Agathodaemon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An agathodaemon ( grc, ἀγαθοδαίμων, ) or agathos daemon (, , ) was a spirit (''
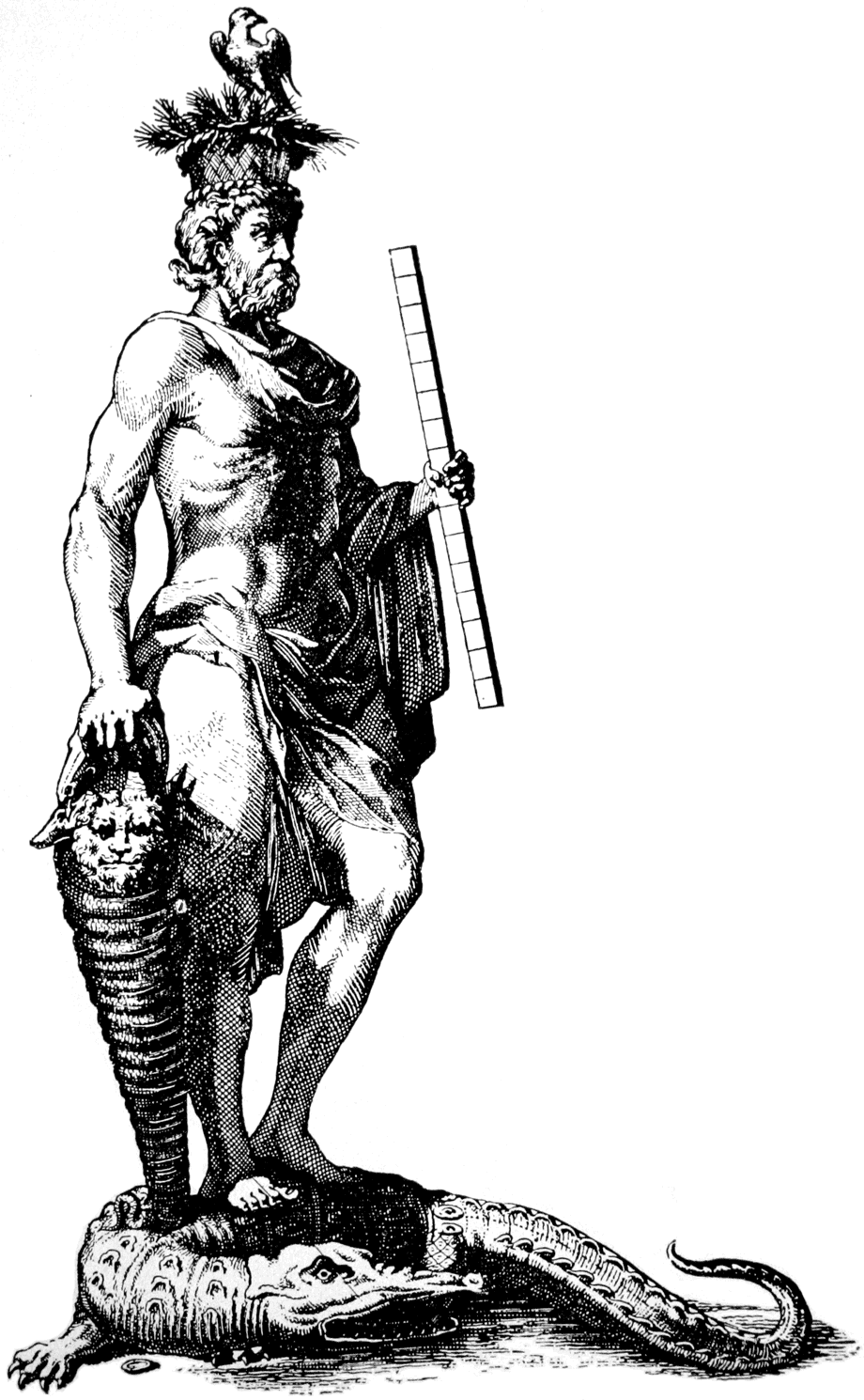 In the syncretic atmosphere of
In the syncretic atmosphere of
Theoi.com:
Greek and Latin sources in translation {{Authority control Agricultural gods Greek gods Health gods Fortune gods Wisdom gods Legendary serpents Epithets of Zeus Religion in ancient Arcadia Hellenistic deities Tutelary deities
daemon
Daimon or Daemon (Ancient Greek: , "god", "godlike", "power", "fate") originally referred to a lesser deity or guiding spirit such as the daimons of ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology and of later Hellenistic religion and Hell ...
'') of ancient Greek religion. They were personal or supernatural companion spirits, comparable to the Roman '' genii'', who ensured good luck, fertility, health, protection and wisdom.
During the classical period
Though little noted inGreek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities ...
(Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to:
*Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
* Pausanias of Sicily, physician of t ...
conjectured that the name was merely an epithet of Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek reli ...
), he was prominent in Greek folk religion; it was customary to drink or pour out a few drops of unmixed wine to honor him in every symposium or formal banquet. In Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; grc, Ἀριστοφάνης, ; c. 446 – c. 386 BC), son of Philippus, of the deme Kydathenaion ( la, Cydathenaeum), was a comic playwright or comedy-writer of ancient Athens and a poet of Old Attic Comedy. Eleven of his for ...
' ''Peace
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
'', when War has trapped Peace (Εἰρήνη '' Eirene'') in a deep pit, Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
comes to give aid: "Now, oh Greeks! is the moment when, freed of quarrels and fighting, we should rescue sweet ''Eirene'' and draw her out of this pit... This is the moment to drain a cup in honor of the ''Agathos Daimon''." A temple dedicated to them was situated on the road from Megalopolis
A megalopolis () or a supercity, also called a megaregion, is a group of metropolitan areas which are perceived as a continuous urban area through common systems of transport, economy, resources, ecology, and so on. They are integrated enoug ...
to Maenalus
Maenalus or Mainalos ( grc, Μαίναλος) was a town of ancient Arcadia, and the capital of the district Maenalia (Μαιναλία), which formed part of the territory of Megalopolis upon the foundation of the latter city. Maenalus was in ru ...
in Arcadia.
An ''Agathos Daimon'' was the spouse or companion of ''Tyche
Tyche (; Ancient Greek: Τύχη ''Túkhē'', 'Luck', , ; Roman equivalent: Fortuna) was the presiding tutelary deity who governed the fortune and prosperity of a city, its destiny. In Classical Greek mythology, she is the daughter of Aphrodite ...
Agathe'' (, "Good Fortune"; la, Agatha). "Tyche we know at Lebadeia
Livadeia ( el, Λιβαδειά ''Livadiá'', ; grc, Λεβάδεια, Lebadeia or , ''Lebadia'') is a town in central Greece. It is the capital of the Boeotia regional district. Livadeia lies north-west of Athens, west of Chalkida, south-eas ...
as the wife of the Agathos Daimon, the Good or Rich Spirit". Their numinous presence could be represented in art as a serpent
Serpent or The Serpent may refer to:
* Snake, a carnivorous reptile of the suborder Serpentes
Mythology and religion
* Sea serpent, a monstrous ocean creature
* Serpent (symbolism), the snake in religious rites and mythological contexts
* Serp ...
or more concretely as a young man bearing a cornucopia
In classical antiquity, the cornucopia (), from Latin ''cornu'' (horn) and ''copia'' (abundance), also called the horn of plenty, was a symbol of abundance and nourishment, commonly a large horn-shaped container overflowing with produce, flowers ...
and a bowl in one hand, and a poppy and an ear of grain in the other. The agathodaemon was later adapted into a general daemon of ''fortuna
Fortuna ( la, Fortūna, equivalent to the Greek goddess Tyche) is the goddess of fortune and the personification of luck in Roman religion who, largely thanks to the Late Antique author Boethius, remained popular through the Middle Ages until at ...
'', particularly of the continued abundance of a family's good food and drink.Later some other versions have described agathodaemons as psychopomp
Psychopomps (from the Greek word , , literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are supernatural creatures, spirits, entities, angels, demons or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly deceased souls from Earth to the afte ...
beings which takes the dead ones which are on their card to the afterlife (Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwor ...
) but he doesn't judges them Agathodaemons have been described as personal guardians, helpers or protectors of people.According to the ancient Greeks each person was born with each personalities, the agathodaemon and the cacodaemon
A cacodemon (or cacodaemon) is an evil spirit or (in the modern sense of the word) a demon. The opposite of a cacodemon is an ''agathodaemon'' or ''eudaemon'', a good spirit or angel. The word ''cacodemon'' comes through Latin from the Ancient ...
.
During late antiquity
 In the syncretic atmosphere of
In the syncretic atmosphere of Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, agathodaemons could be bound up with Egyptian bringers of security and good fortune: a gem carved with magic emblems bears the images of Serapis
Serapis or Sarapis is a Graeco-Egyptian deity. The cult of Serapis was promoted during the third century BC on the orders of Greek Pharaoh Ptolemy I Soter of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt as a means to unify the Greeks and Egyptians in his r ...
with crocodile, sun-lion and Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He wa ...
mummy surrounded by the lion-headed snake Chnum–Agathodaemon– Aion, with Harpocrates
Harpocrates ( grc, Ἁρποκράτης, Phoenician: 𐤇𐤓𐤐𐤊𐤓𐤈, romanized: ḥrpkrṭ, ''harpokrates'') was the god of silence, secrets and confidentiality in the Hellenistic religion developed in Ptolemaic Alexandria (and also ...
on the reverse.Illustrated in W. Fauth, ''Helios Megistos: zur synkretistischen Theologie der Spätantike'' (Leiden: Brill) 1995:85.
See also
*Cacodaemon
A cacodemon (or cacodaemon) is an evil spirit or (in the modern sense of the word) a demon. The opposite of a cacodemon is an ''agathodaemon'' or ''eudaemon'', a good spirit or angel. The word ''cacodemon'' comes through Latin from the Ancient ...
*Eudaemon
Arabia Felix (literally: Fertile/Happy Arabia; also Ancient Greek: Εὐδαίμων Ἀραβία, ''Eudaemon Arabia'') was the Latin name previously used by geographers to describe South Arabia, or what is now Yemen.
Etymology
The term Arabi ...
*Genius
Genius is a characteristic of original and exceptional insight in the performance of some art or endeavor that surpasses expectations, sets new standards for future works, establishes better methods of operation, or remains outside the capabili ...
References
*Bibliography
*External links
Theoi.com:
Greek and Latin sources in translation {{Authority control Agricultural gods Greek gods Health gods Fortune gods Wisdom gods Legendary serpents Epithets of Zeus Religion in ancient Arcadia Hellenistic deities Tutelary deities