Armenian Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Armenia, also the Kingdom of Greater Armenia, or simply Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք '; la, Armenia Maior), sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire, was a monarchy in the Ancient Near East which existed from 331 BC to 428 AD. Its history is divided into the successive reigns of three royal dynasties:

 The
The
 Armenia came under the
Armenia came under the
Երկնէր երկին, երկնէր երկիր,
Երկնէր և ծովն ծիրանի,
Երկն ի ծովուն ունէր և զկարմրիկն եղեգնիկ։
Ընդ եղեգան փող ծուխ ելանէր,
Ընդ եղեգան փող բոց ելանէր,
Եւ ի բոցոյն վազէր խարտեաշ պատանեկիկ։
Նա հուր հեր ունէր,
Բոց ունէր մօրուս,
Եւ աչքունքն էին արեգակունք։
Translation
In travail were heaven and earth,
In travail, too, the purple sea,
The travail held in the sea the small red reed.
Through the hollow of the stalk came forth smoke,
Through the hollow of the stalk came forth flame,
And out of the flame a youth ran․
Fiery hair had he,
Ay, too, he had flaming beard,
And his eyes, they were as suns.
 By the 2nd century BC, according to
By the 2nd century BC, according to
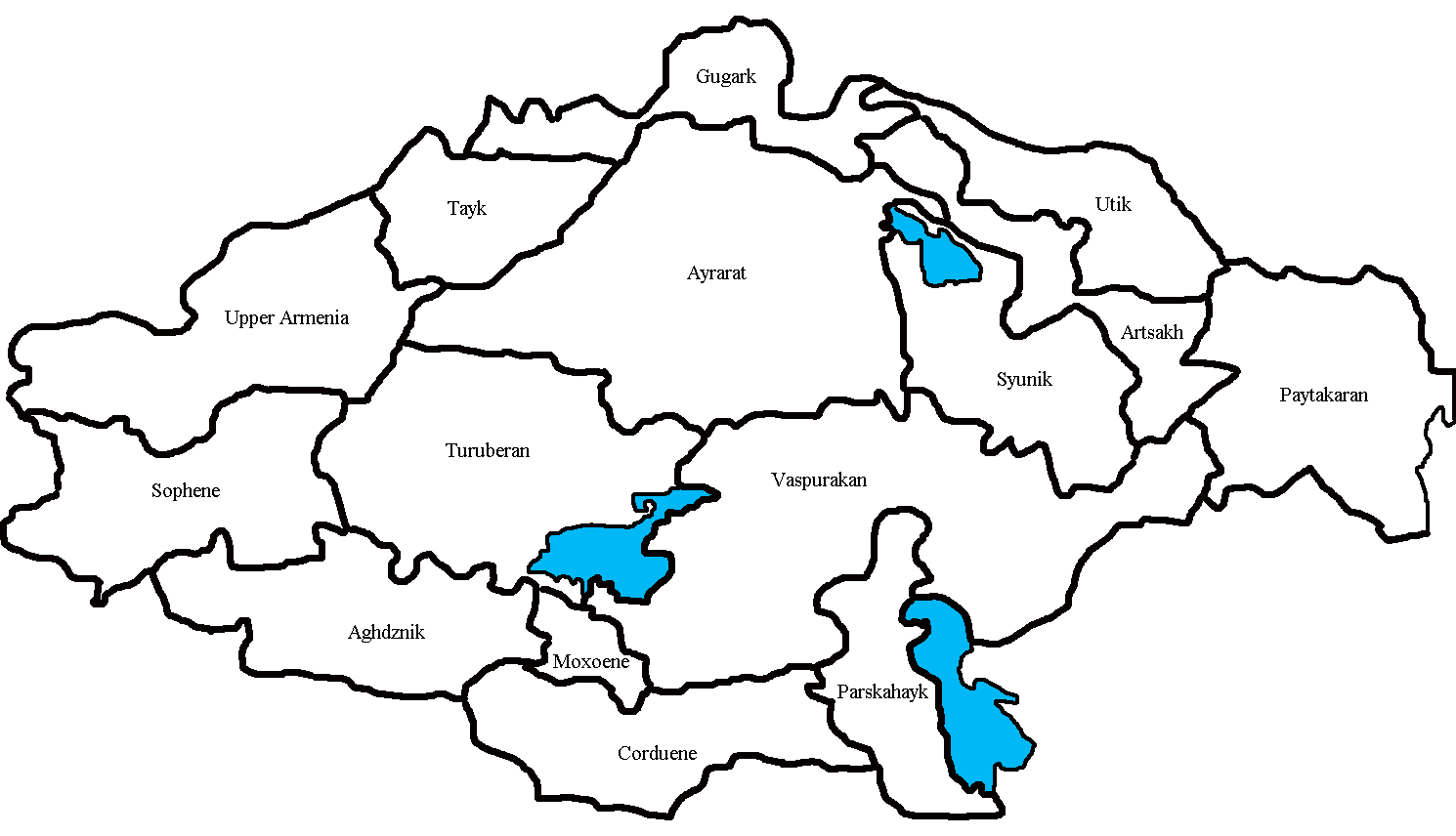
 The 15 provinces of the Kingdom of Armenia with their capitals are as follows:
*
The 15 provinces of the Kingdom of Armenia with their capitals are as follows:
*
File:East-Hem 323bc.jpg, World in 323 BC
File:East-Hem 200bc.jpg, World in 200 BC
File:East-Hem 100bc.jpg, World in 100 BC
File:Orontid Armenia -250-en.svg, Orontid Armenia
File:Maps of the Armenian Empire of Tigranes.gif, Armenian Empire under Tigranes the Great
File:Arshakuni Armenia 150-en.svg, Arshakuni Armenia in 150 AD
File:Persian Armenia.gif, Persian Armenia
File:Map of Byzantine Armenia, 387-536.gif, Byzantine Armenia
Orontid
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after th ...
(331 BC–200 BC), Artaxiad (189 BC–12 AD) and Arsacid
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquer ...
(52–428).
The root of the kingdom lies in one of the satrapies
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with con ...
of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia called Armenia (Satrapy of Armenia
The Satrapy of Armenia (Old Persian: 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴 or 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴𐎹 ), a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty (570–201 BC), was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an ind ...
), which was formed from the territory of the Kingdom of Ararat (860 BC–590 BC) after it was conquered by the Median Empire
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
in 590 BC. The satrapy became a kingdom in 321 BC during the reign of the Orontid dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after t ...
after the conquest of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, which was then incorporated as one of the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
kingdoms of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
.
Under the Seleucid Empire (312–63 BC), the Armenian throne was divided in two—Armenia Maior and Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
—both of which passed to members of the Artaxiad dynasty in 189 BC. During the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
's eastern expansion, the Kingdom of Armenia, under Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
, reached its peak, from 83 to 69 BC, after it reincorporated Sophene and conquered the remaining territories of the falling Seleucid Empire, effectively ending its existence and raising Armenia into an empire for a brief period, until it was itself conquered by Rome in 69 BC. The remaining Artaxiad kings ruled as clients of Rome until they were overthrown in 12 AD due to their possible allegiance to Rome's main rival in the region, Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
.
During the Roman–Parthian Wars
The Roman–Parthian Wars (54 BC – 217 AD) were a series of conflicts between the Parthian Empire and the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. It was the first series of conflicts in what would be 682 years of Roman–Persian Wars.
Battles ...
, the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia was founded when Tiridates I, a member of the Parthian Arsacid dynasty, was proclaimed King of Armenia in 52. Throughout most of its history during this period, Armenia was heavily contested between Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and Parthia, and the Armenian nobility
The Armenian nobility ( hy, Հայ ազնվականություն) was a class of persons which enjoyed certain privileges relative to other members of society under the laws and customs of various regimes of Armenia. Governments which recognized o ...
was divided among pro-Roman, pro-Parthian or neutral factions. From 114 to 118, Armenia briefly became a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
of the Roman Empire under Emperor Trajan. The Kingdom of Armenia often served as a client state or vassal at the frontier of the two large empires and their successors, the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
empires. In 301, Tiridates III proclaimed Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
as the state religion of Armenia, making the Armenian kingdom the first state to embrace Christianity officially.
In 387, Armenia was partitioned into Byzantine Armenia
Byzantine Armenia, sometimes known as Western Armenia, is the name given to the parts of Kingdom of Armenia that became part of the Byzantine Empire. The size of the territory varied over time, depending on the degree of control the Byzantine ...
and Persian Armenia
Sasanian Armenia, also known as Persian Armenia and Persarmenia ( hy, Պարսկահայաստան – ''Parskahayastan''), may either refer to the periods in which Armenia ( pal, 𐭠𐭫𐭬𐭭𐭩 – ''Armin'') was under the suzerainty of ...
. The last Arsacid king of Armenia was deposed in 428, ending independent Armenian statehood until the emergence of Bagratid Armenia
The Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia, also known as Bagratid Armenia ( xcl, Բագրատունեաց Հայաստան, or , , 'kingdom of the Bagratunis'), was an independent Armenian state established by Ashot I Bagratuni of the Bagratuni dynasty ...
in the 9th century.
History
Origins
Prior to the 9th century BC, the geographic region known as the Armenian Highlands was inhabited by Proto-Armenian and other tribes which did not yet constitute a unitary state or nation. The first state to rule over a significant part of the Armenian Highlands was theKingdom of Urartu
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, אֲרָרָט ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of V ...
, also known as the Kingdom of Van or Ararat and called Biainili in the Urartian language
Urartian or Vannic is an extinct Hurro-Urartian languages, Hurro-Urartian language which was spoken by the inhabitants of the ancient kingdom of Urartu (''Biaini'' or ''Biainili'' in Urartian), which was centered on the region around Lake Van and ...
used by its rulers. The kingdom competed with Assyria over supremacy in the highlands of Ararat and the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
.
Both kingdoms fell to Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
invaders from the east (the Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, followed by the Achaemenid Persians) in the 6th century BC. Its territory was reorganized into a satrapy called Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
. The Orontid dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after t ...
ruled as satraps of the Achaemenid Empire for three centuries until the empire was defeated by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's Macedonian Empire
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
at the Battle of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela (; grc, Γαυγάμηλα, translit=Gaugámela), also called the Battle of Arbela ( grc, Ἄρβηλα, translit=Árbela), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great a ...
in 331 BC. After Alexander's death in 323 BC, a Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
general named Neoptolemus
In Greek mythology, Neoptolemus (; ), also called Pyrrhus (; ), was the son of the warrior Achilles and the princess Deidamia, and the brother of Oneiros. He became the mythical progenitor of the ruling dynasty of the Molossians of ancient Ep ...
obtained Armenia until he died in 321 BC and the Orontids returned, not as satraps, but as kings.
Orontid dynasty
Orontes III and the ruler ofLesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
, Mithridates, recognized themselves independent, thus elevating the former Armenian satrapy into a kingdom, giving birth to the kingdoms of Armenia and Lesser Armenia. Orontes III also defeated the Thessalian
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thess ...
commander Menon, who wanted to capture Sper's gold mines.
Weakened by the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
which succeeded the Macedonian Empire, the last Orontid king, Orontes IV, was overthrown in 200/201 BC and the kingdom was taken over by a commander of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, Artaxias (Artashes) I, who is presumed to have been related to the Orontid dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after t ...
himself.
Artaxiad dynasty
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
's influence over Armenia had weakened after it was defeated by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
in the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of ...
in 190 BC. A Hellenistic Armenian state was thus founded in the same year by Artaxias I
Artaxias I (from gr, Άρταξίας; in hy, Արտաշէս, translit=Artašēs) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling ...
alongside the Armenian kingdom of Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
led by Zariadres. Artaxias seized Yervandashat
Yervandashat or Eruandashat ( hy, Երվանդաշատ), was an Armenian city and one of the 13 historic capitals of Armenia, serving as a capital city between 210 and 176 BC during the Orontid rule over Armenia and the beginning of their succes ...
, united the Armenian Highlands at the expense of neighboring tribes and founded the new royal capital of Artaxata
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of t ...
near the Araxes River
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan ex ...
. According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
and Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Pu ...
received hospitality at the Armenian court of Artaxias I. The authors add an apocryphal story of how Hannibal planned and supervised the building of Artaxata. The new city was laid on a strategic position at the juncture of trade routes that connected the Ancient Greek world
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
with Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
which permitted the Armenians to prosper. Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
saw an opportunity for expansion in the constant civil strife to the south. In 83 BC, at the invitation of one of the factions in the interminable civil wars, he entered Syria, and soon established himself as ruler of Syria—putting the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
virtually at an end—and ruled peacefully for 17 years. During the zenith of his rule, Tigranes the Great extended Armenia's territory outside of the Armenian Highland over parts of the Caucasus and the area that is now south-eastern Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
, becoming one of the most powerful states in the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
East.
Roman rule
 Armenia came under the
Armenia came under the Ancient Roman
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–50 ...
sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
in 66 BC, after the battle of Tigranocerta
The Battle of Tigranocerta (, ''Tigranakerti tchakatamart'') was fought on 6 October 69 BC between the forces of the Roman Republic and the army of the Kingdom of Armenia led by King Tigranes the Great. The Roman force, led by Consul Lucius ...
and the final defeat of Armenia's ally, Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
. Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
invaded and defeated the kingdom in 34 BC, but the Romans lost hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
during the Final War of the Roman Republic
The War of Actium (32–30 BC) was the last civil war of the Roman Republic, fought between Mark Antony (assisted by Cleopatra and by extension Ptolemaic Egypt) and Octavian. In 32 BC, Octavian convinced the Roman Senate to declare war on the E ...
in 32–30 BC. In 20 BC, Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
negotiated a truce with the Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
, making Armenia a buffer zone
A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land, usually pertaining to countries. Depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them.
Common types of buffer zones are demili ...
between the two major powers.
Augustus installed Tigranes V as king of Armenia in AD 6, but ruled with Erato of Armenia. The Romans then installed Mithridates of Armenia
Mithridates of Armenia ( ka, მითრიდატე; hy, Միհրդատ Իբերացի, fl. 1st century) was a Pharnavazid prince of the Kingdom of Iberia who served as a King of Armenia under the protection of the Roman Empire.
Mithridat ...
as client king. Mithridates was arrested by Caligula
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), better known by his nickname Caligula (), was the third Roman emperor, ruling from 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the popular Roman general Germani ...
, but later restored by Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor ...
. Subsequently, Armenia was often a focus of contention between Rome and Parthia, with both major powers supporting opposing sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
s and usurper
A usurper is an illegitimate or controversial claimant to power, often but not always in a monarchy. In other words, one who takes the power of a country, city, or established region for oneself, without any formal or legal right to claim it as ...
s. The Parthians forced Armenia into submission in AD 37, but in AD 47 the Romans retook control of the kingdom. In AD 51 Armenia fell to an Iberian invasion sponsored by Parthia, led by Rhadamistus. Tigranes VI of Armenia ruled from AD 58, again installed by Roman support. The period of turmoil ends in AD 66, when Tiridates I of Armenia was crowned king of Armenia by Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
. For the remaining duration of the Armenian kingdom, Rome still considered it a client kingdom ''de jure'', but the ruling dynasty was of Parthian extraction, and contemporary Roman writers thought that Nero had ''de facto'' yielded Armenia to the Parthians.
Arsacid dynasty
UnderNero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
, the Romans fought a campaign (55–63) against the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
, which had invaded the Kingdom of Armenia, allied with the Romans. After gaining Armenia in 60, then losing it in 62, the Romans sent the Legio XV ''Apollinaris'' from Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now west ...
to Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo
Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo ( Peltuinum c. AD 7 – 67) was a popular Roman general, brother-in-law of the emperor Caligula and father-in-law of Domitian. The emperor Nero, highly fearful of Corbulo's reputation, ordered him to commit suicide, which ...
, ''legatus
A ''legatus'' (; anglicised as legate) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman Army, equivalent to a modern high-ranking general officer. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the officer ...
'' of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. In 63, strengthened further by the legions III ''Gallica'', V ''Macedonica'', X ''Fretensis'' and XXII
22 (twenty-two) is the natural number following 21 and preceding 23.
In mathematics
22 is a palindromic number and the eighth semiprime; its proper divisors are 1, 2, and 11. It is the second Smith number, the second Erdős–Woods numbe ...
, General Corbulo entered into the territories of Vologases I of Parthia, who then returned the Armenian kingdom to Tiridates, king Vologases I's brother. An agreement was reached at the Treaty of Rhandeia
The Treaty of Rhandeia was a peace treaty concluded between the Roman Empire and the Parthian Empire at the frontier town of Rhandeia in what is now Turkey in 63. The treaty, which finalized the Roman–Parthian War of 58–63, stipulated that henc ...
in 63, according to which members of the Parthian Arsacid dynasty would rule Armenia as client kings of Rome.
Another campaign was led by Emperor Lucius Verus
Lucius Aurelius Verus (15 December 130 – January/February 169) was Roman emperor from 161 until his death in 169, alongside his adoptive brother Marcus Aurelius. He was a member of the Nerva-Antonine dynasty. Verus' succession together wit ...
in 162–165, after Vologases IV of Parthia had invaded Armenia and installed his chief general on its throne. To counter the Parthian threat, Verus set out for the east. His army won significant victories and retook the capital. Sohaemus, a Roman citizen of Armenian heritage, was installed as the new client king
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
. But during an epidemic within the Roman forces, Parthians retook most of their lost territory in 166. Sohaemus retreated to Syria, and the Arsacid dynasty
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
was restored to power in Armenia.
After the fall of the Arsacid dynasty in Persia, the succeeding Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
aspired to reestablish Persian control. The Sassanid Persians occupied Armenia in 252. However, in 287, Tiridates III the Great was brought to power by the Roman armies. After Gregory the Illuminator
Gregory the Illuminator ( Classical hy, Գրիգոր Լուսաւորիչ, reformed: Գրիգոր Լուսավորիչ, ''Grigor Lusavorich'';, ''Gregorios Phoster'' or , ''Gregorios Photistes''; la, Gregorius Armeniae Illuminator, cu, Svyas ...
's spreading of Christianity in Armenia, Tiridates accepted Christianity and made it his kingdom's official religion. The date of Armenia's conversion to Christianity is traditionally held to be 301, preceding the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
's conversion and the Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan ( la, Edictum Mediolanense; el, Διάταγμα τῶν Μεδιολάνων, ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 AD agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. ( ...
by a dozen years.
In 387, the Kingdom of Armenia was split between the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantino ...
and the Sassanid Empire. Western Armenia first became a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
under the name of Armenia Minor
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and no ...
, and later Byzantine Armenia
Byzantine Armenia, sometimes known as Western Armenia, is the name given to the parts of Kingdom of Armenia that became part of the Byzantine Empire. The size of the territory varied over time, depending on the degree of control the Byzantine ...
; Eastern Armenia
Eastern Armenia ( hy, Արևելյան Հայաստան ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') comprises the eastern part of the Armenian Highlands, the traditional homeland of the Armenian people. Between the 4th and the 20th centuries, Armenia was partitione ...
remained a kingdom within Persia until, in 428, the local nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The character ...
overthrew the king, and the Sassanids installed a ''marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the suffix ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ''Marzbān'') were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension milita ...
'' (governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
) in his place, beginning the Marzpanate period over Persian Armenia
Sasanian Armenia, also known as Persian Armenia and Persarmenia ( hy, Պարսկահայաստան – ''Parskahayastan''), may either refer to the periods in which Armenia ( pal, 𐭠𐭫𐭬𐭭𐭩 – ''Armin'') was under the suzerainty of ...
. Those parts of historical Armenia remained firmly under Persian control until the Muslim conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
The ...
, while the Byzantine parts remained until being conquered, also by invading Arabic armies, in the 7th century. In 885, after years of Roman, Persian, and Arab rule, Armenia regained its independence under the Bagratuni dynasty
The Bagratuni or Bagratid dynasty ( hy, Բագրատունի, ) was an Armenian royal dynasty which ruled the medieval Kingdom of Armenia from c. 885 until 1045. Originating as vassals of the Kingdom of Armenia of antiquity, they rose to bec ...
.
Army
Under Tigranes the Great
The army of the Kingdom of Armenia reached its peak under the reign ofTigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
. According to the author of '' Judith'', his army included chariots and 12,000 cavalrymen, most likely heavy cavalry or cataphract
A cataphract was a form of armored heavy cavalryman that originated in Persia and was fielded in ancient warfare throughout Eurasia and Northern Africa.
The English word derives from the Greek ' (plural: '), literally meaning "armored" or ...
s, a unit also commonly used by Seleucids and Parthians. His army consisted mainly of 120,000 infantrymen and 12,000 mounted archers, also an important feature of the Parthian army
The Parthian army was the army of the Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD). Having no standing army, the Arsacid king mainly relied on his vassal kings, regional and tribal lords, and garrison commanders. Mercenaries were also sometimes used in the ...
. Like the Seleucids, the bulk of Tigranes' army were foot soldiers. The Jewish historian Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
talks of 500,000 men in total, including camp followers. These followers consisted of camels, donkeys, and mules used for baggage, sheep, cattle, and goats for food, said to be stocked in abundance for each man, and hoards of gold and silver. As a result, the marching Armenian army was listed as "a huge, irregular force, too many to count, like locusts or the dust of the earth", not unlike many other enormous Eastern armies of the time. The smaller Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
n, Graeco-Phoenician, and Nabataean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern L ...
armies were generally no match for the sheer number of soldiers, with the organized Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
with its legions eventually posing a much greater challenge to the Armenians.
Note that the numbers given by Israelite historians of the time were probably exaggerated, considering the fact that the Hasmonean Jews lost the war against Tigranes.
Ayrudzi
From ancient times in Armenia there existed "Azatavrear" cavalry which consisted of the Armenian elite. "Azatavrear" cavalry made up the main part of the Armenian king's court. In medieval times "Azatavrear" cavalry were collected from nobles (usually the youngest sons of Armenian lords), and were known as Ayrudzi, or "horsemen." During times of peace, Armenian cavalry were divided into small groups which took the roles of guarding the King and other Armenian lords, as well as their families. Some part of the Armenian cavalry force was always patrolling Armenian borders, under the command of an Armenian general (sparapet). The group of Armenian cavalry whose main mission was the protection of the Armenian king and his family consisted of 6000 heavily armored horsemen in the ancient period, and 3000 horsemen in the medieval period. During times of war, the number of Armenian cavalry would rise, with estimates ranging from 10,000 to at least 20,000 horsemen. Besides heavy cavalry, there was also light cavalry, which primarily consisted of mounted archers.Legio I Armeniaca-Armenian First Legion
"Legio Armeniaca" translates from Latin as "Armenian Legion" and "prima" as "first". The Armenian First Legion was one of the later-period Roman imperial legions. This Legion was mentioned in the late-antique text known asNotitia Dignitatum
The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (Latin for "The List of Offices") is a document of the late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very few surviving documents o ...
. It is most likely that the Armenian First Legion was formed in the 2nd or 3rd century AD, in the western part of the Kingdom, with the mission to protect the lands of Armenia from intrusion. It might first have been the garrison of Armenian lands which had been under the control of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
. The Armenian First Legion took part in the ill-fated Persian campaign of the emperor Julianus Apostata in 363.
Legio II Armeniaca-Armenian Second Legion
"Legio Armeniaca" translates from Latin as "ArmenianLegion
Legion may refer to:
Military
* Roman legion, the basic military unit of the ancient Roman army
* Spanish Legion, an elite military unit within the Spanish Army
* Legion of the United States, a reorganization of the United States Army from 179 ...
" and "Secunda" as "Second". Like the First legion, the Armenian Second Legion was one of the later-period Roman imperial legions. This legion is also mentioned in the Notitia Dignitatum. The Armenian Second Legion was thought to have been created around the end of the 3rd century or in the beginning of the 4th century. The Armenian Second Legion had a permanent camp in one of the Northern provinces of the Orient, and built a camp in Satala. The Armenian Second legion is mentioned in the year 360 AD as a part of the garrison of Bezabda (anciently called Phoencia) in upper Tigris. In Bezabde
Bezabde or Bazabde was a fortress city on the eastern Roman frontier. Located in Zabdicene, it played a role in the Roman-Persian Wars of the 4th century. It was besieged two times in 360, narrated in detail by Ammianus Marcellinus. The Sasanian ...
the Armenian Second Legion served together with the Legions Parthica and II Flavia. In 390 AD Bezabde
Bezabde or Bazabde was a fortress city on the eastern Roman frontier. Located in Zabdicene, it played a role in the Roman-Persian Wars of the 4th century. It was besieged two times in 360, narrated in detail by Ammianus Marcellinus. The Sasanian ...
was taken by the Persian army, and a terrible bloodbath ensued against the inhabitants and garrison. The legion seemed to have survived this battle, because it appears in Notitia Dignitatum, which was written in the 5th century.
Later on, the Armenian Second legion became a part of the Byzantine army.
Mythology and pre-Christian religion
The pre-Christian Armenian pantheon included: * Aramazd - Cognate of the IranianAhura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna'' ...
(or Ormazd
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna''. ...
). Head of the pantheon, identified with Zeus in the ''interpretatio graeca
''Interpretatio graeca'' (Latin, "Greek translation") or "interpretation by means of Greek odels is a discourse used to interpret or attempt to understand the mythology and religion of other cultures; a comparative methodology using ancient G ...
''.
* Amanor and/or Vanatur
Vanatur, is a former village and a neighborhood within the town of Hrazdan, Kotayk Province, Armenia.
See also
*Kotayk Province
Kotayk ( hy, Կոտայք, ), is a province ('' marz'') of Armenia. It is located at the central part of the ...
- God of the Armenian new year, Navasard, at the end of July. His temple was located in Diyadin.
* Anahit
Anahit ( hy, Անահիտ, fa, آناهید) was the goddess of fertility and healing, wisdom and water in Armenian mythology. In early periods she was the goddess of war. By the 5th century BCE she was the main deity in Armenia along with Ar ...
- Cognate of the Iranian Anahita. The goddess of fertility and birth, and daughter or wife of Aramazd, Anahit is identified with Artemis
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Artemis (; grc-gre, Ἄρτεμις) is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. She was heavily identified with ...
and Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols incl ...
. Temples dedicated to Anahit were established in Armavir, Artashat
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of t ...
, Ashtishat
Ashtishat (, ''Aštišat''; Western Armenian: ''Ashdishad'') is a locality and archaeological site in Muş Province of eastern Turkey. It is located near the village of Yücetepe, Muş at 38° 58' 20"N and 41° 27' 04" E on the Murat river east ...
.
* Ara
ARA may refer to:
Media and the arts
* American-Romanian Academy of Arts and Sciences
* '' Artistička Radna Akcija'', compilation album released in former Yugoslavia
* Associate of the Royal Academy, denoting membership in the British Royal Acad ...
''the Beautiful'' - a dying-and-rising god
A dying-and-rising, death-rebirth, or resurrection deity is a religious motif in which a god or goddess dies and is resurrected.Leeming, "Dying god" (2004)Miles 2009, 193 Examples of gods who die and later return to life are most often cited f ...
slain in a war against Semiramis
''Samīrāmīs'', hy, Շամիրամ ''Šamiram'') was the semi-legendary Lydian- Babylonian wife of Onnes and Ninus, who succeeded the latter to the throne of Assyria, according to Movses Khorenatsi. Legends narrated by Diodorus Siculus, who dr ...
.
* Astghik - Cognate of the Semitic Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
. Fertility goddess and consort of Vahagn
Vahagn or Vahakn ( hy, Վահագն), also known as Vahagn Vishapakagh ( hy, Վահագն Վիշապաքաղ, lit=Vahagn the Dragon-reaper, label=none), is a warrior god in Armenian mythology. Scholars consider him to be either the thunder, or s ...
, sharing a temple with him at Derik. The holiday of Vardavar
Vardavar or Vartavar ( hy, Վարդավառ, Homshetsi: ''Vartevor'' or ''Behur'')) is an Armenian festival in Armenia where people drench each other with water. Origin
Vardavar's history dates back to pagan times. The ancient festival is tradi ...
was originally in honor of Astghik.
* Barsamin - God of sky and weather, probably derived from the Semitic god Baal Shamin
Baalshamin ( arc, ܒܥܠ ܫܡܝܢ ''Baʿal Šāmīn'' or ''Bʿel Šmīn'' Blit. "Lord of Heaven ), also called Baal Shamem ( phn, 𐤁𐤏𐤋 𐤔𐤌𐤌 ''Baʿl Šāmēm'') and Baal Shamaim ( he, ''Baʿal Šāmayīm''), was a Northwest Semit ...
.
* Hayk
Hayk ( hy, Հայկ, ), also known as Hayk Nahapet (, , ), is the legendary patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation. His story is told in the '' History of Armenia'' attributed to the Armenian historian Moses of Chorene ( Movses Khorenats ...
- Legendary forefather of the Armenian people, archer
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
, and slayer of the Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
Bel.
* Mihr - Cognate with the Persian Mithra
Mithra ( ae, ''Miθra'', peo, 𐎷𐎰𐎼 ''Miça'') commonly known as Mehr, is the Iranian deity of covenant, light, oath, justice and the sun. In addition to being the divinity of contracts, Mithra is also a judicial figure, an all-seein ...
. God of the sun and light, son of Aramazd, the brother of Anahit
Anahit ( hy, Անահիտ, fa, آناهید) was the goddess of fertility and healing, wisdom and water in Armenian mythology. In early periods she was the goddess of war. By the 5th century BCE she was the main deity in Armenia along with Ar ...
and Nane. His center of worship was located in Bagaharich, and the temple of Garni was dedicated to him.
* Nane - Possible cognate of the Sumerian Nanaya
Nanaya ( Sumerian , DNA.NA.A; also transcribed as "Nanāy", "Nanaja", "Nanāja", '"Nanāya", or "Nanai"; antiquated transcription: "Nanâ"; in Greek: ''Ναναια'' or ''Νανα''; Aramaic: ''ננױננאױ;'' Syriac: ܢܢܝ) was a Mesopo ...
. Daughter of Aramazd, war and motherhood goddess. Her cult was related to Anahit
Anahit ( hy, Անահիտ, fa, آناهید) was the goddess of fertility and healing, wisdom and water in Armenian mythology. In early periods she was the goddess of war. By the 5th century BCE she was the main deity in Armenia along with Ar ...
, both of their temples located near each other in Gavar
Gavar ( hy, Գավառ) is a town and urban municipal community in Armenia serving as the administrative centre of Gegharkunik Province. It is situated among the high mountains of Gegham range to the west of Lake Sevan, with an average height ...
.
* Tir or Tiur - God of wisdom, culture, science and studies, he also was an interpreter of dreams. He was the messenger of the gods and was associated with Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
. Tir's temple was located near Artashat
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of t ...
.
* Tsovinar - Also called Nar, she was the goddess of rain, sea and water, though she was actually a fiery being who forced rain to fall.
* Vahagn
Vahagn or Vahakn ( hy, Վահագն), also known as Vahagn Vishapakagh ( hy, Վահագն Վիշապաքաղ, lit=Vahagn the Dragon-reaper, label=none), is a warrior god in Armenian mythology. Scholars consider him to be either the thunder, or s ...
- Cognate of the Iranian Verethragna
Verethragna ( ae, 𐬬𐬆𐬭𐬆𐬚𐬭𐬀𐬖𐬥𐬀 ') is an Indo-Iranian deity.
The neuter noun ''verethragna'' is related to Avestan ''verethra'', 'obstacle' and ''verethragnan'', 'victorious'. Representing this concept is the divin ...
. The storm god and herculean dragon slayer. Derik housed the central temple to Vahagn.
During the 1st century AD, Christianity spread through Armenia due to (according to legend) the efforts of the apostles Bartholomew
Bartholomew (Aramaic: ; grc, Βαρθολομαῖος, translit=Bartholomaîos; la, Bartholomaeus; arm, Բարթողիմէոս; cop, ⲃⲁⲣⲑⲟⲗⲟⲙⲉⲟⲥ; he, בר-תולמי, translit=bar-Tôlmay; ar, بَرثُولَماو� ...
and Thaddeus
Thaddeus (Latin ''Thaddaeus'', Ancient Greek Θαδδαῖος ''Thaddaĩos'', from Aramaic תדי ''Ṯaday'') is a male given name.
As of the 1990 Census, ''Thaddeus'' was the 611th most popular male name in the United States, while ''Thad' ...
. After persecutions by kings Sanatruk
Sanatruk ( hy, Սանատրուկ, Latinized as ''Sanatruces'') was a member of the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia who succeeded Tiridates I of Armenia as King of Armenia at the end of the 1st century. He was also King of Osroene (reigned 91–109 ...
, Axidares
Axidares or Ashkhadar also known as Exedares or Exedates (flourished second half of the 1st century & first half of the 2nd century, died 113) was a Parthian Prince who served as a Roman Client King of Armenia.
Axidares was one of the three son ...
, Khosrov I, and Tiridates III, Christianity was adopted as the state religion by Tiridates III after he was converted by Gregory the Illuminator
Gregory the Illuminator ( Classical hy, Գրիգոր Լուսաւորիչ, reformed: Գրիգոր Լուսավորիչ, ''Grigor Lusavorich'';, ''Gregorios Phoster'' or , ''Gregorios Photistes''; la, Gregorius Armeniae Illuminator, cu, Svyas ...
. Armenia's adoption of Christianity as the state religion (the first country to do so) distinguished it from Parthian and Mazdaen influence.
Zoroastrianism
Until the late Parthian period, Armenia was a predominantly Zoroastrian-adhering land. With the advent of Christianity, both paganism and Zoroastrianism gradually started to diminish. The founder of the Arsacid branch in Armenia, Tiridates I was a Zoroastrian priest or magus. A noted episode which illustrates the observance by the Armenian Arsacids is the famous journey of Tiridates I to Rome in A.D. 65–66. With the adoption of Christianity in the early 4th century, Zoroastrianism's influence in the kingdom gradually started to decline.Literature
Little is known about pre-Christian Armenian literature. Many literature pieces known to us were saved and then presented to us by Moses of Chorene. This is a pagan Armenian song, telling about the birth ofVahagn
Vahagn or Vahakn ( hy, Վահագն), also known as Vahagn Vishapakagh ( hy, Վահագն Վիշապաքաղ, lit=Vahagn the Dragon-reaper, label=none), is a warrior god in Armenian mythology. Scholars consider him to be either the thunder, or s ...
:
Armenian version
Language
Before theArmenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet ( hy, Հայոց գրեր, ' or , ') is an alphabetic writing system used to write Armenian. It was developed around 405 AD by Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader. The system originally ha ...
was created, Armenians used the Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
and Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as ...
s, the last of which had a great influence on the Armenian alphabet.
The Armenian alphabet was created by Saint Mesrop Mashtots Mesrob or Mesrop ( hy, Մեսրոպ) is an Armenian given name.
Mesrob / Mesrop may refer to:
* Mesrop Mashtots, also Saint Mesrop, Armenian monk, theologian and linguist. Inventor of the Armenian alphabet
** Mesrop Mashtots Institute of Ancient M ...
and Isaac of Armenia
Isaac or Sahak of Armenia (354–439) was Catholicos of All Armenians, Catholicos (or Patriarch) of the Armenian Apostolic Church. He is sometimes known as "Isaac the Great," and as "Sahak the Parthian" (Armenian language, Armenian: Սահակ � ...
(Sahak Partev) in AD 405, primarily for a Bible translation
The Bible has been translated into many languages from the biblical languages of Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek. all of the Bible has been translated into 724 languages, the New Testament has been translated into an additional 1,617 languages, and ...
into the Armenian language
Armenian (Classical Armenian orthography, classical: , Armenian orthography reform, reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia ...
. Traditionally, the following phrase translated from Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
's ''Book of Proverbs
The Book of Proverbs ( he, מִשְלֵי, , "Proverbs (of Solomon)") is a book in the third section (called Ketuvim) of the Hebrew Bible and a book of the Christian Old Testament. When translated into Greek and Latin, the title took on differen ...
'' is said to be the first sentence to be written down in Armenian by Mashtots:
 By the 2nd century BC, according to
By the 2nd century BC, according to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, the inhabitants of Greater Armenia spoke the Armenian language
Armenian (Classical Armenian orthography, classical: , Armenian orthography reform, reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia ...
, implying that modern Armenians descended from that population.
Capitals
*Yervandashat
Yervandashat or Eruandashat ( hy, Երվանդաշատ), was an Armenian city and one of the 13 historic capitals of Armenia, serving as a capital city between 210 and 176 BC during the Orontid rule over Armenia and the beginning of their succes ...
– The ancient town sits upon an escarpment overlooking the junction of the Arax River and Akhurian River
The Akhuryan ( hy, Ախուրյան ''Axuryan''; xcl, Ախուրեան ''Axurean''; russian: Арпачай or Ахурян), or Arpachay ( tr, Arpaçay) is a river in the South Caucasus. It originates in Armenia and flows from Lake Arpi, al ...
. According to Movses Kaghankatvatsi Movses Kaghankatvatsi ( hy, Մովսէս Կաղանկատուացի ''Movses Kaġankatvac’i''), or Movses Daskhurantsi ( ''Movses Dasxuranc’i'') is the reputed author (or authors) of a tenth-century Classical Armenian historiographical work on C ...
, Orontes IV founded Yervandashat to replace Armavir as his capital after Armavir had been left dry by a shift of the Arax. The archaeological site has not been subject of major research, but fortifications and some remains of palaces have been uncovered. Ancient Yervandashat was destroyed by the army of the Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
n King Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian King of Kings ( Shahanshah) of Iran. The longest-reigning monarch in Iranian history, he reign ...
in the 360s.
* Artashat
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of t ...
– King Artashes I founded Artashat in 185 BC in the region of Vostan within the historical province of Ayrarat
Ayrarat () was the central province of the ancient kingdom Armenia, located in the plain of the upper Aras River. Most of the historical capitals of Armenia were located in this province, including Armavir, Yervandashat, Artashat, Vagharshapat, ...
(Ararat), at the point where the Araks river was joined by the Metsamor river during the ancient era, near the heights of Khor Virap
Khor Virap ( hy, Խոր Վիրապ, lit=deep dungeon) is an Armenian monastery located in the Ararat Plain in Armenia, near the border with Turkey, about south of Artashat, Ararat Province, within the territory of ancient Artaxata. The monaster ...
. The story of the foundation is given by the Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi of the 5th century: "Artashes traveled to the location of the confluence of the Yeraskh
Yeraskh ( hy, Երասխ, formerly, Arazdayan) is a village in the Ararat Province of Armenia. Yeraskh is the closest Armenian village to the closed border with Azerbaijan. The settlement is adjacent to Heydarabad, Azerbaijan across the borde ...
and Metsamor
Metsamor ( hy, Մեծամոր, ), is a town and urban municipal community in the Armavir Province of Armenia. It is famous for being home to Armenia's Metsamor Nuclear Power Plant, the only nuclear plant in the Transcaucasian region. As of the ...
ivers Ivers is the Name of the following people:
* Donald L. Ivers (born 1941), former judge of the United States Court of Appeals for Veterans Claims
*Eileen Ivers
Eileen Ivers (born July 13, 1965) is an American fiddler.
Ivers was born in New Yor ...
and taking a liking to the position of the hills (adjacent to Mount Ararat
Mount Ararat or , ''Ararat''; or is a snow-capped and dormant compound volcano in the extreme east of Turkey. It consists of two major volcanic cones: Greater Ararat and Little Ararat. Greater Ararat is the highest peak in Turkey and th ...
), he chose it as the location of his new city, naming it after himself." Movses Khorenatsi. '' History of Armenia, 5th Century'' (''Հայոց Պատմություն, Ե Դար''). Annotated translation and commentary by Stepan Malkhasyants
Stepanos Sargsi Malkhasiants ( hy, Ստեփան Սարգսի Մալխասյանց; – July 21, 1947) was an Armenian academician, philologist, linguist, and lexicographer. An expert in classical Armenian literature, Malkhasiants wrote the ...
. Gagik Sargsyan
Gagik Sargsyan ( hy, Գագիկ Խորենի Սարգսյան; 6 April 1926, in Yerevan – 25 August 1998, in Yerevan) was an Armenian historian, who served as the vice president of the Armenian Academy of Sciences.
Biography
He studied at Yer ...
(ed.) Yerevan: Hayastan Publishing, 1997, 2.49, p. 164. . According to the accounts given by Greek historians Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
and Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, Artashat is said to have been chosen and developed on the advice of the Carthaginian general Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Pu ...
. The city's strategic position in the Araks valley on the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
soon made Artashat a centre of bustling economic activity and thriving international trade, linking Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
with the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
and Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. Its economic wealth can be gauged in the numerous bathhouses, markets, workshops, and administrative buildings that sprang up during the reign of Artashes I. The city had its own treasury and customs. The amphitheatre of Artashat was built during the reign of king Artavasdes II (55–34 BC). The remains of the huge walls surrounding the city built by King Artashes I can still be found in the area. After losing its status as a capital, Artashat gradually lost its significance.
* Tigranakert was founded by the Armenian emperor Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
in the 1st century BC. Tigranakert was founded as the new capital of the Armenian Empire in order to be in a more central position within the boundaries of the expanding empire. Its population was 120,000 and it also had many temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
s and an amphitheater
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ...
.
* Vagharshapat
Vagharshapat ( hy, Վաղարշապատ ) is the 4th-largest city in Armenia and the most populous municipal community of Armavir Province, located about west of the capital Yerevan, and north of the closed Turkish-Armenian border. It is c ...
– In the first half of the 1st century, during the reign of the Armenian Arshakuni king Vologases I (Vagharsh I) (117–144), the old town of Vardgesavan was renovated and renamed Vaghasrhapat (Վաղարշապատ), which still persists as the official appellation of the city. The original name, as preserved by Byzantine historian Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gen ...
(''Persian Wars''), was Valashabad—"Valash/Balash city" named after king Balash/Valash/Valarsh of Armenia. The name evolved into its later form by the shift in the medial L into a Gh, which is common in Armenian language
Armenian (Classical Armenian orthography, classical: , Armenian orthography reform, reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia ...
. Khorenatsi mentions that the town of Vardges was totally rebuilt and fenced by Vagharsh I, eventually becoming known as Noarakaghak (The New City) or Vagharshapat. The city served as a capital for the Ashakuni Kingdom of Armenia between 120 and 330 AD and remained the country's most important city until the end of the 4th century. When Christianity became the state religion of Armenia, Vagharshapat was eventually called Ejmiatsin (or Etchmiadzin), after the name of the Mother Cathedral. Starting in 301, the city became the spiritual centre of the Armenian nation, home to the Armenian Catholicosate, one of the oldest religious organizations in the world. Vagharshapat was home to one of the oldest schools established by Saint Mashtots and the home of the first manuscripts library in Armenia founded in 480 AD. Starting in the 6th century, the city slowly lost its importance—especially after the transfer of the seat of the Catholicosate to Dvin in 452—until the foundation of the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia
The Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia, also known as Bagratid Armenia ( xcl, Բագրատունեաց Հայաստան, or , , 'kingdom of the Bagratunis'), was an independent Armenian state established by Ashot I Bagratuni of the Bagratuni dynasty ...
in 885. After the fall of the Bagratid dynasty in 1045, the city gradually became an insignificant place until 1441, when the seat of the Armenian Catholicosate was transferred from the Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
n town of Sis back to Etchmiadzin.
* Dvin – The ancient city of Dvin was built by Khosrov III the Small
Khosrov III the Small ( hy, Խոսրով Գ Կոտակ, ''Khosrov III Kotak''; ''Kotak'' means "little, short, small") was the king of Arsacid Armenia .
Khosrov was the son and successor of King Tiridates III. Khosrov received the epithet ''Ko ...
in 335 on the site of an ancient settlement and fortress from the 3rd millennium BC. Since then the city had been used as the primary residence of the Armenian kings of the Arshakuni dynasty. Dvin had a population of about 100,000 citizens of various professions including arts and crafts, trade, fishing, etc. After the fall of the Armenian Kingdom in 428, Dvin became the residence of Sassanid-appointed ''marzpans'' (governors), Byzantine ''kouropalates'' and later Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
and Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
-appointed ''ostikans'' (governors), all of whom were of senior nakharar
''Nakharar'' ( hy, նախարար ''naxarar'', from Parthian ''naxvadār'' "holder of the primacy""նախարար" in H. Ačaṙean (1926–35), ''Hayerēn Armatakan Baṙaran'' (Yerevan: Yerevan State University), 2nd ed., 1971–79) was a here ...
stock. In 640 Dvin was the center of the emirate of Armenia.
Political geography
The Kingdom of Armenia was bordered byCaucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among t ...
in the east, Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese language, Aragonese and Occitan language, Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a pe ...
in the north, the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
in the west, and Parthia, later succeeded by Sassanian Empire, in the south. The border between Iberia and the Kingdom of Armenia was the Kur River, which was also the border between Caucasian Albania and Kingdom of Armenia.
After 331 BC, Armenia was divided into Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
(a region of the Kingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( grc-gre, Πόντος ) was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus (region), Pontus and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty (of Persian people, Persian origin), which possibly may have been di ...
), the Kingdom of Armenia (corresponding to Armenia Major) and the Kingdom of Sophene
The Kingdom of Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopʻkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnḗ), was a Hellenistic-era political entity situated between ancient Armenia and Syria. Ruled by the Orontid dynasty, the kingdom was culturally mixed ...
. In 189 BC when Artashes I
Artaxias I (from gr, Άρταξίας; in hy, Արտաշէս, translit=Artašēs) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling d ...
's reign began, many neighboring countries (Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
, Caucasian Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages ...
, Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
) exploiting the weakened state of the kingdom, conquered its remote regions. Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
says that Artaxias I campaigned in the east and reunited Caspiane Caspiane or Kaspiane ( gr, Κασπιανή, hy, Կասպք ''Kaspkʿ'') was the land populated by the tribe of Caspians, after whom it received its name. Originally a province of the Medes in the 3rd-2nd centuries BC, the land of the Caspians was ...
and Paytakaran
Paytakaran ( hy, Փայտակարան, translit=Pʻaytakaran) was the easternmost province ( or ) of the Kingdom of Armenia. The province was located in the area of the lower courses of the Kura and Arax rivers, adjacent to the Caspian Sea. It ...
, then campaigned in the north, defeated the Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amon ...
, reuniting Gugark
Gugark ( hy, Գուգարք, lat, Gogarene, Greek: ''Γογαρινή'') was the 13th province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia. It now comprises parts of northern Armenia, northeast Turkey, and southwest Georgia.
Etymology
Etymologically ...
(Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
also notes that Iberia recognized themselves as vassals of the Kingdom of Armenia at this time), to the west, reuniting Karin, Ekeghik and Derjan and to the south, where, after many battles with the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, he reunited Tmorik. Artaxias I was not able to reunite Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
, Corduene
Corduene hy, Կորճայք, translit=Korchayk; ; romanized: ''Kartigini'') was an ancient historical region, located south of Lake Van, present-day eastern Turkey.
Many believe that the Kardouchoi—mentioned in Xenophon’s Anabasis as havin ...
, and Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
, something completed by his grandson Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
. At its peak, under Tigranes the Great, it incorporated, besides Armenia Major, Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese language, Aragonese and Occitan language, Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a pe ...
, Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
, Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
, Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
, Armenian Mesopotamia
Armenian Mesopotamia was a region in Northern Mesopotamia that was inhabited partly by Armenians. Tigranes the Great seized Northern Mesopotamia,The city of the Moon god: religious traditions of Harran By Tamara M. Green - Page 46 and from 401 BC ...
, Osroene
Osroene or Osrhoene (; grc-gre, Ὀσροηνή) was an ancient region and state in Upper Mesopotamia. The ''Kingdom of Osroene'', also known as the "Kingdom of Edessa" ( syc, ܡܠܟܘܬܐ ܕܒܝܬ ܐܘܪܗܝ / "Kingdom of Urhay"), according to ...
, Adiabene
Adiabene was an ancient kingdom in northern Mesopotamia, corresponding to the northwestern part of ancient Assyria. The size of the kingdom varied over time; initially encompassing an area between the Zab Rivers, it eventually gained control of N ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
, Commagene
Commagene ( grc-gre, Κομμαγηνή) was an ancient Greco-Iranian kingdom ruled by a Hellenized branch of the Iranian Orontid dynasty that had ruled over Armenia. The kingdom was located in and around the ancient city of Samosata, which s ...
, Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
, Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous so ...
and Atropatene
Atropatene ( peo, Ātṛpātakāna; grc, Ἀτροπατηνή), also known as Media Atropatene, was an ancient Iranian kingdom established in by the Persian satrap Atropates. The kingdom, centered in present-day northern Iran, was ruled by A ...
. Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
and also some Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
tribes were vassals of Tigranes the Great.
Provinces

 The 15 provinces of the Kingdom of Armenia with their capitals are as follows:
*
The 15 provinces of the Kingdom of Armenia with their capitals are as follows:
* Upper Armenia
Upper Armenia ( hy, Բարձր Հայք ''Bardzr Hayq'') was the first province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in present-day Turkey, roughly corresponding to the modern province of Erzincan, to the west of the Kura River. Within th ...
( Garin)
* Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro ...
(Arsamosata
Arsamosata ( Middle Persian ''*Aršāmšād''; Old Persian ''*Ṛšāma-šiyāti-'', grc, Ἀρσαμόσατα, ) was an ancient and medieval city situated on the bank of the Murat River, near the present-day city of Elâzığ. It was founded ...
)
* Aghdznik
Arzanene ( el, Ἀρζανηνή) or Aghdznik () was a historical region in the southwest of the ancient kingdom of Armenia. It was ruled by one of the four ''bdeashkhs'' (''bidakhsh'', ''vitaxa'') of Armenia, the highest ranking nobles below t ...
( Tigranakert)
* Turuberan (Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and th ...
)
* Corduene
Corduene hy, Կորճայք, translit=Korchayk; ; romanized: ''Kartigini'') was an ancient historical region, located south of Lake Van, present-day eastern Turkey.
Many believe that the Kardouchoi—mentioned in Xenophon’s Anabasis as havin ...
( Pinik)
* Moxoene (Moks
Moxoene or Mokk' ( hy, Մոկք, translit=Mokkʿ, ku, Miks) was a territory of Kingdom of Armenia and later Sasanian Armenia, located east of Arzanene from south of Lake Van to north of Bohtan river. The territory was ruled by a local dynasty.
...
)
* Nor Shirakan
Nor Shirakan ( hy, Նոր Շիրական), Parskahayk ( hy, Պարսկահայք) or Persarmenia, was the seventh province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, situated on the western shore of Lake Urmia, bordered on Adiabene and Atropatene, now i ...
(Her
Her is the objective and possessive form of the English-language feminine pronoun she.
Her, HER or H.E.R. may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Music
* H.E.R. (born 1997), American singer
** ''H.E.R.'' (album), 2017
* HIM (Finnish ...
)
* Vaspurakan
Vaspurakan (, Western Armenian pronunciation: ''Vasbouragan'') was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now southeast ...
(Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
)
* Syunik (Baghaberd
Baghaberd ( hy, Բաղաբերդ; also David Bek's Castle) is a 4th to 12th century Armenian fortress located along a ridge overlooking the Voghji River, northwest of the village of Kapan in the Syunik Province of Armenia. Baghaberd is at an ele ...
)
* Artsakh (Shusha
/ hy, Շուշի
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = ShushaCollection2021.jpg
, image_caption = Landmarks of Shusha, from top left:Ghazanchetsots Cathedral • Yukhari Govha ...
)
* Paytakaran
Paytakaran ( hy, Փայտակարան, translit=Pʻaytakaran) was the easternmost province ( or ) of the Kingdom of Armenia. The province was located in the area of the lower courses of the Kura and Arax rivers, adjacent to the Caspian Sea. It ...
(Paytakaran
Paytakaran ( hy, Փայտակարան, translit=Pʻaytakaran) was the easternmost province ( or ) of the Kingdom of Armenia. The province was located in the area of the lower courses of the Kura and Arax rivers, adjacent to the Caspian Sea. It ...
)
* Utik
Utik ( hy, Ուտիք, also known as Uti, Utiq, or Outi) was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia. It was ceded to Caucasian Albania following the partition of Armenia between Sassanid Persia and the Eastern Roman Empire in 387 AD. Most ...
( Partav)
* Gugark
Gugark ( hy, Գուգարք, lat, Gogarene, Greek: ''Γογαρινή'') was the 13th province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia. It now comprises parts of northern Armenia, northeast Turkey, and southwest Georgia.
Etymology
Etymologically ...
(Ardahan
Ardahan (, ka, არტაანი, tr, hy, Արդահան, translit=Ardahan Russian: Ардаган) is a city in northeastern Turkey, near the Georgian border.
It is the capital of Ardahan Province.
History
Ancient and medieval
Ardaha ...
)
* Tayk (Olti
Oltu (; ) is a town and district of Erzurum Province in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey. The mayor is Necmettin Taşçı, from the AKP. The population was 31,087 in 2020.
History
An inscription found in Oltu’s castle has been dated to the ...
)
* Ayrarat
Ayrarat () was the central province of the ancient kingdom Armenia, located in the plain of the upper Aras River. Most of the historical capitals of Armenia were located in this province, including Armavir, Yervandashat, Artashat, Vagharshapat, ...
( Armavir)
Other Armenian regions:
* Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
(Nikopolis
Nicopolis ( grc-gre, Νικόπολις, Nikópolis, City of Victory) or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus Vetus. It was located in the western part of the modern state of Greece. The city was founded in 29 ...
)
* Armenian Mesopotamia
Armenian Mesopotamia was a region in Northern Mesopotamia that was inhabited partly by Armenians. Tigranes the Great seized Northern Mesopotamia,The city of the Moon god: religious traditions of Harran By Tamara M. Green - Page 46 and from 401 BC ...
(Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroe ...
)
Maps
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* M. Chahin, ''The Kingdom of Armenia'' (1987, reissued 1991) *Vahan Kurkjian
Vahan M. Kurkjian ( hy, Վահան Մ. Քուրքջյան; 1863–1961) was an Armenian author, historian, teacher, and community leader.
In 1904, in Cairo, he published the Armenian newspaper ''Loussaper'' (''The Morning Star''), in the pag ...
, ''Tigran the Great'' (1958)
* Ashkharbek Kalantar, ''Armenia: From the Stone Age to the Middle Ages,'' Civilisations du Proche Orient, Série 1, Vol. 2, Recherches et Publications, Neuchâtel, Paris, 1994;
* Ashkharbek Kalantar, ''The Mediaeval Inscriptions of Vanstan, Armenia,'' Civilisations du Proche-Orient: Series 2 – Philologie – CDPOP 2, Vol. 2, Recherches et Publications, Neuchâtel, Paris, 1999;
* Ashkharbek Kalantar, ''Materials on Armenian and Urartian History'' (with a contribution by Mirjo Salvini), Civilisations du Proche-Orient: Series 4 – Hors Série – CPOHS 3, Neuchâtel, Paris, 2004;
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Armenia, Kingdom Of Seleucid Empire successor states Roman Anatolia Ancient history of Georgia (country) Ancient history of Turkey Ancient history of Azerbaijan Christian states