Armée de l'Air on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The French Air and Space Force (AAE) (french: Armée de l'air et de l'espace, ) is the



 Military aeronautics was established as a "special arm" by the law of 8 December 1922. It remained under the auspices of the
Military aeronautics was established as a "special arm" by the law of 8 December 1922. It remained under the auspices of the
 After 1945, France rebuilt its aircraft industry. The French Air Force participated in several colonial wars during the Empire such as French Indochina after the Second World War. Since 1945, the French Air Force was notably engaged in Indochina (1945–1954).
The French Air Force was active in
After 1945, France rebuilt its aircraft industry. The French Air Force participated in several colonial wars during the Empire such as French Indochina after the Second World War. Since 1945, the French Air Force was notably engaged in Indochina (1945–1954).
The French Air Force was active in  Accordingly, from 1962, the French political leadership shifted its military emphasis to nuclear deterrence, implementing a complete reorganisation of the Air Force, with the creation of four air regions and seven major specialised commands, among which were the Strategic Air Forces Command, COTAM, the Air Command of Aerial Defense Forces (, CAFDA), and the (FATac). In 1964, the Second Tactical Air Command was created in Nancy to take command of air units stationed in France but not assigned to
Accordingly, from 1962, the French political leadership shifted its military emphasis to nuclear deterrence, implementing a complete reorganisation of the Air Force, with the creation of four air regions and seven major specialised commands, among which were the Strategic Air Forces Command, COTAM, the Air Command of Aerial Defense Forces (, CAFDA), and the (FATac). In 1964, the Second Tactical Air Command was created in Nancy to take command of air units stationed in France but not assigned to  CFAS had two squadrons of S2 and S-3 IRBMs at the Plateau d'Albion, six squadrons of Mirage IVAs (at Mont de Marsan, Cazaux, Orange, Istres, St Dizier, and EB 3/94 at Luxeuil - Saint-Sauveur Air Base), and three squadrons of C-135F, as well as a training/reconnaissance unit, CIFAS 328, at Bordeaux. The tactical air command included wings EC 3, EC 4, EC 7, EC 11, EC 13, and ER 33, with a total of 19 squadrons of Mirage III, Jaguars, two squadrons flying the
CFAS had two squadrons of S2 and S-3 IRBMs at the Plateau d'Albion, six squadrons of Mirage IVAs (at Mont de Marsan, Cazaux, Orange, Istres, St Dizier, and EB 3/94 at Luxeuil - Saint-Sauveur Air Base), and three squadrons of C-135F, as well as a training/reconnaissance unit, CIFAS 328, at Bordeaux. The tactical air command included wings EC 3, EC 4, EC 7, EC 11, EC 13, and ER 33, with a total of 19 squadrons of Mirage III, Jaguars, two squadrons flying the 
 The French Air Force entered a phase of inventory replacement and expansion. The Air Force ordered the Airbus A400M military transport aircraft, then in development. By November 2016, 11 had already been delivered to ET00.061 at Orleans-Bricy, and integration of the new
The French Air Force entered a phase of inventory replacement and expansion. The Air Force ordered the Airbus A400M military transport aircraft, then in development. By November 2016, 11 had already been delivered to ET00.061 at Orleans-Bricy, and integration of the new  On 13 July 2019, President Emmanuel Macron announced the creation of a space command, which would come into being within the French Air Force by September 2019, and the transformation of the French Air Force into the French Air and Space Force. According to Defense Minister
On 13 July 2019, President Emmanuel Macron announced the creation of a space command, which would come into being within the French Air Force by September 2019, and the transformation of the French Air Force into the French Air and Space Force. According to Defense Minister
. Site de l'Armée de l'air accessed 16 November 2015. The problems caused by having the aircraft maintenance units not responsible to the flying squadrons they supported eventually forced the change. Four were reformed in the first phase: * at
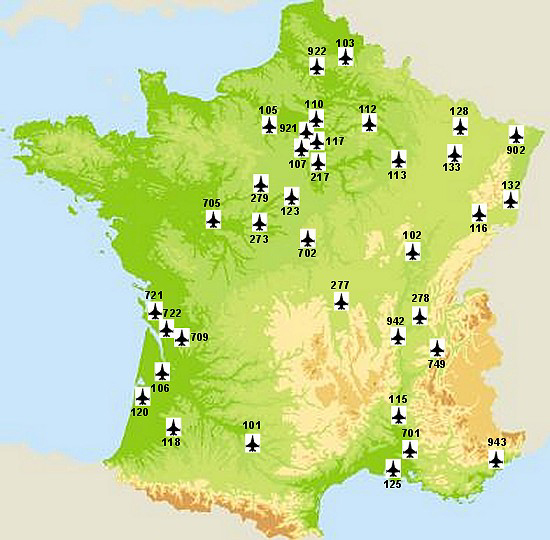 Flying activity in France is carried out by a network of bases, platforms and French air and space defence radar systems. It is supported by bases, which are supervised and maintained by staff, operational centres, warehouses, workshops, and schools. Both in France and abroad, bases have similar infrastructure to provide standardised support.
The French Air and Space Force has, as of 1 August 2014:
* Within the metropolitan territory of France, 27 airbases, out of the which 18 aeronautical platform with perceived runways and 5 Bases non-platform, two schools, 3 air detachments and " one attached air element " (EAR).
* Beyond the metropole/Europe, 7 Aerial Bases or permanent detachments in overseas or country.
Flying activity in France is carried out by a network of bases, platforms and French air and space defence radar systems. It is supported by bases, which are supervised and maintained by staff, operational centres, warehouses, workshops, and schools. Both in France and abroad, bases have similar infrastructure to provide standardised support.
The French Air and Space Force has, as of 1 August 2014:
* Within the metropolitan territory of France, 27 airbases, out of the which 18 aeronautical platform with perceived runways and 5 Bases non-platform, two schools, 3 air detachments and " one attached air element " (EAR).
* Beyond the metropole/Europe, 7 Aerial Bases or permanent detachments in overseas or country.

 Some French airbases house radar units (e.g. Lyon, Mont-Verdun, Drachenbronn, Cinq-Mars-la-Pile, Nice, Mont-Agel) to carry out air defence radar surveillance and air traffic control. Others house material warehouses or command posts. Temporary and semi-permanent foreign deployments include transport aircraft at Dushanbe ( Tajikistan, Operation Héraclès), and fighter aircraft in
Some French airbases house radar units (e.g. Lyon, Mont-Verdun, Drachenbronn, Cinq-Mars-la-Pile, Nice, Mont-Agel) to carry out air defence radar surveillance and air traffic control. Others house material warehouses or command posts. Temporary and semi-permanent foreign deployments include transport aircraft at Dushanbe ( Tajikistan, Operation Héraclès), and fighter aircraft in  * BA 105
* BA 105
Rafale replaced the
File:French Mirage 2000 finishes refueling from KC-10A 2009-12-06.JPG, Mirage 2000C
File:Mirage 2000D (26432497715).jpg, Mirage 2000D
File:Rafale RIAT 2016 3468.jpg, Rafale C
File:Boeing E-3F Sentry (8).jpg, E-3F Sentry
File:Transall C-160R R213 64-GM (9410577524).jpg, Transall C-160R
File:A400M - RIAT 2010 (6703188983).jpg, A400M
File:Airbus A330 MRTT F-UJCG - French Air Force.jpg, A330 MRTT
File:HERCULES C-130 FRENCH AIR FORCE (50111092793).jpg, C-130J
File:Boeing C-135FR Stratotanker France - Air Force, RHE Reims (Champagne), France PP1246782647.jpg, C-135FR
 Since the end of the Algerian War, the French Air and Space Force has comprised about 17 to 19% of the French Armed Forces. In 1990, at the end of the Cold War, numbers reached 56,400 military personnel under contract, out of which 36,300 were part of conscription and 5,400 civilians.Bilan social 90, Editor : Direction de la fonction militaire et du personnel civil, 1990, total pages 62, passage 6 to
Since the end of the Algerian War, the French Air and Space Force has comprised about 17 to 19% of the French Armed Forces. In 1990, at the end of the Cold War, numbers reached 56,400 military personnel under contract, out of which 36,300 were part of conscription and 5,400 civilians.Bilan social 90, Editor : Direction de la fonction militaire et du personnel civil, 1990, total pages 62, passage 6 to
format=PDF
In 2008, forecasts for personnel of the French Air Force were expected to number 50,000 out of which 44,000 aviators on the horizon in 2014. In 2010, the number personnel of the French Air Force was reduced to 51,100 men and women (20%) out of which: 13% officers; 55% sous-officier; 29% air military technicians (MTA); 3% volunteers of national service and aspirant volunteers; 6,500 civilians (14%). They form several functions: ; Non-flying personnel Non-navigating personnel of the French Air and Space Force include and are not limited to : Systems Aerial Mechanics (french: mécanicien système aéronautique), Aerial Controllers (french: contrôleur aérien),
 Officers, within their recruitment and future specialty, are trained at:
*
Officers, within their recruitment and future specialty, are trained at:
*
Official website
* *
appendix of the budget bill for 2006,
air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
and space force of the French Armed Forces. It was the first military aviation force in history, formed in 1909 as the , a service arm of the French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
; it became an independent military branch in 1934 as the French Air Force. On 10 September 2020, it assumed its current name, the French Air and Space Force, to reflect an "evolution of its mission" into the area of outer space.
The number of aircraft in service with the French Air and Space Force varies depending on the source; the Ministry of Armed Forces gives a figure of 658 aircraft in 2014. According to 2018 data, this figure includes 210 combat aircraft: 115 Dassault Mirage 2000
The Dassault Mirage 2000 is a French multirole, single-engine, fourth-generation jet fighter manufactured by Dassault Aviation. It was designed in the late 1970s as a lightweight fighter to replace the Mirage III for the French Air Force (''A ...
and 95 Dassault Rafale
The Dassault Rafale (, literally meaning "gust of wind", and "burst of fire" in a more military sense) is a French twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter aircraft designed and built by Dassault Aviation. Equipped with a wide range ...
. As of 2021, the French Air and Space Force employs a total of 40,500 regular personnel, with a reserve element of 5,187 in 2014.
The Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force (CEMAAE) is a direct subordinate of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA), a high-ranking military officer who in turn answers to the civilian Minister of the Armed Forces.
History
In the beginning
Establishment of the
The founding of the began in 1909, when the French War Minister approved the purchase of a Wright Biplane. The following year, another Wright biplane, a Bleriot, and twoFarman
Farman Aviation Works (french: Avions Farman) was a French aircraft company founded and run by the brothers Richard, Henri, and Maurice Farman. They designed and constructed aircraft and engines from 1908 until 1936; during the French national ...
s were added to the lone acquisition. On 22 October 1910, General Pierre Roques was appointed Inspector General of what was becoming referred to as the Cinquieme Arme, or Fifth Service.''Over the Front: The Complete Record of the Fighter Aces and Units of the United States and French Air Services, 1914–1918'', p. 84
In March 1912, the French parliament enacted legislation to establish the air arm. It was projected to consist of three distinct branches based on aircraft missions—reconnaissance, bombing, or countering other aircraft.
Inventing the fighter plane
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
was one of the first states to start building aircraft. At the beginning of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, France had a total of 148 planes (eight from French Naval Aviation ()) and 15 airships.''History of light aviation of the French Army 1794–2008'', Lavauzelle, Collection of History, Memory and Patrimony, Général André Martini, 2005, Paris, pages 36,42,
In August 1914, as France entered World War I, French airpower consisted of 24 squadrons () supporting ground forces, including three squadrons assigned to cavalry units. By 8 October, expansion to 65 squadrons was being planned. By December, the plans called for 70 new squadrons.
Meanwhile, even as procurement efforts scaled up, inventive airmen were trying to use various light weapons against opposing airplanes. Roland Garros invented a crude method of firing a machine gun through the propeller arc by cladding his propeller with metal wedges deflecting any errant bullets. After destroying three German airplane, Garros came down behind enemy lines on 18 April 1915. His secret weapon was thus exposed, and Anthony Fokker came up with the synchronization gear that by July 1, 1915, that turned airplanes into flying gun platforms.''Over the Front: The Complete Record of the Fighter Aces and Units of the United States and French Air Services, 1914–1918'', pp. 84–85



Founding fighter formations
On 21 February 1916, the Verdun Offensive began. New weapons demand new tactics.Commandant
Commandant ( or ) is a title often given to the officer in charge of a military (or other uniformed service) training establishment or academy. This usage is common in English-speaking nations. In some countries it may be a military or police ran ...
Charles de Tricornet de Rose was the original French pilot, having learned to fly in March 1911. This experienced flier was given a free hand to select pilots and airplanes for a new unit tasked with keeping German observation craft from over the French lines. The ad hoc
Ad hoc is a Latin phrase meaning literally 'to this'. In English, it typically signifies a solution for a specific purpose, problem, or task rather than a generalized solution adaptable to collateral instances. (Compare with '' a priori''.)
C ...
unit commandeered all available Morane-Saulnier
Aéroplanes Morane-Saulnier was a French aircraft manufacturing company formed in October 1911 by Raymond Saulnier (1881–1964) and the Morane brothers, Léon (1885–1918) and Robert (1886–1968). The company was taken over and diversified ...
s and Nieuport 11s, as well as the 15 best pilots regardless of posting. This ad hoc
Ad hoc is a Latin phrase meaning literally 'to this'. In English, it typically signifies a solution for a specific purpose, problem, or task rather than a generalized solution adaptable to collateral instances. (Compare with '' a priori''.)
C ...
unit patrolling the skies over Verdun was the first French . The was successful despite Tricornet's death in a mishap. Under the leadership of new commander Captain Auguste de Reverand, such flying aces as Georges Guynemer
Georges Guynemer (, 24 December 1894 – 11 September 1917 MIA) was the second highest-scoring French fighter ace with 54 victories during World War I, and a French national hero at the time of his death. Guynemer's death was a profound s ...
, Charles Nungesser, and Albert Deullin began their careers.''Over the Front: The Complete Record of the Fighter Aces and Units of the United States and French Air Services, 1914–1918'', p. 85
Encouraged by the success of their original , the French massed several squadrons for the Battle of the Somme. The burgeoning French aircraft inventory afforded the formation of under Captain Felix Brocard. The was formed on 1 July 1916 with a posting of four Nieuport squadrons: Squadron N.3, N.26, N.73, and N.103. Three other squadrons-- Squadron N.37, N.62, and N.65 were temporarily attached at various times.
On 19 October 1916, three fixed were established, each to consist of four squadron. Numbered 11, 12, and 13, they were only the first three .
Concentrating airpower
During March 1917, and were formed. Again, each new was assigned four Nieuport fighter squadrons; again, each was sent to support a different French field army. On 10 January 1918, was formed from four SPAD squadrons. In February, five more were founded from SPAD squadrons: number 17, 18, 19, 20, and 21. The various Nieuport models were now being phased out as the new SPADs filled the inventories of the French. With the success, the French were encouraged to amass airpower into still larger tactical units. On 4 February 1918, was created out of , , and . It was followed by , formed on the 27th from , , and . Each would be stocked with 72 fighters.''Over the Front: The Complete Record of the Fighter Aces and Units of the United States and French Air Services, 1914–1918'', p. 86 The were not the end of the French accumulation of air power. On 14 May 1918, they were grouped into the . As bombing aircraft were also being concentrated into larger units, the new division would also contain and . The bombing units were both equipped with 45Breguet 14 Breguet or Bréguet may refer to:
* Breguet (watch), watch manufacturer
**Abraham-Louis Breguet (1747–1823), Swiss watchmaker
**Louis-François-Clement Breguet (1804–1883), French physicist, watchmaker, electrical and telegraph work
* Bréguet ...
bombers. The last addition to the new division was five protection squadrons, operating 75 Caudron R.11 gunships to fly escort for the Breguets.
On 25 June 1918, was founded. followed soon thereafter. A couple of night bombardment were also founded.''Over the Front: The Complete Record of the Fighter Aces and Units of the United States and French Air Services, 1914–1918'', pp. 86–87
Committing the ''Division Aerienne''
Then, on 15 July 1918, the Division was committed to theSecond Battle of the Marne
The Second Battle of the Marne (french: Seconde Bataille de la Marne) (15 July – 18 July 1918) was the last major German offensive on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack failed when an Allied counterattack, supported by s ...
. From then on, whether in whole or in part, the fought until war's end. By the time of the Battle of Saint-Mihiel, the French could commit 27 fighter squadrons to the effort, along with reconnaissance and bombing squadrons. The 1,137 airplanes dedicated to the battle were the most numerous used in a World War I battle.''Over the Front: The Complete Record of the Fighter Aces and Units of the United States and French Air Services, 1914–1918'', p. 87
When the 11 November 1918 armistice came, French air power had expanded to 336 squadrons, 74 of which were SPAD fighter squadrons. France had 3,608 planes in service. Confirmed claims of 2,049 destroyed enemy airplanes included 307 that had been brought down within French lines. French airmen had also destroyed 357 observation balloons. However, 5,500 pilots and observers were killed out of the 17,300 engaged in the conflict, amounting to 31%. A 1919 newspaper article reported that the French Air Force had suffered losses of 61%.
Interwar period
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
. It was not until 2 July 1934, that the "special arm" became an independent service and was totally independent.
The initial air arm was the cradle of French military parachuting, responsible for the first formation of the Air Infantry Groups () in the 1930s, out of which the Air Parachute Commandos () descended.
The French Air Force maintained a continuous presence across the French colonial empire, particularly from the 1920s to 1943.
World War II
The French Air Force played an important role in WWII, most notably during the Battle of France in 1940. TheVichy French Air Force
The Air Force (french: Armée de l'air), usually referred to as the Air Force of Vichy (''Armée de l'air de Vichy'') or Armistice Air Force (''Armée de l'Air de l'armistice'') for clarity, was the aerial branch of the Armistice Army of Vichy Fran ...
had later a significant presence in the French Levant.
The engagement of the Free French Air Forces
The Free French Air Forces (french: Forces Aériennes Françaises Libres, FAFL) were the air arm of the Free French Forces in the Second World War, created by Charles de Gaulle in 1940. The designation ceased to exist in 1943 when the Free Frenc ...
from 1940 to 1943, and then the engagement of the aviators of the French Liberation Army, were also important episodes in the history of the French Air Force. The sacrifices of Commandant
Commandant ( or ) is a title often given to the officer in charge of a military (or other uniformed service) training establishment or academy. This usage is common in English-speaking nations. In some countries it may be a military or police ran ...
René Mouchotte
Commandant René Mouchotte DFC (21 August 1914 – 27 August 1943) was a World War II pilot of the French Air Force, who escaped from Vichy French–controlled Oran to join the Free French forces. Serving with RAF Fighter Command, he rose to c ...
and Lieutenant Marcel Beau illustrated their devotion.
1945–present
 After 1945, France rebuilt its aircraft industry. The French Air Force participated in several colonial wars during the Empire such as French Indochina after the Second World War. Since 1945, the French Air Force was notably engaged in Indochina (1945–1954).
The French Air Force was active in
After 1945, France rebuilt its aircraft industry. The French Air Force participated in several colonial wars during the Empire such as French Indochina after the Second World War. Since 1945, the French Air Force was notably engaged in Indochina (1945–1954).
The French Air Force was active in Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
from 1952 until 1962 and Suez
Suez ( ar, السويس '; ) is a seaport city (population of about 750,000 ) in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez (a branch of the Red Sea), near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same bou ...
(1956), later Mauritania and Chad, the Persian Gulf (1990–1991), ex-Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and more recently in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, Mali and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
.
From 1964 until 1971 the French Air Force had the unique responsibility for the French nuclear arm via Dassault Mirage IV or ballistic missiles of Air Base 200 Apt-Saint-Christol on the Plateau d'Albion.
 Accordingly, from 1962, the French political leadership shifted its military emphasis to nuclear deterrence, implementing a complete reorganisation of the Air Force, with the creation of four air regions and seven major specialised commands, among which were the Strategic Air Forces Command, COTAM, the Air Command of Aerial Defense Forces (, CAFDA), and the (FATac). In 1964, the Second Tactical Air Command was created in Nancy to take command of air units stationed in France but not assigned to
Accordingly, from 1962, the French political leadership shifted its military emphasis to nuclear deterrence, implementing a complete reorganisation of the Air Force, with the creation of four air regions and seven major specialised commands, among which were the Strategic Air Forces Command, COTAM, the Air Command of Aerial Defense Forces (, CAFDA), and the (FATac). In 1964, the Second Tactical Air Command was created in Nancy to take command of air units stationed in France but not assigned to NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
. The Military Air Transport Command had previously been formed in February 1962 from the . Also created in 1964 was the (EFCA), seemingly grouping all FCA units. The Dassault Mirage IV, the principal French strategic bomber, was designed to strike Soviet positions as part of the French nuclear triad
A nuclear triad is a three-pronged military force structure that consists of land-launched nuclear missiles, nuclear-missile-armed submarines, and strategic aircraft with nuclear bombs and missiles. Specifically, these components are land-based ...
.
In 1985, the Air Force had four major flying commands, the Strategic Air Forces Command, the Tactical Air Forces Command, the Military Air Transport Command, and CAFDA (air defence).
 CFAS had two squadrons of S2 and S-3 IRBMs at the Plateau d'Albion, six squadrons of Mirage IVAs (at Mont de Marsan, Cazaux, Orange, Istres, St Dizier, and EB 3/94 at Luxeuil - Saint-Sauveur Air Base), and three squadrons of C-135F, as well as a training/reconnaissance unit, CIFAS 328, at Bordeaux. The tactical air command included wings EC 3, EC 4, EC 7, EC 11, EC 13, and ER 33, with a total of 19 squadrons of Mirage III, Jaguars, two squadrons flying the
CFAS had two squadrons of S2 and S-3 IRBMs at the Plateau d'Albion, six squadrons of Mirage IVAs (at Mont de Marsan, Cazaux, Orange, Istres, St Dizier, and EB 3/94 at Luxeuil - Saint-Sauveur Air Base), and three squadrons of C-135F, as well as a training/reconnaissance unit, CIFAS 328, at Bordeaux. The tactical air command included wings EC 3, EC 4, EC 7, EC 11, EC 13, and ER 33, with a total of 19 squadrons of Mirage III, Jaguars, two squadrons flying the Mirage 5
The Dassault Mirage 5 is a French supersonic attack aircraft designed by Dassault Aviation during the 1960s and manufactured in France and a number of other countries. It was derived from Dassault's popular Mirage III fighter and spawned sever ...
F (EC 2/13 and EC 3/13, both at Colmar), and a squadron flying the Mirage F.1CR. CoTAM counted 28 squadrons, of which ten were fixed-wing transport squadrons, and the remainder helicopter and liaison squadrons, at least five of which were overseas. CAFDA numbered 14 squadrons mostly flying the Mirage F.1C. Two other commands had flying units, the Air Force Training Command, and the Air Force Transmissions Command, with four squadrons and three trials units.
Dassault Aviation led the way mainly with delta-wing
A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ).
Although long studied, it did not find significant applications until the Jet Age, when it proved suitab ...
designs, which formed the basis for the Dassault Mirage III
The Dassault Mirage III () is a family of single/dual-seat, single-engine, fighter aircraft developed and manufactured by French aircraft company Dassault Aviation. It was the first Western European combat aircraft to exceed Mach number, Mach 2 ...
series of fighter jets. The Mirage demonstrated its abilities in the Six-Day War, Yom Kippur War, Falklands War, and Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
, becoming one of the most popular jet fighters of its day and being widely sold.
In 1994, the Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air
The ''Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air'' (French for "Fusilier commandos of the Air (force)") of the French Air and Space Force are equivalent to the United Kingdom's RAF Regiment, German Air Force Regiment or the United States Air Force Security For ...
command was reestablished under a different form.

Dassault Rafale
The Dassault Rafale (, literally meaning "gust of wind", and "burst of fire" in a more military sense) is a French twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter aircraft designed and built by Dassault Aviation. Equipped with a wide range ...
multi-role jet fighter was underway; the first 20-aircraft squadron became operational in 2006 at Saint-Dizier.
In 2009, France rejoined the NATO Military Command Structure
The Structure of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization is complex and multi-faceted. The decision-making body is the North Atlantic Council (NAC), and the member state representatives also sit on the Defence Policy and Planning Committee (DPPC ...
, having been absent since 1966. France was a leading nation, alongside the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
in implementing the UN sponsored no-fly zone in Libya (NATO Operation Unified Protector
Operation Unified Protector was a NATO operation in 2011 enforcing United Nations Security Council resolutions 1970 and 1973 concerning the Libyan Civil War and adopted on 26 February and 17 March 2011, respectively. These resolutions imposed ...
), deploying 20 fighter aircraft to Benghazi in defense of rebel-held positions and the civilian population.
The last remaining squadron of Dassault Mirage F1s retired the aircraft in July 2014 and replaced them with Dassault Rafale
The Dassault Rafale (, literally meaning "gust of wind", and "burst of fire" in a more military sense) is a French twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter aircraft designed and built by Dassault Aviation. Equipped with a wide range ...
s.
Florence Parly
Florence Parly (born 8 May 1963) is a French politician who served as Minister of the Armed Forces under President Emmanuel Macron from 2017 to 2022. A former member of the Socialist Party (PS), she previously served as Secretary of State for t ...
, France reserves the right to arm French satellites with lasers for defensive purposes.
The official renaming occurred on 24 July 2020, with the new Air and Space Force logo unveiled on 11 September 2020.
Structure
The Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force (CEMAAE) determines French Air and Space Force doctrines application and advises the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA) on the deployment, manner, and use of the Air and Space Force. They are responsible for the preparation and logistic support of the French Air and Space Force. The CEMAA is assisted by a Deputy Chief, the . Finally, the CEMAA is assisted by the Inspectorate of the French Air and Space Force (IAA) and by the French Air and Space Force Health Service Inspection (ISSAA). The Air and Space Force is organized in accordance with Chapter 4, Title II, Book II of the Third Part of the French Defense Code (french: code de la Défense), which replaced decree n° 91-672 dated 14 July 1991. Under the authority of the Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force (CEMAAE) inParis
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
, the Air and Space Force includes:
* Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force, heading the (EMAAE)
* Forces
* Air Bases
* Directorate of Human Resources of the French Air and Space Force
* ServicesLégifrance, base CDEF(R), numéro R3224-8, Code de la Défense, Art. R.3224-8
The Air and Space Force headquarters, employing 150 personnel, are located alongside the Chief of the Defence Staff's offices (EMA) and the Army and Navy headquarters at the Balard armed forces complex in Paris. The new site replaced the former Paris Air Base
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
(BA 117) which served as air staff headquarters until 25 June 2015.
Commands
The French Air and Space Force has had three commands: two grand operational commands (CDAOA and CFAS) and one organic command (CFA). * Commandement de la Défense Aérienne et des Opérations Aériennes (English: Air Defense and Air Operations Command (CDAOA)), is responsible for surveillance of French airspace, as well as all aerial operations in progress. It does not possess aircraft. Instead it exercises operational control over units of the Air Forces Command (''CFA''). ** Air Defence and Air Operations Staff () composed of the: *** Air Force Operational Staff () and the *** Permanent readiness command center (), both situated at the Balard complex (the French Air and Space Force main HQ) *** direct reporting units: **** Air Force Operations Brigade () (all units at BA 942 Lyon-Mont Verdun air base) ***** National Air Operations Center () ***** Core Joint Force Air Component HQ (''Core JFAC HQ'') ***** Operational Center for Military Surveillance of Space Objects () ***** Analysis and Simulation Center for Air Operations Preparation () **** Air Force Operational Awareness and Planning Brigade () ***** Air Force Intelligence Center () at BA 942 Lyon-Mont Verdun air base ***** National Target Designation Center () at BA 110 Creil-Senlis air base ***** Satellite Observation Military Center 01.092 ''"Bourgogne"'' () at BA 110 Creil-Senlis air base ***** Land-based Electronic Warfare Squadron () at BA 123 Orléans-Bricy air base ***** Intelligence Training Squadron 20.530 () (Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand ...
), training air and space force and naval officers, integrated in the Joint Intelligence Training Center (''CFIAR'') in Strasbourg
*** territorial units:
**** Detection and Control Center 07.927 () Tours – Cinq-Mars-la-Pile (Codename: ''Raki'', AOR: Northwestern France)
**** Detection and Control Center 04.930 () Mont-de-Marsan (Codename: ''Marina'', AOR: Southwestern France)
**** Detection and Control Center 05.942 () Lyon – Mont Verdun (Codename: ''Rambert'', AOR: Southeastern France)
**** Detection and Control Center 05.901 () Drachenbronn (Codename: ''Riesling'', AOR: Northeastern France) – disbanded in 2015, functions absorbed into the Lyon – Mont Verdun DCC
* Strategic Air Forces Command (CFAS)), is responsible for the air force's nuclear strike units ( Dassault Rafale B armed with ASMP-A missiles), as well as the tanker / strategic transport aircraft ( C-135FR, Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker).
* Air Forces Command (CFA)), Bordeaux-Mérignac Air Base, as an organic command, prepares units to fulfill operational missions. From September 2013, the former organic commands CFA and CSFA were merged into CFA. CFA is organized in six brigades:
** Fighter Brigade – (french: Brigade Aérienne de l'Aviation de Chasse (BAAC)), is responsible for all air defense, air-to-ground and reconnaissance aircraft (including Dassault Rafale
The Dassault Rafale (, literally meaning "gust of wind", and "burst of fire" in a more military sense) is a French twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter aircraft designed and built by Dassault Aviation. Equipped with a wide range ...
, Mirage 2000-5F, Mirage 2000B/C/D, Transall C-160
The Transall C-160 is a military transport aircraft, produced as a joint venture between France and Germany. "Transall" is an abbreviation of the manufacturing consortium Transporter Allianz, comprising the companies of MBB, Aerospatiale, and ...
Gabriel). In February 2016 it was commanded by Brigadier General (Air) Philippe Lavigne
Philippe Lavigne is a French general. He was the Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space from 2018 to 2021 and the current Supreme Allied Commander Transformation HQ since 23 September 2021.
He graduated from Prytanée National Militaire in ...
.
** Projection and Support Air Force Brigade
Projection, projections or projective may refer to:
Physics
* Projection (physics), the action/process of light, heat, or sound reflecting from a surface to another in a different direction
* The display of images by a projector
Optics, graphic ...
(french: Brigade Aérienne d'Appui et de Projection (BAAP)), is responsible for all tactical transport and liaison aircraft (aircraft and helicopters: Transall, C-160, Hercules C-130, A310/319, Dassault Falcon 50
The Dassault Falcon 50 is a French super-midsize, long-range business jet, featuring a trijet layout with an S-duct air intake for the central engine. It has the same fuselage cross-section and similar capacity as the earlier twin-engined Falcon ...
/900, Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma
The Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma is a four-bladed, twin-engined medium transport/utility helicopter that was designed and originally produced by the French aerospace manufacturer Sud Aviation. It is capable of carrying up to 20 passengers as well as ...
, Eurocopter Fennec
The Eurocopter (now Airbus Helicopters) AS550 Fennec (now H125M) and AS555 Fennec 2 are lightweight, multipurpose military helicopters manufactured by Eurocopter Group (now Airbus Helicopters). Based on the AS350 Ecureuil and AS355 Ecureuil 2 ...
, Eurocopter AS332 Super Puma
The Airbus Helicopters H215 (formerly Eurocopter AS332 Super Puma) is a four-bladed, twin-engine, medium-size utility helicopter developed and initially produced by the French aerospace company Aérospatiale. It has been subsequently manufactu ...
, SOCATA TBM
The SOCATA TBM (now Daher TBM) is a family of high-performance single-engine turboprop business and utility light aircraft manufactured by Daher. It was originally collaboratively developed between the American Mooney Airplane Company and F ...
);
** Airspace Control Brigade (french: Brigade Aérienne de Contrôle de l'Espace (BACE)), is responsible for ( Airborne early warning and control aircraft, and ground radar, ground-based air defense systems and missile defence, communication networks) airspace surveillance, constituting the Système de Commandement et de Conduite des Opérations Aérospatiales). Since 2007 the command, control and information systems network of the air and space force have been is integrated into the Joint Directorate of Infrastructure Networks and Information Systems (DIRISI)).
** Air Force Security and Intervention Forces Brigade
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
(french: Brigade Aérienne des Forces de Sécurité et d'Intervention (BAFSI)), is responsible for units of the French Air and Space Force's commando riflemen (Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air
The ''Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air'' (French for "Fusilier commandos of the Air (force)") of the French Air and Space Force are equivalent to the United Kingdom's RAF Regiment, German Air Force Regiment or the United States Air Force Security For ...
, tasked with special operations, CSAR and target acquisition), amongst which the most elite is the Air Force Parachute Commando n° 10, C.P.A 10 (, unit of the French Special Forces
The Commandement des Opérations Spéciales ( en, Special Operations Command) or COS is a joint staff charged with overseeing the various special forces of the French Army, Navy and Air and Space Force, bringing them all under a single operationa ...
. The BAFSI also includes the security units of the air bases (34 squadrons (of company strength) and detachments (of platoon strength)) and the rescue and firefighting personnel (called ''incident technicians'' and grouped into ''squadrons'' of company size);
** Air Force Aerial Weapon Systems Brigade
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
(french: Brigade Aérienne des Systèmes d'Armes Aériens (BASAA)) provides the maintenance and repair of aerial weapons and target systems.
** Air Force Maneuver Support Brigade (french: Brigade Aérienne d'Appui à la Manœuvre Aérienne (BAAMA)) provides the ground-based engineer and logistics personnel (including expeditionary) needed for the sustainment of air operations.
* French Space Command (french: Commandement de l'espace (CDE))
These last two brigades belonged until 2013 to the Air Force Support Command (CSFA), which maintained the arms systems, equipment, information and communication systems (SIC) as well as infrastructure. The CSFA supported the human element, the military logistics (supply and transport), wherever, previously, forces of the French Air and Space Force operated or trained. These two brigades are now subordinate to the CFA.
The official designation of the service was changed in July 2019 from Air Army () to Air and Space Army (), when the previous joint Inter-Service Space Command ( (''CIE'')) under the French General Staff was transformed into the Space Command ( (''CDE'')) and absorbed into the Air and Space Force as its fourth command.
All air regions were disestablished on 1 January 2008. In the 1960s, there were five air regions (RA). The number was then reduced to four by a decree of 30 June 1962 with the disestablishment of the 5th Aerial Region ( French North Africa). The decree of 14 July 1991 reduced the air regions to three: « RA Atlantic », « RA Mediterranean » and « RA North-East ». On 1 July 2000 was placed into effect an organization consisting of « RA North » (RAN) and « RA South » (RAS). The territorial division was abolished by decree n°2007-601 of 26 April 2007.
From 2008 to 2010 the French Air Force underwent the "Air 2010" streamlining process. The main targets of this project were to simplify the command structure, to regroup all military and civil air force functions and to rationalise and optimise all air force units. Five major commands, were formed, instead of the former 13, and several commands and units were disbanded.
Support services
The Directorate of Human Resources of the Air and Space Force (DRH-AAE) recruits, trains, manages, administers, and converts personnel of the Air and Space Force. Since January 2008, the DRH-AAE groups the former Air Force directorate of military personnel (DPMMA) and some tasks of the former Air Force Training Command. The directorate is responsible for Air and Space Force recruitment via the recruiting bureau. French joint defence service organisations, supporting the air and space force, include: * The Integrated Structure of Maintaining Operational Conditioning of Aeronautical Defense Materials (french: Structure Intégrée de Maintien en Condition Opérationnelle des Matériels Aéronautiques de la Défense) (SIMMAD). * The Aeronautical Industrial Service (french: Service Industriel de l'Aéronautique) (SIAE). * The " Air Commissariat " (french: " Commissariat de l'Air ") between 1947 and 2007, then " Financial and General Administration Service " (french: " Service de l'Administration Générale et des Finances " (SAGF)) from 2008 until 2009, and finally the " Commissariat Service of the Armed Forces " (SCA) (french: Service du Commissariat des Armées) since 2010, have successively been designated as administrative services of the French Air and Space Force. The Commissioners as well as Civilians of this service carry out : operations support, individual legal rights, judicial, internal control accountability, financial and purchase executions, and support and protection of the combatant.Wings
Commanded by a Lieutenant-colonel or Colonel, the is a formation that assembles various units and personnel dedicated to the same mission. In 1932, the "regiment" designation was replaced with "Escadre", which until 1994 was a unit consisting of the following: * units (escadrons or groups) generally equipped with the same type of aircraft or at least assuring the same type of mission * units of maintenance and support. (wings
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expre ...
) were dissolved from 1993 as part of the reorganisation, were reestablished in 2014.Nouvelles escadres aériennes : une cohérence opérationnelle accrue, des valeurs renforcées. Site de l'Armée de l'air accessed 16 November 2015. The problems caused by having the aircraft maintenance units not responsible to the flying squadrons they supported eventually forced the change. Four were reformed in the first phase: * at
Istres-Le Tubé Air Base
Istres-Le Tubé Air Base (french: Base Aérienne 125 or BA 125) is a large multi-role tasked French Air and Space Force base located near Istres, northwest of Marseille, France. The airport facilities are also known as Istres - Le Tubé (I ...
on 27 August 2014
* at Avord Air Base
Avord Air Base or BA 702 (french: Base Aérienne 702 Capitaine Georges Madon), named after Captain Georges Madon, is a base of the French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) located north northwest of Avord in central France.
...
on 5 September 2014
* (ESADA – 1er RAA) at Avord Air Base
Avord Air Base or BA 702 (french: Base Aérienne 702 Capitaine Georges Madon), named after Captain Georges Madon, is a base of the French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) located north northwest of Avord in central France.
...
(3 September 2014)
* the at Nancy-Ochey Air Base (5 September 2014)
In the second phase, the French Air Force announced in August 2015 the creation of six additional wings:
* the at Cazaux Air Base
Cazaux Air Base (french: Base aérienne 120 Cazaux) is a French Air and Space Force (french: Armée de l'air et de l'espace) base. The base is located in the village of Cazaux, part of the town of La Teste-de-Buch, and is approximately southwe ...
(25 August 2015)
* the at Saint-Dizier ( 26 August 2015)
* the at Évreux-Fauville Air Base
Évreux-Fauville Air Base (''Base aérienne 105 Évreux'' or BA 105) is a French Air and Space Force base located about 2 miles (3 km) east of the town of Évreux in the Eure ''département'', on the north side of the Route nationale 13 ...
(27 August 2015)
* the at Luxeuil - Saint-Sauveur Air Base (3 September 2015)
* the () at Orléans – Bricy Air Base
Orléans – Bricy Air Base (french: Base aérienne 123 « Commandant Charles Paoli ») is a French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) (ALAE) base. The base is located approximately north-northwesst of Ingré near the city of Or ...
(1 September 2015)
* the at Mont-de-Marsan Air Base
Mont-de-Marsan Air Base (French: Base aérienne 118 Mont-de-Marsan) (ICAO: LFBM) is a front-line French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) (ALAE) fighter base located approximately 2 km north of Mont-de-Marsan, in the Land ...
(3 September 2015).
Also established was the at Évreux-Fauville Air Base
Évreux-Fauville Air Base (''Base aérienne 105 Évreux'' or BA 105) is a French Air and Space Force base located about 2 miles (3 km) east of the town of Évreux in the Eure ''département'', on the north side of the Route nationale 13 ...
on 27 August 2015.
The French Air and Space Force announced in August 2015 that unit numbering, moves of affected aircraft, and the transfer of historic material (flags, traditions and names) would be completed in 2016.
* the was re-constituted at Orléans – Bricy Air Base
Orléans – Bricy Air Base (french: Base aérienne 123 « Commandant Charles Paoli ») is a French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) (ALAE) base. The base is located approximately north-northwesst of Ingré near the city of Or ...
on 5 September 2017, taking over C-130 Hercules operations from so the latter could specialise in A400M Atlas operations.
Another air force wing was added on September 5, 2019:
* the at Cognac – Châteaubernard Air Base
Cognac – Châteaubernard Air Base (french: Base aérienne 709 Cognac-Châteaubernard or BA 709) is a base of the French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) located in Châteaubernard, 2.8 kilometres south of Cognac, France, C ...
, operating the air and space force's drone fleet.
Squadrons and flights
Commanded by a lieutenant-colonel, the Escadron is the basic operational unit. This term replaced that of Group as of 1949 with the aim to standardize usage with the allies ofNATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
who were using the term 'squadron'. However, the term Group did not entirely disappear: the term was retained for the Aerial Group 56 Mix Vaucluse, specialized in Special Operations or Group – Groupe de Ravitaillement en Vol 02.091 Bretagne (french: Groupe de Ravitaillement en Vol 02.091 Bretagne) which is still carrying the same designation since 2004.
A fighter squadron () can number some twenty machines, spread in general in three Escadrilles. A Transport Escadron () can theoretically count a dozen Transall C-160
The Transall C-160 is a military transport aircraft, produced as a joint venture between France and Germany. "Transall" is an abbreviation of the manufacturing consortium Transporter Allianz, comprising the companies of MBB, Aerospatiale, and ...
, however, numbers are usually much less for heavier aircraft (three Airbus A310-300
The Airbus A310 is a wide-body aircraft, designed and manufactured by Airbus Industrie, then a consortium of European aerospace manufacturers.
Airbus had identified a demand for an aircraft smaller than the A300, the first twin-jet wide-bod ...
and two Airbus A340-200
The Airbus A340 is a long-range, wide-body passenger airliner that was developed and produced by Airbus.
In the mid-1970s, Airbus conceived several derivatives of the A300, its first airliner, and developed the A340 quadjet in parallel wi ...
for the Transport Escadron 3/60 Estérel (french: Escadron de Transport 3/60 Estérel)).
The squadrons have retained the designations of the former Escadres disbanded during the 1990s. For instance: Transport Escadron 1/64 Béarn (french: escadron de transport 1/64 Béarn) (more specifically Transport Escadron 01.064 Béarn), which belonged to the 64th Transport Escadre (french: 64e Escadre de Transport) during the dissolution of the later (recreated in August 2015). Not all escadrons (Squadrons) are necessarily attached to an Escadre.
The Escadrille (flight) has both an administrative and operational function, even of the essential operational control is done at the level of the Esacdron. A pilot is assigned to the Escadrille, however the equipment and material devices, on the other hand, are assigned to the Escadron. Since the ESTA (Aeronautic Technical Support Escadrons) came into being, material devices and the mechanics have been assigned directly to the base then put at disposition of the based Escadrons.
The Escadrilles adopted the traditions of the prestigious units out of which most (SPA and SAL), are those traditions of the First World War.
Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air
TheFusiliers Commandos de l'Air
The ''Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air'' (French for "Fusilier commandos of the Air (force)") of the French Air and Space Force are equivalent to the United Kingdom's RAF Regiment, German Air Force Regiment or the United States Air Force Security For ...
comprise:
* Protection squadrons (french: Escadrons de protection) (EP)
* Air Parachute Commando 10 (french: Commando parachutiste de l'air) (CPA 10)
* Air Parachute Commando 20 (CPA 20)
* Air Parachute Commando 30 (CPA 30)
Protection Squadrons protect airbases inside and outside the national territory, and in exterior operations as well.
The CPAs carry out common missions, as well as specialized tasks including intervention and reinforcement of protection at the profit of sensible points " air " inside and outside the national territory.
Air bases
 Flying activity in France is carried out by a network of bases, platforms and French air and space defence radar systems. It is supported by bases, which are supervised and maintained by staff, operational centres, warehouses, workshops, and schools. Both in France and abroad, bases have similar infrastructure to provide standardised support.
The French Air and Space Force has, as of 1 August 2014:
* Within the metropolitan territory of France, 27 airbases, out of the which 18 aeronautical platform with perceived runways and 5 Bases non-platform, two schools, 3 air detachments and " one attached air element " (EAR).
* Beyond the metropole/Europe, 7 Aerial Bases or permanent detachments in overseas or country.
Flying activity in France is carried out by a network of bases, platforms and French air and space defence radar systems. It is supported by bases, which are supervised and maintained by staff, operational centres, warehouses, workshops, and schools. Both in France and abroad, bases have similar infrastructure to provide standardised support.
The French Air and Space Force has, as of 1 August 2014:
* Within the metropolitan territory of France, 27 airbases, out of the which 18 aeronautical platform with perceived runways and 5 Bases non-platform, two schools, 3 air detachments and " one attached air element " (EAR).
* Beyond the metropole/Europe, 7 Aerial Bases or permanent detachments in overseas or country.

 Some French airbases house radar units (e.g. Lyon, Mont-Verdun, Drachenbronn, Cinq-Mars-la-Pile, Nice, Mont-Agel) to carry out air defence radar surveillance and air traffic control. Others house material warehouses or command posts. Temporary and semi-permanent foreign deployments include transport aircraft at Dushanbe ( Tajikistan, Operation Héraclès), and fighter aircraft in
Some French airbases house radar units (e.g. Lyon, Mont-Verdun, Drachenbronn, Cinq-Mars-la-Pile, Nice, Mont-Agel) to carry out air defence radar surveillance and air traffic control. Others house material warehouses or command posts. Temporary and semi-permanent foreign deployments include transport aircraft at Dushanbe ( Tajikistan, Operation Héraclès), and fighter aircraft in N'Djamena
N'Djamena ( ) is the capital and largest city of Chad. It is also a special statute region, divided into 10 districts or ''arrondissements''.
The city serves as the centre of economic activity in Chad. Meat, fish and cotton processing are the c ...
(Tchad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republ ...
, Opération Épervier), among others.
As swift as the French Air and Space Force operates, the closure of aerial bases is more constant and immediate, having known a strong acceleration since the 1950s. An air base commander has authority over all units stationed on their base. Depending on the units' tasks, this means that they are responsible for approximately 600 to 2500 personnel.
On average, a base, made up of about 1500 personnel (nearly 3500 people including family), provides a yearly economic boost to its area of about 60 million euros. Consequently, determining the sites for air bases constitutes a major part of regional planning.
 * BA 105
* BA 105 Évreux-Fauville Air Base
Évreux-Fauville Air Base (''Base aérienne 105 Évreux'' or BA 105) is a French Air and Space Force base located about 2 miles (3 km) east of the town of Évreux in the Eure ''département'', on the north side of the Route nationale 13 ...
. Command, operational and logistic support. Air transport units with 27× CASA CN-235M, 9× Transall C-160 NG.
* BA 107 Vélizy – Villacoublay Air Base. Helicopter and heavy air transport units.
* BA 113 Saint-Dizier – Robinson Air Base 4e Escadre de Chasse, 50× Rafale B and Rafale C.
* BA 116 Luxeuil - Saint-Sauveur Air Base. Air defence fighter base with 28× Mirage 2000-5F.
* BA 123 Orléans – Bricy Air Base
Orléans – Bricy Air Base (french: Base aérienne 123 « Commandant Charles Paoli ») is a French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) (ALAE) base. The base is located approximately north-northwesst of Ingré near the city of Or ...
. Air transport units with 17× Airbus A400M Atlas
The Airbus A400M AtlasNamed after the Greek mythological figure. is a European four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft. It was designed by Airbus Military (now Airbus Defence and Space) as a tactical airlifter with strategic capab ...
and 18× Lockheed C-130 Hercules
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 was originally desig ...
. CFPSAA operational command.
* BA 133 Nancy – Ochey Air Base. Three strike fighter squadrons units with 70× Mirage 2000D, SAM sqns.
* BA 279 Châteaudun Air Base. Airplane maintenance, repair and storage airbase.
* BA 702 Avord Air Base
Avord Air Base or BA 702 (french: Base Aérienne 702 Capitaine Georges Madon), named after Captain Georges Madon, is a base of the French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) located north northwest of Avord in central France.
...
. CFAS nuclear strike stockpile. AWACS 4× E-3F Sentry unit. Inflight refueling C-135FR unit.
* BA 705 Tours airbase. Fighter pilot training school were equipped with Alpha Jet
The Dassault/Dornier Alpha Jet is a light attack jet and advanced jet trainer co-manufactured by Dassault Aviation of France and Dornier Flugzeugwerke of Germany. It was developed specifically to perform trainer and light attack missions, as ...
. This school has been moved to BA 709 in 2020.
* DA 273 Romorantin
Romorantin is a traditional French variety of white wine grape, that is a sibling of Chardonnay. Once quite widely grown in the Loire, it has now only seen in the Cour-Cheverny AOC. It produces intense, minerally wines somewhat reminiscent of ...
air detachment. Logistics unit.
* BA 106 Bordeaux-Mérignac Airport. Transport support base for the air staff.
* BA 115 Orange-Caritat Air Base
Air Base 115 Orange-Caritat (french: Base aérienne 115 Orange-Caritat "Capitaine de Seyne" or ''BA 115'', ) is a French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) base in Vaucluse, France. It is equipped with one runway and was named a ...
. Air defence 28× Mirage 2000C and 6× Mirage 2000B-S5.
* BA 118 Mont-de-Marsan Air Base
Mont-de-Marsan Air Base (French: Base aérienne 118 Mont-de-Marsan) (ICAO: LFBM) is a front-line French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) (ALAE) fighter base located approximately 2 km north of Mont-de-Marsan, in the Land ...
. Home to 52× Rafale B and Rafale C. Home of CEAM, the Air and Space Force military experimentation and trials organisation, Air defence radar command reporting centre, and the air traffic control and air defence control training centre.
* BA 120 Cazaux Air Base
Cazaux Air Base (french: Base aérienne 120 Cazaux) is a French Air and Space Force (french: Armée de l'air et de l'espace) base. The base is located in the village of Cazaux, part of the town of La Teste-de-Buch, and is approximately southwe ...
, situated South-west of the port city of Bordeaux. Fighter pilot training squadron equipped with 45× Alpha Jet
The Dassault/Dornier Alpha Jet is a light attack jet and advanced jet trainer co-manufactured by Dassault Aviation of France and Dornier Flugzeugwerke of Germany. It was developed specifically to perform trainer and light attack missions, as ...
. Air and Space Force airplane stockpile.
* BA 125 Istres-Le Tubé Air Base
Istres-Le Tubé Air Base (french: Base Aérienne 125 or BA 125) is a large multi-role tasked French Air and Space Force base located near Istres, northwest of Marseille, France. The airport facilities are also known as Istres - Le Tubé (I ...
. Two Transall C-160
The Transall C-160 is a military transport aircraft, produced as a joint venture between France and Germany. "Transall" is an abbreviation of the manufacturing consortium Transporter Allianz, comprising the companies of MBB, Aerospatiale, and ...
G strategic communication flight. Inflight refueling unit with 4× Airbus A330 MRTT and 14× KC-135FR. CEAM – the Air and Space Force military test centre.
* BA 126 Solenzara Air Base. Fighter gunnery range. SAR unit.
* DA 277 Varennes-sur-Allier
Varennes-sur-Allier (, literally ''Varennes on Allier''; oc, Varenas) is a commune in the Allier department in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes in central France.
History
In 52 BC during the Gallic Wars lived by Julius Caesar, Vercingetorix crosse ...
. Air and Space Force supply depot. DA 277 was dissolved on 30 June 2015.
* Air Base 278 Ambérieu. Logistic support base.
* BA 701 Salon-de-Provence Air Base. Presentation Team equipped with 12× Alpha Jet
The Dassault/Dornier Alpha Jet is a light attack jet and advanced jet trainer co-manufactured by Dassault Aviation of France and Dornier Flugzeugwerke of Germany. It was developed specifically to perform trainer and light attack missions, as ...
. Officer instruction school. Enlisted instruction school.
* BA 709 Cognac – Châteaubernard Air Base
Cognac – Châteaubernard Air Base (french: Base aérienne 709 Cognac-Châteaubernard or BA 709) is a base of the French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) located in Châteaubernard, 2.8 kilometres south of Cognac, France, C ...
. Basic flight training school equipped with 17× Pilatus PC-21
The Pilatus PC-21 is a turboprop-powered advanced trainer with a stepped tandem cockpit. It is manufactured by Pilatus Aircraft of Switzerland.
Development
In November 1997 Pilatus flew a modified PC-7 Mk.II in order to test improvements for a ...
and UAV squadron with 8× MQ-9 Reaper.
* Air Base 721 Rochefort
Rochefort () may refer to:
Places France
* Rochefort, Charente-Maritime, in the Charente-Maritime department
** Arsenal de Rochefort, a former naval base and dockyard
* Rochefort, Savoie in the Savoie department
* Rochefort-du-Gard, in the Ga ...
. Home of the NCO school, the École de formation des sous-officiers de l'armée de l'air.
* BA 942 Lyon – Mont Verdun Air Base. Air defence radar command reporting centre. National Air Operations Command (CNOA) location.
* EAR 943 Nice Mont-Agel. Air defence radar GM 406.
* DA 204 Bordeaux-Beauséjour air detachment. Logistic unit.
* EETAA 722
EETAA 722 is the French acronym for '. It is a well known training school for mechanic apprentices of the French Air and Space Force
The French Air and Space Force (AAE) (french: Armée de l'air et de l'espace, ) is the air and space force o ...
Saintes. Air and Space Force electronic, technical instruction also as Military basic Bootcamp.
* EPA 749 Grenoble
lat, Gratianopolis
, commune status = Prefecture and commune
, image = Panorama grenoble.png
, image size =
, caption = From upper left: Panorama of the city, Grenoble’s cable cars, place Saint- ...
. Air and Space Force child support school.
Overseas
* BA 160 Dakar, Senegal. Mixed units. * Réunion, Indian Ocean. * BA 188 Djibouti, Africa. Mixed units. * Air elements Libreville/Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the nort ...
.
* Air elements N’Djamena/ Chad. Mixed units.
* BA 190 French Polynesia (''Overseas collectivity
The French overseas collectivities (''collectivité d'outre-mer'' or ''COM'') are first-order administrative divisions of France, like the French regions, but have a semi-autonomous status. The COMs include some former French overseas colonies ...
''). Mixed unit.
* BA 365 Martinique (''French department''), West Indies. Mixed unit.
* BA 367 French Guiana (''French department''), South America. Mixed units.
* BA 376 Base aérienne 186 Nouméa, New Caledonia ('' special collectivity of France'')
* BA 104 Abu Dhabi
More than ten bases have been closed since 2009. Doullens Air Base (BA 922) was a former command and reporting centre; Toulouse - Francazal Air Base
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Pari ...
(BA 101), was closed on 1 September 2009; Colmar-Meyenheim Air Base (BA 132) was closed on 16 June 2010; Metz-Frescaty Air Base (BA 128) was closed on 30 June 2011; Brétigny-sur-Orge Air Base
Brétigny-sur-Orge Air Base (french: Base aérienne 217 Bretigny-Sur-Orge) is a former French Air Force french: Armée de l'Air (ALA) base. The base is located approximately southeast of Brétigny-sur-Orge; about south of Paris.
Units
* Inte ...
(BA 217), closed 26 June 2012; Cambrai - Épinoy Air Base (BA 103), was closed on 28 June 2012; Reims – Champagne Air Base (June 2012); Drachenbronn Air Base (BA 901) closed on 17 July 2015; Dijon Air Base
Dijon-Longvic Air Base (french: Base aérienne 102 Dijon, ) was a French Air Force (french: Armée de l'Air) air base. The airfield is located approximately east-southeast of Longvic; about southeast of Paris. Operating as a joint civilian base ...
(BA 102), was vacated on 30 June 2016; Creil Air Base (BA 110) vacated on 31 August 2016; and Taverny Air Base
Taverny Air Base (formerly ''Base Aérienne 921 "Frères Mahé" de Taverny'') is located in the communities of Taverny and Bessancourt in the Val d'Oise département of France, twenty kilometers north of Paris. Until 2011 it was the headquarte ...
(DA 921), the former Strategic Air Forces Command headquarters.
Inventory
Aircraft
Aircraft of the French Air and Space Force include: , - ! style="align: center; background: lavender;" colspan="8",Combat Aircraft
A military aircraft is any fixed-wing or rotary-wing aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed service of any type. Military aircraft can be either combat or non-combat:
* Combat aircraft are designed to destroy enemy equi ...
, -
, Mirage 2000C/5F , , France , , Jet , , Fighter-bomber , , 1983 , , 40 , , , , Mirage 2000C fleet has been withdrawn from service on June 23, 2022 on the BA115 Orange, where the last unit flying the type was based (EC 2/5 "Île-de-France")
, -
, Mirage 2000D , , France , , Jet , , Attack , , 1995 , , 68 , , 68 , , 55 examples of the 2000D variant will be modernized MLU by 2025
, -
, Rafale B/C , , France , , Jet , , Multirole , , 2006 , , 102 , , , , 46 additional Rafale M in naval service.Rafale replaced the
Mirage 2000N
The Dassault Mirage 2000N is a variant of the Dassault Mirage 2000, Mirage 2000 designed for nuclear strike. It formed the core of the French air-based Strategic nuclear weapon, strategic nuclear Deterrence theory, deterrent. The Mirage 2000D ...
in nuclear strike roles
, -
! style="align: center; background: lavender;" colspan="8" , Reconnaissance
, -
, Transall C-160
The Transall C-160 is a military transport aircraft, produced as a joint venture between France and Germany. "Transall" is an abbreviation of the manufacturing consortium Transporter Allianz, comprising the companies of MBB, Aerospatiale, and ...
, , France/Germany , , Propeller , , SIGINT/ELINT , , 1968 , , 2 , , 2 , ,
, -
, Beechcraft Super King Air 350 , , USA , , Propeller , , ISR , , 2018 , , 2 , , 2 , ,
, -
, Boeing E-3F Sentry , , USA , , Jet , , AEW&C , , 1990 , , 4 , , 4 , ,
, -
! style="align: center; background: lavender;" colspan="8" , Transport and Tanker
, -
, Airbus A330 MRTT , , Europe , , Jet , , Tanker & Transport , , 2018 , , 9 , , 9 , , 9 delivered on an order of 15. The 10th, 11th, 12th will be delivered in July, September and December 2023.The final target of 15 aircraft will be reached between 2025 and 2030 by converting the 3 A330-200s
, -
, Boeing C-135FR , , USA , , Jet , , Tanker , , 1964 , , 11 , , 11 , ,
, -
, Airbus A400M Atlas
The Airbus A400M AtlasNamed after the Greek mythological figure. is a European four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft. It was designed by Airbus Military (now Airbus Defence and Space) as a tactical airlifter with strategic capab ...
, , Europe , , Propeller , , Transport , , 2014 , , 20 , , 20 , , 30 more on order
, -
, DHC-6 Twin Otter
The de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter is a Canadian STOL (Short Takeoff and Landing) utility aircraft developed by de Havilland Canada, which produced the aircraft from 1965 to 1988; Viking Air purchased the type certificate, then restarted ...
, , Canada , , Propeller , , Transport , , 1976 , , 5 , , 5 , ,
, -
, CASA CN235M-200/300 , , Spain , , Propeller , , Transport , , 1983 , , 27 , , 27 , ,
, -
, Lockheed C-130 Hercules
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 was originally desig ...
, , USA , , Propeller , , Transport , , 1987 , , 14 , , 14 , , 7 C-130H, 7 C-130H-30
, -
, Lockheed C-130J Super Hercules , , USA , , Propeller , , Tanker & Transport , , 2018–2019 , , 2/2 , , 4 , , 2 KC-130J and 2 C-130J to support Special Forces Operations
, -
! style="align: center; background: lavender;" colspan="8" , VIP Transport
, -
, Airbus A330-243 , , Europe , , Jet , , Transport , , 2020 , , 4 , , 4 , , 1 for presidential transport
, -
, Dassault Falcon 2000 , , France , , Jet , , Transport , , 2011 , , 2 , , 2 , ,
, -
, Dassault Falcon 7X , , France , , Jet , , Transport , , 2009 , , 2 , , 2 , ,
, -
, Dassault Falcon 900
The Dassault Falcon 900, commonly abbreviated as the F900, is a French-built corporate trijet aircraft made by Dassault Aviation.
Development
The Falcon 900 is a development of the Falcon 50, itself a development of the earlier Falcon 20. The ...
, , France , , Jet , , Transport , , 1991 , , 2 , , 2 , ,
, -
, Socata TBM 700 , , France , , Propeller , , Transport , , 1990 , , 15 , , 15 , ,
, -
! style="align: center; background: lavender;" colspan="8" , Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
, -
, Aérospatiale SA330 Puma , , France , , Rotorcraft , , Transport , , 1968 , , 18 , , 18 , , To be replaced by 26 H225M Caracal
, -
, Eurocopter AS555 Fennec , , Europe , , Rotorcraft , , Trainer , , 1990 , , 40 , , 40 , , ,
, -
, Eurocopter EC725 Caracal
The Eurocopter EC725 Caracal, now called Airbus Helicopters H225M, is a long-range tactical transport military helicopter developed from the Eurocopter AS532 Cougar for military use. It is a twin-engined aircraft and can carry up to 28 seated t ...
, , Europe , , Rotorcraft , , CSAR/SOF , , 2006 , , 18 , , 26 , , 8 new on order. More 8 in 2021 transferred from French Army
, -
! style="align: center; background: lavender;" colspan="8" , Trainer aircraft
A trainer is a class of aircraft designed specifically to facilitate flight training of pilots and aircrews. The use of a dedicated trainer aircraft with additional safety features—such as tandem flight controls, forgiving flight characteristi ...
, -
, Diamond HK36 Super Dimona
The Diamond HK36 Super Dimona is an extensive family of Austrian low-wing, T-tailed, two-seat motor gliders that were designed by Wolf Hoffmann and currently produced by Diamond Aircraft Industries.Said, Bob: ''1983 Sailplane Directory, Soa ...
, , Austria , , Propeller , , Trainer , , 2010 , , 5 , , 5 , ,
, -
, Embraer EMB 121 Xingu
The Embraer EMB 121 Xingu (pronounced "''shingoo''") is a twin-turboprop fixed-wing aircraft built by the Brazilian aircraft manufacturer, Embraer. The design is based on the EMB 110 Bandeirante, using its wing and engine design merged with an a ...
, , Brazil , , Propeller , , Trainer , , 1982 , , 22 , , 22 , ,
, -
, Extra EA-300
The Extra Flugzeugbau EA300 is a two-seat aerobatic monoplane capable of Unlimited category competition. It was designed in 1987 by Walter Extra, a German aerobatic pilot, and built by Extra Flugzeugbau.
Design and development
Design of the ...
, , Germany , , Propeller , , Utility , , 2005 , , 3 , , 3 , ,
, -
, Pilatus PC-21
The Pilatus PC-21 is a turboprop-powered advanced trainer with a stepped tandem cockpit. It is manufactured by Pilatus Aircraft of Switzerland.
Development
In November 1997 Pilatus flew a modified PC-7 Mk.II in order to test improvements for a ...
, , Switzerland , , Propeller , , Trainer , , 2018 , , 17 , , 17 , ,
, -
, Mirage 2000B-S5 , , France , , Jet , , Conversion trainer , , 1993 , , 7 , , 7 , , based at Orange-Caritat: EC 2/5 Ile-de-France; unarmed aircraft which will be kept until the withdrawal of the Mirage 2000 D to ensure the conversion to Mirage 2000.
, -
, Alpha Jet
The Dassault/Dornier Alpha Jet is a light attack jet and advanced jet trainer co-manufactured by Dassault Aviation of France and Dornier Flugzeugwerke of Germany. It was developed specifically to perform trainer and light attack missions, as ...
, , France/Germany , , Jet , , Trainer , , 1978 , , 80 , , 80 , , Includes presentation team
, -
! style="align: center; background: lavender;" colspan="8" , UAVs
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controlle ...
, -
, General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper , , USA , , UAV , , ISR/Attack, , 2013 , , 12 , , 12 , , One of the six original crashed in Niger. The drone lost in the Sahel in November 2018 is replaced by a Reaper rented, for two years, to General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (for the annual sum of $1)
Photo gallery with current main aircraft
Air defence
Satellites
Personnel
 Since the end of the Algerian War, the French Air and Space Force has comprised about 17 to 19% of the French Armed Forces. In 1990, at the end of the Cold War, numbers reached 56,400 military personnel under contract, out of which 36,300 were part of conscription and 5,400 civilians.Bilan social 90, Editor : Direction de la fonction militaire et du personnel civil, 1990, total pages 62, passage 6 to
Since the end of the Algerian War, the French Air and Space Force has comprised about 17 to 19% of the French Armed Forces. In 1990, at the end of the Cold War, numbers reached 56,400 military personnel under contract, out of which 36,300 were part of conscription and 5,400 civilians.Bilan social 90, Editor : Direction de la fonction militaire et du personnel civil, 1990, total pages 62, passage 6 to format=PDF
In 2008, forecasts for personnel of the French Air Force were expected to number 50,000 out of which 44,000 aviators on the horizon in 2014. In 2010, the number personnel of the French Air Force was reduced to 51,100 men and women (20%) out of which: 13% officers; 55% sous-officier; 29% air military technicians (MTA); 3% volunteers of national service and aspirant volunteers; 6,500 civilians (14%). They form several functions: ; Non-flying personnel Non-navigating personnel of the French Air and Space Force include and are not limited to : Systems Aerial Mechanics (french: mécanicien système aéronautique), Aerial Controllers (french: contrôleur aérien),
Meteorologist
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies and works in the field of meteorology aiming to understand or predict Earth's atmospheric phenomena including the weather. Those who study meteorological phenomena are meteorologists in research, while t ...
s (french: météorologue), Administrative Personnel, Air Parachute Commandos (french: Commandos parachutistes de l'air), in Informatics, in Infrastructures, in Intelligence, Commissioner of the Armies (french: Commissaire) (Administrator Task).
; Flying personnel
Pilots, Mechanical Navigating Officer (french: Mécanicien Navigant), Navigating Arms Systems Officer (french: Navigateur Officier Système d'Armes) (NOSA), Combat Air Medic (french: Convoyeur de l'Air) (CVA).
Training of personnel
 Officers, within their recruitment and future specialty, are trained at:
*
Officers, within their recruitment and future specialty, are trained at:
* École de l'air
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
(french: École de l'air
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
) (Air School) de Provence
* École Militaire de l'Air (french: École militaire de l'air) (Military Air School)
* École des commissaires des armées (french: École des commissaires des armées) (Commissioners Armies School)
* École de pilotage de l'Armée de l'air (french: École de pilotage de l'Armée de l'air) (Piloting School of the French Air and Space Force)
* École de l'aviation de transport (french: École de l'aviation de transport) (Aviation Transport School)
* École de l'aviation de chasse (french: École de l'aviation de chasse) (Aviation Hunter Fighter Pilot School)
* École de transition opérationnelle (french: École de transition opérationnelle) (Operational Transition School)
Officers of the French Air and Space Force are spread in three corps:
* Air Officer (french: Officiers de l'air)
* Officer Mechanics (french: Officiers Mécaniciens)
* Aerial Base Officer (french: officiers des bases de l'air), amongst which, officers of the Air Parachute Commandos (french: Commandos parachutistes de l'air) are featured.
Non-commissioned officers (Sous-Officiers) are trained at:
* École de formation des sous-officiers de l'Armée de l'air (french: École de formation des sous-officiers de l'Armée de l'air) (EFSOAA) de Rochefort
* École interarmées (french: École interarmées) (Inter-arm School) for administrative specialists
* Escadron de formation des commandos de l'air (french: Escadron de formation des commandos de l'air) (EFCA) at Orange-Caritat Air Base
Air Base 115 Orange-Caritat (french: Base aérienne 115 Orange-Caritat "Capitaine de Seyne" or ''BA 115'', ) is a French Air and Space Force (Armée de l'air et de l'espace) base in Vaucluse, France. It is equipped with one runway and was named a ...
(BA 115) for the personnel concerned
Military Air Technicians (french: militaires techniciens de l’air) having been trained until 1 July 2015 at the Center of Elementary Military Formation (french: " Centre de formation militaire élémentaire ") of the Technical Instruction School of the French Air and Space Force (french: École d'enseignement technique de l'Armée de l'air) of Saintes. Since 1 July 2015, training has taken place at Orange-Caritat Air Base, within the " Operational Combatant Preparation Center of the Air Force " (french: Centre de préparation opérationnelle du combattant de l'Armée de l'air).
Air traffic controller
Air traffic control specialists, abbreviated ATCS, are personnel responsible for the safe, orderly, and expeditious flow of air traffic in the global air traffic control system. Usually stationed in air traffic control centers and control ...
s are trained at the Center of Instruction Control and Air Defense (french: Centre d'Instruction du Contrôle et de la Défense Aérienne).
Ranks
;Officers ;EnlistedSee also
* List of Escadres of the French Air Force * List of French Air and Space Force aircraft squadrons * French Naval Aviation * List of military aircraft of FranceNotes
References
; CitationsFurther reading
* Olivier, Jean-Marc, (ed.), ''Histoire de l'armée de l'air et des forces aériennes françaises du XVIIIe siècle à nos jours" '' istory of the Air Force and French aerial forces since the 18th century to the present Toulouse, Privat, 2014, 552 p. * * Diego Ruiz Palmer, "France's Military Command Structures in the 1990s," in Thomas-Durell Young, Command in NATO After the Cold War: Alliance, National and Multinational Considerations, U.S. Army Strategic Studies Institute, June 1997External links
*Official website
* *
appendix of the budget bill for 2006,
French Senate
The Senate (french: Sénat, ) is the upper house of the French Parliament, with the lower house being the National Assembly, the two houses constituting the legislature of France. The French Senate is made up of 348 senators (''sénateurs'' a ...
{{Authority control
! 03
Military units and formations established in 1909
1909 establishments in France