Archaeogenetics of the Near East on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The genetic history of the Middle East is the subject of research within the fields of human
The genetic history of the Middle East is the subject of research within the fields of human
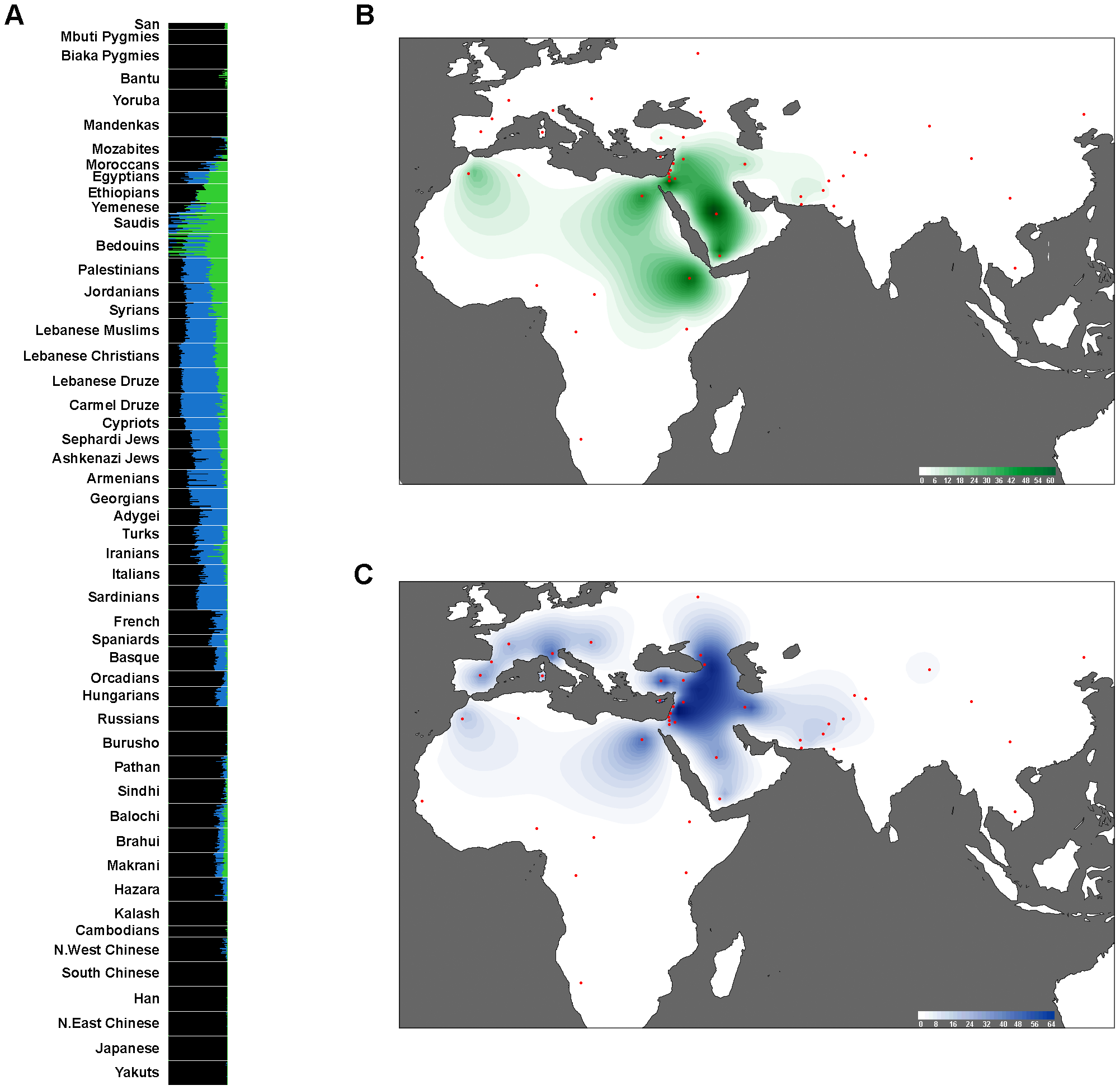

 Turkish genomic variation, along with several other Western Asian populations, looks most similar to genomic variation of South European populations such as Southern Italians. Data from ancient DNA – covering the Paleolithic, the
Turkish genomic variation, along with several other Western Asian populations, looks most similar to genomic variation of South European populations such as Southern Italians. Data from ancient DNA – covering the Paleolithic, the
 The genetic history of the Middle East is the subject of research within the fields of human
The genetic history of the Middle East is the subject of research within the fields of human population genomics Population genomics is the large-scale comparison of DNA sequences of populations. Population genomics is a neologism that is associated with population genetics. Population genomics studies genome-wide effects to improve our understanding of micro ...
, archaeogenetics
Archaeogenetics is the study of ancient DNA using various molecular genetic methods and DNA resources. This form of genetic analysis can be applied to human, animal, and plant specimens. Ancient DNA can be extracted from various fossilized specimen ...
and Middle Eastern studies
Middle Eastern studies (sometimes referred to as Near Eastern studies) is a name given to a number of academic programs associated with the study of the history, culture, politics, economies, and geography of the Middle East, an area that is gene ...
. Researchers use Y-DNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abse ...
, mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
, and other autosomal DNAs to identify the genetic history of ancient and modern populations of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
, and other areas.
History
Developments in DNA sequencing in the 1970s and 1980s provided researchers with the tools needed to studyhuman genetic variation
Human genetic variation is the genetic differences in and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (alleles), a situation called polymorphism.
No two humans are genetically identical. Even ...
and the genetics of human populations to discover founder populations of modern people groups and human migrations.
In 2005, National Geographic launched The Genographic Project
The Genographic Project, launched on 13 April 2005 by the National Geographic Society and IBM, was a genetic anthropological study (sales discontinued on 31 May 2019) that aimed to map historical human migrations patterns by collecting and ...
, led by 12 prominent scientists and researchers, to study and map historical human migration patterns by collecting and analyzing DNA samples from hundreds of thousands of people from around the world.
Egypt
Various DNA studies have found that the genetic variant frequencies ofNorth African
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
populations are intermediate between those of the Near East, the Horn of Africa, Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
and Sub Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
.
A study by Luis et al (2004) performed on a sample of 147 modern Egyptians found that the male haplogroups are E1b1b
E-M215, also known as E1b1b and formerly E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a division of the macro-haplogroup E-M96, which is defined by the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation M215. In other words, it is one of ...
(36.1%, predominantly E-M78
Haplogroup E-V68, also known as E1b1b1a, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup found in North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Western Asia and Europe. It is a subclade of the larger and older haplogroup, known as E1b1b or E-M215 (also roughly ...
), J (32.0%), G (8.8%), T (8.2%), and R (7.5%). The study found that "Egypt's NRY frequency distributions appear to be much more similar to those of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
than to any sub-Saharan African population, suggesting a much larger Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
n genetic component ... The cumulative frequency of typical sub-Saharan lineages (A, B, E1, E2, E3a, and E3b*) is 9% in Egypt ... whereas the haplogroups of Eurasian origin (Groups C, D, and F–Q) account for 59% n Egypt. Cruciani et al. (2007) suggests that E-M78, E1b1b predominant subclade in Egypt, originated in "Northeastern Africa", with a corridor for bidirectional migrations between northeastern and eastern Africa (at least 2 episodes between 23.9–17.3 ky and 18.0–5.9 ky ago), trans-Mediterranean migrations directly from northern Africa to Europe (mainly in the last 13.0 ky), and flow from northeastern Africa to western Asia between 20.0 and 6.8 ky ago. Also, the authors identified the frequency of the E-M78 subclade among modern-day populations in the Northeastern African region, which in the study referred to sample groups in Libya and Egypt. Cruciani et al also proposed that E-M35, the parent clade of E-M78, originated in East Africa during the Palaeolithic and subsequently spread to the region of Egypt.
A 2004 mtDNA study of 58 upper Egyptian individuals included 34 individuals from Gurna, a small settlement on the hills opposite Luxor. The 34 individuals from Gurna exhibited the haplogroups: M1 (6/34 individuals, 17.6%), H (5/34 individuals, 14.7%), L1a (4/34 individuals, 11.8%) and U (3/34 individuals, 8.8%). The M1 haplotype frequency in Gurna individuals (6/34 individuals, 17.6%) is similar to that seen in Ethiopian
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
population (20%), along with a West Eurasian component different in haplogroup distribution in the Gurna individuals. However, the M1 haplotypes from Gurna individuals exhibited a mutation that is not present in Ethiopian population; whereas this mutation was present in non-M1 haplotype individuals from Gurna. Nile Valley Egyptians do not show the characteristics that were shown by the Gurna individuals. The results of the study suggested that the sample of Gurna individuals had retained elements of an ancestral genetic structure from an ancestral East African population, characterized by a high M1 haplogroup frequency. Another 2004 mtDNA study featured the Gurna individuals samples, and clustered them together with the Ethiopian
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
and Yemeni
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
groups, in between the Near Eastern and other African sample groups.
A study by Arredi et al., which analyzed 275 samples from five populations in Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, as well as published data from Moroccan populations, suggests that the North African pattern of Y-chromosomal variation, including in Egypt, is largely of Neolithic origin. The study analyzed North African populations, including North Egyptians and South Egyptians, as well as samples from Southern Europe, the Middle East, and sub-Saharan Africa, and revealed the following conclusions about the male-lineage variation in North Africa: "The lineages that are most prevalent in North Africa are distinct from those in the regions to the immediate north and south: Europe and sub-Saharan Africa ... two haplogroups predominate within North Africa, together making up almost two-thirds of the male lineages: E3b2 and J* (42% and 20%, respectively). E3b2 is rare outside North Africa, and is otherwise known only from Mali, Niger, and Sudan to the immediate south, and the Near East and Southern Europe at very low frequencies. Haplogroup J reaches its highest frequencies in the Middle East".
Keita (2008) examined a published Y-chromosome dataset on Afro-Asiatic populations and found that a key lineage E-M35/E-M78
Haplogroup E-V68, also known as E1b1b1a, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup found in North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Western Asia and Europe. It is a subclade of the larger and older haplogroup, known as E1b1b or E-M215 (also roughly ...
, sub-clade of haplogroup E, was shared between the populations in the locale of original Egyptian speakers and modern Cushitic speakers from the Horn. These lineages are present in Egyptians, Berbers, Cushitic speakers from the Horn of Africa, and Semitic speakers in the Near-East. He noted that variants are also found in the Aegean and Balkans, but the origin of the M35 subclade was in East Africa, and its clades were dominant in a core portion of Afro-Asiatic speaking populations which included Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As o ...
, Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
and Berber groups, in contrast Semitic speakers showed a decline in frequency going west to east in the Levantine-Syria region. Keita identified high frequencies of M35 (>50%) among Omotic populations, but stated that this derived from a small, published sample of 12. Keita also wrote that the PN2 mutation was shared by M35 and M2 lineages and this defined clade originated from East Africa. He concluded that "the genetic data give population profiles that clearly indicate males of African origin, as opposed to being of Asian or European descent" but acknowledged that the biodiversity does not indicate any specific set of skin colors or facial features as populations were subject to microevolutionary pressures.
A study by Hollfelder et al. (2017) analyzed various populations and found that Copts and Egyptians showed low levels of genetic differentiation and lower levels of genetic diversity compared to the northeast African groups. Copts and Egyptians displayed similar levels of European/Middle Eastern ancestry (Copts were estimated to be of 69.54% ± 2.57 European ancestry, and the Egyptians of 70.65% ± 2.47 European ancestry). The study concluded that the Copts and the Egyptians have a common history linked to smaller population sizes, and that the behavior in the admixture analyses is consistent with shared ancestry between Copts and Egyptians and/or additional genetic drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance.
Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and there ...
in the Copts.
A genetic study published in the "''European Journal of Human Genetics"'' (2019) found that Northern Africans (including Egyptians) from a global population sample of 164 were closely related to Europeans and West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
ns as well as to Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
ns. However, the authors acknowledged that the results of the study, which featured the 55 AINSP panel, would have further weight if further extensive population studies from Morocco, Tunisia and Egypt were obtained as only nine population samples were included to represent the North African region.Ancient Egyptians
Contamination from handling and intrusion from microbes create obstacles to the recovery ofAncient DNA
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient specimens. Due to degradation processes (including cross-linking, deamination and fragmentation) ancient DNA is more degraded in comparison with contemporary genetic material. Even under the bes ...
. Consequently, most DNA studies have been carried out on modern Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
populations with the intent of learning about the influences of historical migrations on the population of Egypt. However, DNA grouping methods and classifications have attracted criticism in the view of some scholars for excluding data on African populations. S.O.Y. Keita, a biological anthropologist
Biological anthropology, also known as physical anthropology, is a scientific discipline concerned with the biological and behavioral aspects of human beings, their extinct hominin ancestors, and related non-human primates, particularly from an e ...
, argued in 2022 that genetic studies should be interpreted in a framework with other sources of evidence and also observes that sometimes the interpretation of data
in genetic studies betrays a "default racialist or racist approach". Barry Kemp has noted that DNA studies could only provide firm conclusions about the population of Ancient Egypt if the sample results featured a significant number of individuals, which represented a broad geographical and chronological range.
In 1993, a study was performed on ancient mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
of the 12th Dynasty
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom by Egyptologists. It often is combined with the Eleventh, Thirteenth, and Fourteenth dynasties under the group title, Middle Kingdom. Some ...
, which identified multiple lines of descent, some of which originated from Sub-Saharan Africa but other lineages were not identified.
In 2012 the 20th dynasty mummies of Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great monar ...
and another mummy "Unknown Man E" believed to be Ramesses III's son Pentawer
Pentawer (also Pentawere and Pentaweret) was an ancient Egyptian prince of the 20th Dynasty, a son of Pharaoh Ramesses III and his secondary wife, Tiye (20th dynasty), Tiye., p.193 He was involved in the so-called "harem conspiracy", a plot to kil ...
were analyzed by Albert Zink, Yehia Z Gad and a team of researchers under Zahi Hawass
Zahi Abass Hawass ( ar, زاهي حواس; born May 28, 1947) is an Egyptian archaeologist, Egyptologist, and former Minister of State for Antiquities Affairs, serving twice. He has also worked at archaeological sites in the Nile Delta, the Wes ...
, then Secretary General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, Egypt. Genetic kinship analyses revealed identical haplotypes in both mummies using the Whit Athey's haplogroup predictor, the Y chromosomal haplogroup E1b1a ( E-M2) was predicted.
In 2013, ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'' announced the publication of the first genetic study utilizing next-generation sequencing Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation ...
to ascertain the ancestral lineage of an Ancient Egyptian individual. The research was led by Carsten Pusch of the University of Tübingen
The University of Tübingen, officially the Eberhard Karl University of Tübingen (german: Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen; la, Universitas Eberhardina Carolina), is a public research university located in the city of Tübingen, Baden-W� ...
in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Rabab Khairat, who released their findings in the ''Journal of Applied Genetics''. DNA was extracted from the heads of five Egyptian mummies that were housed at the institution. All the specimens were dated between 806 BC and 124 AD, a timeframe corresponding with the late Dynastic period. The researchers observed that one of the mummified individuals likely belonged to the mtDNA haplogroup I2, a maternal clade that is believed to have originated in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
.
In a 2017 study published in Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
, three ancient Egyptian mummies were obtained spanning around 1,300 years of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
ian history from the late New Kingdom to the Roman period. The study used 135 modern Egyptian samples. Two of the three ancient Egyptians were assigned to haplogroup J and one to haplogroup E1b1b1 both are carried by modern Egyptians. Analyses of the ancient Egyptian samples revealed higher affinities with near eastern populations compared to modern Egyptians, likely due to an 8% increase in African component which occurred predominantly within the last 2000 years. "Genetic continuity between ancient and modern Egyptians cannot be ruled out despite this more recent sub-Saharan African influx, while continuity with modern Ethiopians is not supported." The authors noted that the ancient Egyptian samples were obtained from one site and may not be representative for all of ancient Egypt. They stated that more genetic studies on mummified remains from southern Egypt and Sudan would be needed to reach a conclusive view. Gourdine, Anselin and Keita criticised the methodology of the Scheunemann et al study and argued that the Sub-Saharan "genetic affinities" may be attributed to "early settlers" and "the relevant Sub-Saharan genetic markers" do not correspond with the geography of known trade routes". In 2022, Danielle Candelora criticised the Schuenemann study for its “untested” methodology, limited sample sizes and “problematic comparative” data which she argued served to legitimise racist conceptions of ancient civilizations with “scientific evidence”.
In 2018, the tomb of two high-status Egyptians, Nakht-Ankh and Khnum-Nakht was discovered by Sir William Flinders Petrie
Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie ( – ), commonly known as simply Flinders Petrie, was a British Egyptologist and a pioneer of systematic methodology in archaeology and the preservation of artefacts. He held the first chair of Egyp ...
and Ernest Mackay
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
* Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
* Ernest, ...
in 1907. Nakht-Ankh and Khnum-Nakht lived during the 12th Dynasty
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom by Egyptologists. It often is combined with the Eleventh, Thirteenth, and Fourteenth dynasties under the group title, Middle Kingdom. Some ...
(1985–1773 BCE) in Middle Egypt and were aged 20 years apart. Their tomb was completely undisturbed prior to its excavation. Each mummy has a different physical morphology and in the DNA analysis by the University of Manchester differences between the Y chromosome SNPs indicate different paternal lineages concluding that Nakht-Ankh and Khnum-Nakht were half-brothers but Y chromosome sequences were not complete enough to determine paternal haplogroup. The SNP identities were consistent with mtDNA haplogroup M1a1 with 88.05–91.27% degree of confidence, thus confirming the Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n origins of the two individuals.
In 2020 Yehia Z Gad and other researchers of the Hawass team published results of an analysis of the mitochondrial and Y-chromosomal haplogroups of several mummies of 18th Dynasty Including Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun (, egy, twt-ꜥnḫ-jmn), Egyptological pronunciation Tutankhamen () (), sometimes referred to as King Tut, was an Egyptian pharaoh who was the last of his royal family to rule during the end of the Eighteenth Dynasty (ruled ...
in the journal Human Molecular Genetics, Volume 30, Issue R1, 1 March 2021, Pages R24–R28, Results were used to provide information about the phylogenetic groups of his family members and their presence among the reported contemporary Egyptian population data. The analysis confirmed previous data of the Tutankhamun's ancestry with multiple controls authenticating all results. However, the specific clade of R1b was not determined and the profiles for Tutankhamun and Amenhotep III were incomplete, the analysis produced differing probability figures despite having concordant allele results. Because the relationships of these two mummies with the KV55 mummy had previously been confirmed in an earlier study, the haplogroup prediction of both mummies could be derived from the full profile of the KV55 data. The proposed sibling relationship between Tutankhamun's parents, Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth D ...
and the mummy known as the "younger lady" (KV35YL) is further supported.
In 2010 Hawass et al undertook detailed anthropological, radiological, and genetic studies as part of the King Tutankhamun Family Project. The objectives included attempting to determine familial relationships among 11 royal mummies of the New Kingdom, as well to research for pathological features including potential inherited disorders and infectious diseases. In 2012, Hawass et al undertook an anthropological, forensic, radiological, and genetic study of the 20th dynasty mummies of Ramesses III and an unknown man which were found together. In 2022, S.O.Y. Keita analysed 8 Short Tandem loci (STR) data published as part of these studies by Hawass et al, using an algorithm that only has three choices: Eurasians, sub-Saharan Africans, and East Asians. Using these three options, Keita concluded that the studies showed "a majority to have an affinity with " sub-Saharan" Africans in one affinity analysis". However, Keita cautioned that this does not mean that the royal mummies “lacked other affiliations” which he argued had been obscured in typological thinking. Keita further added that different “data and algorithms might give different results” which reflects the complexity of biological heritage and the associated interpretation.
Blood typing and DNA sampling on ancient Egyptian mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
is scant; however, a 1982 study of blood typing of dynastic mummies found ABO frequencies to be most similar to modern Egyptians and some also to Northern Haratin
Haratin (), also referred to as Haratine, Harratin (singular: Hartani), are an ethnic group found in western Sahel and southwestern Maghreb. The Haratin are mostly found in modern Mauritania (where they form a plurality), Morocco, Western Sahar ...
populations. ABO blood group distribution shows that the Egyptians form a sister group to North African populations, including Berbers, Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of the earliest cradles of ...
and Canary Island
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocco ...
ers.
Iran
Links to Chalcolithic Anatolia
A 2017 study analyzed the autosomal DNA and genome of an Iron Age Iranian sample taken from Teppe Hasanlu (F38_Hasanlu, dated to 971–832 BCE) and revealed it had close affinities to a Chalcolithic North-West Anatolian individual from Kumtepe even closer than Neolithic Iranians. This implies admixture took place between ancient populations of Iran and Anatolia.Gilaks and Mazandaranis
A 2006 genetic research was made by ''Nasidze et al.'' on the North Iranian populations on the Gilaks andMazandaranis
The Mazanderani people ( mzn, مازرونیون or mzn, تبریون) or Tabari people ( mzn, تپورون, links=no) are an Iranian peopleAcademic American Encyclopedia By Grolier Incorporated, page 294 who are indigenous to the Caspian sea r ...
, spanning the southwestern coast of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
, up to the border with neighbouring Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
. The Gilaks and Mazandaranis comprise 7% of the Iranian population. The study suggested that their ancestors came from the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
region, perhaps displacing an earlier group in the South Caspian. Linguistic evidence supports this scenario, in that the Gilaki and Mazandarani languages (but not other Iranian languages) share certain typological features with Caucasian languages
The Caucasian languages comprise a large and extremely varied array of languages spoken by more than ten million people in and around the Caucasus Mountains, which lie between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea.
Linguistic comparison allows t ...
, and specifically South Caucasian languages
The Kartvelian languages (; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian, Kartvelic, and Iberian languagesBoeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primari ...
. There have been patterns analyzed of mtDNA and Y chromosome variation in the Gilaki and Mazandarani.
Based on mtDNA HV1 sequences tested by ''Nasidze et al''., the Gilaks and Mazandarani most closely resemble their geographic and linguistic neighbors, namely other Iranian groups. However, their Y chromosome types most closely resemble those found in groups from the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
.
A scenario that explains these differences is a south Caucasian origin for the ancestors of the Gilani and Mazandarani, followed by introgression of women (but not men) from local Iranian groups, possibly because of patrilocality.
Given that both mtDNA and language are maternally transmitted, the incorporation of local Iranian women would have resulted in the concomitant replacement of the ancestral Caucasian language and mtDNA types of the Gilani and Mazandarani with their current Iranian language and mtDNA types. Concomitant replacement of language and mtDNA may be a more general phenomenon than previously recognized.
The Mazandarani and Gilani groups fall inside a major cluster consisting of populations from the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
and West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
and are particularly close to the South Caucasus groups— Georgians, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, and Azerbaijanis. Iranians from Tehran and Isfahan are situated more distantly from these groups.
Iranian Azeris
The 2013 comparative study on the complete mitochondrial DNA diversity in Iranians has indicated that Iranian Azerbaijanis are more related to the people ofGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, than they are to other Iranians (Like Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
), while the Persians, Armenians and Qashqai on the other hand were more related to each other. It furthermore showed that overall, the complete mtDNA sequence analysis revealed an extremely high level of genetic diversity in the Iranian populations studied which is comparable to the other groups from the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
. The same 2013 research further noted that "the results of AMOVA and MDS analyses did not associate any regional and/or linguistic group of populations in the Anatolia, Caucasus and Iran region pointing to strong genetic affinity of Indo-European speaking Persians and Turkic-speaking Qashqais, thus suggesting their origin from a common maternal ancestral gene pool. The pronounced influence of the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
populations on the maternal diversity of Iranian Azeris
Iranian Azerbaijanis (; az, ایران آذربایجانلیلاری, italics=no ), also known as Iranian Azeris, Iranian Turks, Persian Turks or Persian Azerbaijanis, are Iranians of Azerbaijani ethnicity who may speak the Azerbaijani langu ...
is also evident from the MDS analysis results." The study also notes that "It is worth pointing out the position of Azeris from the Caucasus region, who despite their supposed common origin with Iranian Azeris, cluster quite separately and occupy an intermediate position between the Azeris/Georgians and Turks/Iranians grouping". The MtDNA results from the samples overall on average closely resemble those found in the neighbouring regions of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, and to a lesser extent (Northern) Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
.
Among the most common MtDNA lineages in the nation, namely U3b3, appears to be restricted to populations of Iran and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
, while the sub-cluster U3b1a is common in the whole Near East region.
Iraq
Links to South Asia
A 2013 study based on DNA extracted from the dental remains of four individuals from different time eras (200–300 CE, 2650–2450 BCE, 2200–1900 BCE) unearthed at Tell Ashara (ancientTerqa
Terqa is the name of an ancient city discovered at the site of Tell Ashara on the banks of the middle Euphrates in Deir ez-Zor Governorate, Syria, approximately from the modern border with Iraq and north of the ancient site of Mari, Syria. ...
, in modern Syria) and Tell Masaikh (ancient Kar-Assurnasirpal) suggested a possible genetic link between the people of Bronze Age Mesopotamia and Northern India. According to the study, "We anticipate that the analyzed remains from orthernMesopotamia belonged to people with genetic affinity to the Indian subcontinent since the distribution of identified ancient haplotypes indicates solid link with populations from the region of South Asia-Tibet (Trans-Himalaya). They may have been descendants of migrants from much earlier times, spreading the clades of the macrohaplogroup M throughout Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
and founding regional Mesopotamian groups like that of Terqa or just merchants
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as industry ...
moving along trade routes passing near or through the region." A 2014 study expanding on the 2013 study and based on analysis of 15751 DNA samples arrives at the conclusion, that "M65a, M49 and/or M61 haplogroups carrying ancient Mesopotamians might have been the merchants from India".
Assyrians
In the 1995 book ''The History and Geography of Human Genes'' the authors wrote that: "The Assyrians are a fairly homogeneous group of people, believed to originate from the land of old Assyria in northern Iraq .they are Christians and are bona fide descendants of their ancient namesakes." In a 2006 study of the Y chromosome DNA of six regional populations, including, for comparison, Assyrians and Syrians, researchers found that, "the two Semitic populations (Assyrians and Syrians) are very distinct from each other according to both omparativeaxes. This difference supported also by other methods of comparison points out the weak genetic affinity between the two populations with different historical destinies." A 2008 study on the genetics of "old ethnic groups in Mesopotamia," including 340 subjects from seven ethnic communities ("These populations included Assyrians, Jews, Zoroastrians, Armenians, Arabs and Turkmen (representing ethnic groups from Iran, restricted by rules of their religion), and the Iraqi and Kuwaiti populations from Iraq and Kuwait.") found that Assyrians were homogeneous with respect to all other ethnic groups sampled in the study, regardless of religious affiliation.Marsh Arabs
A study published in 2011 looking at the relationship between Iraq's Marsh Arabs and ancient Sumerians concluded "the modern Marsh Arabs of Iraq harbour mtDNAs and Y chromosomes that are predominantly of Middle Eastern origin. Therefore, certain cultural features of the area such as water buffalo breeding and rice farming, which were most likely introduced from the Indian sub-continent, only marginally affected the gene pool of the autochthonous people of the region. Moreover, a Middle Eastern ancestral origin of the modern population of the marshes of southern Iraq implies that, ''if'' the Marsh Arabs are descendants of the ancient Sumerians, also Sumerians were not of Indian or Southern Asian ancestry." The same 2011 study, when focusing on the genetics of theMaʻdān
The Marsh Arabs ( ar, عرب الأهوار ''ʻArab al-Ahwār'' "Arabs of the Marshlands"), also referred to as the Maʻdān ( ar, معدان "dweller in the plains") or Shroog (Iraqi ar, شروق, "those from the east")—the latter two often ...
people of Iraq, identified Y chromosome haplotypes shared by Marsh Arabs, Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
speaking Iraqis, Assyrians and Mandeans "supporting a common local background."
Levant


Chalcolithic and Bronze Age periods
A 2018 study conducted by scholars fromTel-Aviv University
Tel Aviv University (TAU) ( he, אוּנִיבֶרְסִיטַת תֵּל אָבִיב, ''Universitat Tel Aviv'') is a public research university in Tel Aviv, Israel. With over 30,000 students, it is the largest university in the country. Loc ...
, the Israel Antiquities Authority
The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA, he, רשות העתיקות ; ar, داﺌرة الآثار, before 1990, the Israel Department of Antiquities) is an independent Israeli governmental authority responsible for enforcing the 1978 Law of ...
and Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ...
had discovered that 22 out of the 600 people who were buried in Peki'in
Peki'in (alternatively Peqi'in) ( he, פְּקִיעִין) or Buqei'a ( ar, البقيعة), is a Druze–Arab town with local council status in Israel's Northern District. It is located eight kilometres east of Ma'alot-Tarshiha in the Uppe ...
cave from the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
Period were of both local Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
ine and Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and Zagros
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
area ancestries, or as phrased in the paper itself: "Ancient DNA from Chalcolithic Israel reveals the role of population mixture in cultural transformation," the scientists concluded that the homogeneous community found in the cave could source ~57% of its ancestry from groups related to those of the local Levant Neolithic, ~26% from groups related to those of the Anatolian Neolithic, and ~17% from groups related to those of the Iran Chalcolithic. The scholars noted that the Zagros genetic material held "Certain characteristics, such as genetic mutations contributing to blue eye color, were not seen in the DNA test results of earlier Levantine human remains"...The blue-eyed, fair-skinned community didn’t continue, but at least now researchers have an idea why. "These findings suggest that the rise and fall of the Chalcolithic culture are probably due to demographic changes in the region".
From a 2020 study published in Cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
: "Understanding the nature of this movement was the primary motivation behind this study. Here, we present a large-scale analysis of genome-wide data from key sites of prehistoric Anatolia, the Northern Levant, and the Southern Caucasian lowlands ... In the Northern Levant, we identified a major genetic shift between the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age periods. During this transition, Northern Levantine populations experienced gene flow from new groups harboring ancestries related to both Zagros
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
/Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
and the Southern Levant. This suggests a shift in social orientation, perhaps in response to the rise of urban centers in Mesopotamia, which to date remain genetically unsampled." They further add: "This expansion is recorded in the region of the Northern Levant ca. 2800 BCE and could be associated with the movement/ migration of people from Eastern Anatolia and the Southern Caucasian highlands. However, our results do not support this scenario for a number of reasons". "There are extensive textual references from the end of the EBA through the LBA referring to groups of people arriving into the area of the Amuq Valley. Although these groups were named, likely based on designations (e.g., Amorites
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied lar ...
, Hurrians), the formative context of their (cultural) identity and their geographic origins remain debated. One recent hypothesis (Weiss, 2014, 2017; Akar and Kara, 2020) associates the arrival of these groups with climate-forced population movement during the ‘‘4.2k BP event,’’ a Mega Drought that led to the abandonment of the entire Khabur river valley in Northern Mesopotamia and the search of nearby habitable areas." The study has also shown that the Canaanite population contributed to most present-day Jewish groups and Levantine Arabic-speaking groups. These present-day groups also show ancestries that cannot be modeled by the available ancient DNA data, highlighting the importance of additional major genetic effects on the region since the Bronze Age.
Canaanites and Phoenicians
Zalloua and Wells (2004), under the auspices of a grant fromNational Geographic Magazine
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
, examined the origins of the Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
ite Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
. The debate between Wells and Zalloua was whether haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share ...
J2 (M172) should be identified as that of the Phoenicians or that of its "parent" haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share ...
M89 on the YDNA phylogenetic tree.
Initial consensus suggested that J2 be identified with the Canaanite-Phoenician (North Levantine) population, with avenues open for future research. As Wells commented, "The Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
were the Canaanites" It was reported in the PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educat ...
description of the National Geographic TV Special on this study entitled "Quest for the Phoenicians" that ancient DNA
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient specimens. Due to degradation processes (including cross-linking, deamination and fragmentation) ancient DNA is more degraded in comparison with contemporary genetic material. Even under the bes ...
was included in this study as extracted from the tooth of a 2500-year-old Phoenician mummy
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay fu ...
. Wells identified the haplogroup of the Canaanites as haplogroup J2 which originated from Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
.
Cyprus
A 2016 study on 600Cypriot
Cypriot (in older sources often "Cypriote") refers to someone or something of, from, or related to the country of Cyprus.
* Cypriot people, or of Cypriot descent; this includes:
**Armenian Cypriots
**Greek Cypriots
**Maronite Cypriots
**Turkish C ...
males asserts that "genome-wide studies indicate that the genetic affinity of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
is nearest to current populations of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
". Analyses of Cypriot haplogroup data are consistent with two stages of prehistoric settlement. E-V13
Haplogroup E-V68, also known as E1b1b1a, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup found in North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Western Asia and Europe. It is a subclade of the larger and older haplogroup, known as E1b1b or E-M215 (also roughly ...
and E-M34 are widespread, and PCA suggests sourcing them to the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
and Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
/Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, respectively. Contrasting haplogroups in the PCA were used as surrogates of parental populations. Admixture analyses suggested that the majority of G2a-P15 and R1b-M269 components were contributed by Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
and Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
sources, respectively, while Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
/Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
supplied the majority of E-V13 and J2a-M67. Haplotype-based expansion times were at historical levels suggestive of recent demography. On the other hand, more recent Principal Component Analyses based on autosomal DNA, have placed Cypriots clearly separate from Levantine and Middle Eastern groups, either at the easternmost flank of the Southern European cluster, or in an intermediate position between Southern Europeans and northern Levantines. In a study by Harvard geneticist Iosif Lazarides and colleagues investigating the genetic origins of the Minoans and Mycenaeans, Cypriots were found to be the second least differentiated population from Bronze Age Mycenaeans based on FST index and also genetically differentiated from Levantines.
A 2017 study found that both Turkish Cypriots' and Greek Cypriots' patrilineal ancestry derives primarily from a single pre-Ottoman local gene pool. The frequency of total haplotypes shared between Turkish and Greek Cypriots is 7-8%, with analysis showing that none of these are found in Turkey, thus not supporting a Turkish origin for the shared haplotypes. No shared haplotypes were observed between Greek Cypriots and mainland Turkish populations, while total haplotypes shared between Turkish Cypriots and mainland Turks is 3%. Turkish Cypriots also share haplotypes with North Africans to a lesser extent, and have Eastern Eurasian haplogroups (H, C, N, O, Q) – attributed to the arrival of the Ottomans – at a frequency of ~5.5%. Both Cypriot groups show close genetic affinity to Calabrian (southern Italy) and Lebanese patrilineages. The study states that the genetic affinity between Calabrians and Cypriots can be explained as a result of a common ancient Greek ( Achaean) genetic contribution, while Lebanese affinity can be explained through several migrations that took place from coastal Levant to Cyprus from the Neolithic (early farmers), the Iron Age (Phoenicians), and the Middle Ages (Maronites and other Levantine settlers during the Frankish era). The predominant haplogroups among both Turkish and Greek Cypriots are J2a-M410, E-M78, and G2-P287.
Israel and Palestine
A study published by the National Academy of Sciences found that "the paternal gene pools ofJewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
communities from Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
descended from a common Middle Eastern ancestral population", and suggested that "most Jewish communities have remained relatively isolated from neighbouring non-Jewish communities during and after the Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
". According to geneticist Doron Behar and colleagues (2010), this is "consistent with a historical formulation of the Jewish people as descending from ancient Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
". Approximately 35% to 43% of Jewish men are in the paternal line known as haplogroup J and its sub-haplogroups. This haplogroup is particularly present in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, Horn of Africa, Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
, as well as in Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
. 15% to 30% are in haplogroup E1b1b
E-M215, also known as E1b1b and formerly E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a division of the macro-haplogroup E-M96, which is defined by the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation M215. In other words, it is one of ...
(or E-M35). Studies of mitochondrial DNA of Jewish populations are more recent, debatable, and more heterogeneous.
In a genetic study of Y-chromosomal STRs in two populations from Israel and the Palestinian Authority Area: Christian and Muslim Palestinians showed genetic differences. The majority of Palestinian Christians (31.82%) were a subclade of E1b1b
E-M215, also known as E1b1b and formerly E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a division of the macro-haplogroup E-M96, which is defined by the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation M215. In other words, it is one of ...
, followed by G2a
G2A.COM Limited (commonly referred to as G2A) is a digital marketplace headquartered in the Netherlands, with offices in Poland and Hong Kong. The site specializes in the resale of gaming products by the use of redemption keys. Other product ...
(11.36%), and J1 (9.09%). The majority of Palestinian Muslims were haplogroup J1 (37.82%) followed by E1b1b
E-M215, also known as E1b1b and formerly E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a division of the macro-haplogroup E-M96, which is defined by the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation M215. In other words, it is one of ...
(19.33%), and T (5.88%). The study sample consisted of 44 Palestinian Christians and 119 Palestinian Muslims.
In 2004, a team of geneticists from Stanford University, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Tartu University
The University of Tartu (UT; et, Tartu Ülikool; la, Universitas Tartuensis) is a university in the city of Tartu in Estonia. It is the national university of Estonia. It is the only classical university in the country, and also its biggest ...
(Estonia), Barzilai Medical Center
Barzilai Medical Center ( he, מרכז רפואי ברזילי, ''Merkaz Refu'i Barzilai''; ar, مركز برزيلاي الطبي) is a 617-bed hospital in Ashkelon in southern Israel. The hospital serves a population of 500,000, including a la ...
(Ashkelon, Israel), and the Assaf Harofeh Medical Center
Shamir Medical Center, formerly Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, is a hospital located on , southeast of Tel Aviv, Israel.
History
The Medical Center was named after Asaph the Jew, author of the Oath of Asaph and an early medical text. The facilit ...
(Zerifin, Israel), studied the modern Samaritan ethnic community living in Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
in comparison with modern Israeli populations to explore the ancient genetic history of these people groups. Their findings reported on four family lineages among the Samaritans: the Tsdaka, Joshua-Marhiv, Danfi, and the Cohen family. All Samaritan families were found in haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share ...
s J1 and J2, except the Cohen family which was found in haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share ...
E3b1a-M78. This article predated the E3b1a subclades based on the research of Cruciani, et al.
In a 2005 study of ASPM gene variants, Mekel-Bobrov et al. found that the Israeli Druze
Israeli Druze or Druze Israelis ( ar, الدروز الإسرائيليون; he, דְּרוּזִים יִשְׂרְאֵלִים) are an ethnoreligious minority among the Arab citizens of Israel. In 2019, there were 143,000 Druze people living ...
people of the Carmel region have among the highest rate of the newly evolved ASPM haplogroup D, at 52.2% occurrence of the approximately 6,000-year-old allele. While it is not yet known exactly what selective advantage is provided by this gene variant, the haplogroup D allele is thought to be positively selected in populations and to confer some substantial advantage that has caused its frequency to rapidly increase.
According to DNA testing, Druze are remarkable for the high frequency (35%) of males who carry the Y-chromosomal haplogroup L, which is otherwise uncommon in the Middle East. This haplogroup originates from prehistoric South Asia and has spread from Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
into southern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
.
Lebanon
In a 2011 genetic study by Haber et al which analyzed the male-line Y-chromosome genetics of the different religious groups of Lebanon, revealed no noticeable or significant genetic differentiation between theMaronites
The Maronites ( ar, الموارنة; syr, ܡܖ̈ܘܢܝܐ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and Levant region of the Middle East, whose members traditionally belong to the Maronite Church, with the larg ...
, Greek Orthodox Christians
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
, Greek Catholic Christians, Sunni Muslims, Shia Muslims
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
, and Druze of the region on the more frequent haplogroups. Major differences between Lebanese groups were found among the less frequent haplogroups. In a 2013 interview Pierre Zalloua, pointed out that genetic variation preceded religious variation and divisions: "Lebanon already had well-differentiated communities with their own genetic peculiarities, but not significant differences, and religions came as layers of paint on top". In a 2007 study, geneticist Pierre Zalloua
Pierre Zalloua ( ar, بيار زلّوعة) is a Lebanese biologist. His contributions to biology include numerous researches in genetic predisposition to diseases such as type 1 diabetes and β-thalassemia. He is most noted for taking part in ...
found that the genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns is found among members of all of Lebanon's religious communities.
A 2013 genetic study carried out by Haber at al found that Jews (Sephardi and Ashkenazi) cluster in one branch, Druze from Mount Lebanon and Druze from Mount Carmel are depicted on a private branch, and Lebanese Christians form a private branch with the Christian populations of Armenia and Cyprus. Lebanese Muslims cluster towards the Muslim populations of Syrians, Palestinians, and Jordanians, which in turn cluster on branches with other Muslim populations as distant as Morocco and Yemen. The authors explained that "In particular, conversion of the region's populations to Islam appears to have introduced major rearrangements in populations' relations through admixture with culturally similar but geographically remote populations, leading to genetic similarities between remarkably distant populations like Jordanians, Moroccans, and Yemenis. Conversely, Christians and Druze became genetically isolated in the new cultural environment". In conclusion, the authors reconstructed the genetic structure of ancient Levantines and found that a pre-Islamic expansion Levant was more genetically similar to Europeans than to Arabians.
A 2017 study published by the American Journal of Human Genetics
The ''American Journal of Human Genetics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of human genetics. It was established in 1948 by the American Society of Human Genetics and covers all aspects of heredity in humans, includin ...
, concluded that present-day Lebanese derive most of their ancestry from a Canaanite-related population (Canaanite being a pre-Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n name), which therefore implies substantial genetic continuity in the Levant since at least the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
. Geneticist Chris Tyler-Smith and his colleagues at the Sanger Institute
The Wellcome Sanger Institute, previously known as The Sanger Centre and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, is a non-profit British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust.
It is located on the Wellcome Ge ...
in Britain compared "sampled ancient DNA from five Canaanite people who lived 3,750 and 3,650 years ago" to modern people; the comparison revealed that 93 percent of the genetic ancestry of people in Lebanon come from the Canaanites, and the other 7 percent is of a Eurasian steppe population.
A 2019 study carried out by the Wellcome Sanger Institute
The Wellcome Sanger Institute, previously known as The Sanger Centre and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, is a non-profit British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust.
It is located on the Wellcome ...
analyzed the remains of nine Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
found at a burial site in Lebanon, and concluded that "contrary to the popular belief, the Crusaders did not leave a lasting effect on the genetics of Lebanese Christians." Instead, according to the study, today’s Lebanese Christians are "more genetically similar to locals from the Roman period, which preceded the Crusades by more than four centuries." A study by Makhoul et al on Beta Thalassemia Heterogeneity in Lebanon found out that the thalassemia mutations in some Lebanese Christians are similar to the ones observed in Macedonia, which "may confirm the ancient Macedonian origin of certain Lebanese Christians".
Turkey
 Turkish genomic variation, along with several other Western Asian populations, looks most similar to genomic variation of South European populations such as Southern Italians. Data from ancient DNA – covering the Paleolithic, the
Turkish genomic variation, along with several other Western Asian populations, looks most similar to genomic variation of South European populations such as Southern Italians. Data from ancient DNA – covering the Paleolithic, the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
, and the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
periods – showed that Western Asian genomes, including Turkish ones, have been greatly influenced by early agricultural populations in the area; later population movements, such as those of Turkic speakers, also contributed. The first and only (as of 2017) whole genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a ...
study in Turkey was done in 2014. Moreover, the genetic variation of various populations in Central Asia "has been poorly characterized"; Western Asian populations may also be "closely related to populations in the east". An earlier 2011 review had suggested that "small-scale, irregular punctuated migration events" caused changes in language and culture "among Anatolia's diverse autochthonous inhabitants," which explains Anatolian populations' profile today.
See also
* Biblical terminology for race * Caucasus hunter-gatherer *Early human migrations
Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by '' Homo erect ...
*Ethnic groups in the Middle East
The ethnic groups in the Middle East in the transcontinental region commonly known with its geopolitical term; the Middle East. The region has historically been a crossroad of different cultures and languages. Since the 1960s, the changes in poli ...
*Genetic history of Europe
The Genetic history of Europe deals with the formation, ethnogenesis, and other DNA-specific information about populations indigenous, or living in Europe.
The most significant recent dispersal of modern humans from Africa gave rise to an u ...
*Genetic history of North Africa
The genetic history of North Africa has been heavily influenced by geography. The Sahara desert to the south and the Mediterranean Sea to the North were important barriers to gene flow from sub-Saharan Africa and Europe in prehistoric times. How ...
*Genetic studies on Arabs
Genetic studies on Arabs refers to the analyses of the genetics of ethnic Arab populations within the Middle East and North Africa. The Arab world has one of the highest rates of genetic disorders globally; some 906 pathologies are endemic to the ...
*History of the Middle East
The Middle East, interchangeable with the Near East, is home to one of the Cradles of Civilization and has seen many of the world's oldest cultures and civilizations. The region's history started from the earliest human settlements and continues ...
* Middle Bronze Age migrations (ancient Near East)
*Middle Eastern studies
Middle Eastern studies (sometimes referred to as Near Eastern studies) is a name given to a number of academic programs associated with the study of the history, culture, politics, economies, and geography of the Middle East, an area that is gene ...
* Near Eastern bioarchaeology
*Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of the Near East Listed here are notable ethnic groups and populations from Western Asia, Egypt and South Caucasus by human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups based on relevant studies. The samples are taken from individuals identified with the ethnic and linguistic desig ...
References
Bibliography
* * * *Zalloua, P., Wells, S. (2004) "Who Were the Phoenicians?" ''National Geographic Magazine'', October 2004. {{DEFAULTSORT:Genetic history of the Middle EastMiddle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
Ancient peoples of the Near East
Archaeology of the Near East
Demographics of the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
History of the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
Middle Eastern studies
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...