Ankylosauridae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to
 Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on cranial bones that cover some skull openings and form wedge-shaped, horn-like structures. Along the ankylosaurid torso are scute rows, which are filled in with smaller
Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on cranial bones that cover some skull openings and form wedge-shaped, horn-like structures. Along the ankylosaurid torso are scute rows, which are filled in with smaller
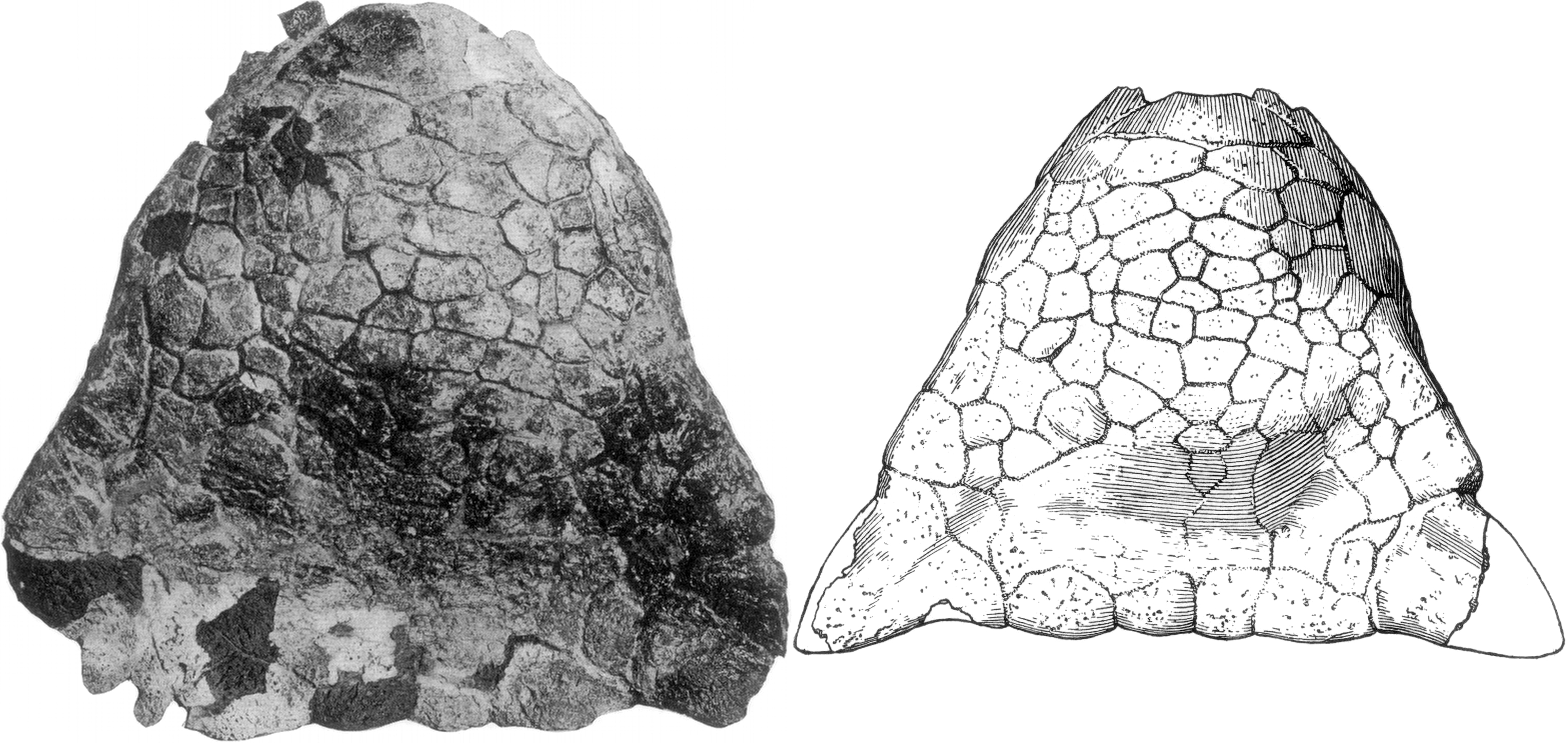 Barnum Brown and Peter Kaisen discovered the first ankylosaurid genus, ''
Barnum Brown and Peter Kaisen discovered the first ankylosaurid genus, ''
 In 1978, W.P. Coombs, Jr. classified almost all valid species of Ankylosauria within either Nodosauridae or Ankylosauridae. This was a pivotal study and described many characters of ankylosaurs in the earliest phylogenetic analyses of the group.
Later in 1998,
In 1978, W.P. Coombs, Jr. classified almost all valid species of Ankylosauria within either Nodosauridae or Ankylosauridae. This was a pivotal study and described many characters of ankylosaurs in the earliest phylogenetic analyses of the group.
Later in 1998,  Most recently, Arbour and Currie have presented a phylogenetic analysis of Ankylosauridae consisting of '' Gastonia'', ''
Most recently, Arbour and Currie have presented a phylogenetic analysis of Ankylosauridae consisting of '' Gastonia'', ''
 It is difficult to establish the geographical origin of Ankylosauridae at present. There is a mix of basal ankylosaurids from both North America and Asia, which carries on through accepted cladistic analyses. It appears that in the mid-
It is difficult to establish the geographical origin of Ankylosauridae at present. There is a mix of basal ankylosaurids from both North America and Asia, which carries on through accepted cladistic analyses. It appears that in the mid-
 There are a few prevailing theories for ankylosaurid tail club function. The first is agonistic behaviour within a species. In most vertebrates, including dinosaurs, this behaviour is accompanied by structures for display or combat. Some researchers believe this phenomenon would have been implausible considering there is no modern tetrapod analogue that uses the tail for this purpose. These paleontologists instead propose that ankylosaurids made use of their broad, flat skull for head-butting between individuals.
The second theory for tail club function is for defense against predators. It has been postulated that the club would be most effective against the metatarsals of an attacking theropod.
The bones that form cranial ornamentation have physiological costs, and so would be inefficient to produce merely for protection against predation. The theory has therefore been posed that these wedge-shaped osteoderms could support a partly sexually selected interpretation.
There are a few prevailing theories for ankylosaurid tail club function. The first is agonistic behaviour within a species. In most vertebrates, including dinosaurs, this behaviour is accompanied by structures for display or combat. Some researchers believe this phenomenon would have been implausible considering there is no modern tetrapod analogue that uses the tail for this purpose. These paleontologists instead propose that ankylosaurids made use of their broad, flat skull for head-butting between individuals.
The second theory for tail club function is for defense against predators. It has been postulated that the club would be most effective against the metatarsals of an attacking theropod.
The bones that form cranial ornamentation have physiological costs, and so would be inefficient to produce merely for protection against predation. The theory has therefore been posed that these wedge-shaped osteoderms could support a partly sexually selected interpretation.
ImageSize = width:800px height:auto barincrement:15px
PlotArea = left:10px bottom:50px top:10px right:10px
Period = from:-201 till:-45
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:-200
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:-201
TimeAxis = orientation:hor
AlignBars = justify
Colors =
#legends
id:CAR value:claret
id:ANK value:rgb(0.4,0.3,0.196)
id:HER value:teal
id:HAD value:green
id:OMN value:blue
id:black value:black
id:white value:white
id:jurassic value:rgb(0.2,0.7,0.79)
id:earlyjurassic value:rgb(0,0.69,0.89)
id:middlejurassic value:rgb(0.52,0.81,0.91)
id:latejurassic value:rgb(0.74,0.89,0.97)
id:cretaceous value:rgb(0.5,0.78,0.31)
id:earlycretaceous value:rgb(0.63,0.78,0.65)
id:latecretaceous value:rgb(0.74,0.82,0.37)
BarData=
bar:eratop
bar:space
bar:periodtop
bar:space
bar:NAM1
bar:NAM2
bar:NAM3
bar:NAM4
bar:NAM5
bar:NAM6
bar:NAM7
bar:NAM8
bar:NAM9
bar:NAM10
bar:NAM11
bar:NAM12
bar:NAM13
bar:NAM14
bar:NAM15
bar:NAM16
bar:NAM17
bar:NAM18
bar:NAM19
bar:NAM20
bar:NAM21
bar:NAM22
bar:NAM23
bar:NAM24
bar:space
bar:period
bar:space
bar:era
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25
shift:(7,-4)
bar:periodtop
from: -201 till: -174 color:earlyjurassic text:
Family TreeAnkylosauridae
Tree of Life web project
Pseudoplocephalus
Blog by an evolutionary biologist and vertebrate palaeontologist specializing in ankylosaurs {{Taxonbar, from=Q517099 Aptian first appearances Taxa named by Barnum Brown Prehistoric dinosaur families
Nodosauridae
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
Description
Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids ...
. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
. These animals were mainly herbivorous and were obligate quadrupeds, with leaf-shaped teeth and robust, scute
A scute or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of birds. The term is also used to describe the anterior po ...
-covered bodies. Ankylosaurids possess a distinctly domed and short snout, wedge-shaped osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amp ...
s on their skull, scutes along their torso, and a tail club.
Ankylosauridae is exclusively known from the northern hemisphere, with specimens found in western North America, Europe, and East Asia. The first discoveries within this family were of the genus ''Ankylosaurus
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of th ...
'', by Peter Kaiser and Barnum Brown
Barnum Brown (February 12, 1873 – February 5, 1963), commonly referred to as Mr. Bones, was an American paleontologist. Named after the circus showman P. T. Barnum, he discovered the first documented remains of '' Tyrannosaurus'' during a career ...
in Montana in 1906. Brown went on to name Ankylosauridae and the subfamily Ankylosaurinae in 1908.
Anatomy
 Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on cranial bones that cover some skull openings and form wedge-shaped, horn-like structures. Along the ankylosaurid torso are scute rows, which are filled in with smaller
Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on cranial bones that cover some skull openings and form wedge-shaped, horn-like structures. Along the ankylosaurid torso are scute rows, which are filled in with smaller ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea). The absence of the auditor ...
to create a fused shield of armour. Only two collars of armour plates can be found on the neck, as opposed to the sister group, nodosaurids, which have three. Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae also share the unique attribute of abundant structural fibres in both primary and secondary bone. Ankylosaurids also have an S-shaped narial passage.
The most distinguishing feature of ankylosaurids is the presence of a tail club. It is made out of modified interlocking distal caudal vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
e and enlarged, bulbous osteoderms. The “handle” of the tail club involves the vertebrae, and requires elongated prezygapophyses to overlap at least half of the preceding vertebral centrum length. These distal caudal vertebrae also lack transverse processes and neural spines, and therefore tend to be longer than they are wide; the reverse is true for proximal caudal vertebrae. Derived ankylosaurids possess a fusion of posterior dorsal, sacral, and sometimes anterior caudal vertebrae, which forms a singular structure called a “synsacrum complex”. There is a complete fusion between centra, neural arches, zygapophyses, and sometimes neural spines.
In 2017, Victoria M. Arbour and David C. Evans described a new genus of ankylosaurine that preserved extensive soft tissues along the body. This animal, named '' Zuul'' after its resemblance to the '' Ghostbusters'' monster, is also the first ankylosaur from the Judith River Formation.
History of study
 Barnum Brown and Peter Kaisen discovered the first ankylosaurid genus, ''
Barnum Brown and Peter Kaisen discovered the first ankylosaurid genus, ''Ankylosaurus
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of th ...
'', in 1906 in the Hell Creek Beds in Montana. The fossil material they found was a portion of the skull, two teeth, some vertebrae, a distorted scapula, ribs and more than thirty osteoderms. Reconstruction of the specimen was initially met with skepticism by those who believed it to be at least very close to, or completely a part of the genus ''Stegopelta'', and Brown himself placed it within the suborder Stegosauria.
It has previously been interpreted that variation in ankylosaurid tail club shape is due to sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
, which assumes that tail club morphology has a sex-linked intraspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species.
Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organis ...
function. This is possible if the tail club was used for agonistic behaviour. However, a sexual dimorphism theory would predict roughly equal numbers of individuals with two distinct sizes of tail clubs. Obvious sexual dimorphism has not been documented, but if the clubs of one sex are much larger, then there would be a bias for preservation and discovery towards that sex.
Phylogeny
 In 1978, W.P. Coombs, Jr. classified almost all valid species of Ankylosauria within either Nodosauridae or Ankylosauridae. This was a pivotal study and described many characters of ankylosaurs in the earliest phylogenetic analyses of the group.
Later in 1998,
In 1978, W.P. Coombs, Jr. classified almost all valid species of Ankylosauria within either Nodosauridae or Ankylosauridae. This was a pivotal study and described many characters of ankylosaurs in the earliest phylogenetic analyses of the group.
Later in 1998, Paul Sereno
Paul Callistus Sereno (born October 11, 1957) is a professor of paleontology at the University of Chicago and a National Geographic "explorer-in-residence" who has discovered several new dinosaur species on several continents, including at si ...
formally defined Ankylosauridae as all ankylosaurs more closely related to ''Ankylosaurus
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of th ...
'' than to '' Panaplosaurus''. Ankylosaurs not known to possess a tail club were included in Kenneth Carpenter's 2001 phylogeny of Ankylosauridae.
In a study done in 2004 by Vickaryous et al., '' Gargoyleosaurus'', '' Gastonia,'' and ''Minmi
Michiko Evwana (born December 8, 1974), better known by her stage name , is a Japanese hip-hop and reggae musician,, United Daily News (in Chinese), August 22, 2008 as well as a singer-songwriter and record producer. She is the first soca a ...
'' were recorded as basal ankylosaurids, with the rest of the ankylosaurids filled out with '' Gobisaurus'', ''Shamosaurus
''Shamosaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous (Aptian to Albian stage) deposits of Höövör, Mongolia.
Discovery and naming
In 1977, a Soviet-Mongolian expedition discovered the skeleto ...
'', and ankylosaurines from China, Mongolia, and North America.
In 2012, Thompson et al. undertook an analysis of almost all known valid ankylosaurs and outgroup taxa at the time. They based their resulting phylogeny on characters representing cranial, post-cranial, and osteodermal anatomy, and details of synapomorphies for each recovered clade. This study placed '' Gargoyleosaurus'' and '' Gastonia'' within basal Nodosauridae, and put ''Cedarpelta
''Cedarpelta'' is a extinct genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian to lower Turonian stage, 98.2 to 93 Ma) in what is now the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formati ...
'' and '' Liaoningosaurus'' as basal ankylosaurids.
 Most recently, Arbour and Currie have presented a phylogenetic analysis of Ankylosauridae consisting of '' Gastonia'', ''
Most recently, Arbour and Currie have presented a phylogenetic analysis of Ankylosauridae consisting of '' Gastonia'', ''Cedarpelta
''Cedarpelta'' is a extinct genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian to lower Turonian stage, 98.2 to 93 Ma) in what is now the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formati ...
'', '' Chuanqilong'', other basal ankylosaurids, and a number of derived ankylosaurids. Their phylogeny includes some uncertain phylogenetic relationships, between ''Ankylosaurus
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of th ...
'', '' Anodontosaurus'', '' Scolosaurus'', and ''Ziapelta
''Ziapelta'' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid. Its fossils have been found in the Hunter Wash and De-na-zin members of the Kirtland Formation of Upper Cretaceous (Campanian) New Mexico. It was named in 2014, in a research paper led by ankylos ...
''.
Paleobiology
Posture and locomotion
Ankylosaurids were likely very slow-moving animals. In all Ankylosauria, thefibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity ...
is more slender than the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it conn ...
, suggesting that the tibia carried most of the weight of the animal, while the fibula served as an area of muscular attachment. Hindlimb muscles of ''Euoplocephalus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''.
The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1 ...
'' have been restored and the placement of several muscles inserting on the femur have very short moment arms. Muscles inserting on the tibia and fibula have longer moment arms. This pattern of retractor muscles points to an elephantine locomotion, consistent with columnar posture.
Restoration of ''Euoplocephalus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''.
The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1 ...
'' forelimbs demonstrate similarities to crocodilian forelimb musculature. The most well developed muscles in the pectoral region had more of a weight-bearing function than a rotational one. It has also been postulated that the carpals
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the ...
and metacarpals bear resemblance to those of tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s with fossorial (burrowing) habits.
Several muscles in the posterior of ankylosaurids (dorsalis caudae, ilio-caudalis, coccygeo-femoralis brevis, coccygeo-femoralis longus, ilio-tibialis, and ischio caudalis) were used for motion of the tail and tail club. Ankylosaurids tend to have horizontal rather than an obliquely vertical orientation of zygapophyseal articulations in the free caudal vertebrae of the tail. This arrangement is most effective for side-to-side rather than vertical mobility. The absence of musculature to elevate the tail, and this orientation of zygapophyses suggest that the tail and its club swept parallel to and slightly above the ground.
Biogeography
 It is difficult to establish the geographical origin of Ankylosauridae at present. There is a mix of basal ankylosaurids from both North America and Asia, which carries on through accepted cladistic analyses. It appears that in the mid-
It is difficult to establish the geographical origin of Ankylosauridae at present. There is a mix of basal ankylosaurids from both North America and Asia, which carries on through accepted cladistic analyses. It appears that in the mid-Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
, Asian nodosaurids were replaced by ankylosaurine ankylosaurids. Some researchers postulate that Ankylosaurines migrated into North America from Asia between the Albian
The Albian is both an age of the geologic timescale and a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early/Lower Cretaceous Epoch/ Series. Its approximate time range is 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 100.5 ± 0 ...
and Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
, where they diversified into a clade of ankylosaurines characterized by arched snouts and flat cranial bone plates (caputegulae). There is no evidence for ankylosaurids in Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
.
Variation
Within Ankylosauridae there is much individual and interspecific variation in expression of armour. However, the most researched aspect of ankylosaurid armour is the tail club. There has been substantialontogenetic
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the s ...
and individual variability found in the morphology of this feature. There have been at least 16 caudal vertebrae included in the handle of the tail club of ''Pinacosaurus grangeri
''Pinacosaurus'' (meaning "Plank lizard") is a genus of ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous (Santonian-Campanian, roughly 75 million to 71 million years ago), mainly in Mongolia and China.
The first ...
'', and ''Euoplocephalus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''.
The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1 ...
'' has an estimated 9 – 11 coossified caudals.
Variations in tail knob shape, thickness, and length are attributed to individual variation, taxonomy, or representation of different growth phases. There are difficulties with this last aspect, however, in that known clubs do not conform to a single growth series, yet some differences must be ontogenetic and allometric.
Lifestyle
Most ankylosaurid teeth were leaf-shaped, implying a mainly herbivorous diet. Their teeth could be smooth or fluted, or may differ on labial and lingual surfaces. ''Euoplocephalus tutus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''.
The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1897 ...
'' possess ridges and grooves on their teeth that have no relation to their marginal cusps. With their downward-facing neck and head, it is plausible for ankylosaurids to feed in a grazing pattern.
Non-herbivorous habits have been implicated for some species, however. '' Pinacosaurus'' has been speculated as being an ant-eater-like long tongued insectivore,Hill, R., D’Emic, M., Bever, G., Norell, M. 2015. A complex hyobranchial apparatus in a Cretaceous dinosaur and the antiquity of avian paraglossalia. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. doi: 10.1111/zoj.12293 while '' Liaoningosaurus'' has been proposed to be a piscivore. Either would be exceptional evidence of carnivory among ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek ...
ns.
 There are a few prevailing theories for ankylosaurid tail club function. The first is agonistic behaviour within a species. In most vertebrates, including dinosaurs, this behaviour is accompanied by structures for display or combat. Some researchers believe this phenomenon would have been implausible considering there is no modern tetrapod analogue that uses the tail for this purpose. These paleontologists instead propose that ankylosaurids made use of their broad, flat skull for head-butting between individuals.
The second theory for tail club function is for defense against predators. It has been postulated that the club would be most effective against the metatarsals of an attacking theropod.
The bones that form cranial ornamentation have physiological costs, and so would be inefficient to produce merely for protection against predation. The theory has therefore been posed that these wedge-shaped osteoderms could support a partly sexually selected interpretation.
There are a few prevailing theories for ankylosaurid tail club function. The first is agonistic behaviour within a species. In most vertebrates, including dinosaurs, this behaviour is accompanied by structures for display or combat. Some researchers believe this phenomenon would have been implausible considering there is no modern tetrapod analogue that uses the tail for this purpose. These paleontologists instead propose that ankylosaurids made use of their broad, flat skull for head-butting between individuals.
The second theory for tail club function is for defense against predators. It has been postulated that the club would be most effective against the metatarsals of an attacking theropod.
The bones that form cranial ornamentation have physiological costs, and so would be inefficient to produce merely for protection against predation. The theory has therefore been posed that these wedge-shaped osteoderms could support a partly sexually selected interpretation.
Timeline of genera
Early
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
from: -174 till: -163 color:middlejurassic text: Middle
from: -163 till: -145 color:latejurassic text: Late
from: -145 till: -100 color:earlycretaceous text:Early
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
from: -100 till: -66 color:latecretaceous text: Late
bar:eratop
from: -201 till: -145 color:jurassic text:Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
from: -145 till: -66 color:cretaceous text:Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
PlotData=
align:left fontsize:M mark:(line,white) width:5 anchor:till align:left
color:cretaceous bar:NAM1 from:-122 till:-120 text: Liaoningosaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM2 from:-119 till:-113 text:Minmi
Michiko Evwana (born December 8, 1974), better known by her stage name , is a Japanese hip-hop and reggae musician,, United Daily News (in Chinese), August 22, 2008 as well as a singer-songwriter and record producer. She is the first soca a ...
color:cretaceous bar:NAM3 from:-113 till:-110 text:Shamosaurus
''Shamosaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous (Aptian to Albian stage) deposits of Höövör, Mongolia.
Discovery and naming
In 1977, a Soviet-Mongolian expedition discovered the skeleto ...
color:cretaceous bar:NAM4 from:-108.5 till:-108 text:Cedarpelta
''Cedarpelta'' is a extinct genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian to lower Turonian stage, 98.2 to 93 Ma) in what is now the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formati ...
color:cretaceous bar:NAM5 from:-105 till:-100 text: Zhongyuansaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM6 from:-98 till:-83 text:Talarurus
''Talarurus'' ( ; meaning "basket tail" or "wicker tail") is a genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 96 million to 89 million years ago. The first remains of ''Talarurus'' were discovered in ...
color:cretaceous bar:NAM7 from:-98 till:-83 text:Tsagantegia
''Tsagantegia'' (; meaning Tsagan Teg) is a genus of medium-sized ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The genus is monotypic, including only the type species, ''T. longicranialis''. The specime ...
color:cretaceous bar:NAM8 from:-92 till:-90 text: Gobisaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM9 from:-80 till:-79 text: Minotaurasaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM10 from:-80 till:-75 text: Pinacosaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM11 from:-76.5 till:-76 text: Scolosaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM12 from:-76.5 till:-76 text: Dyoplosaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM13 from:-76.4 till:-75.5 text:Euoplocephalus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''.
The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1 ...
color:cretaceous bar:NAM14 from:-76.2 till:-75.2 text: Zuul
color:cretaceous bar:NAM15 from:-76 till:-75 text:Nodocephalosaurus
''Nodocephalosaurus'' (meaning "knob headed lizard") is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from New Mexico that lived during the Late Cretaceous (late Campanian to early Maastrichtian stage, 73.49 to 73.04 Ma) in what is now the De-n ...
color:cretaceous bar:NAM16 from:-76 till:-74 text: Ahshislepelta
color:cretaceous bar:NAM17 from:-75 till:-74 text: Aletopelta
color:cretaceous bar:NAM18 from:-75 till:-74 text: Tianzhenosaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM19 from:-75 till:-74 text: Shanxia
color:cretaceous bar:NAM20 from:-74 till:-73 text: Oohkotokia
color:cretaceous bar:NAM21 from:-72.8 till:-67 text: Anodontosaurus
color:cretaceous bar:NAM22 from:-70 till:-69 text: Saichania
color:cretaceous bar:NAM23 from:-70 till:-69 text: Tarchia
color:cretaceous bar:NAM24 from:-66.5 till:-66 text:Ankylosaurus
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of th ...
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25
bar:period
from: -201 till: -174 color:earlyjurassic text:Early
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
from: -174 till: -163 color:middlejurassic text: Middle
from: -163 till: -145 color:latejurassic text: Late
from: -145 till: -100 color:earlycretaceous text:Early
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
from: -100 till: -66 color:latecretaceous text: Late
bar:era
from: -201 till: -145 color:jurassic text:Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
from: -145 till: -66 color:cretaceous text:Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
See also
* Timeline of ankylosaur researchReferences
*''Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s and other Prehistoric Creatures'', edited by Ingrid Cranfield (2000), Salamander books, pg. 250-257.
*
* Kirkland, J. I. (1996). Biogeography of western North America's mid-Cretaceous faunas - losing European ties and the first great Asian-North American interchange. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 16 (Suppl. to 3): 45A
External links
Family Tree
Tree of Life web project
Pseudoplocephalus
Blog by an evolutionary biologist and vertebrate palaeontologist specializing in ankylosaurs {{Taxonbar, from=Q517099 Aptian first appearances Taxa named by Barnum Brown Prehistoric dinosaur families