Arghandab River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arghandab is a river in Afghanistan, about in length. It rises in Ghazni Province, west of the city of Ghazni, and flows southwest passing near the city of Kandahar, and then joins the
Helmand River
The Helmand River (also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand; Pashto/ Persian: ; Greek: ' (''Etýmandros''); Latin: ') is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin. It emerges in the Sanglak ...
below Grishk
Grishk ( ps, ګرِشک, translit=Grishk; fa, گِرِشک, translit=Gereshk), also spelled Gereshk, is a town in Grishk District of Helmand province, geographically located along the Helmand River in Afghanistan, some northwest of Kandahar, a ...
. In its lower course, it is much used for irrigation, under the control of the Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority
The Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority (HAVA) based in Lashkar Gah, Afghanistan, originally named the Helmand Valley Authority (HVA) until its expansion in 1965,Arachotus is to be identified with the Arghandab or with its chief confluent the Tarnak, which joins it on the left southwest of Kandahar. The Tarnak, which flows south of Kandahar, is much shorter (length about 320 km or 200 miles) and less copious.
 The river was known to the ancient Iranians as ''Haraxvaiti'' in Avestan and ''Harahuvati'' in Old Persian, which are cognate with Rigvedic '' Sarasvati'' (as described in its "family books"). Scholars such as Boyce and Parpola have identified Greek ''
The river was known to the ancient Iranians as ''Haraxvaiti'' in Avestan and ''Harahuvati'' in Old Persian, which are cognate with Rigvedic '' Sarasvati'' (as described in its "family books"). Scholars such as Boyce and Parpola have identified Greek ''
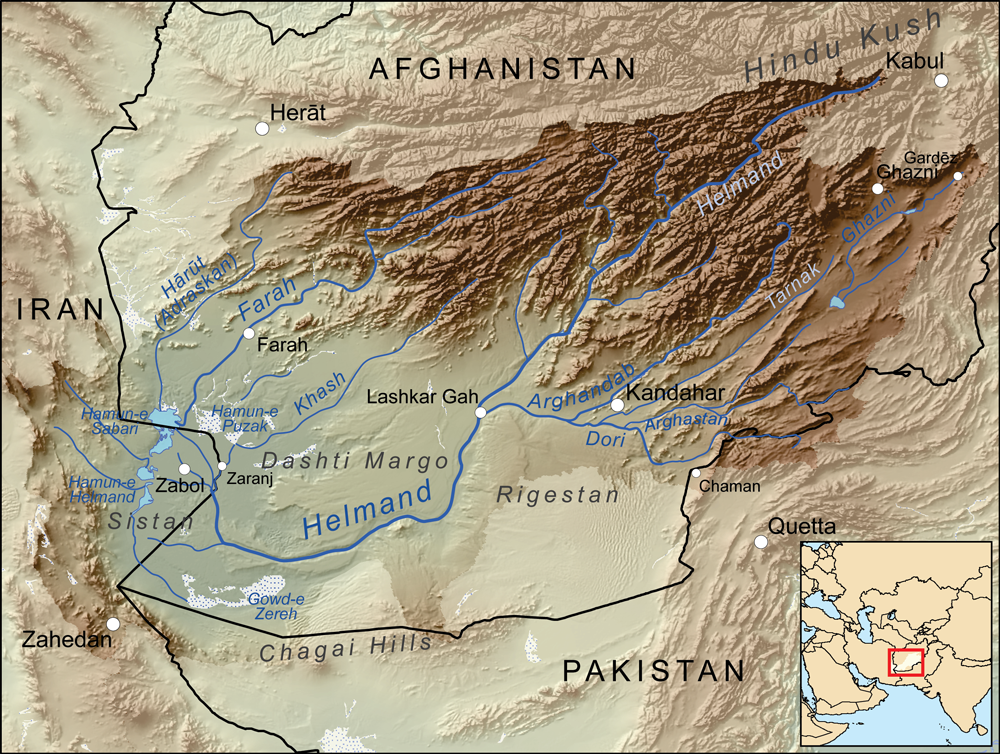 The upper course of the Arghandab river is relatively unexplored. The ''Historical and Political Gazetteer of Afghanistan'' cites the explorations of Major G. Lynch in 1841,
according to whom the origin of the Arghandab is 20 to 30 miles north of Sang-e-Masha. This places the source in the mountains southwest of the Nawar basin. Lynch also described the upper course of the river as being a "mountain torrent, dashing over great granite rocks and about 3 feet deep where fordable".
The upper course of the Arghandab river is relatively unexplored. The ''Historical and Political Gazetteer of Afghanistan'' cites the explorations of Major G. Lynch in 1841,
according to whom the origin of the Arghandab is 20 to 30 miles north of Sang-e-Masha. This places the source in the mountains southwest of the Nawar basin. Lynch also described the upper course of the river as being a "mountain torrent, dashing over great granite rocks and about 3 feet deep where fordable".
 There is a good deal of cultivation along the river, but few villages. The Kabul-Kandahar Highway passes this way (another reason for supposing the Tarnak to be Arachotus), and the people live off the road to avoid the onerous duties of hospitality.
There is a good deal of cultivation along the river, but few villages. The Kabul-Kandahar Highway passes this way (another reason for supposing the Tarnak to be Arachotus), and the people live off the road to avoid the onerous duties of hospitality.
Distance Learning Module 3 - Rivers of the Hindu Kush, Pamir, and Hindu Raj
the University of Nebraska, Center for Afghanistan Studies, Retrieved 15 April 2018. {{Coord, 31, 50, 58, N, 65, 53, 18, E, source:frwiki_region:AF, display=title Rivers of Afghanistan Helmand River drainage basin Helmand River Landforms of Helmand Province Landforms of Kandahar Province Landforms of Ghazni Province
Historical background
 The river was known to the ancient Iranians as ''Haraxvaiti'' in Avestan and ''Harahuvati'' in Old Persian, which are cognate with Rigvedic '' Sarasvati'' (as described in its "family books"). Scholars such as Boyce and Parpola have identified Greek ''
The river was known to the ancient Iranians as ''Haraxvaiti'' in Avestan and ''Harahuvati'' in Old Persian, which are cognate with Rigvedic '' Sarasvati'' (as described in its "family books"). Scholars such as Boyce and Parpola have identified Greek ''Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the ...
'' as a Hellenization of the name, meaning the land of ''Haraxvaiti''. Rigveda's hymn VI.61.2 describes it with the words:
Historian Asko Parpola
Asko Parpola (born 12 July 1941, in Forssa) is a Finnish Indologist, current professor emeritus of South Asian studies at the University of Helsinki. He specializes in Sindhology, specifically the study of the Indus script.
Biography
Parpola i ...
states: "Arghandab ..descends from a height of nearly four kilometers down to about 700 meters when it joins the Helmand River, which eventually forms shallow lakes." ''Sarasvatī-'' is interpreted to mean "full of lakes".
Some historians, however, assert that the Avestan ''Haraxvaiti'' as well as the Rigvedic ''Sarasvati'' refer to the Helmand River
The Helmand River (also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand; Pashto/ Persian: ; Greek: ' (''Etýmandros''); Latin: ') is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin. It emerges in the Sanglak ...
. The Rigvedic name of Arghandab is then believed to be Drishadvati.
The ruins at Ulan Robat, supposed to represent the city Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the ...
, are in its basin; and the lake known as Ab-i Istada
Ab-i Istada ("standing water") is an endorheic salt lake in Nawa District, Ghazni Province, Afghanistan. It lies in a large depression created by the Chaman Fault system in the southern foothills of the Hindu Kush, south-southwest of Ghazni.
...
, the most probable representative of Lake Arachotus, is near the head of the Tarnak, though not communicating with it. The Tarnak is dammed for irrigation at intervals, and in the hot season almost dries up.
Upper course
 The upper course of the Arghandab river is relatively unexplored. The ''Historical and Political Gazetteer of Afghanistan'' cites the explorations of Major G. Lynch in 1841,
according to whom the origin of the Arghandab is 20 to 30 miles north of Sang-e-Masha. This places the source in the mountains southwest of the Nawar basin. Lynch also described the upper course of the river as being a "mountain torrent, dashing over great granite rocks and about 3 feet deep where fordable".
The upper course of the Arghandab river is relatively unexplored. The ''Historical and Political Gazetteer of Afghanistan'' cites the explorations of Major G. Lynch in 1841,
according to whom the origin of the Arghandab is 20 to 30 miles north of Sang-e-Masha. This places the source in the mountains southwest of the Nawar basin. Lynch also described the upper course of the river as being a "mountain torrent, dashing over great granite rocks and about 3 feet deep where fordable".
Lower course
 There is a good deal of cultivation along the river, but few villages. The Kabul-Kandahar Highway passes this way (another reason for supposing the Tarnak to be Arachotus), and the people live off the road to avoid the onerous duties of hospitality.
There is a good deal of cultivation along the river, but few villages. The Kabul-Kandahar Highway passes this way (another reason for supposing the Tarnak to be Arachotus), and the people live off the road to avoid the onerous duties of hospitality.
Dahla dam
In 2008 a project was initiated to rehabilitate theDahla Dam
The Dahla Dam, also known as Arghandab Dam and Kasa, is located in the Shah Wali Kot District of Kandahar Province in Afghanistan, approximately north of the provincial capital Kandahar. Constructed in 1952, it is said to be the second largest dam ...
and associated irrigation system.
See also
*List of rivers of Afghanistan
This is a list of rivers wholly or partly in Afghanistan, arranged geographically by river basin.
Flowing into the Arabian Sea
*''Indus River (Pakistan)''
**Gomal River
*** Kundar River
***Zhob River
**Kurram River
** Kabul River
***Bara ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *External links
Distance Learning Module 3 - Rivers of the Hindu Kush, Pamir, and Hindu Raj
the University of Nebraska, Center for Afghanistan Studies, Retrieved 15 April 2018. {{Coord, 31, 50, 58, N, 65, 53, 18, E, source:frwiki_region:AF, display=title Rivers of Afghanistan Helmand River drainage basin Helmand River Landforms of Helmand Province Landforms of Kandahar Province Landforms of Ghazni Province