Attack transport on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

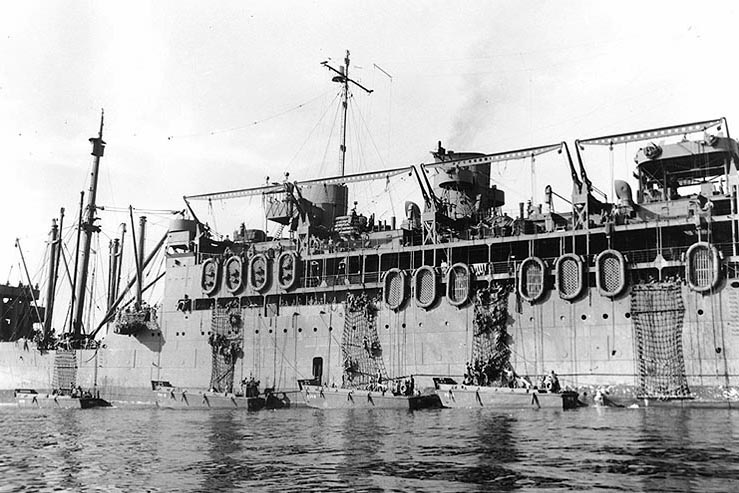 Attack transport is a
Attack transport is a
Retrieved July 22, 2015. Despite an impressive assembly of forces, the Aleutian campaign and the Northern Pacific Theater ranked as Admiral Nimitz's third priority in the overall Pacific Theater for receiving materiel and support. As a result, only attack transport (APA) ships were assigned for the assault, without support from any companion attack cargo (AKA) ships. This created extreme logistics burdens for the invasion force because it resulted in considerable overloading of the transports with both men and equipment. To compound problems, these forces were not able to assemble or train together before executing the Aleutian invasion on 11 May 1943. Lack of equipment and training subsequently resulted in confusion during the landings on Attu.
AWAY ALL BOATS
/ref>
APA/LPA -- Attack Transports
by the US

 Attack transport is a
Attack transport is a United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
ship classification for a variant of ocean-going troopship
A troopship (also troop ship or troop transport or trooper) is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable land troops directly on shore, typicall ...
adapted to transporting invasion forces ashore. Unlike standard troopships – often drafted from the merchant fleet – that rely on either a quay
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more berths ( mooring locatio ...
or tenders, attack transports carry their own fleet of landing craft, such as the landing craft, vehicle, personnel (LCVP) or Higgins boat.
They are not to be confused with landing ship
An amphibious warfare ship (or amphib) is an amphibious vehicle warship employed to land and support ground forces, such as marines, on enemy territory during an amphibious assault.
Specialized shipping can be divided into two types, most crud ...
s, which beach themselves to bring their troops directly ashore, or their general British equivalent, the Landing ship, infantry.
A total of 388 APA (troop) and AKA (cargo) attack transports were built for service in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
in at least fifteen classes. Depending on class they were armed with one or two 5-inch guns and a variety of 40 mm and 20 mm anti-aircraft weapons.
By the late 1960s, 41 of these ships were redesignated with the hull symbol (LPA) Landing Platform, Amphibious, but they all retained their names and hull numbers.
Classification
In the early 1940s, as theUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
expanded in response to the threat of involvement in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, a number of civilian passenger ships and some freighters were acquired, converted to transports and given hull number
Hull number is a serial identification number given to a boat or ship. For the military, a lower number implies an older vessel. For civilian use, the HIN is used to trace the boat's history. The precise usage varies by country and type.
United ...
s in the AP series. Some of these were outfitted with heavy boat davits and other arrangements to enable them to handle landing craft for amphibious assault
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducted ...
operations.
In 1942, when the AP number series had already extended beyond 100, it was decided that these amphibious warfare ships really constituted a separate category of warship from conventional transports. Therefore, the new classification of Auxiliary Personnel, Attack (APA) was created and numbers assigned to fifty-eight APs (AP #s 2, 8-12, 14-18, 25-27, 30, 34-35, 37-40, 48-52, 55-60, 64-65 and 78-101) then in commission or under construction. APA are in the classification of US Navy Auxiliary ship
An auxiliary ship is a naval ship designed to support combatant ships and other naval operations. Auxiliary ships are not primary combatant vessels, though they may have some limited combat capacity, usually for purposes of self-defense.
Auxil ...
s.
The actual reclassification of these ships was not implemented until February 1943, by which time two ships that had APA numbers assigned ( and ) had been lost. Another two transports sunk in 1942, and , were also configured as attack transports but did not survive to be reclassified as such.
As World War II went on, dozens of new construction merchant ships of the United States Maritime Commission
The United States Maritime Commission (MARCOM) was an independent executive agency of the U.S. federal government that was created by the Merchant Marine Act of 1936, which was passed by Congress on June 29, 1936, and was abolished on May 24, 195 ...
's S4, C2, C3 and VC2 ("Victory
The term victory (from Latin ''victoria'') originally applied to warfare, and denotes success achieved in personal combat, after military operations in general or, by extension, in any competition. Success in a military campaign constitutes ...
") types were converted to attack transports, taking the list of APA numbers to 247, though fourteen ships (APAs 181-186 and APAs 240-247) were cancelled before completion. In addition, as part of the 1950s modernization of the Navy's amphibious force with faster ships, two more attack transports (APA-248 and APA-249) were converted from new Type C4-class ships, the s.
Classes
Classes of attack transports included: * (2 ships) ** both built by the Furness Shipbuilding Company ca. 1928 and acquired by the navy in 1940 ** , originally AP-10 ** , AP-11 * (5 ships) ** all built by theAlameda Works Shipyard
The Alameda Works Shipyard, in Alameda, California, United States, was one of the largest and best equipped shipyards in the country. The only building remaining from the yard is the Union Iron Works Powerhouse, which is listed on the National R ...
as merchant ships ca. 1918 and acquired by the navy in 1940
** , AP-12
**
** , AP-14
** , AP-15
** , AP-16
* , AP-17
*
*
*
* (8 ships)
* Type P1 ship
The Type P1 ship is a United States Maritime Administration (MARAD) designation for World War II passenger ships. P1 was used in World War II, Korean War and Vietnam War. Type P1 were the smallest of the P-class ships, at long. Two P1-S2-L2 ships ...
** (2 ships)
* Type S4 ship
** (32 ships)
* Victory Ship
The Victory ship was a class of cargo ship produced in large numbers by North American shipyards during World War II to replace losses caused by German submarines. They were a more modern design compared to the earlier Liberty ship, were sli ...
** (117 ships)
* Type C2 ship
Type C2 ships were designed by the United States Maritime Commission (MARCOM) in 1937–38. They were all-purpose cargo ships with five holds, and U.S. shipyards built 328 of them from 1939 to 1945. Compared to ships built before 1939, the C2s we ...
** (3 ships)
** (4 ships)
* Type C3 ship
Type C3-class ships were the third type of cargo ship designed by the United States Maritime Commission (MARCOM) in the late 1930s. As it had done with the Type C1 ships and Type C2 ships, MARCOM circulated preliminary plans for comment. The desi ...
** (3 ships)
** (4 ships)
** (2 ships)
** (9 ships)
** (34 ships)
** (7 ships)
* Type C4 ship
The Type C4-class ship were the largest cargo ships built by the United States Maritime Commission (MARCOM) during World War II. The design was originally developed for the American-Hawaiian Lines in 1941, but in late 1941 the plans were taken o ...
** (2 ship)
In use
During World War II, attack transport served in the Pacific Theatre, taking part in many of the Navy'sisland hopping
Leapfrogging, also known as island hopping, was a military strategy employed by the Allies in the Pacific War against the Empire of Japan during World War II.
The key idea is to bypass heavily fortified enemy islands instead of trying to captu ...
campaigns. Some attack transports were assigned to the European Theatre, participating in the invasions of North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
. The last use was for the final WW2 Battle of Okinawa.Keegan: ''The Times Atlas of the Second World War'' pg. 169The National Archives: Heroes and VillainsRetrieved July 22, 2015. Despite an impressive assembly of forces, the Aleutian campaign and the Northern Pacific Theater ranked as Admiral Nimitz's third priority in the overall Pacific Theater for receiving materiel and support. As a result, only attack transport (APA) ships were assigned for the assault, without support from any companion attack cargo (AKA) ships. This created extreme logistics burdens for the invasion force because it resulted in considerable overloading of the transports with both men and equipment. To compound problems, these forces were not able to assemble or train together before executing the Aleutian invasion on 11 May 1943. Lack of equipment and training subsequently resulted in confusion during the landings on Attu.
Notable incidents
* was torpedoed off Cape Palos, Spain, 7 November 1942, and abandoned after going aground in Algiers Harbor, 25 November 1942. * on 12 November 1942 was torpedoed by ''U-130'' commanded byErnst Kals
Ernst Kals (2 August 1905 – 2 November 1979) was a '' Kapitän zur See'' with the ''Kriegsmarine'' during World War II. He commanded the Type IXC U-boat on five patrols. He was awarded the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross.
Career
Kals joined ...
who slipped past the escort screen to sink three transports. ''Edward Rutledge''s crew attempted to beach her but all power had been lost; she settled rapidly by the stern and sank with the loss of 15 men.
* on 11 November 1942 took a torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, s ...
hit in No. 2 hold from ''U-173''. The transport settled by the bow and began filling rapidly with water and the order was given to abandon ship. Sank with Captain Smith and approximately 100 seamen.
* was sunk by enemy action, 13 August 1943.
* had Kamikaze attack damage on 1 April 1945 at Okinawa. Over 15 men were killed. The extensive engine room damage was later repaired.
* had Kamikaze attack damage on 2 April 1945 at Okinawa. 37 Navy and 14 Army personnel were killed. At 1828 two 250 pound bombs penetrated two deck levels and exploded on the main deck, resulting in fires and flooding that were not brought under control until 2100.
* on 2 April 1945 was hit by kamikaze attacked, the plane hit the side of the ship then dropped into the sea. She was later repaired.
* on 13 August 1945 damaged in last kamikaze attack of WW2, 21 sailors killed and 89 wounded.
* had mine damage on 17 September 1945, off Okinawa, this caused the death of three men and damaged the ship extensively.
Demise
By the end of the 1950s, it was clear that boats would soon be superseded by amphibious tractors (LVTs) and air assault helicopters for landing combat assault troops. These could not be supported by attack transports in the numbers required, and new categories of amphibious ships began to replace APAs throughout the 1960s. By 1969, when the surviving attack transports were redesignated as "amphibious transports" (LPA) (retaining their previous numbers), only a few remained in commissioned service. The last of these were decommissioned in 1980 and sold abroad, leaving only a few thoroughly obsolete World War II era hulls still laid up in theMaritime Administration Maritime administrations, or flag state administrations, are the executive arms/state bodies of each government responsible for carrying out the shipping responsibilities of the state, and are tasked to administer national shipping and boating issue ...
's reserve fleet. The APA/LPA designation may, therefore, now be safely considered extinct.
In fiction
The 1956 movie ''Away All Boats
''Away All Boats'' is a 1956 American war film directed by Joseph Pevney and starring Jeff Chandler, George Nader, Lex Barker, and Julie Adams. It was produced by Howard Christie from a screenplay by Ted Sherdeman based on the 1953 novel by Kenn ...
'' presents operations on an attack transport. It was based on a popular novel of the same name, written by an officer who served on one during World War 2./ref>
See also
* Amphibious cargo ship (AKA/LKA). Nearly identical ships used to transport vehicles, supplies and landing craft. * Landing ship, infantry * High-speed transport APDReferences
APA/LPA -- Attack Transports
by the US
Naval Historical Center
The Naval History and Heritage Command, formerly the Naval Historical Center, is an Echelon II command responsible for the preservation, analysis, and dissemination of U.S. naval history and heritage located at the historic Washington Navy Yard. ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:attack transport
Ship types
United States Navy in the 20th century
Amphibious warfare vessels