Agriculture on the prehistoric Great Plains on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Agriculture on the precontact Great Plains describes the agriculture of the
Agriculture on the precontact Great Plains describes the agriculture of the
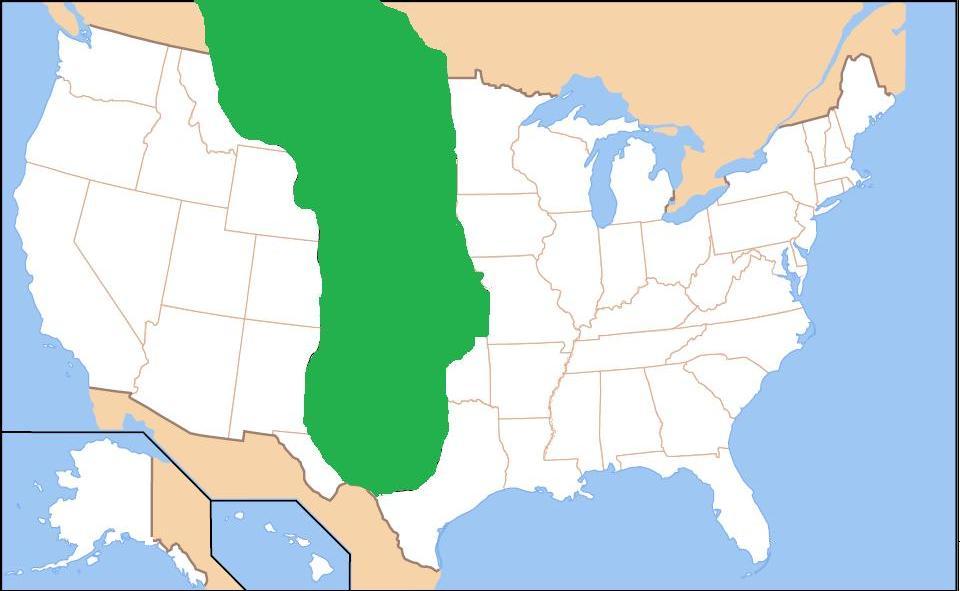 The primary constraint on agriculture on the Great Plains is that precipitation is often deficient for growing
The primary constraint on agriculture on the Great Plains is that precipitation is often deficient for growing
 Gathering wild plants, such as the prairie turnip ('' Psoralea esculenta'') and chokecherry (''
Gathering wild plants, such as the prairie turnip ('' Psoralea esculenta'') and chokecherry (''
''Archaeology of Prehistoric Native America: An Encyclopedia''.
p. 24. . The historic descendants of the Southern Plains villagers are possibly the Wichita and
File:Corncobs edit1.jpg,
''People and Plants in Ancient Eastern North America.''
University of Arizona Press, 2010. . * Wilson, Gilbert L. ''Buffalo Bird Woman's Garden: Agriculture of the Hidatsa Indians''. St Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 1987. {{ISBN, 978-0-873-51219-0. Great Plains Archaeology of the Great Plains Great Plains Pre-Columbian Great Plains cuisine Crops originating from Pre-Columbian North America Indigenous culture of the Great Plains * History of agriculture in the United States History of agriculture in Canada Canadian Prairies Flora of the Great Plains (North America) Flora of the United States Flora of the North-Central United States Flora of the South-Central United States
 Agriculture on the precontact Great Plains describes the agriculture of the
Agriculture on the precontact Great Plains describes the agriculture of the Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
peoples of the Great Plains of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and southern Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
in the Pre-Columbian era
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
and before extensive contact with European explorers, which in most areas occurred by 1750. The principal crops grown by Indian farmers were maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
(corn), beans
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes thr ...
, and squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, including pumpkins. Sunflowers, goosefoot, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, gourd
Gourds include the fruits of some flowering plant species in the family Cucurbitaceae, particularly ''Cucurbita'' and '' Lagenaria''. The term refers to a number of species and subspecies, many with hard shells, and some without. One of the ear ...
s, and plums, were also grown.
Evidence of agriculture is found in all Central Plains complexes. Archaeological sites in Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
reveal cultivated crops such as little barley ('' Hordeum pusillum''), sunflowers ('' Helianthus annuus''), goosefoot (''Chenopodium berlandieri
''Chenopodium berlandieri'', also known by the common names pitseed goosefoot, lamb's quarters (or lambsquarters), and ''huauzontle'' (Nahuatl) is an annual herbaceous plant in the family Amaranthaceae.
The species is widespread in North Ameri ...
''), marsh elder ('' Iva annua''), and maize ('' Zea mays''). Tribes periodically switched from farming to hunting throughout their history during the Plains Village period, AD 950–1850.
Environment
 The primary constraint on agriculture on the Great Plains is that precipitation is often deficient for growing
The primary constraint on agriculture on the Great Plains is that precipitation is often deficient for growing maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, the primary crop of Indian farmers. In addition, on the northern Great Plains the growing season is short. Agriculture on the Plains seems to have had an ebb and flow, advancing westward into the drier areas in favorable wet periods and retreating in drier periods. The periodic abundance or scarcity of bison was also a factor in human settlements on the plains. The animal was an important food resource for Plains people, as well as providing skins for clothing and shelters.
Precontact
 Gathering wild plants, such as the prairie turnip ('' Psoralea esculenta'') and chokecherry (''
Gathering wild plants, such as the prairie turnip ('' Psoralea esculenta'') and chokecherry (''Prunus virginiana
''Prunus virginiana'', commonly called bitter-berry, chokecherry, Virginia bird cherry, and western chokecherry (also black chokecherry for ''P. virginiana'' var. ''demissa''), is a species of bird cherry (''Prunus'' subgenus ''Padus'') nat ...
'') for food was undoubtedly a practice of Indian societies on the Great Plains since their earliest habitation 13,000 or more years ago. Over time Plains people learned to grow or facilitate the growth of native plants useful as food. Many native plants cultivated by Indians in the Eastern Agricultural Complex
The Eastern Agricultural Complex in the woodlands of eastern North America was one of about 10 independent centers of plant domestication in the pre-historic world. Incipient agriculture dates back to about 5300 BCE. By about 1800 BCE the Native ...
were also cultivated on the Great Plains.
Squash and beans were cultivated in what is now the United States, independent of Mesoamerica. Maize is a tropical crop first cultivated in Mexico several thousand years ago, which found its way northward to what is now the United States more than one thousand years ago. Maize agriculture began on the Great Plains by AD 900, initiating the Southern Plains villagers period of western Oklahoma and Texas. It probably came about as an extension westward and northward of the Caddoan cultures of eastern Texas. The Plains Village culture consisted of hamlets and semi-permanent villages along major rivers such as the Red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
, Washita, and Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
. Subsistence was a combination of agriculture and hunting. A drying climatic trend beginning AD 1000 or 1100 may have tipped the subsistence scale more toward hunting and less toward a dependence upon agriculture. The Antelope Creek Phase of Plains villagers, dated from AD 1200 to 1450 in the Texas panhandle was influenced by the Southwestern Pueblo people
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Z ...
of the Rio Grande valley in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
.
The contemporaneous Apishapa culture
The Apishapa culture, or Apishapa Phase, a prehistoric culture from 1000 to 1400, was named based upon an archaeological site in the Lower Apishapa canyon in Colorado.Gibbon, Guy E.; Ames, Kenneth M. (1998''Archaeology of Prehistoric Native Americ ...
of southeastern Colorado depended mostly upon hunting.Gibbon, Guy E.; Ames, Kenneth M. (1998''Archaeology of Prehistoric Native America: An Encyclopedia''.
p. 24. . The historic descendants of the Southern Plains villagers are possibly the Wichita and
Pawnee Pawnee initially refers to a Native American people and its language:
* Pawnee people
* Pawnee language
Pawnee is also the name of several places in the United States:
* Pawnee, Illinois
* Pawnee, Kansas
* Pawnee, Missouri
* Pawnee City, Nebraska ...
Indians.
The earliest known dates for maize agriculture on the northern Great Plains are from AD 1000 to 1200. The Missouri River Valley in present-day North Dakota was probably the northern limit of pre-historic maize cultivation on the Great Plains. Prehistoric evidence of maize cultivation north of the border of the United States and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
on the Great Plains is lacking but by the 1790s maize was being grown by Indian farmers as far north as the mouth of the Red River north of Winnipeg, Manitoba
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749,6 ...
.
The principal known Indian peoples who farmed extensively on the Great Plains when first discovered by European explorers were, from south to north, Caddoans in the Red River drainage, Wichita people along the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
, Pawnee Pawnee initially refers to a Native American people and its language:
* Pawnee people
* Pawnee language
Pawnee is also the name of several places in the United States:
* Pawnee, Illinois
* Pawnee, Kansas
* Pawnee, Missouri
* Pawnee City, Nebraska ...
in the Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
and Platte River
The Platte River () is a major river in the State of Nebraska. It is about long; measured to its farthest source via its tributary, the North Platte River, it flows for over . The Platte River is a tributary of the Missouri River, which itsel ...
drainages, and the Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish,
''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
, ''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
Mandan
The Mandan are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains who have lived for centuries primarily in what is now North Dakota. They are enrolled in the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation. About half of the Mandan still re ...
, and Hidatsa along the Missouri River in the Dakotas. Other peoples migrated or were pushed westward onto the Great Plains in late prehistoric or proto-historic times. Some of them, such as the Sioux and Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enr ...
, gave up agriculture to become nomadic; other such as the Dhegiha
The Dhegihan languages are a group of Siouan languages that include Kansa– Osage, Omaha–Ponca, and Quapaw. Their historical region included parts of the Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys, the Great Plains, and southeastern North America. T ...
(the Osage, Kaw
Kaw or KAW may refer to:
Mythology
* Kaw (bull), a legendary bull in Meitei mythology
* Johnny Kaw, mythical settler of Kansas, US
* Kaw (character), in ''The Chronicles of Prydain''
People
* Kaw people, a Native American tribe
Places
* Kaw, Fr ...
, Omaha, and Ponca) and the Chiwere
Chiwere (also called Iowa-Otoe-Missouria or Báxoje-Jíwere-Ñút'achi) is a Siouan language originally spoken by the Missouria, Otoe, and Iowa peoples, who originated in the Great Lakes region but later moved throughout the Midwest and plains. ...
(Otoe
The Otoe (Chiwere: Jiwére) are a Native American people of the Midwestern United States. The Otoe language, Chiwere, is part of the Siouan family and closely related to that of the related Iowa, Missouria, and Ho-Chunk tribes.
Historically, t ...
, Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
, and Missouria
The Missouria or Missouri (in their own language, Niúachi, also spelled Niutachi) are a Native American tribe that originated in the Great Lakes region of what is now the United States before European contact.May, John D"Otoe-Missouria"''Oklaho ...
) continued to farm while also hunting buffalo for a major part of their livelihood.
Archaeologists have found evidence of agriculture practiced by Apache people (the Dismal River culture) living on the Great Plains in western Kansas and Nebraska in the 17th century. The semi-nomadic Apache were pushed southward and off the Great Plains by the fully nomadic Comanche in the 18th century.
Cultivation and yields
Lacking iron tools and draft animals the prehistoric Indian farmer on the Great Plains primarily cleared and cultivated wooded land along rivers, especially the lighter soils on elevated river terraces which periodically flooded, renewing their fertility. They avoided cultivating the heavy soils of the open prairie with their deep mats of fibrous roots. Rather than being concentrated, the cultivated fields of the Great Plains farmer were dispersed along river terraces. Fields cultivated by the Pawnee were as much as eight miles from their villages. The high productivity of maize enabled Indian farmers to produce large crops with simple tools on a small per capita amount of cultivated land—although farming on the drought-prone Great Plains was always a risky endeavor. The amount of land needed by a farming household was between two and seven acres (.8 to 2.8 ha) of cultivated land each year, the difference accounted for by the quality of the land. Fields were usually cultivated for two or three years and then fallowed. Fallowed acreage was two to three times that which was cultivated in a given year. Counting both cultivated and fallowed fields, a household needed 4 to 21 acres (1.6 to 8.5 ha) for subsistence. Households which depended more on hunting and gathering cultivated smaller amounts of land. Yields of maize plots on the Great Plains are estimated at of 10-20 bushels (627 - 1,254 kg) per acre. Higher yields of up to 40 bushels (2,508 kg) per acre have been reported on newly cleared land. Land declined in fertility in subsequent crop years. Among the Hidatsa, typical of Great Plains farmers, fields were cleared by burning which also fertilized the soil. The three implements used by Indian farmers were the digging stick, hoe, and rake. The digging stick was a sharpened and fire-hardened stick, three or more feet long, that was used to loosen soil, uproot weeds, and make planting holes. The hoe was made from a buffalo or elk shoulder blade bone, orscapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eith ...
, lashed to a wooden handle. The rake was made from wood or an antler. Some Indian women preferred the bone hoe even after the iron hoe was introduced by European traders and settlers.
Sunflowers were the earliest crop planted in spring. Sunflowers were planted in clumps around the edges of fields. Maize was next planted. Indian planting techniques are called Three Sisters agriculture. About five maize seeds were sown in a low mound of soil. The mounds were spaced about five feet apart. When the maize plants were a few inches high, climbing beans and squash seeds were planted between the mounds. The large squash leaves shaded the soil, preserving moisture and crowding out weeds. The beans fixed nitrogen in the soil and climbed up the corn stalks as support. The Wichita, and possibly other southern peoples, planted or tended thickets of low-growing Chickasaw Plum trees separating and bordering their maize fields. Tobacco was planted in separate fields and tended by old men. Women did most of the other farming, although men assisted in clearing land.
Indian farmers did not fertilize their fields with manure. As the soil declined in fertility with each crop year, unproductive fields were fallowed for two years and then replanted.
Subsistence
Archaeologists have computed the subsistence of people in the Medicine Creek valley in Nebraska near the western limit of cultivation in pre-historic times. During the years 1000 to 1450 CE, the diet of the people of Medicine Creek depended upon game (mostly bison) for 30 percent of their subsistence, 30 percent frommaize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, 20 percent from other cultigens (squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, beans
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes thr ...
, and sunflowers
''Helianthus'' () is a genus comprising about 70 species of annual and perennial flowering plants in the daisy family Asteraceae commonly known as sunflowers. Except for three South American species, the species of ''Helianthus'' are native to N ...
), and 20 percent from wild plant resources.. From ''Medicine Creek: Seventy Years of Archaeological Investigations'' edited by Donna C. Roper. Downloaded from Project MUSE
Project MUSE, a non-profit collaboration between libraries and publishers, is an online database of peer-reviewed academic journals and electronic books. Project MUSE contains digital humanities and social science content from over 250 univers ...
. Further east where agriculture was more reliable due to greater precipitation, the percentage of cultivated crops in the diet may have been greater. The dependence on agriculture and hunting for subsistence varied due to climatic conditions as the Great Plains had periods of greater and lesser precipitation.
Farming year
The Pawnee in Nebraska were among the best of the Plains Indian farmers and had elaborate rituals connected with the planting and harvesting of maize. In spring, they planted 10 varieties of maize, seven varieties of pumpkins and squashes, and eight varieties of beans. The maize included flour,flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
, and sweet
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, ketone ...
corn plus one ancient variety raised only for inclusion in the "sacred bundles" common among Plains Indians. The Indians were aware that the different varieties of maize could hybridize if grown in close proximity and planted different varieties in fields a substantial distance apart.
One of the rituals of the Pawnees during the spring planting season to ensure the fertility of the soil was the Morning Star ceremony and the ritual sacrifice of a young girl captured from an enemy tribe. The Morning Star sacrifice did not take place every year. The last human sacrifice by the Pawnee was in 1838.
Common to many other Plains farmers, the Pawnee left their villages in late June when their corn crop was about knee high to live in tipi
A tipi , often called a lodge in English, is a conical tent, historically made of animal hides or pelts, and in more recent generations of canvas, stretched on a framework of wooden poles. The word is Siouan, and in use in Dakhótiyapi, Lakȟó ...
s and roam the plains on a summer buffalo hunt. They returned about the first of September to harvest their crops. Maize, beans, and pumpkins were dried, packed into rawhide bags, and stored in bell-shaped underground storage pits. The Pawnee followed the harvest with a month of celebrations and in early December departed their villages again for a winter hunt, their stored agricultural products hidden beneath the ground. This yearly cycle of life was common among the Plains farmers, especially after the acquisition of the horse in the late 17th and 18th century gave them the mobility to undertake lengthy hunts far from their permanent villages.
Trade
Trade between the farming and the nomadic hunting Indians was important on the Great Plains. The Mandan and Hidatsa villages on the Missouri River in the Dakotas conducted a large trade with the non-agricultural hunting Indians. In fall 1737, the French explorer La Vérendrye found a group ofAssiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
planning to undertake their annual two-month-long, thousand-kilometer round trip south to the Mandan villages to trade bison meat for agricultural goods. Abundant evidence of similar long-distance trading between farmers and hunters occurred among other tribes of the Plains.McGeshick, Joseph R., Smith, Dennis J., and Shanley, James. ''The History of the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation, Montana, 1800-2000'', Montana Historical Society, 2008, pp. 15-16
Gallery
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
File:Cucurbita pepo var. styriaca05.jpg, Squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
See also
*History of agriculture in Canada
In the 16th century Samuel de Champlain and Gabriel Sagard recorded that the Iroquois and Huron cultivated the soil for maize or "Indian corn". Maize (''Zea mays''), potatoes (''Solanum tuberosum''), beans (''phaseolus''), squash (''Cucurbita'' ...
Notes
References
* Minnis, Paul E''People and Plants in Ancient Eastern North America.''
University of Arizona Press, 2010. . * Wilson, Gilbert L. ''Buffalo Bird Woman's Garden: Agriculture of the Hidatsa Indians''. St Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 1987. {{ISBN, 978-0-873-51219-0. Great Plains Archaeology of the Great Plains Great Plains Pre-Columbian Great Plains cuisine Crops originating from Pre-Columbian North America Indigenous culture of the Great Plains * History of agriculture in the United States History of agriculture in Canada Canadian Prairies Flora of the Great Plains (North America) Flora of the United States Flora of the North-Central United States Flora of the South-Central United States