Aristotle's biology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aristotle's biology is the theory of

 Aristotle's biology is constructed on the basis of his theory of form, which is derived from Plato's
Aristotle's biology is constructed on the basis of his theory of form, which is derived from Plato's
 As analysed by the
As analysed by the
 Aristotle's account of metabolism sought to explain how food was processed by the body to provide both heat and the materials for the body's construction and maintenance. The metabolic system for live-bearing tetrapods described in the ''Parts of Animals'' can be modelled as an open system, a branching tree of flows of material through the body.
The system worked as follows. The incoming material, food, enters the body and is concocted into blood; waste is excreted as urine, bile, and faeces, and the element fire is released as heat. Blood is made into flesh, the rest forming other earthy tissues such as bones, teeth, cartilages and sinews. Leftover blood is made into
Aristotle's account of metabolism sought to explain how food was processed by the body to provide both heat and the materials for the body's construction and maintenance. The metabolic system for live-bearing tetrapods described in the ''Parts of Animals'' can be modelled as an open system, a branching tree of flows of material through the body.
The system worked as follows. The incoming material, food, enters the body and is concocted into blood; waste is excreted as urine, bile, and faeces, and the element fire is released as heat. Blood is made into flesh, the rest forming other earthy tissues such as bones, teeth, cartilages and sinews. Leftover blood is made into
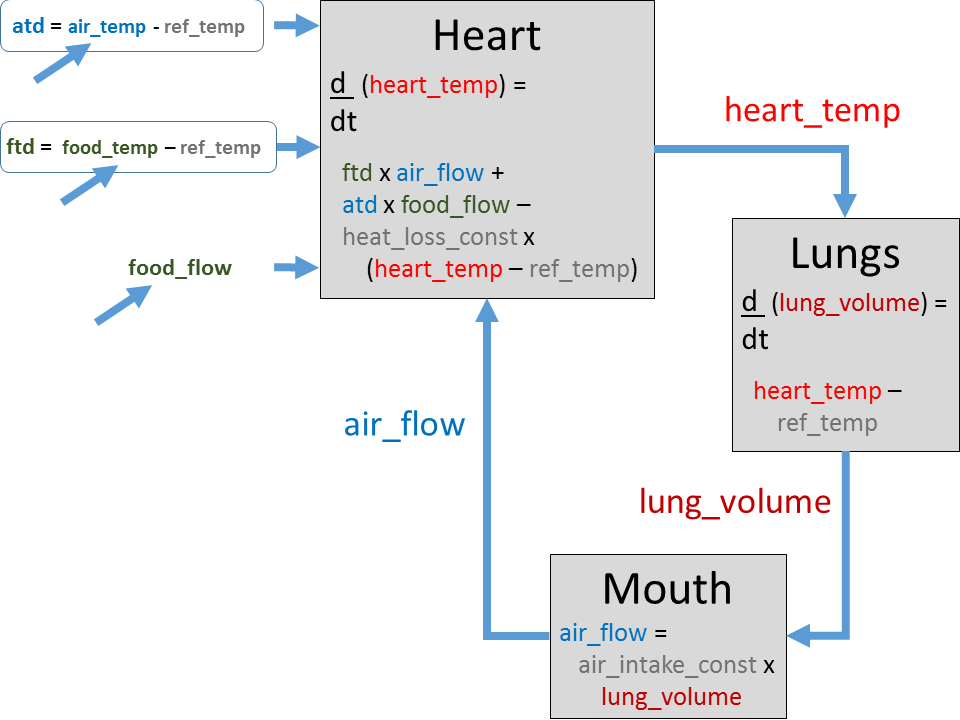 Aristotle's account of temperature regulation sought to explain how an animal maintained a steady temperature and the continued oscillation of the thorax needed for breathing. The system of regulation of temperature and breathing described in ''Youth and Old Age, Life and Death'' 26 is sufficiently detailed to permit modelling as a negative feedback control system (one that maintains a desired property by opposing disturbances to it), with a few assumptions such as a desired temperature to compare the actual temperature against.
The system worked as follows. Heat is constantly lost from the body. Food products reach the heart and are processed into new blood, releasing fire during metabolism, which raises the blood temperature too high. That raises the heart temperature, causing lung volume to increase, in turn raising the airflow at the mouth. The cool air brought in through the mouth reduces the heart temperature, so the lung volume accordingly decreases, restoring the temperature to normal.
The mechanism only works if the air is cooler than the reference temperature. If the air is hotter than that, the system becomes a positive feedback cycle, the body's fire is put out, and death follows. The system as described damps out fluctuations in temperature. Aristotle however predicted that his system would cause lung oscillation (breathing), which is possible given extra assumptions such as of delays or non-linear responses.
Aristotle's account of temperature regulation sought to explain how an animal maintained a steady temperature and the continued oscillation of the thorax needed for breathing. The system of regulation of temperature and breathing described in ''Youth and Old Age, Life and Death'' 26 is sufficiently detailed to permit modelling as a negative feedback control system (one that maintains a desired property by opposing disturbances to it), with a few assumptions such as a desired temperature to compare the actual temperature against.
The system worked as follows. Heat is constantly lost from the body. Food products reach the heart and are processed into new blood, releasing fire during metabolism, which raises the blood temperature too high. That raises the heart temperature, causing lung volume to increase, in turn raising the airflow at the mouth. The cool air brought in through the mouth reduces the heart temperature, so the lung volume accordingly decreases, restoring the temperature to normal.
The mechanism only works if the air is cooler than the reference temperature. If the air is hotter than that, the system becomes a positive feedback cycle, the body's fire is put out, and death follows. The system as described damps out fluctuations in temperature. Aristotle however predicted that his system would cause lung oscillation (breathing), which is possible given extra assumptions such as of delays or non-linear responses.
 Aristotle's information processing model has been named the "centralized incoming and outgoing motions model". It sought to explain how changes in the world led to appropriate behaviour in the animal.
The system worked as follows. The animal's
Aristotle's information processing model has been named the "centralized incoming and outgoing motions model". It sought to explain how changes in the world led to appropriate behaviour in the animal.
The system worked as follows. The animal's
 Aristotle's inheritance model sought to explain how the parents' characteristics are transmitted to the child, subject to influence from the environment.
The system worked as follows. The father's semen and the mother's menses have movements that encode their parental characteristics. The model is partly asymmetric, as only the father's movements define the form or ''eidos'' of the species, while the movements of both the father's and the mother's uniform parts define features other than the form, such as the father's eye colour or the mother's nose shape.
Aristotle's theory has some symmetry, as semen movements carry maleness while the menses carry femaleness. If the semen is hot enough to overpower the cold menses, the child will be a boy; but if it is too cold to do this, the child will be a girl. Inheritance is thus
Aristotle's inheritance model sought to explain how the parents' characteristics are transmitted to the child, subject to influence from the environment.
The system worked as follows. The father's semen and the mother's menses have movements that encode their parental characteristics. The model is partly asymmetric, as only the father's movements define the form or ''eidos'' of the species, while the movements of both the father's and the mother's uniform parts define features other than the form, such as the father's eye colour or the mother's nose shape.
Aristotle's theory has some symmetry, as semen movements carry maleness while the menses carry femaleness. If the semen is hot enough to overpower the cold menses, the child will be a boy; but if it is too cold to do this, the child will be a girl. Inheritance is thus
 Aristotle's model of embryogenesis sought to explain how the inherited parental characteristics cause the formation and development of an embryo.
The system worked as follows. First, the father's semen curdles the mother's menses, which Aristotle compares with how rennet (an
Aristotle's model of embryogenesis sought to explain how the inherited parental characteristics cause the formation and development of an embryo.
The system worked as follows. First, the father's semen curdles the mother's menses, which Aristotle compares with how rennet (an
 Aristotle did not do
Aristotle did not do
 Aristotle was the first person to study biology systematically. He spent two years observing and describing the zoology of
Aristotle was the first person to study biology systematically. He spent two years observing and describing the zoology of
 Aristotle distinguished about 500 species of birds, mammals and fishes in ''History of Animals'' and ''
Aristotle distinguished about 500 species of birds, mammals and fishes in ''History of Animals'' and ''
 Aristotle stated in the ''History of Animals'' that all beings were arranged in a fixed scale of perfection, reflected in their form (''eidos''). They stretched from minerals to plants and animals, and on up to man, forming the '' ''scala naturae'' or great chain of being''. His system had eleven grades, arranged according to the potentiality of each being, expressed in their form at birth. The highest animals gave birth to warm and wet creatures alive, the lowest bore theirs cold, dry, and in thick eggs. The system was based on Aristotle's interpretation of the
Aristotle stated in the ''History of Animals'' that all beings were arranged in a fixed scale of perfection, reflected in their form (''eidos''). They stretched from minerals to plants and animals, and on up to man, forming the '' ''scala naturae'' or great chain of being''. His system had eleven grades, arranged according to the potentiality of each being, expressed in their form at birth. The highest animals gave birth to warm and wet creatures alive, the lowest bore theirs cold, dry, and in thick eggs. The system was based on Aristotle's interpretation of the
 The book was mentioned by
The book was mentioned by
 Renaissance zoologists made use of Aristotle's zoology in two ways. Especially in Italy, scholars such as
Renaissance zoologists made use of Aristotle's zoology in two ways. Especially in Italy, scholars such as
 In the Early Modern period, Aristotle came to represent all that was obsolete, scholastic, and wrong, not helped by his association with medieval theology. In 1632, Galileo represented
In the Early Modern period, Aristotle came to represent all that was obsolete, scholastic, and wrong, not helped by his association with medieval theology. In 1632, Galileo represented
 Zoologists have frequently mocked Aristotle for errors and unverified secondhand reports. However, modern observation has confirmed one after another of his more surprising claims, including the
Zoologists have frequently mocked Aristotle for errors and unverified secondhand reports. However, modern observation has confirmed one after another of his more surprising claims, including the
De Juventute et Senectute, De Vita et Morte, De Respiratione
biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
, grounded in systematic observation and collection of data, mainly zoological
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and dis ...
, embodied in Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, ß╝łŽü╬╣ŽāŽä╬┐Žä╬Ł╬╗╬ĘŽé ''Aristot├®l─ōs'', ; 384ŌĆō322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
's books on the science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
. Many of his observations were made during his stay on the island of Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( el, ╬ø╬ŁŽā╬▓╬┐Žé, L├®svos ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece. It is separated from Asia Minor by the nar ...
, including especially his descriptions of the marine biology of the Pyrrha lagoon, now the Gulf of Kalloni. His theory is based on his concept of form, which derives from but is markedly unlike Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, ╬Ā╬╗╬¼ŽäŽē╬Į ; 428/427 or 424/423 ŌĆō 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
's theory of Forms
The theory of Forms or theory of Ideas is a philosophical theory, fuzzy concept, or world-view, attributed to Plato, that the physical world is not as real or true as timeless, absolute, unchangeable ideas. According to this theory, ideas in th ...
.
The theory describes five major biological processes, namely metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, ╬╝╬ĄŽä╬▒╬▓╬┐╬╗╬« ''metabol─ō'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
, temperature regulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, information processing, embryogenesis, and inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officia ...
. Each was defined in some detail, in some cases sufficient to enable modern biologists to create mathematical models of the mechanisms described. Aristotle's method, too, resembled the style of science used by modern biologists when exploring a new area, with systematic data collection, discovery of patterns, and inference of possible causal explanations from these. He did not perform experiments in the modern sense, but made observations of living animals and carried out dissections. He names some 500 species of bird, mammal, and fish; and he distinguishes dozens of insects and other invertebrates. He describes the internal anatomy of over a hundred animals, and dissected around 35 of these.
Aristotle's writings on biology, the first in the history of science, are scattered across several books, forming about a quarter of his writings that have survived. The main biology texts were the ''History of Animals
''History of Animals'' ( grc-gre, ╬żß┐Č╬Į ŽĆ╬ĄŽüßĮČ ŽäßĮ░ ╬Čß┐Ę╬▒ ß╝▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žü╬╣ß┐Č╬Į, ''Ton peri ta zoia historion'', "Inquiries on Animals"; la, Historia Animalium, "History of Animals") is one of the major texts on biology by the ancient Gr ...
'', ''Generation of Animals
The ''Generation of Animals'' (or ''On the Generation of Animals''; Greek: ''╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į ╬│╬Ą╬Į╬ŁŽā╬ĄŽēŽé'' (''Peri Zoion Geneseos''); Latin: ''De Generatione Animalium'') is one of the biological works of the Corpus Aristotelicum, the col ...
'', ''Movement of Animals
''Movement of Animals'' (or ''On the Motion of Animals''; Greek ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į ╬║╬╣╬Į╬«Žā╬ĄŽēŽé; Latin ''De Motu Animalium'') is one of Aristotle's major texts on biology. It sets out the general principles of animal locomotion
Animal lo ...
'', ''Progression of Animals
''Progression of Animals'' (or ''On the Gait of Animals''; el, ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ŽĆ╬┐Žü╬Ą╬»╬▒Žé ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į; la, De incessu animalium) is one of Aristotle's major texts on biology. It gives details of gait and movement in various kinds of animals, as wel ...
'', ''Parts of Animals
''Parts of Animals'' (or ''On the Parts of Animals''; Greek ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į ╬╝╬┐Žü╬»Žē╬Į; Latin ''De Partibus Animalium'') is one of Aristotle's major texts on biology. It was written around 350 BC. The whole work is roughly a study in animal ...
'', and ''On the Soul
''On the Soul'' (Greek: , ''Peri Psych─ōs''; Latin: ''De Anima'') is a major treatise written by Aristotle c. 350 BC. His discussion centres on the kinds of souls possessed by different kinds of living things, distinguished by their different op ...
'', as well as the lost drawings of ''The Anatomies'' which accompanied the ''History''.
Apart from his pupil, Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, ╬ś╬ĄŽīŽåŽü╬▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žé ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
, who wrote a matching ''Enquiry into Plants
Theophrastus's ''Enquiry into Plants'' or ''Historia Plantarum'' ( grc-gre, ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ŽåŽģŽäß┐Č╬Į ß╝▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žü╬»╬▒, ''Peri phyton historia'') was, along with his mentor Aristotle's ''History of Animals'', Pliny the Elder's '' Natural History'' a ...
'', no research of comparable scope was carried out in ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, ß╝Ö╬╗╬╗╬¼Žé, Hell├Īs) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12thŌĆō9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
, though Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
medicine in Egypt continued Aristotle's inquiry into the mechanisms of the human body. Aristotle's biology was influential in the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
Islamic world. Translation of Arabic versions and commentaries into Latin brought knowledge of Aristotle back into Western Europe, but the only biological work widely taught in medieval universities was ''On the Soul''. The association of his work with medieval scholasticism, as well as errors in his theories, caused Early Modern scientists such as Galileo and William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 ŌĆō 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and propert ...
to reject Aristotle. Criticism of his errors and secondhand reports continued for centuries. He has found better acceptance among zoologists, and some of his long-derided observations in marine biology have been found in modern times to be true.
Context

Aristotle's background
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, ß╝łŽü╬╣ŽāŽä╬┐Žä╬Ł╬╗╬ĘŽé ''Aristot├®l─ōs'', ; 384ŌĆō322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
(384ŌĆō322 BC) studied at Plato's Academy
The Academy (Ancient Greek: ß╝ł╬║╬▒╬┤╬Ę╬╝╬»╬▒) was founded by Plato in c. 387 BC in Athens. Aristotle studied there for twenty years (367ŌĆō347 BC) before founding his own school, the Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenistic p ...
in Athens
Athens ( ; el, ╬æ╬Ė╬«╬Į╬▒, Ath├Łna ; grc, ß╝ł╬Ėß┐å╬Į╬▒╬╣, Ath├¬nai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, remaining there for about 20 years. Like Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, ╬Ā╬╗╬¼ŽäŽē╬Į ; 428/427 or 424/423 ŌĆō 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, he sought universals
In metaphysics, a universal is what particular things have in common, namely characteristics or qualities. In other words, universals are repeatable or recurrent entities that can be instantiated or exemplified by many particular things. For exa ...
in his philosophy, but unlike Plato he backed up his views with detailed and systematic observation, notably of the natural history of the island of Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( el, ╬ø╬ŁŽā╬▓╬┐Žé, L├®svos ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece. It is separated from Asia Minor by the nar ...
, where he spent about two years, and the marine life in the seas around it, especially of the Pyrrha lagoon in the island's centre. This study made him the earliest scientist whose written work survives. No similarly detailed work on zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and ...
was attempted until the sixteenth century; accordingly Aristotle remained highly influential for some two thousand years. He returned to Athens and founded his own school, the Lycaeum, where he taught for the last dozen years of his life. His writings on zoology form about a quarter of his surviving work. Aristotle's pupil Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, ╬ś╬ĄŽīŽåŽü╬▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žé ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
later wrote a similar book on botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
, ''Enquiry into Plants''.
Aristotelian forms
 Aristotle's biology is constructed on the basis of his theory of form, which is derived from Plato's
Aristotle's biology is constructed on the basis of his theory of form, which is derived from Plato's theory of Forms
The theory of Forms or theory of Ideas is a philosophical theory, fuzzy concept, or world-view, attributed to Plato, that the physical world is not as real or true as timeless, absolute, unchangeable ideas. According to this theory, ideas in th ...
, but significantly different from it. Plato's Forms were eternal and fixed, being "blueprints in the mind of God". Real things in the world could, in Plato's view, at best be approximations to these perfect Forms. Aristotle heard Plato's view and developed it into a set of three biological concepts. He uses the same Greek word, (''eidos''), to mean first of all the set of visible features that uniquely characterised a kind of animal. Aristotle used the word ╬│╬Ł╬Į╬┐Žé (g├®nos) to mean a kind. For example, the kind of animal called a bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
has feathers, a beak, wings, a hard-shelled egg, and warm blood.
Aristotle further noted that there are many bird forms within the bird kind ŌĆō cranes, eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
s, crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
s, bustard
Bustards, including floricans and korhaans, are large, terrestrial birds living mainly in dry grassland areas and on the steppes of the Old World. They range in length from . They make up the family Otididae (, formerly known as Otidae). Bustar ...
s, sparrows, and so on, just as there are many forms of fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
es within the fish kind. He sometimes called these ''atoma eid─ō'', indivisible forms. Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
is one of these indivisible forms: Socrates and the rest of us are all different individually, but we all have human form.
Finally, Aristotle observed that the child does not take just any form, but is given it by the parents' seeds, which combine. These seeds thus contain form, or in modern terms information. Aristotle makes clear that he sometimes intends this third sense by giving the analogy of a woodcarving. It takes its form from wood (its material cause); the tools and carving technique used to make it (its efficient cause); and the design laid out for it (its ''eidos'' or embedded information). Aristotle further emphasises the informational nature of form by arguing that a body is compounded of elements like earth and fire, just as a word is compounded of letters in a specific order.
System
Soul as system
 As analysed by the
As analysed by the evolutionary biologist
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life for ...
Armand Leroi
Armand Marie Leroi (born 16 July 1964) is a New Zealand-born Dutch author, broadcaster, and professor of evolutionary developmental biology at Imperial College in London. He received the Guardian First Book Award in 2004 for his book ''Mutant ...
, Aristotle's biology included five major interlocking processes:
# a metabolic process, whereby animals take in matter, change its qualities, and distribute these to use to grow, live, and reproduce
# a cycle of temperature regulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, whereby animals maintain a steady state, but which progressively fails in old age
# an information processing model whereby animals receive sensory information, alter it in the seat of sensation, and use it to drive movements of the limbs. He thus separated sensation from thought, unlike all previous philosophers except Alcmaeon.
# the process of inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officia ...
.
# the processes of embryonic development and of spontaneous generation
Spontaneous generation is a superseded scientific theory that held that living creatures could arise from nonliving matter and that such processes were commonplace and regular. It was hypothesized that certain forms, such as fleas, could arise f ...
The five processes formed what Aristotle called the soul: it was not something extra, but the system consisting exactly of these mechanisms. The Aristotelian soul died with the animal and was thus purely biological. Different types of organism possessed different types of soul. Plants had a vegetative soul, responsible for reproduction and growth. Animals had both a vegetative and a sensitive soul, responsible for mobility and sensation. Humans, uniquely, had a vegetative, a sensitive, and a rational soul, capable of thought and reflection.
Processes
Metabolism
 Aristotle's account of metabolism sought to explain how food was processed by the body to provide both heat and the materials for the body's construction and maintenance. The metabolic system for live-bearing tetrapods described in the ''Parts of Animals'' can be modelled as an open system, a branching tree of flows of material through the body.
The system worked as follows. The incoming material, food, enters the body and is concocted into blood; waste is excreted as urine, bile, and faeces, and the element fire is released as heat. Blood is made into flesh, the rest forming other earthy tissues such as bones, teeth, cartilages and sinews. Leftover blood is made into
Aristotle's account of metabolism sought to explain how food was processed by the body to provide both heat and the materials for the body's construction and maintenance. The metabolic system for live-bearing tetrapods described in the ''Parts of Animals'' can be modelled as an open system, a branching tree of flows of material through the body.
The system worked as follows. The incoming material, food, enters the body and is concocted into blood; waste is excreted as urine, bile, and faeces, and the element fire is released as heat. Blood is made into flesh, the rest forming other earthy tissues such as bones, teeth, cartilages and sinews. Leftover blood is made into fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
, whether soft suet
Suet is the raw, hard fat of beef, lamb or mutton found around the loins and kidneys.
Suet has a melting point of between 45 ┬░C and 50 ┬░C (113 ┬░F and 122 ┬░F) and congelation between 37 ┬░C and 40 ┬░C (98.6& ...
or hard lard. Some fat from all around the body is made into semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Sem ...
.
All the tissues are in Aristotle's view completely uniform parts with no internal structure of any kind; a cartilage for example was the same all the way through, not subdivided into atoms as Democritus
Democritus (; el, ╬ö╬Ę╬╝Žī╬║Žü╬╣Žä╬┐Žé, ''D─ōm├│kritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; ŌĆō ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
(c. 460ŌĆōc. 370 BC) had argued. The uniform parts can be arranged on a scale of Aristotelian qualities, from the coldest and driest, such as hair, to the hottest and wettest, such as milk.
At each stage of metabolism, residual materials are excreted as faeces, urine, and bile.
Temperature regulation
 Aristotle's account of temperature regulation sought to explain how an animal maintained a steady temperature and the continued oscillation of the thorax needed for breathing. The system of regulation of temperature and breathing described in ''Youth and Old Age, Life and Death'' 26 is sufficiently detailed to permit modelling as a negative feedback control system (one that maintains a desired property by opposing disturbances to it), with a few assumptions such as a desired temperature to compare the actual temperature against.
The system worked as follows. Heat is constantly lost from the body. Food products reach the heart and are processed into new blood, releasing fire during metabolism, which raises the blood temperature too high. That raises the heart temperature, causing lung volume to increase, in turn raising the airflow at the mouth. The cool air brought in through the mouth reduces the heart temperature, so the lung volume accordingly decreases, restoring the temperature to normal.
The mechanism only works if the air is cooler than the reference temperature. If the air is hotter than that, the system becomes a positive feedback cycle, the body's fire is put out, and death follows. The system as described damps out fluctuations in temperature. Aristotle however predicted that his system would cause lung oscillation (breathing), which is possible given extra assumptions such as of delays or non-linear responses.
Aristotle's account of temperature regulation sought to explain how an animal maintained a steady temperature and the continued oscillation of the thorax needed for breathing. The system of regulation of temperature and breathing described in ''Youth and Old Age, Life and Death'' 26 is sufficiently detailed to permit modelling as a negative feedback control system (one that maintains a desired property by opposing disturbances to it), with a few assumptions such as a desired temperature to compare the actual temperature against.
The system worked as follows. Heat is constantly lost from the body. Food products reach the heart and are processed into new blood, releasing fire during metabolism, which raises the blood temperature too high. That raises the heart temperature, causing lung volume to increase, in turn raising the airflow at the mouth. The cool air brought in through the mouth reduces the heart temperature, so the lung volume accordingly decreases, restoring the temperature to normal.
The mechanism only works if the air is cooler than the reference temperature. If the air is hotter than that, the system becomes a positive feedback cycle, the body's fire is put out, and death follows. The system as described damps out fluctuations in temperature. Aristotle however predicted that his system would cause lung oscillation (breathing), which is possible given extra assumptions such as of delays or non-linear responses.
Information processing
 Aristotle's information processing model has been named the "centralized incoming and outgoing motions model". It sought to explain how changes in the world led to appropriate behaviour in the animal.
The system worked as follows. The animal's
Aristotle's information processing model has been named the "centralized incoming and outgoing motions model". It sought to explain how changes in the world led to appropriate behaviour in the animal.
The system worked as follows. The animal's sense organ
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system re ...
is altered when it detects an object. This causes a perceptual change in the animal's seat of sensation, which Aristotle believed was the heart ( cardiocentrism) rather than the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
. This in turn causes a change in the heart's heat, which causes a quantitative change sufficient to make the heart transmit a mechanical impulse to a limb, which moves, moving the animal's body. The alteration in the heat of the heart also causes a change in the consistency of the joints, which helps the limb to move.
There is thus a causal chain which transmits information from a sense organ to an organ capable of making decisions, and onwards to a motor organ. In this respect, the model is analogous to a modern understanding of information processing such as in sensory-motor coupling Sensory-motor coupling is the coupling or integration of the sensory system and motor system. Sensorimotor integration is not a static process. For a given stimulus, there is no one single motor command. "Neural responses at almost every stage of a ...
.
Inheritance
 Aristotle's inheritance model sought to explain how the parents' characteristics are transmitted to the child, subject to influence from the environment.
The system worked as follows. The father's semen and the mother's menses have movements that encode their parental characteristics. The model is partly asymmetric, as only the father's movements define the form or ''eidos'' of the species, while the movements of both the father's and the mother's uniform parts define features other than the form, such as the father's eye colour or the mother's nose shape.
Aristotle's theory has some symmetry, as semen movements carry maleness while the menses carry femaleness. If the semen is hot enough to overpower the cold menses, the child will be a boy; but if it is too cold to do this, the child will be a girl. Inheritance is thus
Aristotle's inheritance model sought to explain how the parents' characteristics are transmitted to the child, subject to influence from the environment.
The system worked as follows. The father's semen and the mother's menses have movements that encode their parental characteristics. The model is partly asymmetric, as only the father's movements define the form or ''eidos'' of the species, while the movements of both the father's and the mother's uniform parts define features other than the form, such as the father's eye colour or the mother's nose shape.
Aristotle's theory has some symmetry, as semen movements carry maleness while the menses carry femaleness. If the semen is hot enough to overpower the cold menses, the child will be a boy; but if it is too cold to do this, the child will be a girl. Inheritance is thus particulate
Particulates ŌĆō also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) ŌĆō are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The te ...
(definitely one trait or another), as in Mendelian genetics
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later populari ...
, unlike the Hippocratic
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, ß╝╣ŽĆŽĆ╬┐╬║Žü╬¼Žä╬ĘŽé ßĮü ╬Üß┐Ę╬┐Žé, Hippokr├Īt─ōs ho K├┤ios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
model which was continuous and blending.
The child's sex can be influenced by factors that affect temperature, including the weather, the wind direction, diet, and the father's age. Features other than sex also depend on whether the semen overpowers the menses, so if a man has strong semen, he will have sons who resemble him, while if the semen is weak, he will have daughters who resemble their mother.
Embryogenesis
 Aristotle's model of embryogenesis sought to explain how the inherited parental characteristics cause the formation and development of an embryo.
The system worked as follows. First, the father's semen curdles the mother's menses, which Aristotle compares with how rennet (an
Aristotle's model of embryogenesis sought to explain how the inherited parental characteristics cause the formation and development of an embryo.
The system worked as follows. First, the father's semen curdles the mother's menses, which Aristotle compares with how rennet (an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
from a cow's stomach) curdles milk in cheesemaking
Cheesemaking (or caseiculture) is the craft of making cheese. The production of cheese, like many other food preservation processes, allows the nutritional and economic value of a food material, in this case milk, to be preserved in concentr ...
. This forms the embryo; it is then developed by the action of the ''pneuma'' (literally, breath or spirit) in the semen. The ''pneuma'' first makes the heart appear; this is vital, as the heart nourishes all other organs. Aristotle observed that the heart is the first organ seen to be active (beating) in a hen's egg. The ''pneuma'' then makes the other organs develop.
Method
Aristotle has been called unscientific by philosophers fromFrancis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 ŌĆō 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both ...
onwards for at least two reasons: his scientific style, and his use of explanation
An explanation is a set of statements usually constructed to describe a set of facts which clarifies the causes, context, and consequences of those facts. It may establish rules or laws, and may clarify the existing rules or laws in relatio ...
. His explanations are in turn made cryptic by his complicated system of causes. However, these charges need to be considered in the light of what was known in his own time. His systematic gathering of data, too, is obscured by the lack of modern methods of presentation, such as tables of data: for example, the whole of ''History of Animals
''History of Animals'' ( grc-gre, ╬żß┐Č╬Į ŽĆ╬ĄŽüßĮČ ŽäßĮ░ ╬Čß┐Ę╬▒ ß╝▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žü╬╣ß┐Č╬Į, ''Ton peri ta zoia historion'', "Inquiries on Animals"; la, Historia Animalium, "History of Animals") is one of the major texts on biology by the ancient Gr ...
'' Book VI is taken up with a list of observations of the life histories of birds that "would now be summarized in a single table in ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'' ŌĆō and in the Online Supplementary Information at that".
Scientific style
experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome oc ...
s in the modern sense. He used the ancient Greek term ''pepeiramenoi'' to mean observations, or at most investigative procedures, such as (in ''Generation of Animals'') finding a fertilised hen's egg of a suitable stage and opening it so as to be able to see the embryo's heart inside.
Instead, he practised a different style of science: systematically gathering data, discovering patterns common to whole groups of animals, and inferring possible causal explanations from these. This style is common in modern biology when large amounts of data become available in a new field, such as genomics. It does not result in the same certainty as experimental science, but it sets out testable hypotheses and constructs a narrative explanation of what is observed. In this sense, Aristotle's biology is scientific.
From the data he collected and documented, Aristotle inferred quite a number of rules
Rule or ruling may refer to:
Education
* Royal University of Law and Economics (RULE), a university in Cambodia
Human activity
* The exercise of political or personal control by someone with authority or power
* Business rule, a rule pert ...
relating the life-history features of the live-bearing tetrapods (terrestrial placental mammals) that he studied. Among these correct predictions are the following. Brood size decreases with (adult) body mass, so that an elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
has fewer young (usually just one) per brood than a mouse. Lifespan increases with gestation period, and also with body mass, so that elephants live longer than mice, have a longer period of gestation, and are heavier. As a final example, fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the natural capability to pr ...
decreases with lifespan, so long-lived kinds like elephants have fewer young in total than short-lived kinds like mice.
Mechanism and analogy
Aristotle's use of explanation has been considered "fundamentally unscientific". The French playwrightMoli├©re
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin (, ; 15 January 1622 (baptised) – 17 February 1673), known by his stage name Moli├©re (, , ), was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the greatest writers in the French language and worl ...
's 1673 play '' The Imaginary Invalid'' portrays the quack Aristotelian doctor Argan blandly explaining that opium causes sleep by virtue of its dormitive leep-makingprinciple, its ''virtus dormitiva''. Argan's explanation is at best empty (devoid of mechanism), at worst vitalist
Vitalism is a belief that starts from the premise that "living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things." Wher ...
. But the real Aristotle did provide biological mechanisms, in the form of the five processes of metabolism, temperature regulation, information processing, embryonic development, and inheritance that he developed. Further, he provided mechanical, non-vitalist analogies for these theories, mentioning bellows
A bellows or pair of bellows is a device constructed to furnish a strong blast of air. The simplest type consists of a flexible bag comprising a pair of rigid boards with handles joined by flexible leather sides enclosing an approximately airtig ...
, toy carts, the movement of water through porous pots, and even automatic puppets.
Complex causality
Readers of Aristotle have found thefour causes
The four causes or four explanations are, in Aristotelian thought, four fundamental types of answer to the question "why?", in analysis of change or movement in nature: the material, the formal, the efficient, and the final. Aristotle wrote th ...
that he uses in his biological explanations opaque, something not helped by many centuries of confused exegesis
Exegesis ( ; from the Greek , from , "to lead out") is a critical explanation or interpretation of a text. The term is traditionally applied to the interpretation of Biblical works. In modern usage, exegesis can involve critical interpretation ...
. For a biological system, these are however straightforward enough. The material cause is simply what a system is constructed from. The goal (final cause
The four causes or four explanations are, in Aristotelian thought, four fundamental types of answer to the question "why?", in analysis of change or movement in nature: the material, the formal, the efficient, and the final. Aristotle wrote th ...
) and formal cause are what something is for, its function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
: to a modern biologist, such teleology describes adaptation under the pressure of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. The efficient cause is how a system develops and moves: to a modern biologist, those are explained by developmental biology and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
. Biologists continue to offer explanations of these same kinds.
Empirical research
 Aristotle was the first person to study biology systematically. He spent two years observing and describing the zoology of
Aristotle was the first person to study biology systematically. He spent two years observing and describing the zoology of Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( el, ╬ø╬ŁŽā╬▓╬┐Žé, L├®svos ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece. It is separated from Asia Minor by the nar ...
and the surrounding seas, including in particular the Pyrrha
In Greek mythology, Pyrrha (; Ancient Greek: ╬ĀŽŹŽüŽü╬▒) was the daughter of Epimetheus and Pandora and wife of Deucalion of whom she had three sons, Hellen, Amphictyon, Orestheus; and three daughters Protogeneia, Pandora II and Thyia. Accordi ...
lagoon in the centre of Lesbos. His data are assembled from his own observations, statements given by people with specialised knowledge such as beekeeper
A beekeeper is a person who keeps honey bees.
Beekeepers are also called honey farmers, apiarists, or less commonly, apiculturists (both from the Latin '' apis'', bee; cf. apiary). The term beekeeper refers to a person who keeps honey bees i ...
s and fishermen
A fisher or fisherman is someone who captures fish and other animals from a body of water, or gathers shellfish.
Worldwide, there are about 38 million commercial and subsistence fishers and fish farmers. Fishers may be professional or recreati ...
, and less accurate accounts provided by travellers from overseas.
His observations on catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive ...
, electric fish (''Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, s ...
'') and angler fish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence c ...
are detailed, as is his writing on cephalopods including the octopus, cuttlefish and paper nautilus. He reported that fishermen had asserted that the octopusŌĆÖs hectocotyl arm was used in sexual reproduction. He admitted its use in mating 'only for the sake of attachment', but rejected the idea that it was useful for generation, since "it is outside the passage and indeed outside the body". In the 19th century, biologists found that the reported function was correct. He separated the aquatic mammals from fish, and knew that shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s and rays were part of the group he called ''Selach─ō'' (roughly, the modern zoologist's selachians).
Among many other things, he gave accurate descriptions of the four-chambered stomachs of ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The ...
s, and of the ovoviviparous
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ...
embryological development of the dogfish. His accounts of about 35 animals are sufficiently detailed to convince biologists that he dissected those species, indeed vivisecting some; he mentions the internal anatomy of roughly 110 animals in total.
Classification
 Aristotle distinguished about 500 species of birds, mammals and fishes in ''History of Animals'' and ''
Aristotle distinguished about 500 species of birds, mammals and fishes in ''History of Animals'' and ''Parts of Animals
''Parts of Animals'' (or ''On the Parts of Animals''; Greek ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į ╬╝╬┐Žü╬»Žē╬Į; Latin ''De Partibus Animalium'') is one of Aristotle's major texts on biology. It was written around 350 BC. The whole work is roughly a study in animal ...
''. His system of classification, one of the earliest in scientific taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
, was influential for over two thousand years. Aristotle distinguished animals with blood, ''Enhaima'' (the modern zoologist's vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
) and animals without blood, ''Anhaima'' (invertebrates
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordat ...
).
Animals with blood included live-bearing tetrapods, ''Z┼Źiotoka tetrapoda'' (roughly, the mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
), being warm, having four legs, and giving birth to their young.
The cetaceans, ''K─ōt┼Źd─ō'', also had blood and gave birth to live young, but did not have legs, and therefore formed a separate group (''megista gen─ō'', defined by a set of functioning "parts").
The birds, ''Ornithes'' had blood and laid eggs, but had only 2 legs and were a distinct form (''eidos'') with feathers and beaks instead of teeth, so they too formed a distinct group, of over 50 kinds.
The egg-bearing tetrapods, ''┼īiotoka tetrapoda'' ( reptiles and amphibians) had blood and four legs, but were cold and laid eggs, so were a distinct group.
The snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s, ''Opheis'', similarly had blood, but no legs, and laid dry eggs, so were a separate group.
The fishes
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, ''Ikhthyes'', had blood but no legs, and laid wet eggs, forming a definite group. Among them, the selachians ''Selakh─ō'' (sharks and rays), had cartilages instead of bones.
Animals without blood were divided into soft-shelled ''Malakostraka'' (crabs
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, ╬▓Žü╬▒ŽćŽŹŽé , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
, lobsters
Lobsters are a family (Nephropidae, synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs have claws, including the first pair, ...
, and shrimps
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion ŌĆō most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
); hard-shelled ''Ostrakoderma'' (gastropods
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. The ...
and bivalves); soft-bodied ''Malakia'' ( cephalopods); and divisible animals ''Entoma'' (insects
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of j ...
, spiders
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species di ...
, scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always en ...
s, tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s). Other animals without blood included fish lice, hermit crab
Hermit crabs are anomuran decapod crustaceans of the superfamily Paguroidea that have adapted to occupy empty scavenged mollusc shells to protect their fragile exoskeletons. There are over 800 species of hermit crab, most of which possess an as ...
s, red coral
Precious coral, or red coral, is the common name given to a genus of marine corals, ''Corallium''. The distinguishing characteristic of precious corals is their durable and intensely colored red or pink-orange skeleton, which is used for ma ...
, sea anemones, sponges, starfish and various worms: Aristotle did not classify these into groups.
Scale of being
 Aristotle stated in the ''History of Animals'' that all beings were arranged in a fixed scale of perfection, reflected in their form (''eidos''). They stretched from minerals to plants and animals, and on up to man, forming the '' ''scala naturae'' or great chain of being''. His system had eleven grades, arranged according to the potentiality of each being, expressed in their form at birth. The highest animals gave birth to warm and wet creatures alive, the lowest bore theirs cold, dry, and in thick eggs. The system was based on Aristotle's interpretation of the
Aristotle stated in the ''History of Animals'' that all beings were arranged in a fixed scale of perfection, reflected in their form (''eidos''). They stretched from minerals to plants and animals, and on up to man, forming the '' ''scala naturae'' or great chain of being''. His system had eleven grades, arranged according to the potentiality of each being, expressed in their form at birth. The highest animals gave birth to warm and wet creatures alive, the lowest bore theirs cold, dry, and in thick eggs. The system was based on Aristotle's interpretation of the four elements
Classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Tibet, and India had simi ...
in his ''On Generation and Corruption
''On Generation and Corruption'' ( grc, ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬│╬Ą╬Į╬ŁŽā╬ĄŽēŽé ╬║╬▒ßĮČ Žå╬Ė╬┐ŽüߊȎé; la, De Generatione et Corruptione), also known as ''On Coming to Be and Passing Away'' is a treatise by Aristotle. Like many of his texts, it is both scie ...
'': Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames a ...
(hot and dry); Air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
(hot and wet); Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
(cold and wet); and Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
(cold and dry). These are arranged from the most energetic to the least, so the warm, wet young raised in a womb
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ut ...
with a placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
were higher on the scale than the cold, dry, nearly mineral eggs of birds. However, Aristotle is careful never to insist that a group fits perfectly in the scale; he knows animals have many combinations of attributes, and that placements are approximate.
Influence
On Theophrastus
Aristotle's pupil and successor at theLyceum
The lyceum is a category of educational institution defined within the education system of many countries, mainly in Europe. The definition varies among countries; usually it is a type of secondary school. Generally in that type of school the t ...
, Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, ╬ś╬ĄŽīŽåŽü╬▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žé ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
, wrote the '' History of Plants'', the first classical book of botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
. It has an Aristotelian structure, but rather than focus on formal causes, as Aristotle did, Theophrastus described how plants functioned. Where Aristotle expanded on grand theories, Theophrastus was quietly empirical. Where Aristotle insisted that species have a fixed place on the ''scala naturae'', Theophrastus suggests that one kind of plant can transform into another, as when a field sown to wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
turns to the weed darnel.
On Hellenistic medicine
After Theophrastus, though interest in Aristotle's ideas survived, they were generally taken unquestioningly.Annas, "Classical Greek Philosophy", 2001, p. 252. In Boardman, John; Griffin, Jasper; Murray, Oswyn (ed.) ''The Oxford History of the Classical World''.Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. It is not until the age of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ┘▒┘ä┘Æžź┘Éž│┘Æ┘ā┘Ä┘å┘Æž»┘Äž▒┘É┘Ŗ┘Ä┘æž®┘Å ; grc-gre, ╬æ╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬¼╬Į╬┤Žü╬Ą╬╣╬▒, Alex├Īndria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
under the Ptolemies that advances in biology resumed. The first medical teacher at Alexandria, Herophilus of Chalcedon, corrected Aristotle, placing intelligence in the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
, and connected the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes ...
to motion and sensation. Herophilus also distinguished between vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenat ...
s and arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
, noting that the latter pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the n ...
while the former do not.
On Islamic zoology
Many classical works including those of Aristotle were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle remained the principal authority in biology for the next two thousand years. The ''Kit─üb al-Hayaw─ün
The ''Kit─üb al-ßĖżayaw─ün'' ( ar, ┘āž¬ž¦ž© ž¦┘䞣┘Ŗ┘łž¦┘å, , ''LINA saadouni'') is an Arabic translation for hayawan (Arabic: , maq─ül─üt).
''Historia Animalium'': treatises 1ŌĆō10;
'' De Partibus Animalium'': treatises 11ŌĆō14;
''De Generatione ...
'' (┘āž¬ž¦ž© ž¦┘䞣┘Ŗ┘łž¦┘å, ''Book of Animals'') is a 9th-century Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
translation of ''History of Animals'': 1ŌĆō10, ''On the Parts of Animals'': 11ŌĆō14, and ''Generation of Animals'': 15ŌĆō19.
 The book was mentioned by
The book was mentioned by Al-Kind─½
Ab┼½ Y┼½suf Ya╩╗q┼½b ibn ╩╝IsßĖź─üq aß╣Ż-ß╣óabb─üßĖź al-Kind─½ (; ar, žŻž©┘ł ┘Ŗ┘łž│┘ü ┘Ŗž╣┘é┘łž© ž©┘å žźž│žŁž¦┘é ž¦┘䞥ž©┘枦žŁ ž¦┘ä┘ā┘åž»┘Ŗ; la, Alkindus; c. 801ŌĆō873 AD) was an Arab Muslim philosopher, polymath, mathematician, physician ...
(d. 850), and commented on by Avicenna (Ibn S─½n─ü) in his '' Kit─üb al-┼Āif─ü'' (┌®ž¬ž¦ž© ž¦┘äž┤┘üž¦žĪ, ''The Book of Healing''). Avempace
Ab┼½ Bakr MußĖźammad ibn YaßĖźy├Ā ibn aß╣Ż-ß╣ó─üŌĆÖigh at-T┼½j─½b─½ ibn B─üjja ( ar, žŻž©┘ł ž©┘āž▒ ┘ģžŁ┘ģž» ž©┘å ┘ŖžŁ┘Ŗ┘ē ž©┘å ž¦┘䞥ž¦ž”ž║ ž¦┘䞬ž¼┘Ŗž©┘Ŗ ž©┘å ž©ž¦ž¼ž®), best known by his Latinised name Avempace (; – 1138), was an A ...
(Ibn B─üjja) and Averroes
Ibn Rushd ( ar, ; full name in ; 14 April 112611 December 1198), often Latinized as Averroes ( ), was an
Andalusian polymath and jurist who wrote about many subjects, including philosophy, theology, medicine, astronomy, physics, psy ...
(Ibn Rushd) commented on ''On the Parts of Animals'' and ''Generation of Animals'', Averroes criticising Avempace's interpretations.
On medieval science
When the ChristianAlfonso VI of Castile
Alphons (Latinized ''Alphonsus'', ''Adelphonsus'', or ''Adefonsus'') is a male given name recorded from the 8th century (Alfonso I of Asturias, r. 739ŌĆō757) in the Christian successor states of the Visigothic kingdom in the Iberian peninsula. ...
retook the Kingdom of Toledo
The Kingdom of Toledo ( es, Reino de Toledo) was a realm in the central Iberian Peninsula, created after the capture of Toledo by Alfonso VI of Le├│n in 1085. It continued in existence until 1833; its region is currently within Spain.
Bac ...
from the Moors in 1085, an Arabic translation of Aristotle's works, with commentaries by Avicenna and Averroes
Ibn Rushd ( ar, ; full name in ; 14 April 112611 December 1198), often Latinized as Averroes ( ), was an
Andalusian polymath and jurist who wrote about many subjects, including philosophy, theology, medicine, astronomy, physics, psy ...
emerged into European medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
scholarship. Michael Scot
Michael Scot (Latin: Michael Scotus; 1175 ŌĆō ) was a Scottish mathematician and scholar in the Middle Ages. He was educated at Oxford and Paris, and worked in Bologna and Toledo, where he learned Arabic. His patron was Frederick II of the H ...
translated much of Aristotle's biology into Latin, c. 1225, along with many of Averroes's commentaries. Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus (c. 1200 ŌĆō 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop. Later canonised as a Catholic saint, he was known during his li ...
commented extensively on Aristotle, but added his own zoological observations and an encyclopedia of animals based on Thomas of Cantimpr├®
Thomas of Cantimpr├® (Latin: Thomas Cantimpratensis or Thomas Cantipratensis) (Sint-Pieters-Leeuw, 1201 ŌĆō Louvain, 15 May 1272) was a Flemish Catholic medieval writer, preacher, theologian and a friar belonging to the Dominican Order. He is bes ...
. Later in the 13th century, Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 ŌĆō 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wit ...
merged Aristotle's metaphysics with Christian theology. Whereas Albert had treated Aristotle's biology as science, writing that experiment was the only safe guide and joining in with the types of observation that Aristotle had made, Aquinas saw Aristotle purely as theory, and Aristotelian thought became associated with scholasticism. The scholastic natural philosophy
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wo ...
curriculum omitted most of Aristotle's biology, but included ''On the Soul''.
On Renaissance science
 Renaissance zoologists made use of Aristotle's zoology in two ways. Especially in Italy, scholars such as
Renaissance zoologists made use of Aristotle's zoology in two ways. Especially in Italy, scholars such as Pietro Pomponazzi
Pietro Pomponazzi (16 September 1462 – 18 May 1525) was an Italian philosopher. He is sometimes known by his Latin name, ''Petrus Pomponatius''.
Biography
Pietro Pomponazzi was born in Mantua and began his education there. He completed h ...
and Agostino Nifo lectured and wrote commentaries on Aristotle. Elsewhere, authors used Aristotle as one of their sources, alongside their own and their colleagues' observations, to create new encyclopedias such as Konrad Gessner's 1551 ''Historia Animalium
''History of Animals'' ( grc-gre, ╬żß┐Č╬Į ŽĆ╬ĄŽüßĮČ ŽäßĮ░ ╬Čß┐Ę╬▒ ß╝▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žü╬╣ß┐Č╬Į, ''Ton peri ta zoia historion'', "Inquiries on Animals"; la, Historia Animalium, "History of Animals") is one of the major texts on biology by the ancient Gr ...
''. The title and the philosophical approach were Aristotelian, but the work was largely new. Edward Wotton similarly helped to found modern zoology by arranging the animals according to Aristotle's theories, separating out folklore from his 1552 ''De differentiis animalium''.
Early Modern rejection
 In the Early Modern period, Aristotle came to represent all that was obsolete, scholastic, and wrong, not helped by his association with medieval theology. In 1632, Galileo represented
In the Early Modern period, Aristotle came to represent all that was obsolete, scholastic, and wrong, not helped by his association with medieval theology. In 1632, Galileo represented Aristotelianism
Aristotelianism ( ) is a philosophical tradition inspired by the work of Aristotle, usually characterized by deductive logic and an analytic inductive method in the study of natural philosophy and metaphysics. It covers the treatment of the so ...
in his '' Dialogo sopra i due massimi sistemi del mondo'' (Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems) by the strawman
A straw man (sometimes written as strawman) is a form of argument and an informal fallacy of having the impression of refuting an argument, whereas the real subject of the argument was not addressed or refuted, but instead replaced with a false o ...
Simplicio ("Simpleton"). That same year, William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 ŌĆō 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and propert ...
proved Aristotle wrong by demonstrating that blood circulates.
Aristotle still represented the enemy of true science into the 20th century. Leroi noted that in 1985, Peter Medawar
Sir Peter Brian Medawar (; 28 February 1915 ŌĆō 2 October 1987) was a Brazilian-British biologist and writer, whose works on graft rejection and the discovery of acquired immune tolerance have been fundamental to the medical practice of tissu ...
stated in "pure seventeenth century" tones that Aristotle had assembled "a strange and generally speaking rather tiresome farrago of hearsay
Hearsay evidence, in a legal forum, is testimony from an under-oath witness who is reciting an out-of-court statement, the content of which is being offered to prove the truth of the matter asserted. In most courts, hearsay evidence is inadmiss ...
, imperfect observation, wishful thinking and credulity amounting to downright gullibility".
19th century revival
Zoologists working in the 19th century, including Georges Cuvier, Johannes Peter M├╝ller, and Louis Agassiz admired Aristotle's biology and investigated some of his observations.D'Arcy Thompson
Sir D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson CB FRS FRSE (2 May 1860 ŌĆō 21 June 1948) was a Scottish biologist, mathematician and classics scholar. He was a pioneer of mathematical and theoretical biology, travelled on expeditions to the Bering Strait a ...
translated ''History of Animals'' in 1910, making a classically-educated zoologist's informed attempt to identify the animals that Aristotle names, and to interpret and diagram his anatomical descriptions.
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 ŌĆō 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
quoted a passage from Aristotle's ''Physics'' II 8 in ''The Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'', which entertains the possibility of a selection process following the random combination of body parts. Darwin comments that "We here see the principle of natural selection shadowed forth". However, two things mitigate against this interpretation. Firstly, Aristotle immediately rejected the possibility of such a process of assembling body parts. Secondly, according to Leroi, Aristotle was in any case discussing ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the s ...
, the Empedoclean coming into being of an individual from component parts, not phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spe ...
and natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. Darwin considered Aristotle the most important early contributor to biological thought; in an 1882 letter he wrote that "Linnaeus and Cuvier have been my two gods, though in very different ways, but they were mere schoolboys to old Aristotle."
20th and 21st century interest
 Zoologists have frequently mocked Aristotle for errors and unverified secondhand reports. However, modern observation has confirmed one after another of his more surprising claims, including the
Zoologists have frequently mocked Aristotle for errors and unverified secondhand reports. However, modern observation has confirmed one after another of his more surprising claims, including the active camouflage
Active camouflage or adaptive camouflage is camouflage that adapts, often rapidly, to the surroundings of an object such as an animal or military vehicle. In theory, active camouflage could provide perfect concealment from visual detection.
Activ ...
of the octopus and the ability of elephants to snorkel with their trunks while swimming.
Aristotle remains largely unknown to modern scientists, though zoologists are perhaps most likely to mention him as "the father of biology"; the MarineBio Conservation Society notes that he identified "crustaceans
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
, echinoderms, mollusks, and fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
", that cetaceans are mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
, and that marine vertebrates could be either oviparous or viviparous
Among animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the parent. This is opposed to oviparity which is a reproductive mode in which females lay developing eggs that complete their development and hatch externally from the ...
, so he "is often referred to as the father of marine biology". The evolutionary zoologist Armand Leroi
Armand Marie Leroi (born 16 July 1964) is a New Zealand-born Dutch author, broadcaster, and professor of evolutionary developmental biology at Imperial College in London. He received the Guardian First Book Award in 2004 for his book ''Mutant ...
has taken an interest in Aristotle's biology. The concept of homology began with Aristotle, and the evolutionary developmental biologist Lewis I. Held commented that
Works
Aristotle did not write anything that resembles a modern, unified textbook of biology. Instead, he wrote a large number of "books" which, taken together, give an idea of his approach to the science. Some of these interlock, referring to each other, while others, such as the drawings of ''The Anatomies'' are lost, but referred to in the ''History of Animals'', where the reader is instructed to look at the diagrams to understand how the animal parts described are arranged. Aristotle's main biological works are the five books sometimes grouped as ''On Animals'' (De Animalibus), namely, with the conventional abbreviations shown in parentheses: * ''History of Animals'', or ''Inquiries into Animals'' (Historia Animalium) (HA) * ''Generation of Animals
The ''Generation of Animals'' (or ''On the Generation of Animals''; Greek: ''╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į ╬│╬Ą╬Į╬ŁŽā╬ĄŽēŽé'' (''Peri Zoion Geneseos''); Latin: ''De Generatione Animalium'') is one of the biological works of the Corpus Aristotelicum, the col ...
'' (De Generatione Animalium) (GA)
* ''Movement of Animals
''Movement of Animals'' (or ''On the Motion of Animals''; Greek ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į ╬║╬╣╬Į╬«Žā╬ĄŽēŽé; Latin ''De Motu Animalium'') is one of Aristotle's major texts on biology. It sets out the general principles of animal locomotion
Animal lo ...
'' (De Motu Animalium) (DM)
* ''Parts of Animals
''Parts of Animals'' (or ''On the Parts of Animals''; Greek ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬Čß┐┤Žē╬Į ╬╝╬┐Žü╬»Žē╬Į; Latin ''De Partibus Animalium'') is one of Aristotle's major texts on biology. It was written around 350 BC. The whole work is roughly a study in animal ...
'' (De Partibus Animalium) (PA)
* ''Progression of Animals'' or ''On the Gait of Animals'' (De Incessu Animalium) (IA)
together with ''On the Soul
''On the Soul'' (Greek: , ''Peri Psych─ōs''; Latin: ''De Anima'') is a major treatise written by Aristotle c. 350 BC. His discussion centres on the kinds of souls possessed by different kinds of living things, distinguished by their different op ...
'' (De Anima) (DA).
In addition, a group of seven short works, conventionally forming the '' Parva Naturalia'' ("Short treatises on Nature"), is also mainly biological:
* '' Sense and Sensibilia'' (Sense)
* ''On Memory
''On Memory'' (Greek: ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ╬╝╬Į╬«╬╝╬ĘŽé ╬║╬▒ßĮČ ß╝Ć╬Į╬▒╬╝╬Į╬«Žā╬ĄŽēŽé; Latin: ''De memoria et reminiscentia'') is one of the short treatises that make up Aristotle's '' Parva Naturalia''. It is frequently published together, and read together ...
''
* ''On Sleep
''On Sleep'' (or ''On Sleep and Sleeplessness''; Greek ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ ßĮĢŽĆ╬Į╬┐Žģ ╬║╬▒ßĮČ ß╝É╬│Žü╬Ę╬│ŽīŽüŽā╬ĄŽēŽé; Latin: ''De somno et vigilia'') is a text by Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, ß╝łŽü╬╣ŽāŽä╬┐Žä╬Ł╬╗╬ĘŽé ''Aristot├®l─ōs'', ; 384ŌĆ ...
''
* '' On Dreams''
* ''On Divination in Sleep
''On Divination in Sleep'' (or ''On Prophesying by Dreams''; grc-gre, ╬Ā╬ĄŽüßĮČ Žäß┐åŽé ╬║╬▒╬ĖߊĮ ßĮĢŽĆ╬Į╬┐╬Į ╬╝╬▒╬ĮŽä╬╣╬║ß┐åŽé; Latin: ''De divinatione per somnum'') is a text by Aristotle in which he discusses precognitive dreams
Precognit ...
''
* '' On Length and Shortness of Life''
* '' On Youth, Old Age, Life and Death, and Respiration''Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 History of biology Philosophy of Aristotle History of zoology Ancient Greek science