Altmark on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
:''See German tanker Altmark for the ship named after Altmark and Stary Targ for the Polish village named Altmark in  The (English: Old MarchHansard, ''The Parliamentary Debates from the Year 1803 to the Present Time ...'', Volume 32. 1 February to 6 March 1816, T.C. Hansard, 1816
The (English: Old MarchHansard, ''The Parliamentary Debates from the Year 1803 to the Present Time ...'', Volume 32. 1 February to 6 March 1816, T.C. Hansard, 1816
pp. 82
Article XXIII of the Final Act of the Congress of Vienna) is a historic region in
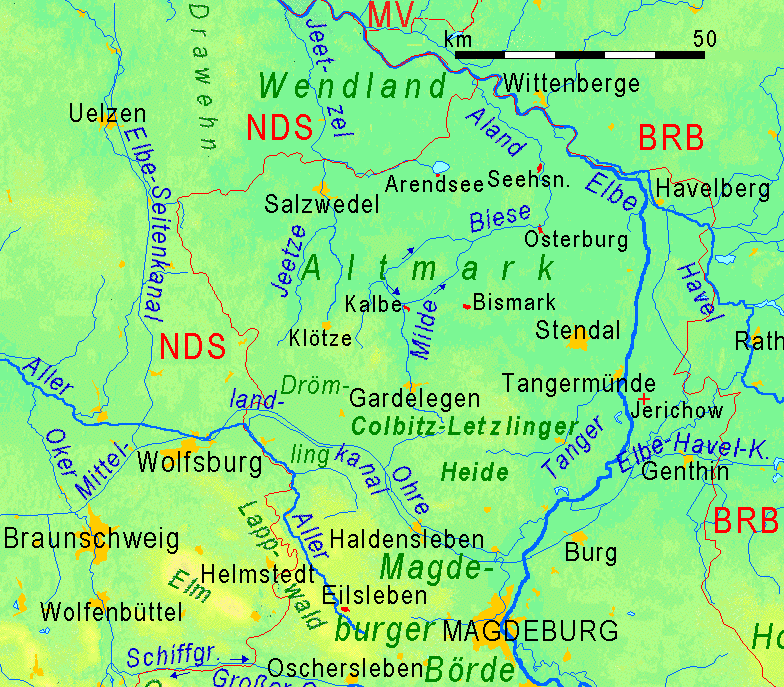 The Altmark is located west of the
The Altmark is located west of the
 As the Brandenburg margraves expanded their territory during the course of the , the original western territory of the Northern March became known as the Altmark (literally "Old March") in contrast to the (Middle March) and (New March) beyond the Oder river; the written record first mentions it in 1304 as .
As part of Brandenburg, from 1415 held by the House of Hohenzollern, the Altmark became part of
As the Brandenburg margraves expanded their territory during the course of the , the original western territory of the Northern March became known as the Altmark (literally "Old March") in contrast to the (Middle March) and (New March) beyond the Oder river; the written record first mentions it in 1304 as .
As part of Brandenburg, from 1415 held by the House of Hohenzollern, the Altmark became part of
 The region is drained by the
The region is drained by the
 * Salzwedel
* Oebisfelde
* Arendsee
* Seehausen
*
* Salzwedel
* Oebisfelde
* Arendsee
* Seehausen
*
Altmarkwiki
the regional wiki for the Altmark
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
.''
 The (English: Old MarchHansard, ''The Parliamentary Debates from the Year 1803 to the Present Time ...'', Volume 32. 1 February to 6 March 1816, T.C. Hansard, 1816
The (English: Old MarchHansard, ''The Parliamentary Debates from the Year 1803 to the Present Time ...'', Volume 32. 1 February to 6 March 1816, T.C. Hansard, 1816pp. 82
Article XXIII of the Final Act of the Congress of Vienna) is a historic region in
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, comprising the northern third of Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making i ...
. As the initial territory of the March of Brandenburg, it is sometimes referred to as the "Cradle of Prussia", as by Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of ...
, a native from Schönhausen
Schönhausen ( Low Saxon: ''Schöönhusen'') is a municipality in the district of Stendal in Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. It is the seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Elbe-Havel-Land.
Geography
The village is situated on ...
near Stendal.
Geography
 The Altmark is located west of the
The Altmark is located west of the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
river between the cities of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
and Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label=Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river.
Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Magdebu ...
, mostly included in the districts of Altmarkkreis Salzwedel and Stendal. In the west, the Drawehn hill range and the Drömling depression separate it from the Lüneburg Heath
Lüneburg Heath (german: Lüneburger Heide) is a large area of heath, geest, and woodland in the northeastern part of the state of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. It forms part of the hinterland for the cities of Hamburg, Hanover and Bremen ...
in Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
; the Altmark also borders the Wendland
The Wendland is a region in Germany on the borders of the present states of Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt. Its heart is the Hanoverian Wendland in the county of Lüchow-Dannenberg in Lower Saxony.
In ...
region in the north and the Magdeburg Börde
The Magdeburg Börde (german: Magdeburger Börde) is the central landscape unit of the state of Saxony-Anhalt and lies to the west and south of the eponymous state capital Magdeburg. Part of a loess belt stretching along the southeastern rim of ...
in the south. Adjacent east of the Elbe is the historical Prignitz region.
The population is small. The cultural landscape within the North European Plain is rural and widely covered with forests and heathlands
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a cooler a ...
. The largest towns are Stendal, with a population of 39,000, and Salzwedel (21,500).
History
Before theMigration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
of 300 to 700 AD, the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
had settled the future Altmark. Subsequently, Old Germanic Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
tribes lived in the northwest and Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Ger ...
in the eastern territories along the Elbe. After the Saxon Wars
The Saxon Wars were the campaigns and insurrections of the thirty-three years from 772, when Charlemagne first entered Saxony with the intent to conquer, to 804, when the last rebellion of tribesmen was defeated. In all, 18 campaigns were fought ...
, waged by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
from 772 to 804, the lands became part of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
. They formed part of the Eastphalian territory of the Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the C ...
, which, from 843 onwards, constituted the eastern borderlands of East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire int ...
under Louis the German
Louis the German (c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the P ...
. The bishops of Verden and of Halberstadt promoted the Christianisation of the Saxon population.
In 936 the German king Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
allotted the territory of the later Altmark to the Saxon Count Gero, in order to subdue the West Slavic Wends settling on the Elbe. Gero thereafter campaigned in the Slavic lands far beyond the river Elbe and thereafter established the Saxon stretching up to the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
in the east. Upon Gero's death in 965, his was split and the Northern March
The Northern March or North March (german: Nordmark) was created out of the division of the vast '' Marca Geronis'' in 965. It initially comprised the northern third of the ''Marca'' (roughly corresponding to the modern state of Brandenburg) and ...
was granted to Dietrich of Haldensleben, who nevertheless turned out to be an incapable ruler and lost all the territories east of the Elbe in the Slavic Lutici uprising of 983. He retained only his margravial title and the initial land basis of his predecessor Gero's conquests west of the river.
For over one and a half century, the lands east of the Elbe defied German control, until in 1134 Emperor Lothair of Supplinburg
Lothair III, sometimes numbered Lothair II and also known as Lothair of Supplinburg (1075 – 4 December 1137), was Holy Roman Emperor from 1133 until his death. He was appointed Duke of Saxony in 1106 and elected King of Germany in 1125 before ...
bestowed the Northern March on the Ascanian
The House of Ascania (german: Askanier) was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.
The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ''Schlos ...
count Albert the Bear
Albert the Bear (german: Albrecht der Bär; 1100 – 18 November 1170) was the first margrave of Brandenburg from 1157 to his death and was briefly duke of Saxony between 1138 and 1142.
Life
Albert was the only son of Otto, Count of Bal ...
. Albert signed an inheritance contract with the Slavic Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
prince Pribislav and in 1150 succeeded him in his eastern territory around the fortress of Brandenburg an der Havel, which became the nucleus of his newly established Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
in 1157.
 As the Brandenburg margraves expanded their territory during the course of the , the original western territory of the Northern March became known as the Altmark (literally "Old March") in contrast to the (Middle March) and (New March) beyond the Oder river; the written record first mentions it in 1304 as .
As part of Brandenburg, from 1415 held by the House of Hohenzollern, the Altmark became part of
As the Brandenburg margraves expanded their territory during the course of the , the original western territory of the Northern March became known as the Altmark (literally "Old March") in contrast to the (Middle March) and (New March) beyond the Oder river; the written record first mentions it in 1304 as .
As part of Brandenburg, from 1415 held by the House of Hohenzollern, the Altmark became part of Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohe ...
and (from 1701) of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
. After Prussia's defeat at the hands of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in 1806, the terms of the Treaty of Tilsit (1807) assigned the territory of the Altmark to the new Kingdom of Westphalia. Prussia regained the area upon Napoleon's defeat (per Article XXIII of the Final Act of the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
, 1815); however, it was incorporated into the new Prussian Province of Saxony
The Province of Saxony (german: link=no, Provinz Sachsen), also known as Prussian Saxony () was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.
It was formed by the merg ...
rather than being attached to the Province of Brandenburg
The Province of Brandenburg (german: Provinz Brandenburg) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1945. Brandenburg was established in 1815 from the Kingdom of Prussia's core territory, comprised the bulk of the historic Margraviate of Brandenburg ...
. Within Prussian Saxony, the Altmark was subdivided into the districts of Salzwedel, Gardelegen, Osterburg, and Stendal, all administered within the of Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label=Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river.
Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Magdebu ...
.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
the Altmark, lying to the east of the inner German border
The inner German border (german: Innerdeutsche Grenze or ; initially also ) was the border between the German Democratic Republic (GDR, East Germany) and the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG, West Germany) from 1949 to 1990. Not including the ...
, became part of the new state of Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making i ...
in the Soviet occupation zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a ...
. The regional administration of East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In t ...
saw it administered within from 1952 to 1990. With German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
in 1990, the Altmark became part of a reconstituted Saxony-Anhalt.
Rivers and lakes
 The region is drained by the
The region is drained by the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
, joined by the Havel
The Havel () is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mo ...
at Havelberg, and its left tributaries of the Milde-Biese- Aland system and the Jeetzel river.
The largest natural lake of the Altmark is the Arendsee.
Transport
Road
The Altmark is located off the main traffic routes. TheBundesautobahn 14
is an autobahn in eastern Germany.
The route comprises two disconnected sections:
* The old A 241. A North-South route in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern which runs from Wismar to Schwerin.
* The original A 14. A West-East route which start ...
leads to the Bundesautobahn 2
is an autobahn in Germany that connects the Ruhr area in the west to Berlin in the east. The A 2 starts at the junction with the A3 near the western city of Oberhausen, passes through the north of the Ruhr valley, through the Münsterl ...
from Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
, it however ends north of Magdeburg. A continuation through the Altmark towards Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
is planned. Beside which the Federal roads B71, B107, B188, B189, B190, B248 run through the region.
Rail
Stendal station is a stop on the Hanover–Berlin high-speed railway. Other lines include: * Stendal–Salzwedel–Uelzen * Wittenberge– Salzwedel– Oebisfelde * Magdeburg–Stendal–Wittenberge * Bismark– Kalbe (Milde) * Stendal– TangermündeTowns
 * Salzwedel
* Oebisfelde
* Arendsee
* Seehausen
*
* Salzwedel
* Oebisfelde
* Arendsee
* Seehausen
* Diesdorf
Diesdorf is a municipality (''Flecken'') in the district Altmarkkreis Salzwedel, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany.
Geography
Diesdorf is situated in the western Altmark about east of the border between Saxony-Anhalt and Lower Saxony, which between ...
* Beetzendorf
* Klötze
Klötze is a town in the Altmarkkreis Salzwedel (district), in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated approximately 20 km northwest of Gardelegen, and 35 km northeast of Wolfsburg.
It was mentioned first in 1144 with the name ''Cloetze' ...
* Mieste
* Gardelegen
* Kalbe (Milde)
* Bismark
* Osterburg
* Stendal
* Havelberg
* Tangermünde
* Tangerhütte
* Uchtspringe
External links
Altmarkwiki
the regional wiki for the Altmark
Notes and references
{{Authority control Margraviate of Brandenburg Regions of Saxony-Anhalt Former states and territories of Saxony-Anhalt Historical regions in Germany