Antiochus the Great on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek
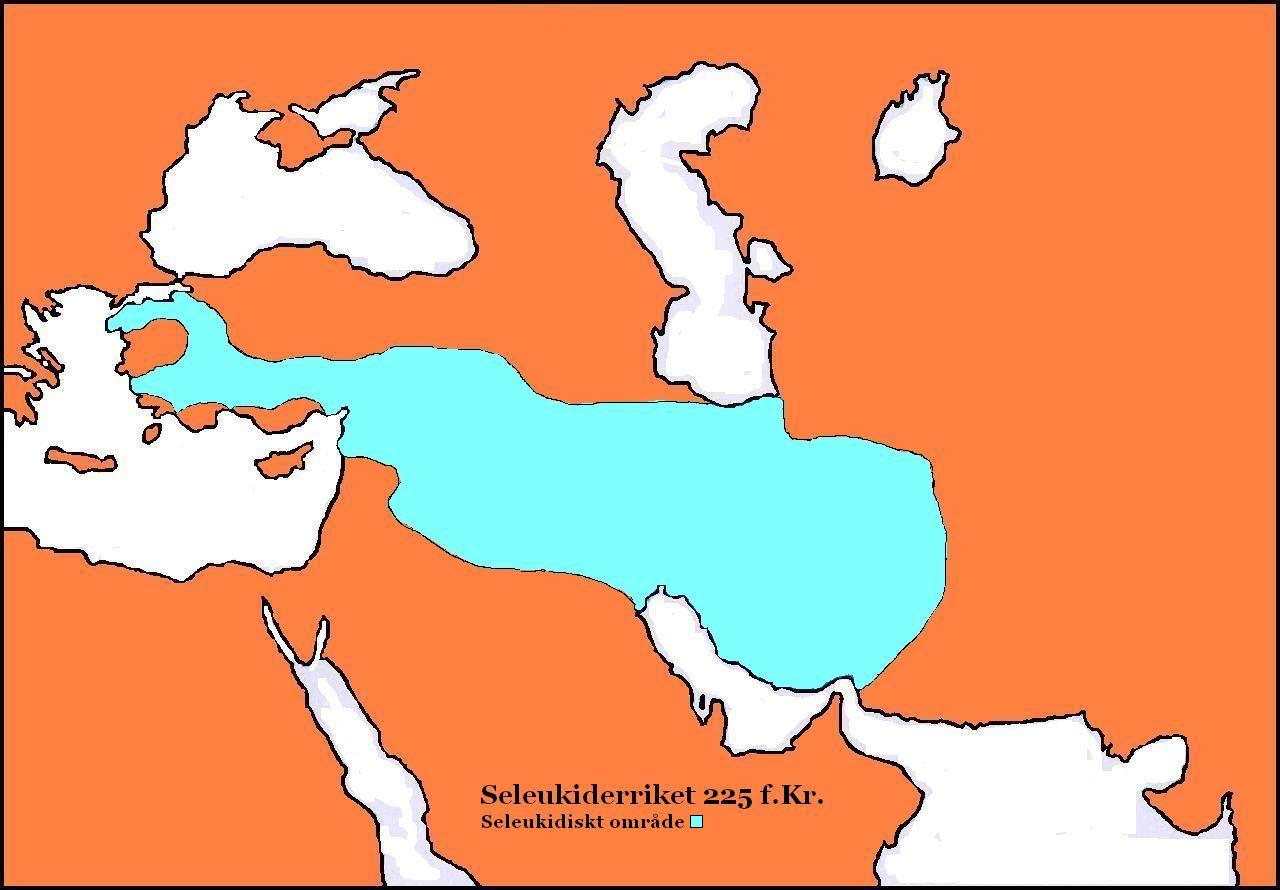 Antiochus III was a member of the
Antiochus III was a member of the
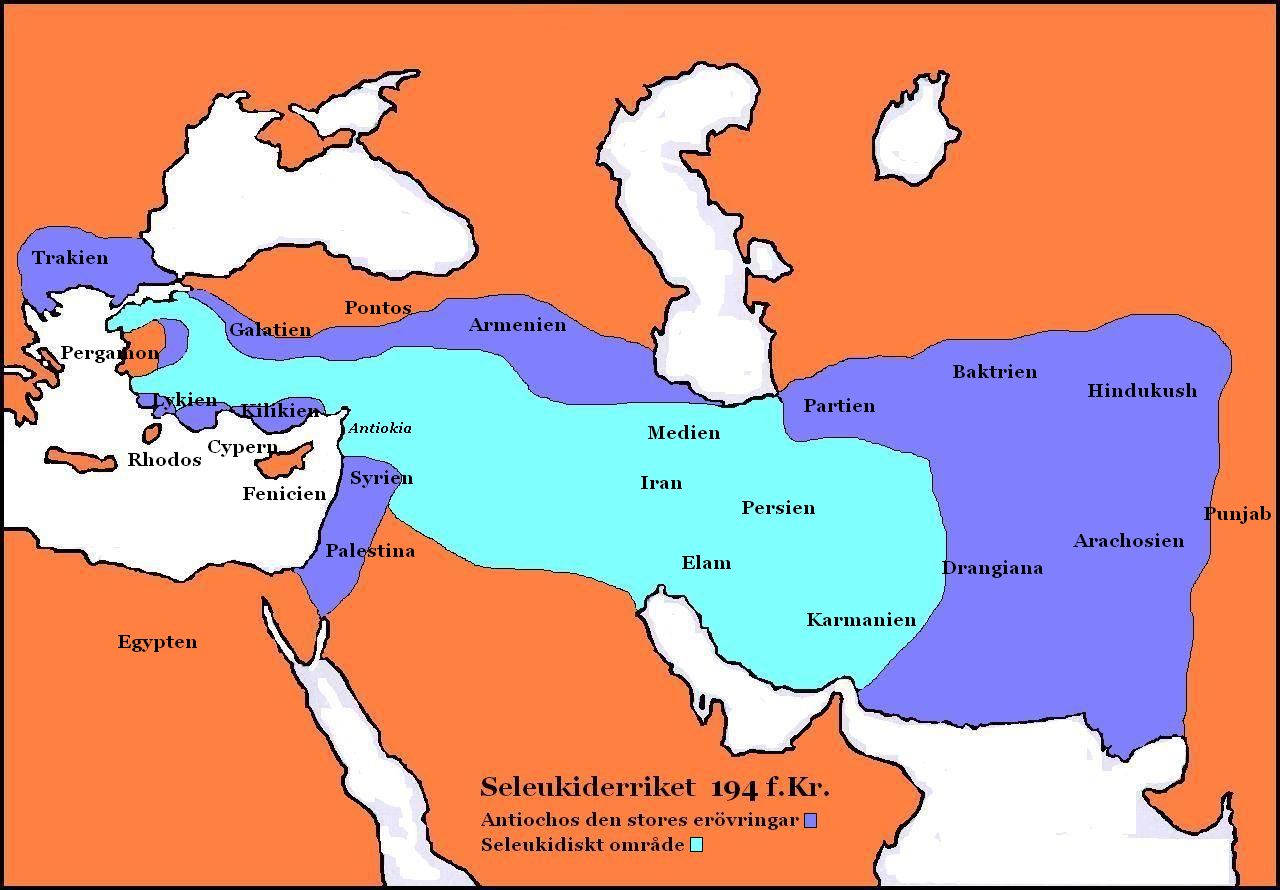 The campaigns of 219 BC and 218 BC carried the Seleucid armies almost to the confines of the Ptolemaic Kingdom, but in 217 BC
The campaigns of 219 BC and 218 BC carried the Seleucid armies almost to the confines of the Ptolemaic Kingdom, but in 217 BC
 In 222 BC, Antiochus III married Princess Laodice of Pontus, a daughter of King Mithridates II of Pontus and Princess Laodice of the Seleucid Empire. The couple were first cousins through their mutual grandfather,
In 222 BC, Antiochus III married Princess Laodice of Pontus, a daughter of King Mithridates II of Pontus and Princess Laodice of the Seleucid Empire. The couple were first cousins through their mutual grandfather,
1 Maccabees 1:10
when Antiochus IV is introduced as "son of King Antiochus ntiochus III. Antiochus III is mentioned later i
1 Maccabees 8
which describes Judas Maccabeus' knowledge of the deeds of the Roman Republic, including an allusion to the defeat of Antiochus III by the Romans. The
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria
Syria ( Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other ...
and large parts of the rest of western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King
Great king, and the equivalent in many languages, refers to historical titles of certain monarchs, suggesting an elevated status among the host of kings and princes. This title is most usually associated with the '' shahanshah'' (shah of shahs ...
"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome.
Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domination", Antiochus III waged a four-year war against the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
beginning in mainland Greece in the autumn of 192 BC before being decisively defeated at the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pe ...
. He died three years later on campaign in the east.
Biography
Background and early reign
 Antiochus III was a member of the
Antiochus III was a member of the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
Seleucid dynasty. He was the son of king Seleucus II Callinicus
Seleucus II Callinicus Pogon ( el, ; ''Kallinikos'' means "beautifully triumphant"; ''Pogon'' means "the Beard"; July/August 265 BC – December 225 BC),, . was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, who reigned from 246 BC to 225 BC. Faced ...
and Laodice II
Laodice II ( grc, Λαοδίκη, Laodíkē; lived in the 3rd century BC), was the wife of Seleucus II Callinicus. According to the express statement of Polybius, she was the sister of Andromachus and therefore the aunt of her husband. Laodice II ...
, aunt of Seleucus, and was born around 242 BC near Susa in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. He may have borne a non-dynastic name (starting with Ly-), according to a Babylonian chronicle. He succeeded, under the name Antiochus, his brother Seleucus III Ceraunus
Seleucus III Soter, called Seleucus Ceraunus (Greek: ; c. 243 BC – April/June 223 BC, ruled December 225 – April/June 223 BC), was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Kingdom, the eldest son of Seleucus II Callinicus and Laodice II.
Biograph ...
, upon the latter's murder in Anatolia; he was in Babylon at the time.
Antiochus III inherited a disorganized state. Not only had Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
become detached, but the easternmost provinces had broken away, Bactria under the Seleucid Diodotus of Bactria
Diodotus I Soter (Greek: , ''Diódotos Sōtḗr''; c. 315-300 BC – c. 235 BC), was the first Hellenistic King of Bactria. Diodotus became independent of the Seleucid empire around 255 or 245 BC, and established the Diodotid Bactrian Kingdom, w ...
, and Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
under the rebel satrap Andragoras in 247–245 BC, who was himself later vanquished by the nomad chieftain Arsaces Arsaces or Arsakes (, , Graecized form of Old Persian ) is the eponymous Greek form of the dynastic name of the Parthian Empire of Iran adopted by all epigraphically attested rulers of the Arsacid dynasties. The indigenous Parthian and Armenian f ...
. In 222 BC, soon after Antiochus's accession, Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
and Persis
Persis ( grc-gre, , ''Persís''), better known in English as Persia ( Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, ''Parsa''; fa, پارس, ''Pârs''), or Persia proper, is the Fars region, located to the southwest of modern-day Iran, now a province. T ...
revolted under their governors, the brothers Molon
Molon ( or ) or Molo (; grc, Mόλων; died 220 BC) was a general and satrap of the Seleucid king Antiochus the Great (223–187 BC). He held the satrapy of Media at the accession of that monarch (223 BC); in addition to which, Antiochus c ...
and Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
. The young king, under the influence of the minister Hermeias
Hermeias () or Hermias (; Greek: Ἑρμείας or Ἑρμίας; died 220 BC) was a Carian by birth, who had raised himself to be the favourite and chief minister of Seleucus III Ceraunus (225–223 BC), and was left at the head of affairs i ...
, headed an attack on Ptolemaic Syria instead of going in person to face the rebels. The attack against the Ptolemaic empire proved a fiasco, and the generals sent against Molon and Alexander met with disaster. Only in Asia Minor, where the king's cousin, Achaeus, represented the Seleucid cause, did its prestige recover, driving the Pergamene power back to its earlier limits.
In 221 BC Antiochus at last went far east, and the rebellion of Molon and Alexander collapsed which Polybios attributes in part to his following the advice of Zeuxis rather than Hermeias. The submission of Lesser Media, which had asserted its independence under Artabazanes, followed. Antiochus rid himself of Hermeias by assassination and returned to Syria (220 BC). Meanwhile, Achaeus himself had revolted and assumed the title of king in Asia Minor. Since, however, his power was not well enough grounded to allow an attack on Syria, Antiochus considered that he might leave Achaeus for the present and renew his attempt on Ptolemaic Syria.
Early wars against other Hellenistic rulers
Ptolemy IV
egy, Iwaennetjerwymenkhwy Setepptah Userkare Sekhemankhamun Clayton (2006) p. 208.
, predecessor = Ptolemy III
, successor = Ptolemy V
, horus = ''ḥnw-ḳni sḫꜤi.n-sw-it.f'Khunuqeni sekhaensuitef'' The strong youth whose f ...
defeated Antiochus at the Battle of Raphia
The Battle of Raphia, also known as the Battle of Gaza, was fought on 22 June 217 BC near modern Rafah between the forces of Ptolemy IV Philopator, king and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt and Antiochus III the Great of the Seleucid Empire durin ...
. This defeat nullified all Antiochus's successes and compelled him to withdraw north of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
. In 216 BC his army marched into western Anatolia to suppress the local rebellion led by Antiochus's own cousin Achaeus, and had by 214 BC driven him from the field into Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
. Capturing Achaeus, Antiochus had him executed. The citadel managed to hold out until 213 BC under Achaeus's widow Laodice who surrendered later.
Having thus recovered the central part of Asia Minor (for the Seleucid government had perforce to tolerate the dynasties in Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
, Bithynia and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
), Antiochus turned to recovering the outlying provinces of the north and east. He besieged Xerxes of Armenia
Xerxes ( grc, Ξέρξης; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠) was king of Sophene and Commagene from 228 BC to 212 BC. He was the son and successor of Arsames I.
Name
''Xérxēs'' () is the Greek and Latin (''Xerxes'', ''Xerses'') transliter ...
in 212 BC, who had refused to pay tribute, and forced his capitulation. In 209 BC Antiochus invaded Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
, occupied the capital Hecatompylos
Qumis ( fa, قومس; Middle Persian ''𐭪𐭥𐭬𐭩𐭮 Kōmis''), also known as Hecatompylos ( grc, Ἑκατόμπυλος, in fa, صددروازه, ''Saddarvazeh'') was an ancient city which was the capital of the Arsacid dynasty by 200 ...
and pushed forward into Hyrcania
Hyrcania () ( el, ''Hyrkania'', Old Persian: 𐎺𐎼𐎣𐎠𐎴 ''Varkâna'',Lendering (1996) Middle Persian: 𐭢𐭥𐭫𐭢𐭠𐭭 ''Gurgān'', Akkadian: ''Urqananu'') is a historical region composed of the land south-east of the Caspian ...
, winning the Battle of Mount Labus
The Battle of Mount Labus was a battle fought in 209 BCE between the Seleucid Empire under Antiochus the Third and the Parthians of Arsaces the Second. The battle ended in a Seleucid victory and the Parthians becoming Seleucid vassals
Backgro ...
. The Parthian king Arsaces II apparently successfully sued for peace.
Bactrian campaign and Indian expedition
The year 209 BC saw Antiochus in Bactria, where theGreco-Bactrian
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the India ...
king Euthydemus I
Euthydemus I (Greek: , ''Euthydemos'') c. 260 BC – 200/195 BC) was a Greco-Bactrian king and founder of the Euthydemid dynasty. He is thought to have originally been a governor (Satrap) of Sogdia, who seized the throne by force from Diodotus I ...
had supplanted the original rebel. Antiochus again met with success. Euthydemus was defeated by Antiochus at the Battle of the Arius
The Battle of the Arius was an engagement that was fought in 208 BC between the Seleucid Empire and the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom. The Seleucids were led by Antiochus III the Great, who launched an invasion of Bactria to recover his ancestor's past d ...
but after sustaining a famous siege in his capital Bactra
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
(''Balkh''), he obtained an honourable peace by which Antiochus promised Euthydemus's son Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
the hand of Laodice, his daughter.
Antiochus next, following in the steps of Alexander, crossed into the Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
valley, reaching the realm of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n king Sophagasenus
Sophagasenos also spelt Sophagasenus or Sophagasenas was a local ruler of Kabul and Kapisa valley ( Paropamisade of the classical writings) during the last decade of 3rd century BCE. Sophagasenus finds reference only in "The Histories" of Polybi ...
and returned west by way of Seistan and Kerman (206/5). According to Polybius:
Persia and Coele Syria campaigns
FromSeleucia on the Tigris
Seleucia (; grc-gre, Σελεύκεια), also known as or , was a major Mesopotamian city of the Seleucid empire. It stood on the west bank of the Tigris River, within the present-day Baghdad Governorate in Iraq.
Name
Seleucia ( grc-gre, Σ ...
he led a short expedition down the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
against the Gerrha
Gerrha ( grc, Γέρρα, translit=Gérrha) was an ancient and renowned city within Eastern Arabia, on the west side of the Persian Gulf.
History
Prior to Gerrha, the area belonged to the Dilmun civilization, which was conquered by the Assyria ...
eans of the Arabian coast (205 BC/204 BC). Antiochus seemed to have restored the Seleucid empire in the east, which earned him the title of "the Great" (Antiochos Megas). In 205/204 BC the infant Ptolemy V Epiphanes succeeded to the Egyptian throne, and Antiochus is said (notably by Polybius) to have concluded a secret pact with Philip V of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon ag ...
for the partition of the Ptolemaic possessions. Under the terms of this pact, Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an Classical antiquity, ancient monarchy, kingdom on the periphery of Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. Th ...
was to receive the Ptolemaic possessions around the Aegean Sea and Cyrene, while Antiochus would annex Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
and Egypt.
Once more Antiochus attacked the Ptolemaic province of Coele Syria and Phoenicia, and by 199 BC he seems to have had possession of it before the Aetolian leader Scopas
Scopas ( grc-gre, Σκόπας; born in Paros, fl. 4th century BCE) was an ancient Greek sculptor and architect, most famous for his statue of Meleager, the copper statue of Aphrodite, and the head of goddess Hygieia, daughter of Asclepius.
Ea ...
recovered it for Ptolemy. But that recovery proved brief, for in 198 BC Antiochus defeated Scopas at the Battle of Panium
The Battle of Panium (also known as Paneion, grc, Πάνειον, or Paneas, Πανειάς) was fought in 200 BC near Paneas (Caesarea Philippi) between Seleucid and Ptolemaic forces as part of the Fifth Syrian War. The Seleucids were led by ...
, near the sources of the Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, a battle which marks the end of Ptolemaic rule in Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
.
War against Rome and death
Antiochus then moved to Asia Minor, by land and by sea, to secure the coast towns which belonged to the remnants of Ptolemaic overseas dominions and the independent Greek cities. This enterprise earned him the antagonism of theRoman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
, since Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to promi ...
and Lampsacus
Lampsacus (; grc, Λάμψακος, translit=Lampsakos) was an ancient Greek city strategically located on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been transmitte ...
appealed to the Republic, which at the time acted as a defender of Greek freedom. The tension grew when Antiochus in 196 BC established a footing in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
. The evacuation of Greece by the Romans gave Antiochus his opportunity, and he now had the fugitive Hannibal at his court to urge him on.
In 192 BC Antiochus invaded Greece with a 10,000-man army, and was elected the commander in chief of the Aetolian League
The Aetolian (or Aitolian) League ( grc-gre, Κοινὸν τῶν Αἰτωλῶν) was a confederation of tribal communities and cities in ancient Greece centered in Aetolia in central Greece. It was probably established during the early Hellen ...
. In 191 BC, however, the Romans under Manius Acilius Glabrio routed him at Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
, forcing him to withdraw to Asia Minor. The Romans followed up their success by invading Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, and the decisive victory of Scipio Asiaticus
Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus (properly Asiagenes; 3rd century BC – after 183 BC) was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. He was the son of Publius Cornelius Scipio and the younger brother of Scipio Africanus. He was elected co ...
at Magnesia ad Sipylum
Magnesia Sipylum ( el, Mαγνησία ἡ πρὸς Σιπύλῳ or ; modern Manisa, Turkey) was a city of Lydia, situated about 65 km northeast of Smyrna (now İzmir) on the river Hermus (now Gediz) at the foot of Mount Sipylus. The ci ...
(190 BC), following the defeat of Hannibal at sea off Side
Side or Sides may refer to:
Geometry
* Edge (geometry) of a polygon (two-dimensional shape)
* Face (geometry) of a polyhedron (three-dimensional shape)
Places
* Side (Ainis), a town of Ainis, ancient Thessaly, Greece
* Side (Caria), a town of an ...
, delivered Asia Minor into their hands.
By the Treaty of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopylae ...
(188 BC) Antiochus abandoned all the country north and west of the Taurus
Taurus is Latin for 'bull' and may refer to:
* Taurus (astrology), the astrological sign
* Taurus (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
* Taurus (mythology), one of two Greek mythological characters named Taurus
* '' Bos tauru ...
, most of which the Roman Republic gave either to Rhodes or to the Attalid ruler Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης Σωτήρ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus ...
, its allies (many Greek cities were left free). As a consequence of this blow to the Seleucid power, the outlying provinces of the empire, recovered by Antiochus, reasserted their independence. Antiochus mounted a fresh eastern expedition in Luristan, where he was killed while pillaging a temple of Bel at Elymaïs, Persia, in 187 BC.
Family
Antiochus II Theos
Antiochus II Theos ( grc-gre, Ἀντίοχος Θεός, ; 286 – July 246 BC) was a Greek king of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire who reigned from 261 to 246 BC. He succeeded his father Antiochus I Soter in the winter of 262–61 BC. He wa ...
. Antiochus and Laodice had eight children (three sons and five daughters):
* Antiochus (221–193 BC), Antiochus III's first heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
and joint-king with his father from 210–193 BC
*Seleucus IV Philopator
Seleucus IV Philopator (Greek: Σέλευκος Φιλοπάτωρ; c. 218 – 3 September 175 BC), ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, reigned from 187 BC to 175 BC over a realm consisting of Syria (now including Cilicia and Judea), Mesop ...
(c. 220175 BC), Antiochus III's successor
*Ardys
*unnamed daughter, betrothed
An engagement or betrothal is the period of time between the declaration of acceptance of a marriage proposal and the marriage itself (which is typically but not always commenced with a wedding). During this period, a couple is said to be ''fi ...
in about 206 BC to Demetrius I of Bactria
Demetrius I Anicetus ( grc, Δημήτριος Ἀνίκητος, Dēmētrios Anikētos, "the unconquered"), also called Damaytra was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek king (Yona in Pali language, "Yavana" in Sanskrit) (reigned c. 200–167 ...
*Laodice IV
Laodice IV (flourished second half 3rd century BC and first half 2nd century BC) was a Greek Princess, Head Priestess and Queen of the Seleucid Empire. Antiochus III appointed Laodice in 193 BC, as the chief priestess of the state cult dedicated ...
, married all three of her brothers in succession and became Queen of the Seleucid Empire through her second and third marriages
*Cleopatra I Syra
Cleopatra I Syra (Greek: Κλεοπάτρα ἡ Σύρα; c. 204 – 176 BC) was a princess of the Seleucid Empire, Queen of Ptolemaic Egypt by marriage to Ptolemy V of Egypt, and regent of Egypt during the minority of their son, Ptolemy VI ...
(c. 204176 BC), married in 193 BC Ptolemy V Epiphanes of Egypt
*Antiochis The name Antiochis ( grc, Ἀντιoχίς) is the female name of Antiochus.
Women Seleucid Princesses & Hellenistic Queen Consorts
*Antiochis, a daughter of Achaeus and granddaughter of Seleucus I Nicator. She married Attalus and became the moth ...
, married in 194 BC King Ariarathes IV of Cappadocia
* Mithridates (215–164 BC), succeeded his brother Seleucus IV Philopator
Seleucus IV Philopator (Greek: Σέλευκος Φιλοπάτωρ; c. 218 – 3 September 175 BC), ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, reigned from 187 BC to 175 BC over a realm consisting of Syria (now including Cilicia and Judea), Mesop ...
in 175 BC under the regnal name
A regnal name, or regnant name or reign name, is the name used by monarchs and popes during their reigns and, subsequently, historically. Since ancient times, some monarchs have chosen to use a different name from their original name when they ...
Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his dea ...
In 191 BC, Antiochus III married a girl from Chalcis, whom he named "Euboea". They had no children. Laodice III may have fallen in disgrace; however, she clearly survived Antiochus III, and appears in Susa in 183 BC.
Antiochus and the Jews
Antiochus III resettled 2000 Jewish families from Babylonia into the Hellenistic Anatolian regions of Lydia and Phrygia.Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
portrays him as friendly towards the Jews of Jerusalem and cognizant of their loyalty to him (see Antiquities of the Jews, Book XII, Chapter 3), in stark contrast to the attitude of his son. In fact, Antiochus III lowered taxes, granted subventions to the Temple, and let the Jews live, as Josephus puts it, "according to the law of their forefathers."
Books of Maccabees
Antiochus III is mentioned in thedeuterocanonical
The deuterocanonical books (from the Greek meaning "belonging to the second canon") are books and passages considered by the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox Churches, and the Assyrian Church of the East to be ...
''Books of the Maccabees
The Books of the Maccabees or the Sefer HaMakabim (the ''Book of the Maccabees'') recount the history of the Maccabees, the leaders of the Jewish rebellion against the Seleucid dynasty.
List of books
The Books of the Maccabees refers to a series o ...
.'' The subject of Maccabees is the Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ende ...
against Antiochus' son, Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his dea ...
. Antiochus III is first mentioned i1 Maccabees 1:10
when Antiochus IV is introduced as "son of King Antiochus ntiochus III. Antiochus III is mentioned later i
1 Maccabees 8
which describes Judas Maccabeus' knowledge of the deeds of the Roman Republic, including an allusion to the defeat of Antiochus III by the Romans. The
NRSV
The New Revised Standard Version (NRSV) is an English translation of the Bible published in 1989 by the National Council of Churches.he Romansalso had defeated Antiochus the Great, king of
1 Maccabees 8:6-8
Antiochus III "the Great"
entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antiochus 03 the Great 240s BC births 187 BC deaths Year of birth uncertain 3rd-century BC Babylonian kings 2nd-century BC Babylonian kings 3rd-century BC Seleucid rulers 2nd-century BC Seleucid rulers People from Khuzestan Province Kings of Syria
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
, who went to fight against them with one hundred twenty elephants and with cavalry and chariots and a very large army. He was crushed by them; they took him alive and decreed that he and those who would reign after him should pay a heavy tribute and give hostages and surrender some of their best provinces, the countries of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
, and Lydia. These they took from him and gave to King Eumenes."1 Maccabees 8:6-8
Cultural portrayals
*TheCaroline era
The Caroline era is the period in English and Scottish history named for the 24-year reign of Charles I (1625–1649). The term is derived from ''Carolus'', the Latin for Charles. The Caroline era followed the Jacobean era, the reign of Charles's ...
play ''Believe as You List
''Believe as You List'' is a Caroline era tragedy by Philip Massinger, famous as a case of theatrical censorship.
Censorship
The play originally dealt with the legend that Sebastian of Portugal had survived the battle of Alcácer Quibir, and the ...
'' is centered around Antiochus's resistance to the Romans after the Battle of Thermopylae. The play was originally about Sebastian of Portugal
Sebastian ( pt, Sebastião I ; 20 January 1554 – 4 August 1578) was King of Portugal from 11 June 1557 to 4 August 1578 and the penultimate Portuguese monarch of the House of Aviz.
He was the son of João Manuel, Prince of Portugal, and hi ...
surviving the Battle of Alcazar and returning, trying to gather support to return to the throne. This first version was censored for being considered "subversive
Subversion () refers to a process by which the values and principles of a system in place are contradicted or reversed in an attempt to transform the established social order and its structures of power, authority, hierarchy, and social norms. Sub ...
" because it portrayed Sebastian being deposed, its comments in favor of an Anglo-Spanish alliance and possible pro-Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, which led to the final version changing to the story of Antiochus (which led to historical inaccuracy in exaggerating his defeat at that phase in history to fit the earlier text), turning Spaniards into Romans and the Catholic eremite
A hermit, also known as an eremite (adjectival form: hermitic or eremitic) or solitary, is a person who lives in seclusion. Eremitism plays a role in a variety of religions.
Description
In Christianity, the term was originally applied to a Ch ...
into a Stoic
Stoic may refer to:
* An adherent of Stoicism; one whose moral quality is associated with that school of philosophy
* STOIC, a programming language
* ''Stoic'' (film), a 2009 film by Uwe Boll
* ''Stoic'' (mixtape), a 2012 mixtape by rapper T-Pain
* ...
philosopher.
*Antiochus features towards the end of Norman Barrow's historical novel, ''The High Priest'' (Faber & Faber, 1947), after his forces have reacquired Jerusalem from the Ptolemaic occupation. The book was noted by John Betjeman in the Daily Herald (UK newspaper)
The ''Daily Herald'' was a British daily newspaper, published in London from 1912 to 1964 (although it was weekly during the First World War). It was published in the interest of the labour movement and supported the Labour Party. It unde ...
as ''"interesting"''.
See also
*List of Syrian monarchs
The title King of Syria appeared in the second century BC in referring to the Seleucid kings who ruled the entirety of the region of Syria. It was also used to refer to Aramean kings in the Greek translations of the Old Testament, mainly indicati ...
* Timeline of Syrian history
__NOTOC__
This is a timeline of Syrian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Syria and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of Syria.
Millennia: 1st ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Antiochus III "the Great"
entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antiochus 03 the Great 240s BC births 187 BC deaths Year of birth uncertain 3rd-century BC Babylonian kings 2nd-century BC Babylonian kings 3rd-century BC Seleucid rulers 2nd-century BC Seleucid rulers People from Khuzestan Province Kings of Syria