Arundhati (Hinduism) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arundhati ( sa, अरुन्धती, translit=Arundhatī) is the wife of the sage
 Arundhati is identified with the
Arundhati is identified with the
Vasishtha
Vasishtha ( sa, वसिष्ठ, IAST: ') is one of the oldest and most revered Vedic rishis or sages, and one of the Saptarishis (seven great Rishis). Vashistha is credited as the chief author of Mandala 7 of the '' Rigveda''. Vashishtha ...
, one of the seven sages (Saptarshi
The Saptarishi () are the seven rishis of ancient India who are extolled in the Vedas, and other Hindu literature. The Vedic Samhitas never enumerate these rishis by name, although later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do so.
...
) of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
.
Etymology
The name inSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
literally means 'washed from the rays of sun', from 'sun rays', and , 'washed'.
Legend
Arundhati's birth and life are mentioned in various Hindu scriptures. The birth of Arundhati is found in theShiva Purana
The ''Shiva Purana'' is one of eighteen major texts of the ''Purana'' genre of Sanskrit texts in Hinduism, and part of the Shaivism literature corpus. It primarily revolves around the Hindu god Shiva and goddess Parvati, but references and ...
and Bhagavata Purana
The ''Bhagavata Purana'' ( sa, भागवतपुराण; ), also known as the ''Srimad Bhagavatam'', ''Srimad Bhagavata Mahapurana'' or simply ''Bhagavata'', is one of Hinduism's eighteen great Puranas (''Mahapuranas''). Composed in S ...
. The instruction by Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp ...
to Arundhati is described in the Uttara Kanda of the Ramcharitmanas
''Ramcharitmanas'' ( deva, श्रीरामचरितमानस, Rāmacaritamānasa), is an epic poem in the Awadhi language, based on the '' Ramayana'', and composed by the 16th-century Indian bhakti poet Tulsidas (c. 1532–1623). Thi ...
. The rivalry between Vishvamitra
Vishvamitra ( sa, विश्वामित्र, ) is one of the most venerated rishis or sages of ancient India. According to Hindu tradition, he is stated to have written most of the Mandala 3 of the Rigveda, including the Gayatri Man ...
and Vasishtha which leads to the death of her hundred sons is described in the Balakanda
''Bala Kanda'' ( sa, बालकाण्ड; IAST: ', ) is the first book of the Valmiki ''Ramayana'', which is one of the two great epics of India (the other being the ''Mahabharata''). There has been debate as to whether ''Bala Kanda'' was c ...
of Valmiki
Valmiki (; Sanskrit: वाल्मीकि, ) is celebrated as the harbinger-poet in Sanskrit literature. The epic ''Ramayana'', dated variously from the 5th century BCE to first century BCE, is attributed to him, based on the attributio ...
's Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages ...
. The Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
and several Brahmana
The Brahmanas (; Sanskrit: , ''Brāhmaṇam'') are Vedic śruti works attached to the Samhitas (hymns and mantras) of the Rig, Sama, Yajur, and Atharva Vedas. They are a secondary layer or classification of Sanskrit texts embedded within ...
works describe her sons, including Shakti, and grandson Parashara. Arundhati's meetings with Sita
Sita (; ) also called as Janaki and Vaidehi is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic, ''Ramayana''. She is the consort of Rama, the avatar of the god Vishnu, and is regarded as a form of Vishnu's consort, Lakshmi. She ...
and Rama
Rama (; ), Ram, Raman or Ramar, also known as Ramachandra (; , ), is a major deity in Hinduism. He is the seventh and one of the most popular '' avatars'' of Vishnu. In Rama-centric traditions of Hinduism, he is considered the Supreme Bei ...
are mentioned in the Ramayana, Ramcharitmanas and Vinaya Patrika.Rambhadracharya 1994, pp. ''iii—vi''. Her role in pleading Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
to marry Parvati
Parvati ( sa, पार्वती, ), Uma ( sa, उमा, ) or Gauri ( sa, गौरी, ) is the Hindu goddess of power, energy, nourishment, harmony, love, beauty, devotion, and motherhood. She is a physical representation of Mahadevi i ...
is described in the sixth canto of Kumarasambhava of Kalidasa
Kālidāsa (''fl.'' 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on the Vedas, the Rāmāyaṇa, the Mahābhārata and t ...
.Kale, pp. 197-199
As per the Bhagavata Purana, Arundhati is the eighth among the nine daughters of Kardama and Devahuti. She is the grandmother of Parashara and the great-grandmother of Vyasa
Krishna Dvaipayana ( sa, कृष्णद्वैपायन, Kṛṣṇadvaipāyana), better known as Vyasa (; sa, व्यासः, Vyāsaḥ, compiler) or Vedavyasa (वेदव्यासः, ''Veda-vyāsaḥ'', "the one who cl ...
. The Shiva Purana describes her as being ''Sandhya'', the mind-born daughter of Brahma, in a previous birth. On instruction of Vasishtha, Sandhya pleased Shiva by penance in order to purify herself from passion, and Shiva asked her to jump into Medhatithi's fire. She was then born as Medhatithi's daughter and married Vasishtha. Some other Purana
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
s describe her as the daughter of Kashyapa
Kashyapa ( sa, कश्यप}, ) is a revered Vedic sage of Hinduism., Quote: "Kasyapa (Rudra),(Vedic Seer)..." He is one of the Saptarishis, the seven ancient sages of the ''Rigveda''. Kashyapa is the most ancient and venerated rishi, ...
and sister of Narada
Narada ( sa, नारद, ), or Narada Muni, is a sage divinity, famous in Hindu traditions as a travelling musician and storyteller, who carries news and enlightening wisdom. He is one of mind-created children of Brahma, the creator god. He ...
and Parvata, and she was offered in marriage to Vasishtha by Narada.Garg 1992, pp. 647-648
The Mahabharata describes Arundhati as an ascetic who used to give discourses to even the seven sages. The wife of Agni
Agni (English: , sa, अग्नि, translit=Agni) is a Sanskrit word meaning fire and connotes the Vedic fire deity of Hinduism. He is also the guardian deity of the southeast direction and is typically found in southeast corners of Hi ...
, Svaha
Svaha (Sanskrit: स्वाहा, IAST: Svāhā), also referred to as Manyanti, is the Hindu goddess of sacrifices featured in the Vedas. She is the consort of Agni, and the daughter of either Daksha or Brihaspati, depending on the literary ...
, could therefore assume the form of the wives of the other six seers amongst Saptarshi but not that of Arundhati. The epic also narrates how once she pleased Shiva when it did not rain for 12 years and the seven seers were suffering without roots and fruits. Her chastity and service to her husband is mentioned as unparalleled in the Mahabharata.
As per the Valmiki Ramayana, she bore a hundred sons, who were all cursed to die by Vishvamitra
Vishvamitra ( sa, विश्वामित्र, ) is one of the most venerated rishis or sages of ancient India. According to Hindu tradition, he is stated to have written most of the Mandala 3 of the Rigveda, including the Gayatri Man ...
. She then bore a son named Shakti
In Hinduism, especially Shaktism (a theological tradition of Hinduism), Shakti (Devanagari: शक्ति, IAST: Śakti; lit. "Energy, ability, strength, effort, power, capability") is the primordial cosmic energy, female in aspect, and r ...
and later another one named Suyagya, who studied with Rama at Vasishtha's hermitage. Some sources say she had eight sons including Shakti and Chitraketu.
The life of Arundhati is described in the eponymous Hindi epic poem ''Arundhati'' composed by Jagadguru Rambhadracharya
Jagadguru Ramanandacharya Swami Rambhadracharya (born Pandit Giridhar on 14 January 1950) is an Indian Hindu spiritual leader, educator, Sanskrit scholar, polyglot, poet, author, textual commentator, philosopher, composer, singer, playwrigh ...
in 1994.
Traditions
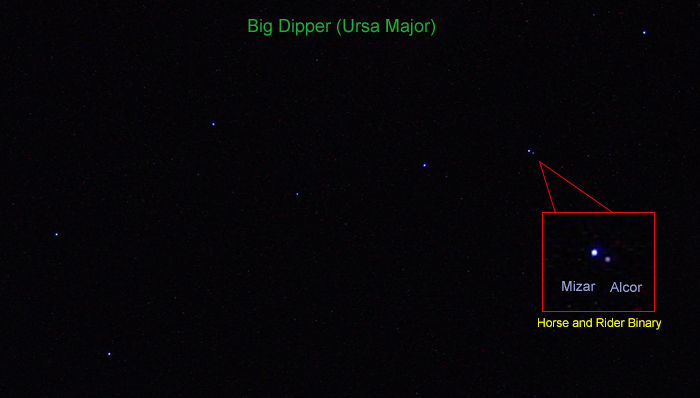
 Arundhati is identified with the
Arundhati is identified with the morning star
Morning Star, morning star, or Morningstar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Morning star, most commonly used as a name for the planet Venus when it appears in the east before sunrise
** See also Venus in culture
* Morning star, a name for the star Siri ...
and with the star Alcor
ALCOR (ALGOL Converter, acronym) is an early computer language definition created by the ALCOR Group, a consortium of universities, research institutions and manufacturers in Europe and the United States which was founded in 1959 and which had 60 m ...
, which forms a double star with Mizar (identified as Vasishtha Maharshi) in Ursa Major. Arundhati, though the wife of one of the seven seers, is accorded the same status as the seven seers and is worshipped with them as such. In Vedic and Puranic literature, she is regarded as the epitome of chastity, conjugal bliss and wifely devotion. In post-Puranic epic poems in Sanskrit and Hindi, she has been described as "chaste and revered" and with a character that is "unblemished, inspiring and worthy of imitation". In the Hindu culture
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or ''dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global po ...
, there are several beliefs, practices and traditions centred on Arundhati including a ritual in the marriage ceremony after the Saptapadi, a fast, a belief about imminent death, and a maxim.
In one of the rituals of a Hindu marriage, the groom shows the bride the double stars of Vasishtha and Arundhati as an ideal couple, symbolic of marital fulfilment and loyalty. The couples are asked to look up the constellation symbolizing conjugal love and affection. On the second bright day of the lunar month of Chaitra
Chaitra (Hindi: चैत्र) is a month of the Hindu calendar.
In the standard Hindu calendar and India's national civil calendar, Chaitra is the first month of the year. It is the last month in the Bengali calendar, where it is called Ch ...
, a fast in her honour is observed in certain regions of India by ladies whose husbands are alive. This fast is observed with the belief that the ladies observing it would not be widowed.Garg 1992, p. 649
Since the Arundhati star is faintly visible, there is a belief that when someone is near death, they can not see the Arundhati star.Apte 2000, p. 51. Due to its faintness, the Arundhati used to be shown in steps, first showing the brighter stars, and then relative to that the faint Arundhati star is directed. The maxim in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
called the ''Arundhatīdarśananyāyaḥ'' (IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during ...
: अरुन्धतीदर्शनन्यायः), used in the meaning of inferring the unknown from that which is known, is named after Arundhati.Apte 2000, p. 305.
References
External links
* * * * * {{Ramayana Rishis Hindu sages Sages in the Ramayana