Ascomycota on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ascomycota is a
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
of the kingdom Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
that, together with the Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Bas ...
, forms the subkingdom Dikarya
Dikarya is a subkingdom of Fungi that includes the divisions Ascomycota and Basidiomycota, both of which in general produce dikaryons, may be filamentous or unicellular, but are always without flagella. The Dikarya are most of the so-called " ...
. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, ...
s, called ascospore
An ascus (; ) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera ...
s, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffle
A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus ''Tuber''. In addition to ''Tuber'', many other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including '' Geopora'', '' Pe ...
s, brewers' and bakers' yeast
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been o ...
, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi
The Pezizaceae (commonly referred to as cup fungi) are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota which produce mushrooms that tend to grow in the shape of a "cup". Spores are formed on the inner surface of the fruit body (mushroom). The cup shape typ ...
. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota.
Ascomycota is a
 The hypha that creates the sporing (conidiating) tip can be very similar to the normal hyphal tip, or it can be differentiated. The most common differentiation is the formation of a bottle shaped cell called a , from which the spores are produced. Not all of these asexual structures are a single hypha. In some groups, the conidiophores (the structures that bear the conidia) are aggregated to form a thick structure.
E.g. In the order ''Moniliales,'' all of them are single hyphae with the exception of the aggregations, termed as coremia or synnema. These produce structures rather like corn-stokes, with many conidia being produced in a mass from the aggregated conidiophores.
The diverse conidia and conidiophores sometimes develop in asexual sporocarps with different characteristics (e.g. acervulus, pycnidium, sporodochium). Some species of ''Ascomycetes'' form their structures within plant tissue, either as parasite or saprophytes. These fungi have evolved more complex asexual sporing structures, probably influenced by the cultural conditions of plant tissue as a substrate. These structures are called the . This is a cushion of conidiophores created from a pseudoparenchymatous stroma in plant tissue. The is a globose to flask-shaped parenchymatous structure, lined on its inner wall with conidiophores. The is a flat saucer shaped bed of conidiophores produced under a plant cuticle, which eventually erupt through the cuticle for dispersal.
The hypha that creates the sporing (conidiating) tip can be very similar to the normal hyphal tip, or it can be differentiated. The most common differentiation is the formation of a bottle shaped cell called a , from which the spores are produced. Not all of these asexual structures are a single hypha. In some groups, the conidiophores (the structures that bear the conidia) are aggregated to form a thick structure.
E.g. In the order ''Moniliales,'' all of them are single hyphae with the exception of the aggregations, termed as coremia or synnema. These produce structures rather like corn-stokes, with many conidia being produced in a mass from the aggregated conidiophores.
The diverse conidia and conidiophores sometimes develop in asexual sporocarps with different characteristics (e.g. acervulus, pycnidium, sporodochium). Some species of ''Ascomycetes'' form their structures within plant tissue, either as parasite or saprophytes. These fungi have evolved more complex asexual sporing structures, probably influenced by the cultural conditions of plant tissue as a substrate. These structures are called the . This is a cushion of conidiophores created from a pseudoparenchymatous stroma in plant tissue. The is a globose to flask-shaped parenchymatous structure, lined on its inner wall with conidiophores. The is a flat saucer shaped bed of conidiophores produced under a plant cuticle, which eventually erupt through the cuticle for dispersal.

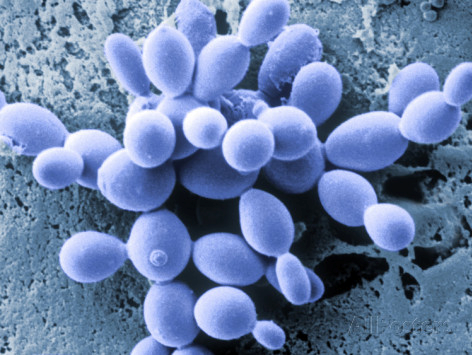 The initial events of budding can be seen as the development of a ring of chitin around the point where the bud is about to appear. This reinforces and stabilizes the cell wall. Enzymatic activity and turgor pressure act to weaken and extrude the cell wall. New cell wall material is incorporated during this phase. Cell contents are forced into the progeny cell, and as the final phase of mitosis ends a cell plate, the point at which a new cell wall will grow inwards from, forms.
The initial events of budding can be seen as the development of a ring of chitin around the point where the bud is about to appear. This reinforces and stabilizes the cell wall. Enzymatic activity and turgor pressure act to weaken and extrude the cell wall. New cell wall material is incorporated during this phase. Cell contents are forced into the progeny cell, and as the final phase of mitosis ends a cell plate, the point at which a new cell wall will grow inwards from, forms.
monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gr ...
group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomycetes are now identified and classified based on morphological or physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemica ...
similarities to ascus-bearing taxa, and by phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
analyses of DNA sequences.
The ascomycetes are of particular use to humans as sources of medicinally important compounds, such as antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and preventio ...
, for fermenting bread, alcoholic beverages and cheese. '' Penicillium'' species on cheeses and those producing antibiotics for treating bacterial infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s are examples of ascomycetes.
Many ascomycetes are pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
s, both of animals, including humans, and of plants. Examples of ascomycetes that can cause infections in humans include '' Candida albicans'', '' Aspergillus niger'' and several tens of species that cause skin infections Skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs), also referred to as skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), or acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSIs), are infections of skin and associated soft tissues (such as loose connective ti ...
. The many plant-pathogenic ascomycetes include apple scab, rice blast, the ergot fungi, black knot, and the powdery mildews.
Several species of ascomycetes are biological model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
s in laboratory research. Most famously, '' Neurospora crassa'', several species of yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
s, and '' Aspergillus'' species are used in many genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
and cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
studies.
Asexual reproduction in ascomycetes
Ascomycetes are 'spore shooters'. They are fungi which produce microscopic spores inside special, elongated cells or sacs, known as 'asci', which give the group its name. Asexual reproduction is the dominant form of propagation in the Ascomycota, and is responsible for the rapid spread of these fungi into new areas. Asexual reproduction of ascomycetes is very diverse from both structural and functional points of view. The most important and general is production of conidia, but chlamydospores are also frequently produced. Furthermore, Ascomycota also reproduce asexually through budding.Conidia formation
Asexual reproduction may occur through vegetative reproductive spores, the conidia. The asexual, non-motile haploid spores of a fungus, which are named after the Greek word for dust (conia), are hence also known as . The conidiospores commonly contain one nucleus and are products of mitotic cell divisions and thus are sometimes call , which are genetically identical to the mycelium from which they originate. They are typically formed at the ends of specialized hyphae, the conidiophores. Depending on the species they may be dispersed by wind or water, or by animals. Conidiophores may simply branch off from the mycelia or they may be formed in fruiting bodies. The hypha that creates the sporing (conidiating) tip can be very similar to the normal hyphal tip, or it can be differentiated. The most common differentiation is the formation of a bottle shaped cell called a , from which the spores are produced. Not all of these asexual structures are a single hypha. In some groups, the conidiophores (the structures that bear the conidia) are aggregated to form a thick structure.
E.g. In the order ''Moniliales,'' all of them are single hyphae with the exception of the aggregations, termed as coremia or synnema. These produce structures rather like corn-stokes, with many conidia being produced in a mass from the aggregated conidiophores.
The diverse conidia and conidiophores sometimes develop in asexual sporocarps with different characteristics (e.g. acervulus, pycnidium, sporodochium). Some species of ''Ascomycetes'' form their structures within plant tissue, either as parasite or saprophytes. These fungi have evolved more complex asexual sporing structures, probably influenced by the cultural conditions of plant tissue as a substrate. These structures are called the . This is a cushion of conidiophores created from a pseudoparenchymatous stroma in plant tissue. The is a globose to flask-shaped parenchymatous structure, lined on its inner wall with conidiophores. The is a flat saucer shaped bed of conidiophores produced under a plant cuticle, which eventually erupt through the cuticle for dispersal.
The hypha that creates the sporing (conidiating) tip can be very similar to the normal hyphal tip, or it can be differentiated. The most common differentiation is the formation of a bottle shaped cell called a , from which the spores are produced. Not all of these asexual structures are a single hypha. In some groups, the conidiophores (the structures that bear the conidia) are aggregated to form a thick structure.
E.g. In the order ''Moniliales,'' all of them are single hyphae with the exception of the aggregations, termed as coremia or synnema. These produce structures rather like corn-stokes, with many conidia being produced in a mass from the aggregated conidiophores.
The diverse conidia and conidiophores sometimes develop in asexual sporocarps with different characteristics (e.g. acervulus, pycnidium, sporodochium). Some species of ''Ascomycetes'' form their structures within plant tissue, either as parasite or saprophytes. These fungi have evolved more complex asexual sporing structures, probably influenced by the cultural conditions of plant tissue as a substrate. These structures are called the . This is a cushion of conidiophores created from a pseudoparenchymatous stroma in plant tissue. The is a globose to flask-shaped parenchymatous structure, lined on its inner wall with conidiophores. The is a flat saucer shaped bed of conidiophores produced under a plant cuticle, which eventually erupt through the cuticle for dispersal.

Budding
Asexual reproduction process in ascomycetes also involves the budding which we clearly observe in yeast. This is termed a "blastic process". It involves the blowing out or blebbing of the hyphal tip wall. The blastic process can involve all wall layers, or there can be a new cell wall synthesized which is extruded from within the old wall. The initial events of budding can be seen as the development of a ring of chitin around the point where the bud is about to appear. This reinforces and stabilizes the cell wall. Enzymatic activity and turgor pressure act to weaken and extrude the cell wall. New cell wall material is incorporated during this phase. Cell contents are forced into the progeny cell, and as the final phase of mitosis ends a cell plate, the point at which a new cell wall will grow inwards from, forms.
The initial events of budding can be seen as the development of a ring of chitin around the point where the bud is about to appear. This reinforces and stabilizes the cell wall. Enzymatic activity and turgor pressure act to weaken and extrude the cell wall. New cell wall material is incorporated during this phase. Cell contents are forced into the progeny cell, and as the final phase of mitosis ends a cell plate, the point at which a new cell wall will grow inwards from, forms.
Characteristics of ascomycetes
* Ascomycota are morphologically diverse. The group includes organisms from unicellular yeasts to complex cup fungi. * 98% oflichens
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.marine fungi in the Ascomycota, distributed among 352 genera.
* The cell walls of the hyphae are variably composed of
 Most species grow as filamentous, microscopic structures called
Most species grow as filamentous, microscopic structures called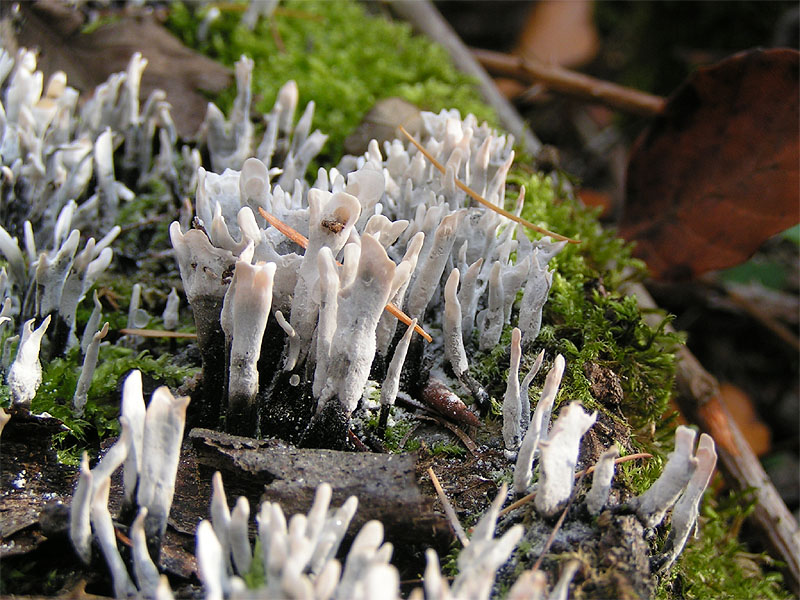  In
In  Large masses of yeast cells, asci or ascus-like cells, or conidia can also form macroscopic structures. For example. ''
Large masses of yeast cells, asci or ascus-like cells, or conidia can also form macroscopic structures. For example. ''
chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
and β-glucans, just as in Basidiomycota. However, these fibers are set in a matrix of glycoprotein containing the sugars galactose and mannose.
* The mycelium of ascomycetes is usually made up of septate hyphae. However, there is not necessarily any fixed number of nuclei in each of the divisions.
* The septal walls have septal pores which provide cytoplasmic continuity throughout the individual hyphae. Under appropriate conditions, nuclei may also migrate between septal compartments through the septal pores.
* A unique character of the Ascomycota (but not present in all ascomycetes) is the presence of Woronin bodies on each side of the septa separating the hyphal segments which control the septal pores. If an adjoining hypha is ruptured, the Woronin bodies block the pores to prevent loss of cytoplasm into the ruptured compartment. The Woronin bodies are spherical, hexagonal, or rectangular membrane bound structures with a crystalline protein matrix.
Modern classification
There are three subphyla that are described and accepted: * The ''Pezizomycotina
Pezizomycotina make up most of the Ascomycota fungi and include most lichenized fungi too. Pezizomycotina contains the filamentous ascomycetes and is a subdivision of the Ascomycota (fungi that form their spores in a sac-like ''ascus''). It is mo ...
'' are the largest subphylum and contains all ascomycetes that produce ascocarps (fruiting bodies), except for one genus, ''Neolecta
''Neolecta'' is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that have fruiting bodies in the shape of unbranched to lobed bright yellowish, orangish to pale yellow-green colored, club-shaped, smooth, fleshy columns up to about 7 cm tall. The species shar ...
'', in the Taphrinomycotina
The Taphrinomycotina are one of three subdivisions constituting the Ascomycota (fungi that form their spores in a sac-like ascus) and is more or less synonymous with the slightly older invalid name Archiascomycetes (sometimes spelled Archaeascomy ...
. It is roughly equivalent to the previous taxon, ''Euascomycetes''. The Pezizomycotina includes most macroscopic "ascos" such as truffle
A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus ''Tuber''. In addition to ''Tuber'', many other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including '' Geopora'', '' Pe ...
s, ergot, ascolichens, cup fungi
The Pezizaceae (commonly referred to as cup fungi) are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota which produce mushrooms that tend to grow in the shape of a "cup". Spores are formed on the inner surface of the fruit body (mushroom). The cup shape typ ...
(discomycetes
Discomycetes is a former taxonomic class of Ascomycete fungi which contains all of the cup, sponge and brain fungi and some club-like fungi. It includes typical cup fungi like the scarlet elf cup and the orange peel fungus, and fungi with fruit ...
), pyrenomycetes, lorchels, and caterpillar fungus
''Ophiocordyceps sinensis'' (formerly known as ''Cordyceps sinensis''), known colloquially as caterpillar fungus, is an entomopathogenic fungus (a fungus that grows on insects) in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae. It is mainly found in the mead ...
. It also contains microscopic fungi such as powdery mildews, dermatophytic fungi, and Laboulbeniales
The Laboulbeniales is an order of Fungi within the class Laboulbeniomycetes. They are also known by the colloquial name beetle hangers or labouls. The order includes around 2,325 species of obligate insect ectoparasites that produce cellular t ...
.
* The ''Saccharomycotina
Saccharomycotina is a subdivision (subphylum) of the division (phylum) Ascomycota in the kingdom Fungi. It comprises most of the ascomycete yeasts. The members of Saccharomycotina reproduce by budding and they do not produce ascocarps (fruitin ...
'' comprise most of the "true" yeasts, such as baker's yeast and '' Candida'', which are single-celled (unicellular) fungi, which reproduce vegetatively by budding. Most of these species were previously classified in a taxon called ''Hemiascomycetes''.
* The ''Taphrinomycotina
The Taphrinomycotina are one of three subdivisions constituting the Ascomycota (fungi that form their spores in a sac-like ascus) and is more or less synonymous with the slightly older invalid name Archiascomycetes (sometimes spelled Archaeascomy ...
'' include a disparate and basal group within the Ascomycota that was recognized following molecular ( DNA) analyses. The taxon was originally named '' Archiascomycetes'' (or '' Archaeascomycetes''). It includes hyphal fungi (''Neolecta
''Neolecta'' is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that have fruiting bodies in the shape of unbranched to lobed bright yellowish, orangish to pale yellow-green colored, club-shaped, smooth, fleshy columns up to about 7 cm tall. The species shar ...
'', ''Taphrina
''Taphrina'' is a fungal genus within the Ascomycota that causes leaf and catkin curl diseases and witch's brooms of certain flowering plants. One of the more commonly observed species causes peach leaf curl. ''Taphrina'' typically grow as yeasts ...
'', ''Archaeorhizomyces
Archaeorhizomycetes is a class of fungi in the subdivision Taphrinomycotina of the Ascomycota. So far, the class has only one described order, Archaeorhizomycetales, family, Archaeorhizomycetaceae, and genus, ''Archaeorhizomyces''. The class wa ...
''), fission yeasts ('' Schizosaccharomyces''), and the mammalian lung parasite ''Pneumocystis
The Pneumocystidomycetes are a class of ascomycete fungi. It includes the single order Pneumocystidales, which contains the single monotypic family Pneumocystidaceae, which in turn contains the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic ...
''.
Outdated taxon names
Several outdated taxon names—based on morphological features—are still occasionally used for species of the Ascomycota. These include the following sexual ( teleomorphic) groups, defined by the structures of their sexual fruiting bodies: theDiscomycetes
Discomycetes is a former taxonomic class of Ascomycete fungi which contains all of the cup, sponge and brain fungi and some club-like fungi. It includes typical cup fungi like the scarlet elf cup and the orange peel fungus, and fungi with fruit ...
, which included all species forming apothecia; the Pyrenomycetes, which included all sac fungi that formed perithecia or pseudothecia, or any structure resembling these morphological structures; and the Plectomycetes, which included those species that form cleistothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mo ...
. Hemiascomycetes
Saccharomycetes belongs to the Ascomycota division of the kingdom Fungi. It is the only class in the subdivision Saccharomycotina, the budding yeasts. Saccharomycetes contains a single order, Saccharomycetales
Saccharomycetales belongs to th ...
included the yeasts and yeast-like fungi that have now been placed into the Saccharomycotina
Saccharomycotina is a subdivision (subphylum) of the division (phylum) Ascomycota in the kingdom Fungi. It comprises most of the ascomycete yeasts. The members of Saccharomycotina reproduce by budding and they do not produce ascocarps (fruitin ...
or Taphrinomycotina
The Taphrinomycotina are one of three subdivisions constituting the Ascomycota (fungi that form their spores in a sac-like ascus) and is more or less synonymous with the slightly older invalid name Archiascomycetes (sometimes spelled Archaeascomy ...
, while the Euascomycetes included the remaining species of the Ascomycota, which are now in the Pezizomycotina
Pezizomycotina make up most of the Ascomycota fungi and include most lichenized fungi too. Pezizomycotina contains the filamentous ascomycetes and is a subdivision of the Ascomycota (fungi that form their spores in a sac-like ''ascus''). It is mo ...
, and the Neolecta
''Neolecta'' is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that have fruiting bodies in the shape of unbranched to lobed bright yellowish, orangish to pale yellow-green colored, club-shaped, smooth, fleshy columns up to about 7 cm tall. The species shar ...
, which are in the Taphrinomycotina.
Some ascomycetes do not reproduce sexually or are not known to produce asci ASCI or Asci may refer to:
* Advertising Standards Council of India
* Asci, the plural of ascus, in fungal anatomy
* Accelerated Strategic Computing Initiative
* American Society for Clinical Investigation
* Argus Sour Crude Index
* Association of ...
and are therefore anamorphic species. Those anamorphs that produce conidia (mitospores) were previously described as mitosporic Ascomycota. Some taxonomists placed this group into a separate artificial phylum, the Deuteromycota (or "Fungi Imperfecti"). Where recent molecular analyses have identified close relationships with ascus-bearing taxa, anamorphic species have been grouped into the Ascomycota, despite the absence of the defining ascus. Sexual and asexual isolates of the same species commonly carry different binomial
Binomial may refer to:
In mathematics
*Binomial (polynomial), a polynomial with two terms
*Binomial coefficient, numbers appearing in the expansions of powers of binomials
*Binomial QMF, a perfect-reconstruction orthogonal wavelet decomposition
* ...
species names, as, for example, '' Aspergillus nidulans'' and ''Emericella nidulans'', for asexual and sexual isolates, respectively, of the same species.
Species of the Deuteromycota were classified as Coelomycetes if they produced their conidia in minute flask- or saucer-shaped conidiomata, known technically as ''pycnidia'' and ''acervuli''. The Hyphomycetes were those species where the conidiophores (''i.e.'', the hyphal structures that carry conidia-forming cells at the end) are free or loosely organized. They are mostly isolated but sometimes also appear as bundles of cells aligned in parallel (described as ''synnematal'') or as cushion-shaped masses (described as ''sporodochial'').
Morphology
 Most species grow as filamentous, microscopic structures called
Most species grow as filamentous, microscopic structures called hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one or ...
e or as budding single cells (yeasts). Many interconnected hyphae form a thallus
Thallus (plural: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or "twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. Many of these organisms ...
usually referred to as the mycelium
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates ...
, which—when visible to the naked eye (macroscopic)—is commonly called mold. During sexual reproduction, many Ascomycota typically produce large numbers of asci ASCI or Asci may refer to:
* Advertising Standards Council of India
* Asci, the plural of ascus, in fungal anatomy
* Accelerated Strategic Computing Initiative
* American Society for Clinical Investigation
* Argus Sour Crude Index
* Association of ...
. The ascus is often contained in a multicellular, occasionally readily visible fruiting structure, the ascocarp (also called an ''ascoma''). Ascocarps come in a very large variety of shapes: cup-shaped, club-shaped, potato-like, spongy, seed-like, oozing and pimple-like, coral-like, nit-like, golf-ball-shaped, perforated tennis ball-like, cushion-shaped, plated and feathered in miniature (Laboulbeniales
The Laboulbeniales is an order of Fungi within the class Laboulbeniomycetes. They are also known by the colloquial name beetle hangers or labouls. The order includes around 2,325 species of obligate insect ectoparasites that produce cellular t ...
), microscopic classic Greek shield-shaped, stalked or sessile. They can appear solitary or clustered. Their texture can likewise be very variable, including fleshy, like charcoal (carbonaceous), leathery, rubbery, gelatinous, slimy, powdery, or cob-web-like. Ascocarps come in multiple colors such as red, orange, yellow, brown, black, or, more rarely, green or blue. Some ascomyceous fungi, such as ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', grow as single-celled yeasts, which—during sexual reproduction—develop into an ascus, and do not form fruiting bodies.
 In
In lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or para ...
colony. Some dimorphic species, such as '' Candida albicans'', can switch between growth as single cells and as filamentous, multicellular hyphae. Other species are pleomorphic, exhibiting asexual (anamorphic) as well as a sexual (teleomorphic) growth forms.
Except for lichens, the non-reproductive (vegetative) mycelium of most ascomycetes is usually inconspicuous because it is commonly embedded in the substrate, such as soil, or grows on or inside a living host, and only the ascoma may be seen when fruiting. Pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compou ...
ation, such as melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
in hyphal walls, along with prolific growth on surfaces can result in visible mold colonies; examples include ''Cladosporium
''Cladosporium'' is a genus of fungi including some of the most common indoor and outdoor molds. Species produce olive-green to brown or black colonies, and have dark-pigmented conidia that are formed in simple or branching chains. Many specie ...
'' species, which form black spots on bathroom caulking and other moist areas. Many ascomycetes cause food spoilage, and, therefore, the pellicles or moldy layers that develop on jams, juices, and other foods are the mycelia of these species or occasionally Mucoromycotina and almost never Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Bas ...
. Sooty mold
Sooty mold (also spelled sooty mould) is a collective term for different Ascomycete fungi, which includes many genera, commonly ''Cladosporium'' and ''Alternaria''. It grows on plants and their fruit, but also environmental objects, like fences, ...
s that develop on plants, especially in the tropics are the thalli of many species.
 Large masses of yeast cells, asci or ascus-like cells, or conidia can also form macroscopic structures. For example. ''
Large masses of yeast cells, asci or ascus-like cells, or conidia can also form macroscopic structures. For example. ''Pneumocystis
The Pneumocystidomycetes are a class of ascomycete fungi. It includes the single order Pneumocystidales, which contains the single monotypic family Pneumocystidaceae, which in turn contains the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic ...
'' species can colonize lung cavities (visible in x-rays), causing a form of pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
. Asci of '' Ascosphaera'' fill honey bee larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e and pupa
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in thei ...
e causing mummification with a chalk-like appearance, hence the name "chalkbrood". Yeasts for small colonies in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
and in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and p ...
, and excessive growth of '' Candida'' species in the mouth or vagina causes "thrush", a form of candidiasis.
The cell walls of the ascomycetes almost always contain chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
and β-glucans, and divisions within the hyphae, called "septa
The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly 4 million people in five c ...
", are the internal boundaries of individual cells (or compartments). The cell wall and septa give stability and rigidity to the hyphae and may prevent loss of cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
in case of local damage to cell wall and cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
. The septa commonly have a small opening in the center, which functions as a cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
ic connection between adjacent cells, also sometimes allowing cell-to-cell movement of nuclei within a hypha. Vegetative hyphae of most ascomycetes contain only one nucleus per cell (''uninucleate
{{Short pages monitor