January 1721) * Joseph Augustus Wilhelm Frederick Franz Xavier Johann Nepomuk (born Pillnitz, 24 October 1721 – died Dresden, 14 March 1728) * Frederick Christian Leopold Johann Georg Franz Xavier (born Dresden, 5 September 1722 – died Dresden, 17 December 1763), successor to his father as Elector of Saxony * Unknown stillborn daughter (Dresden, 23 June 1723) * Maria Amalia Christina Franziska Xaveria Flora Walburga (born Dresden, 24 November 1724 – died Buen Retiro, 27 September 1760); married on 19 June 1738 to Charles VII, King of Naples, later KingCharles III of Spain
it, Carlo Sebastiano di Borbone e Farnese
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Philip V of Spain
, mother = Elisabeth Farnese
, birth_date = 20 January 1716
, birth_place = Royal Alcazar of Madrid, Spain
, death_da ...
* Maria Margaretha Franziska Xaveria (born Dresden, 13 September 1727 – died Dresden, 1 February 1734), died in childhood.
* Maria Anna Sophie Sabina Angela Franziska Xaveria (born Dresden, 29 August 1728 – died Munich, 17 February 1797); married on 9 August 1747 to Maximilian III Joseph, Elector of Bavaria
* Unknown child (1729–1730)
* Franz Xavier Albert August Ludwig Benno (born Dresden, 25 August 1730 – died Dresden, 21 June 1806), Regent of Saxony (1763–1768)
* Maria Josepha Karolina Eleonore Franziska Xaveria (born Dresden, 4 November 1731 – died Versailles, 13 March 1767); married on 9 February 1747 to Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), son of Louis XV of France
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
(she was the mother of Kings Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
, Louis XVIII
Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in ...
and Charles X
Charles X (born Charles Philippe, Count of Artois; 9 October 1757 – 6 November 1836) was King of France from 16 September 1824 until 2 August 1830. An uncle of the uncrowned Louis XVII and younger brother to reigning kings Louis XVI and Lou ...
) of France
* Karl Christian Joseph Ignaz Eugen Franz Xavier (born Dresden, 13 July 1733 – died Dresden, 16 June 1796), Duke of Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia ...
and Zemgale (1758–1763)
* Maria Christina Anna Teresia Salomea Eulalia Franziska Xaveria (born Warsaw, 12 February 1735 – died Brumath, 19 November 1782), Princess-Abbess of Remiremont
Remiremont (; german: Romberg or ) is a town and commune in the Vosges department, northeastern France, situated in southern Grand Est. The town has been an abbatial centre since the 7th century, is an economic crossroads of the Moselle and Mos ...
* Maria Elisabeth Apollonia Casimira Francisca Xaveria (born Warsaw, 9 February 1736 – died Dresden, 24 December 1818), died unmarried.
* Albert Kasimir August Ignaz Pius Franz Xavier (born Moritzburg, near Dresden, 11 July 1738 – died Vienna, 10 February 1822), Duke of Teschen and Governor of the Austrian Netherlands (1781–1793)
* Clemens Wenceslaus August Hubertus Franz Xavier (born Schloss Hubertusburg, Wermsdorf, 28 September 1739 – died Marktoberdorf, Allgäu, 27 July 1812), Archbishop of Trier
* Maria Kunigunde Dorothea Hedwig Franziska Xaveria Florentina (born Warsaw, 10 November 1740 – died Dresden, 8 April 1826), Princess-Abbess of Thorn
Thorn(s) or The Thorn(s) may refer to:
Botany
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, sharp structures on plants
* ''Crataegus monogyna'', or common hawthorn, a plant species
Comics and literature
* Rose and Thorn, the two personalities of two DC Comic ...
and Essen
Essen (; Latin: ''Assindia'') is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and Do ...
Gallery
Ancestry
See also
*History of Saxony
The history of Saxony began with a small tribe living on the North Sea between the Elbe and Eider River in what is now Holstein. The name of this tribe, the Saxons (Latin: ''Saxones''), was first mentioned by the Greek author Ptolemy. The name ' ...
* History of Poland (1569–1795)
* Rulers of Saxony
* List of Lithuanian rulers
* Dresden Castle
Dresden Castle or Royal Palace (german: Dresdner Residenzschloss or ) is one of the oldest buildings in Dresden, Germany. For almost 400 years, it was the residence of the electors (1547–1806) and kings (1806–1918) of Saxony from the Alber ...
– Residence of Augustus III
Notes and references
External links
* . {{DEFAULTSORT:Augustus 03 of Poland 1696 births 1763 deaths 18th-century Polish monarchs Electoral Princes of Saxony Nobility from Dresden Prince-electors of Saxony Grand Dukes of Lithuania Imperial vicars House of Wettin Converts to Roman Catholicism from Lutheranism Polish Roman Catholics Burials at Dresden Cathedral Knights of the Golden Fleece of Austria Polish–Lithuanian military personnel of the War of the Polish Succession Polish people of German descent People of the Silesian Wars Albertine branch Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland)