Angular diameter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an
 The angular diameter of a
The angular diameter of a
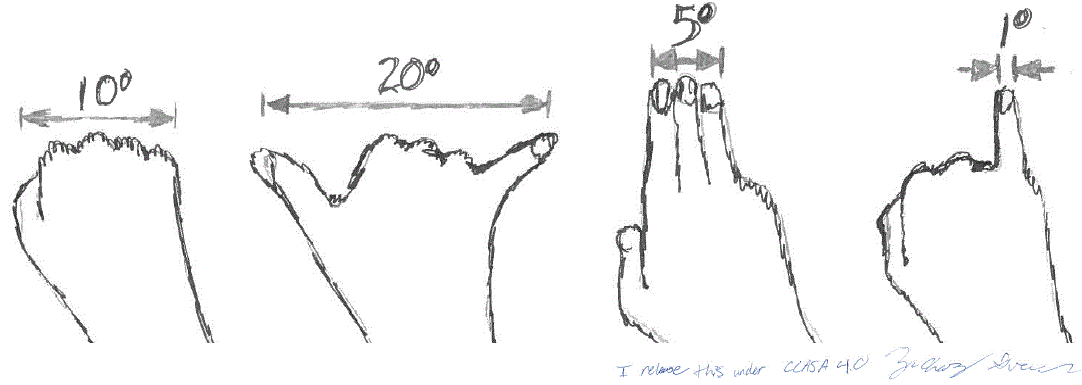 Estimates of angular diameter may be obtained by holding the hand at right angles to a fully extended arm, as shown in the figure.
Estimates of angular diameter may be obtained by holding the hand at right angles to a fully extended arm, as shown in the figure.
 In
In  The table shows that the angular diameter of Sun, when seen from Earth is approximately 32 (1920 or 0.53°), as illustrated above.
Thus the angular diameter of the Sun is about 250,000 times that of
The table shows that the angular diameter of Sun, when seen from Earth is approximately 32 (1920 or 0.53°), as illustrated above.
Thus the angular diameter of the Sun is about 250,000 times that of
Small-Angle Formula
{{Portal bar, Mathematics, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System, Science Elementary geometry Astrometry Angle
angular distance
Angular distance \theta (also known as angular separation, apparent distance, or apparent separation) is the angle between the two sightlines, or between two point objects as viewed from an observer.
Angular distance appears in mathematics (in par ...
describing how large a sphere
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is th ...
or circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is con ...
appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences
Vision science is the scientific study of visual perception. Researchers in vision science can be called vision scientists, especially if their research spans some of the science's many disciplines.
Vision science encompasses all studies of vision ...
, it is called the visual angle
Visual angle is the angle a viewed object subtends at the eye, usually stated in degrees of arc.
It also is called the object's angular size.
The diagram on the right shows an observer's eye looking at a frontal extent (the vertical arrow) tha ...
, and in optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultrav ...
, it is the angular aperture (of a lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
). The angular diameter can alternatively be thought of as the angular displacement
Angular displacement of a body is the angle (in radians, degrees or revolutions) through which a point revolves around a centre or a specified axis in a specified sense. When a body rotates about its axis, the motion cannot simply be analyzed ...
through which an eye or camera must rotate to look from one side of an apparent circle to the opposite side. Humans can resolve with their naked eyes
Naked Eyes are an English new wave band"All Eyes on Pete Byrne", ''Newsday'', 15 October 2013 that rose to prominence in the early 1980s. The band had four US top 40 singles.
The group's first hit, "Always Something There to Remind Me", was ...
diameters of up to about 1 arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
(approximately 0.017° or 0.0003 radians). This corresponds to 0.3 m at a 1 km distance, or to perceiving Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
as a disk under optimal conditions.
Formula
circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is con ...
whose plane is perpendicular to the displacement vector between the point of view and the center of said circle can be calculated using the formula
:
in which is the angular diameter, and is the actual diameter of the object, and is the distance to the object. When , we have , and the result obtained is in radians.
For a spherical object whose ''actual'' diameter equals and where is the distance to the ''center '' of the sphere, the angular diameter can be found by the formula
:
The difference is due to the fact that the apparent edges of a sphere are its tangent points, which are closer to the observer than the center of the sphere. The difference is significant only for spherical objects of large angular diameter, since the following small-angle approximation
The small-angle approximations can be used to approximate the values of the main trigonometric functions, provided that the angle in question is small and is measured in radians:
:
\begin
\sin \theta &\approx \theta \\
\cos \theta &\approx 1 - \ ...
s hold for small values of :
:
Estimating angular diameter using the hand
 Estimates of angular diameter may be obtained by holding the hand at right angles to a fully extended arm, as shown in the figure.
Estimates of angular diameter may be obtained by holding the hand at right angles to a fully extended arm, as shown in the figure.
Use in astronomy
 In
In astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, the sizes of celestial object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often u ...
s are often given in terms of their angular diameter as seen from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
, rather than their actual sizes. Since these angular diameters are typically small, it is common to present them in arcseconds (). An arcsecond is 1/3600th of one degree (1°) and a radian is 180/''π'' degrees. So one radian equals 3,600 × 180/ arcseconds, which is about 206,265 arcseconds (1 rad ≈ 206,264.806247"). Therefore, the angular diameter of an object with physical diameter ''d'' at a distance ''D'', expressed in arcseconds, is given by:
:.
These objects have an angular diameter of 1:
*an object of diameter 1 cm at a distance of 2.06 km
*an object of diameter 725.27 km at a distance of 1 astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
(AU)
*an object of diameter 45 866 916 km at 1 light-year
*an object of diameter 1 AU (149 597 871 km) at a distance of 1 parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, an ...
(pc)
Thus, the angular diameter of Earth's orbit around the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
as viewed from a distance of 1 pc is 2, as 1 AU is the mean radius of Earth's orbit.
The angular diameter of the Sun, from a distance of one light-year, is 0.03, and that of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
0.0003. The angular diameter 0.03 of the Sun given above is approximately the same as that of a human body at a distance of the diameter of Earth.
This table shows the angular sizes of noteworthy celestial bodies as seen from Earth:
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CM ...
. (Sirius has twice the diameter and its distance is 500,000 times as much; the Sun is 1010 times as bright, corresponding to an angular diameter ratio of 105, so Sirius is roughly 6 times as bright per unit solid angle
In geometry, a solid angle (symbol: ) is a measure of the amount of the field of view from some particular point that a given object covers. That is, it is a measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point.
The poi ...
.)
The angular diameter of the Sun is also about 250,000 times that of Alpha Centauri A (it has about the same diameter and the distance is 250,000 times as much; the Sun is 4×1010 times as bright, corresponding to an angular diameter ratio of 200,000, so Alpha Centauri A is a little brighter per unit solid angle).
The angular diameter of the Sun is about the same as that of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
. (The Sun's diameter is 400 times as large and its distance also; the Sun is 200,000 to 500,000 times as bright as the full Moon (figures vary), corresponding to an angular diameter ratio of 450 to 700, so a celestial body with a diameter of 2.5–4 and the same brightness per unit solid angle would have the same brightness as the full Moon.)
Even though Pluto is physically larger than Ceres, when viewed from Earth (e.g., through the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
) Ceres has a much larger apparent size.
Angular sizes measured in degrees are useful for larger patches of sky. (For example, the three stars of the Belt cover about 4.5° of angular size.) However, much finer units are needed to measure the angular sizes of galaxies, nebulae, or other objects of the night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of astronomical object, celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a ...
.
Degrees, therefore, are subdivided as follows:
* 360 degrees (°) in a full circle
* 60 arc-minute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
s () in one degree
* 60 arc-second
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
s () in one arc-minute
To put this in perspective, the full Moon
The full moon is the lunar phase when the Moon appears fully illuminated from Earth's perspective. This occurs when Earth is located between the Sun and the Moon (when the ecliptic longitudes of the Sun and Moon differ by 180°). This means ...
as viewed from Earth is about °, or 30 (or 1800). The Moon's motion across the sky can be measured in angular size: approximately 15° every hour, or 15 per second. A one-mile-long line painted on the face of the Moon would appear from Earth to be about 1 in length.
In astronomy, it is typically difficult to directly measure the distance to an object, yet the object may have a known physical size (perhaps it is similar to a closer object with known distance) and a measurable angular diameter. In that case, the angular diameter formula can be inverted to yield the angular diameter distance to distant objects as
:
In non-Euclidean space, such as our expanding universe, the angular diameter distance is only one of several definitions of distance, so that there can be different "distances" to the same object. See Distance measures (cosmology).
Non-circular objects
Many deep-sky objects such as galaxies and nebulae appear non-circular and are thus typically given two measures of diameter: major axis and minor axis. For example, the Small Magellanic Cloud has a visual apparent diameter of × .Defect of illumination
Defect of illumination is the maximum angular width of the unilluminated part of a celestial body seen by a given observer. For example, if an object is 40 of arc across and is 75% illuminated, the defect of illumination is 10.See also
* Angular diameter distance * Angular resolution *Solid angle
In geometry, a solid angle (symbol: ) is a measure of the amount of the field of view from some particular point that a given object covers. That is, it is a measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point.
The poi ...
* Visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
* Visual angle
Visual angle is the angle a viewed object subtends at the eye, usually stated in degrees of arc.
It also is called the object's angular size.
The diagram on the right shows an observer's eye looking at a frontal extent (the vertical arrow) tha ...
* Perceived visual angle In human visual perception, the visual angle, denoted ''θ'', subtended by a viewed object sometimes looks larger or smaller than its actual value. One approach to this phenomenon posits a subjective correlate to the visual angle: the perceived vis ...
* List of stars with resolved images
* Apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's ...
References
External links
Small-Angle Formula
{{Portal bar, Mathematics, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System, Science Elementary geometry Astrometry Angle