Agent Blue on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
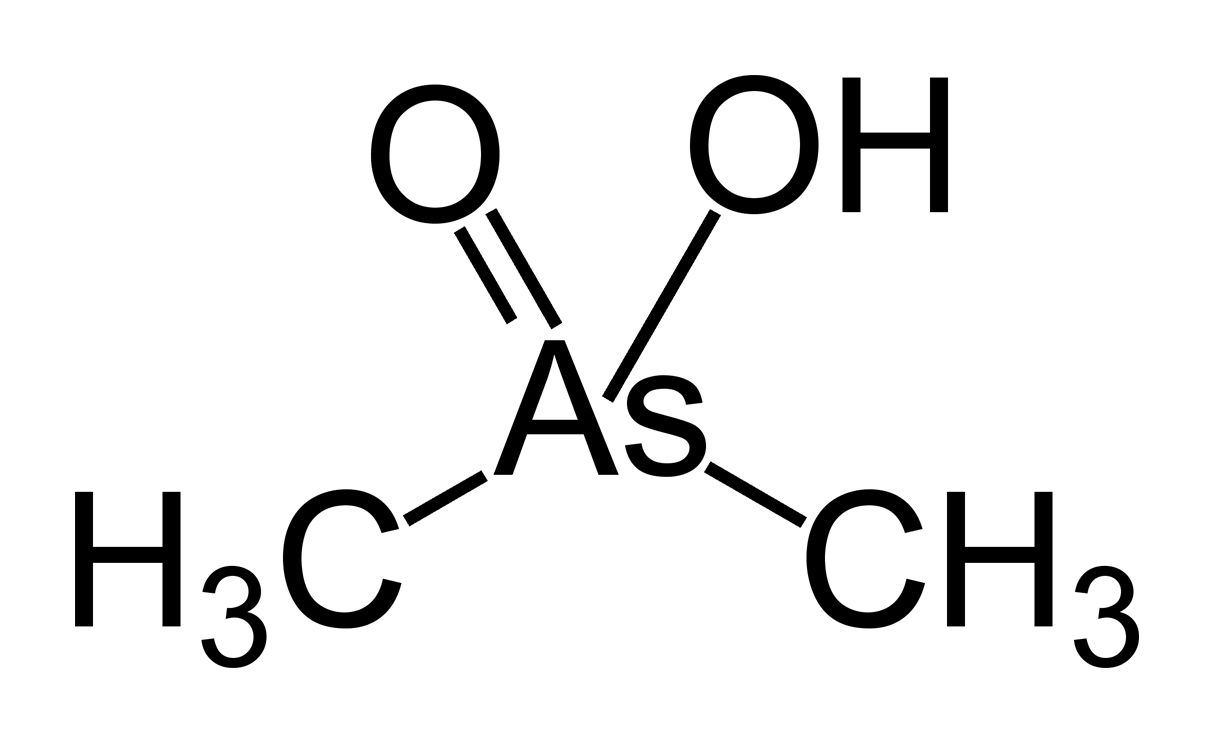 Agent Blue is one of the " rainbow herbicides" that is known for its use by the
Agent Blue is one of the " rainbow herbicides" that is known for its use by the
 Agent Blue is one of the " rainbow herbicides" that is known for its use by the
Agent Blue is one of the " rainbow herbicides" that is known for its use by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
. It contained a mixture of dimethylarsinic acid (also known as cacodylic acid) and its related salt, sodium cacodylate, and water. Largely inspired by the British use of herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
and defoliants
A defoliant is any herbicidal chemical sprayed or dusted on plants to cause their leaves to fall off. Defoliants are widely used for the selective removal of weeds in managing croplands and lawns. Worldwide use of defoliants, along with the ...
during the Malayan Emergency
The Malayan Emergency, also known as the Anti–British National Liberation War was a guerrilla war fought in British Malaya between communist pro-independence fighters of the Malayan National Liberation Army (MNLA) and the military forces ...
, killing rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
was a military strategy from the very start of US military involvement in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
. At first, US soldiers attempted to blow up rice paddies and rice stocks, using mortars
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a villag ...
and hand grenade
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade ...
s. But grains of rice were far more durable than they understood, and were not easily destroyed. Every grain that survived was a seed to be collected and planted again.
A 1967 report to the International War Crimes Tribunal (founded by Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British mathematician, philosopher, logician, and public intellectual. He had a considerable influence on mathematics, logic, set theory, linguistics, a ...
) stated that "The soldiers discovered that rice is one of the most maddeningly difficult substances to destroy; using thermite
Thermite () is a pyrotechnic composition of metal powder and metal oxide. When ignited by heat or chemical reaction, thermite undergoes an exothermic reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction. Most varieties are not explosive, but can create brie ...
metal grenades it is almost impossible to make it burn and, even if one succeeds in scattering the rice, this does not stop it being harvested by patient men." The purpose of Agent Blue was to kill narrow-leafed plants and trees (grass, rice, bamboo, banana, etc.) " Operation Ranch Hand", was military code for spraying of herbicides from U.S. Air Force aircraft in Southeast Asia from 1962 through 1971. The widespread use of herbicides in Southeast Asia during the Vietnam War was a unique military operation in that it was meant to kill the plants that provided cover. The continued use of Agent Blue and the other "Rainbow Herbicides" by the United States was primarily meant as an operation to take away the enemy's advantage on the terrain as well as deprive them of food.
Between 1962 and 1971, the US used an estimated 20 million gallons of herbicides as chemical weapons for "defoliation and crop destruction" which fell mostly on the forest of South Vietnam, but was eventually used in Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
as well to kill crops in order to deprive the communist Viet Cong
,
, war = the Vietnam War
, image = FNL Flag.svg
, caption = The flag of the Viet Cong, adopted in 1960, is a variation on the flag of North Vietnam. Sometimes the lower stripe was green.
, active ...
and North Vietnamese troops of food. It was sprayed on rice paddies and other crops in an attempt to deprive the Viet Cong of the valuable crops the plants provided. Agent Blue is chemically unrelated to the more infamous Agent Orange
Agent Orange is a chemical herbicide and defoliant, one of the "tactical use" Rainbow Herbicides. It was used by the U.S. military as part of its herbicidal warfare program, Operation Ranch Hand, during the Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971. It ...
and other herbicides used during the war.
Agent Blue affects plants by causing them to dry out. As rice is highly dependent on water to live, using Agent Blue on these paddies can destroy an entire field and leave it unsuitable for further planting. This is why Agent Blue was also used where food was not a factor, but the foliage was. The Vietcong had an advantage while fighting in Vietnam because they were used to the abundance of plant life on the battlefield. The US found themselves at a disadvantage and based on the precedent set by the British in Malaya, decided that the best retaliation would be to take the Vietcong's advantage away from them by removing their cover. Along roads, canals, railroads, and other transportation networks, Ranch Hand cleared several hundred yards using the herbicides to make ambushes more difficult for their enemies. In Laos, the herbicide removed the jungle canopy from the roads and trails used for infiltrating men and supplies, making them more vulnerable to attack from the air.
Approximately 4 million gallons of Agent Blue were used in Vietnam during the war. From 1965 on the Ansul Chemical Company delivered the herbicide ''Phytar 560'' with the 26.4% sodium cacodylate and 4.7% cacodylic acid in water.
Cacodylic acid is still used on crops throughout the USA. Taken from ZNet Ecology in 1983: “It has been over twelve years since the last herbicide mission that was done. But there is still big controversy going around about the past missions that were sent out.“
{{quote, Arsenical herbicides containing cacodylic acid as an active ingredient are still used today as weed-killers. It sprayed on cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
fields, drying out the cotton plant
''Gossypium'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Gossypieae of the mallow family, Malvaceae, from which cotton is harvested. It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Old and New Worlds. There are about 50 ''Gossypiu ...
s before harvesting. In 2009, use on athletic fields, parks, residential lawns, forestry, non-bearing fruit and nut trees, and citrus orchards were canceled.{{cite web, url=https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/monosodium-methanearsonate-msma-organic-arsenical , title=Monosodium Methanearsonate (MSMA), an Organic Arsenical, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency , accessdate=2022-10-11
References
{{Reflist {{Rainbow Herbicides Arsenical herbicides Defoliants Military equipment of the Vietnam War