Alternative periodic tables on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alternative periodic tables are tabulations of
 Compared to the common layout, the left-step table has these changes:
* Helium is placed in group 2 (not in group 18).
* Groups 1 and 2 (the s-block), including elements 119 and 120 in extended period 8, are moved to the right side of the table.
* The s-block is shifted upwards one row, and all elements not in the s-block are now one row lower than in the standard table. For example, most of the fourth row in the standard table is the fifth row in this table.
In the result, the order is still consistently by
Compared to the common layout, the left-step table has these changes:
* Helium is placed in group 2 (not in group 18).
* Groups 1 and 2 (the s-block), including elements 119 and 120 in extended period 8, are moved to the right side of the table.
* The s-block is shifted upwards one row, and all elements not in the s-block are now one row lower than in the standard table. For example, most of the fourth row in the standard table is the fifth row in this table.
In the result, the order is still consistently by
 The ADOMAH table is an adaptation of the left step table. Each strictly vertical column of the table has the same value of the principal quantum number ''n''. For example, ''n'' = 3 for Fe. Each block of elements has the same value of the secondary quantum number ''l.'' For example, ''l'' = 2 for Fe. Each element entry together with all preceding elements corresponds to the electron configuration of that element (with 20 exceptions out of 118 known elements). For example, the electron configuration of Fe is determined by starting at H, which is 1s1, and counting in atomic number order. This gives a configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 or, in short form, r4s2 3d6.
The four blocks of the Adomah table can be rearranged such that they fit, equidistantly spaced, inside a regular
The ADOMAH table is an adaptation of the left step table. Each strictly vertical column of the table has the same value of the principal quantum number ''n''. For example, ''n'' = 3 for Fe. Each block of elements has the same value of the secondary quantum number ''l.'' For example, ''l'' = 2 for Fe. Each element entry together with all preceding elements corresponds to the electron configuration of that element (with 20 exceptions out of 118 known elements). For example, the electron configuration of Fe is determined by starting at H, which is 1s1, and counting in atomic number order. This gives a configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 or, in short form, r4s2 3d6.
The four blocks of the Adomah table can be rearranged such that they fit, equidistantly spaced, inside a regular
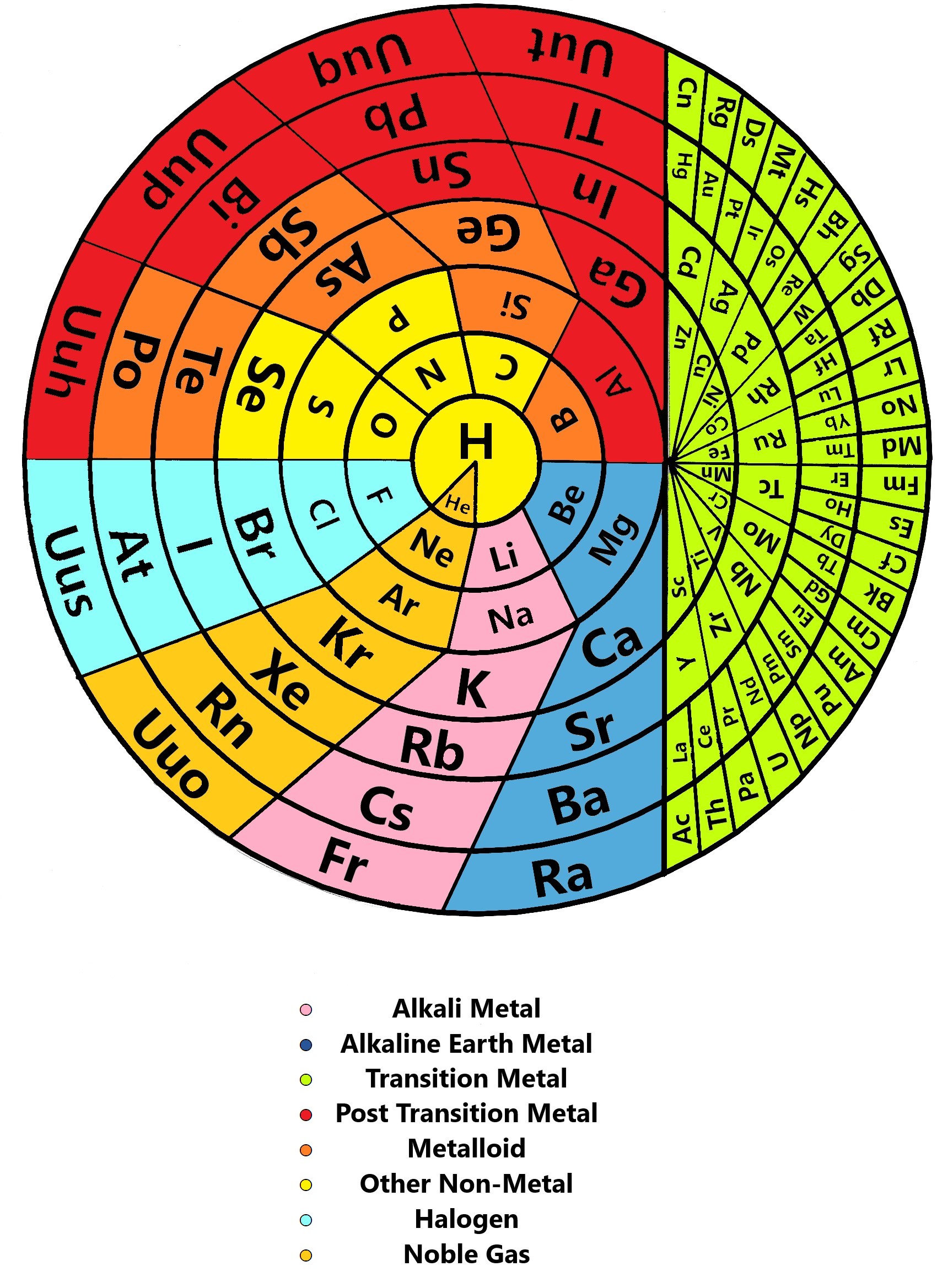 Muzzammil Qureshi's periodic table consists of concentric circles format giving it a more organic and more unified sense than the tabular formats. Discoid means "circular in shape". This table instead of having "
Muzzammil Qureshi's periodic table consists of concentric circles format giving it a more organic and more unified sense than the tabular formats. Discoid means "circular in shape". This table instead of having "
Russian short form table
(2013), which includes all elements and element names until
File:Harrison Spiral Periodic Table.svg, Spiral periodic table (Robert W Harrison)
File:The Ring Of Periodic Elements (TROPE).png, ''The Ring Of Periodic Elements'' (TROPE)
File:The chemical elements and their periodic relationships.svg, Curled ribbon periodic table (J. F. Hyde)
File:Circular form of periodic table.svg, Circular periodic table
File:Alternative circular periodic table.png, Alternative circular periodic table
File:Periodic table (spiral format).SVG, Spiral periodic table (Jan Scholten)
File:Mendeleev flower.jpg, Mendeleev's Flower (Flower periodic table)
File:Periodic table in binary electron shells layout, designed by Eric William McPherson.jpg, Binary electron shells periodic table
File:Periodic system Stowe format.svg, "Stowe" periodic table
File:Periodic system Zmaczynski&Bayley.svg, "Zmaczynski & Bayley" periodic table
File:Periodic system Pyramid format.svg, Pyramidal periodic table
File:Stowe-Janet-Scerri PeriodicTable.svg, Stowe–Janet–Scerri with 3D electron orbitals
File:4DPeriodicTable.png, 4D Stowe–Janet–Scerri periodic table
The periodic table and the philosophy of classification
Knowledge Organization, 38(1), 9–21.
a site curated by the Michigan State University Alumni Association Knowledge Network
Robert Harrison's modern spiral periodic table
as
A Wired Article on Alternate Periodic Tables
*http://periodicspiral.com/ arranges the periodic table in a (hexagonal) spiral. *
Rotaperiod.com
' A new periodic table.
Note
on the T-shirt topology of the Z-spiral.
this is in a square-triangular periodic arrangement.
Periodic Table based on electron configurationsDatabase of Periodic Tables Bob Doyle Periodic Table of the Elements
A regrouping by properties used to better explain electron grouping
Eric Scerri's website about the periodic table
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alternative Periodic Tables Periodic table
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s differing in their organization from the traditional depiction of the periodic system.
Over a thousand have been devised, often for didactic reasons, as not all correlations between the chemical elements are effectively captured by the standard periodic table.
Major alternative structures
Left-step periodic table (Janet, 1928)
Charles Janet
Charles Janet (; 15 June 1849 – 7 February 1932) was a French engineer, company director, inventor and biologist. He is also known for his innovative ''left-step'' presentation of the periodic table of chemical elements.
Life and work
Janet gra ...
's left-step periodic table is the most widely used alternative to the traditional depiction of the periodic system. It organizes elements according to an idealized orbital filling (instead of valence). For example, the elements Sc to Zn are shown as a 3d block implying orbital occupancy r4s2 3dx. (Although Cr and Cu are exceptions in the gas-phase, the idealized configurations are not too far away from the ground state, and the energy difference is small enough to be controlled by the chemical environment.)
atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
(''Z''), 1–120.
Two-dimensional spiral (Benfey, 1964)
InTheodor Benfey :''This is about the German philologist. For Theodor Benfey (born 1925) who developed a spiral periodic table of the elements in 1964, see Otto Theodor Benfey.''
Theodor Benfey (; 28 January 1809, in Nörten near Göttingen26 June 1881, in Götti ...
's periodic table the elements form a two-dimensional spiral, starting from hydrogen, and folding their way around two peninsulas, the transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that ca ...
s, and lanthanides and actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
s. A superactinide
An extended periodic table theorises about chemical elements beyond those currently known in the periodic table and proven. , the element with the highest atomic number known is oganesson (''Z'' = 118), which completes the seventh period (row ...
island is already slotted in. The Benfey table has some unique aspects that very few tables represent. An example of this is the placement hydrogen has in the spiral. In most tables, hydrogen seems like the "odd one out". The reason for this is because hydrogen, whilst having the same valence electron configuration as the alkali metals, has the properties of a halogen. The Benfey table gets around this conundrum by expanding the hydrogen box around both the alkali metals and the halogens.
Three-dimensional, flower-like (Paul Giguère, 1966)
Paul Giguère's 3-D periodic table consists of four connected billboards with the elements written on the front and the back. The first billboard has thegroup 1 element
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
s on the front and the group 2 element
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic iden ...
s at the back, with hydrogen and helium omitted altogether. At a 90° angle the second billboard contains the groups 13 to 18 front and back. Two more billboards each making 90° angles contain the other elements.
Three-dimensional, physicist's (Timothy Stowe, 1986)
Timothy Stowe's physicist's periodic table is three-dimensional with the three axes representing theprincipal quantum number
In quantum mechanics, the principal quantum number (symbolized ''n'') is one of four quantum numbers assigned to each electron in an atom to describe that electron's state. Its values are natural numbers (from 1) making it a discrete variable.
A ...
, orbital quantum number, and orbital magnetic quantum number
In atomic physics, the magnetic quantum number () is one of the four quantum numbers (the other three being the principal, azimuthal, and spin) which describe the unique quantum state of an electron. The magnetic quantum number distinguishes the ...
. Helium is again a group 2 element
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic iden ...
.
Elements repeating (Ronald L. Rich, 2005)
Ronald L. Rich has proposed a periodic table where elements appear more than once when appropriate. He notes that hydrogen shares properties withgroup 1 element
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
s based on valency, with group 17 elements because hydrogen is a non-metal but also with the carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
group based on similarities in chemical bonding to transition metals and a similar electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the ...
. In this rendition of the periodic table carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
and silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
also appear in the same group as titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
and zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'' ...
.
ADOMAH (Valery Tsimmerman, 2006)
tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all th ...
. The latter, in turn, fits into a cube.
Discoid Periodic Table (Muzzammil Qureshi, 2021)
 Muzzammil Qureshi's periodic table consists of concentric circles format giving it a more organic and more unified sense than the tabular formats. Discoid means "circular in shape". This table instead of having "
Muzzammil Qureshi's periodic table consists of concentric circles format giving it a more organic and more unified sense than the tabular formats. Discoid means "circular in shape". This table instead of having "groups
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
" and " periods” possesses "families" and "arcs" for the representation of elements. All the elements in the column are identified vertically by their Family name using the topmost element name. For example, lithium family, beryllium family, and so on. Elements are identified horizontally using the number of arcs. For example, 1st arc, 2nd arc, etc. The periodic table is divided into two parts, namely part A and part B. Part A represents the main-group element
In chemistry and atomic physics, the main group is the group of elements (sometimes called the representative elements) whose lightest members are represented by helium, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine as arrange ...
s, whereas Part B represents the transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that ca ...
s.
Salient Features of this table include:
* Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
are placed at the center of the table, from where it shall share many interstitial chemical properties
A chemical property is any of a material's properties that becomes evident during, or after, a chemical reaction; that is, any quality that can be established only by changing a substance's chemical identity.William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley, ...
with other elements of different families.
* Lanthanides and actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
s are added along with d-block elements without disturbing the overall periodicity of the table.
* The transition metals are modified by having no groups
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
because all transition metals are chemically and physically similar.
Variants of the classical layout
From Mendeleev's original periodic table, elements have been basically arranged by valence (groups in columns) and the repetition therein (periods in rows). Over the years and with discoveries in atomic structure, this schema has been adjusted and expanded, but not changed as a principle. The oldest periodic table is the short form table (columns I–VIII) by Dmitri Mendeleev, which shows secondary chemical kinships. For example, thealkali metals
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
and the coinage metals
The coinage metals comprise, at a minimum, those metallic chemical elements which have historically been used as components in alloys used to mint coins. The term is not perfectly defined, however, since a number of metals have been used to mak ...
(copper, silver, gold) are in the same column because both groups tend to have a valence of one. This format is still used by many, as shown by thiRussian short form table
(2013), which includes all elements and element names until
roentgenium
Roentgenium is a chemical element with the symbol Rg and atomic number 111. It is an extremely radioactive synthetic element that can be created in a laboratory but is not found in nature. The most stable known isotope, roentgenium-282, has a h ...
.
H. G. Deming used the so-called long periodic table (18 columns) in his textbook "General Chemistry", which appeared in the US for the first time in 1923 (Wiley), and was the first to designate the first two and the last five main groups with the notation "A", and the intervening transition groups with the notation "B".
The numeration was chosen so that the characteristic oxides of the B groups would correspond to those of the A groups. The iron, cobalt, and nickel groups were designated neither A nor B. The noble-gas group was originally attached (by Deming) to the left side of the periodic table. The group was later switched to the right side and usually labeled as group VIIIA.
Extension of the periodic table
In theextended periodic table
An extended periodic table theorises about chemical elements beyond those currently known in the periodic table and proven. , the element with the highest atomic number known is oganesson (''Z'' = 118), which completes the seventh period (row ...
, suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg (; April 19, 1912February 25, 1999) was an American chemist whose involvement in the synthesis, discovery and investigation of ten transuranium elements earned him a share of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. His work i ...
in 1969, yet unknown elements are included up to atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
168. Theoretical periods above regular period 7 are added.
In the research field of superatoms, clusters of atoms have properties of single atoms of another element. It is suggested to extend the periodic table with a second layer to be occupied with these cluster compound
In chemistry, an atom cluster (or simply cluster) is an ensemble of bound atoms or molecules that is intermediate in size between a simple molecule and a nanoparticle; that is, up to a few nanometers (nm) in diameter. The term ''microcluster' ...
s. An example addition to this multi-story table is the aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
cluster ion , which behaves like a multivalent germanium atom.
In October 2020, scientists reported a nonempirical way of presenting Mendeleev Numbers, and organizing the chemical space.
Gallery
References
Further reading
*A 1974 review of the tables then known is considered a definitive work on the topic: Mazurs, E. G. Graphical Representations of the Periodic System During One Hundred Years. Alabama; University of Alabama Press, 1974, . *Hjørland, Birger (2011)The periodic table and the philosophy of classification
Knowledge Organization, 38(1), 9–21.
External links
a site curated by the Michigan State University Alumni Association Knowledge Network
Robert Harrison's modern spiral periodic table
as
Meitnerium
Meitnerium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Mt and atomic number 109. It is an extremely radioactive synthetic element (an element not found in nature, but can be created in a laboratory). The most stable known isotope, meitnerium-2 ...
occupies the position that Hassium
Hassium is a chemical element with the symbol Hs and the atomic number 108. Hassium is highly radioactive; its most stable known isotopes have half-lives of approximately ten seconds. One of its isotopes, 270Hs, has magic numbers of both protons ...
should have.A Wired Article on Alternate Periodic Tables
*http://periodicspiral.com/ arranges the periodic table in a (hexagonal) spiral. *
Rotaperiod.com
' A new periodic table.
Note
on the T-shirt topology of the Z-spiral.
this is in a square-triangular periodic arrangement.
Periodic Table based on electron configurations
A regrouping by properties used to better explain electron grouping
Eric Scerri's website about the periodic table
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alternative Periodic Tables Periodic table