Afghanistan–Pakistan relations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Afghanistan–Pakistan relations refer to the bilateral ties between
 Afghan scholar
Afghan scholar
 Relations between Afghanistan and Pakistan began deteriorating again in the 1970s when Afghanistan hosted Pashtun-Baluch militants operating against Pakistan under the leadership of National Awami Party led by Abdul Wali Khan and in retaliation Pakistan started supporting Islamist movements against the progressive and Soviet-influenced Afghan government of
Relations between Afghanistan and Pakistan began deteriorating again in the 1970s when Afghanistan hosted Pashtun-Baluch militants operating against Pakistan under the leadership of National Awami Party led by Abdul Wali Khan and in retaliation Pakistan started supporting Islamist movements against the progressive and Soviet-influenced Afghan government of  During the 1980s, the
During the 1980s, the
by Dr. G. Rauf Roashan. August 11, 2001. A discussion over the Durrand Line between the-then Taliban leader Mohammed Omar and Naseerullah Babar ended abruptly. Omar called Babar, who was an ethnic Pashtun, a traitor for saying that "all problems would be resolved" should the Durrand Line be recognised by the Taliban government. When the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan was toppled and the new Afghan government was formed, President Hamid Karzai began repeating the previous Taliban statement. The In 2007, Afghan intelligence captured Muhammad Hanif, the Taliban spokesman. During his interrogation which was recorded, Hanif claimed that the Taliban leader was being kept in
In 2007, Afghan intelligence captured Muhammad Hanif, the Taliban spokesman. During his interrogation which was recorded, Hanif claimed that the Taliban leader was being kept in
online
* Hussain, Rizwan. '' Pakistan and the Emergence of Islamic Militancy in Afghanistan'' (Ashgate, 2005)
excerpt
* Nadiri, Khalid Homayun. "Old Habits, New Consequences: Pakistan's Posture toward Afghanistan since 2001." ''International Security'' 39.2 (2014): 132–168
online
* Paliwal, Avinash. "Pakistan–Afghanistan Relations Since 2001." in ''Pakistan at the Crossroads'' ed by Christophe Jaffrelot; (Columbia UP, 2016) pp. 191–218. * Rashid, Ahmed. ''Pakistan on the Brink: The future of Pakistan, Afghanistan and the West'' (Penguin, 2012). * Raza, Muhammad Amjad, and Ghulam Mustufa. "Indo-Afghan Relations: Implications for Pakistan." ''Central Asia'' 84.Summer (2019): 53–79
online
* Shahrani, M Nazif, ed. ''Modern Afghanistan: The Impact of 40 Years of War'' (Indiana UP, 2018) * Siddique, Abubakar. ''The Pashtun Question The Unresolved Key to the Future of Pakistan and Afghanistan'' (Hurst, 2014) * Zahab, Mariam Abou, and Olivier Roy. ''Islamist Networks: The Afghan-Pakistan Connection'' (Columbia UP, 2004)
Former British Commander Cautions Taliban May Get Control of Pakistan Nuclear Weapons
Pakistan-Afghanistan Nuclear Sectarian Policy emerges after Benazir Bhutto Nuclear Sectarian policy with Iran leaks
Pakistan Ranked 1st in Muslim Countries Nuclear Business
Afghanistan-Pakistan Drug Sales in International Airports
{{DEFAULTSORT:Afghanistan-Pakistan relations
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
and the Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
. In August 1947, the partition of British India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. T ...
led to the emergence of Pakistan along Afghanistan's eastern frontier, and the two countries have since had a strained relationship; Afghanistan was the sole country to vote against Pakistan's admission into the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
following the latter's independence. Various Afghan government officials and Afghan nationalists have made irredentist claims to large swathes of Pakistan's territory in modern-day Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the northwestern region of the country, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa ...
and Pakistani Balochistan
Balochistan (; bal, بلۏچستان; ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southwestern region of the country, Balochistan is the largest province of Pakistan by land area but is the least populated one. It shares land ...
, which complete the traditional homeland of "Pashtunistan
Pashtunistan ( ps, پښتونستان, lit=land of the Pashtuns) is a historical region in Central Asia and South Asia, inhabited by the indigenous Pashtun people of Afghanistan and western Pakistan. Wherein Pashtun culture, the Pashto language, ...
" for the Pashtun people
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
. Afghan territorial claims over Pashtun-majority areas that are in Pakistan were coupled with discontent over the permanency of the Durand Line, for which Afghanistan demanded a renegotiation, with the aim of having it shifted eastward to the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
. Territorial disputes and conflicting claims prevented the normalization of bilateral ties between the two countries throughout the mid-20th century. Further Afghanistan–Pakistan tensions have arisen concerning a variety of issues, including the Afghanistan conflict
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
*Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see als ...
and Afghan refugees in Pakistan
Afghans in Pakistan ( ur, , , ) are temporary residents from Afghanistan who are registered in Pakistan as refugees and asylum seekers. They fall under the jurisdiction of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR). Most of them ...
, water-sharing rights, and a continuously warming relationship between Afghanistan and India.
Shortly after Pakistani independence, Afghanistan materially supported the failed armed secessionist movement headed by Mirzali Khan against Pakistan. Afghanistan's immediate support of secessionist movements within Pakistan prevented normalised ties from emerging between the two states.
In 1952 the government of Afghanistan published a tract in which it laid claim not only to Pashtun territory within Pakistan, but also to the Pakistani province of Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
. Diplomatic relations were cut off between 1961 and 1963 after Afghanistan supported more armed separatists in Pakistan, leading to skirmishes between the two states earlier in 1960, and Pakistan's subsequent closure of the port of Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
to Afghan transit trade. Mohammed Daoud Khan
Mohammed Daoud Khan ( ps, ), also romanized as Daud Khan or Dawood Khan (18 July 1909 – 28 April 1978), was an Afghan politician and general who served as prime minister of Afghanistan from 1953 to 1963 and, as leader of the 1973 Afghan cou ...
became President of Afghanistan
The president of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was constitutionally the head of state and head of government of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (2004–2021) and Commander-in-Chief of the Afghan Armed Forces.
On 15 August 2021, as th ...
in 1973, Afghanistan—with Soviet support—again pursued a policy of arming Pashtun separatists within Pakistan.
In 2017, the Pakistani military have accused Afghanistan of sheltering various terrorist groups which launch attacks into Pakistan, while Afghan authorities have blamed Pakistan's intelligence agency, the ISI
ISI or Isi may refer to:
Organizations
* Intercollegiate Studies Institute, a classical conservative organization focusing on college students
* Ice Skating Institute, a trade association for ice rinks
* Indian Standards Institute, former name of ...
, for funding warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
s and the Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state (polity), state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalism, Islamic fundamentalist, m ...
, and for basing terrorist camps within Pakistani territory to target Afghanistan. There is considerable anti-Pakistan sentiment in Afghanistan, while negative sentiment towards the Afghan refugees is widespread in Pakistan, even in Pashtun-dominated regions.
However, former Afghan President Hamid Karzai
Hamid Karzai (; Pashto/ fa, حامد کرزی, , ; born 24 December 1957) is an Afghan statesman who served as the fourth president of Afghanistan from July 2002 to September 2014, including as the first elected president of the Islamic Repub ...
(in office 2004–2014) has described Pakistan and Afghanistan as "inseparable brothers" while also alleging that Pakistan uses terrorism against Afghanistan, which is due to the historical, religious, and ethnolinguistic connections between the Pashtun
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
people and other ethnic groups of both countries, as well as to trade and other ties. Each of the two countries features amongst the other's largest trading partners, and Pakistan serves as a major conduit for transit trade involving landlocked Afghanistan. Both countries are member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
, Economic Cooperation Organization and South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan ...
.
Historical context
Southern and eastern Afghanistan is predominatelyPashto
Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani ().
Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
-speaking, like the adjacent Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Federally Administered Tribal Areas
, conventional_long_name = Federally Administered Tribal Areas
, nation = Pakistan
, subdivision = Autonomous territory
, image_flag = Flag of FATA.svg
, image_coat = File:Coat of arms ...
, and northern Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
regions in Pakistan. This entire area is inhabited by the indigenous Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
who belong to different Pashtun tribes
The Pashtun tribes ( ps, پښتانه قبايل), historically also known as Afghan tribes, are the tribes of the Pashtun people, a large Eastern Iranian ethnic group who use the Pashto language and follow Pashtunwali code of conduct. They a ...
. The Pashtuns were known as (Pathans in Pakistan and India) and have lived in this region for thousands of years, since at least the 1st millennium BC.
The Durand Line border was established after the 1893 ''Durand Line Agreement'' between Mortimer Durand of colonial British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and Amir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
Abdur Rahman Khan
Abdur Rahman Khan GCSI (Pashto/ Dari: ) (between 1840 and 1844 – 1 October 1901) was Emir of Afghanistan from 1880 to his death in 1901. He is known for uniting the country after years of internal fighting and negotiation of the Durand Lin ...
of Afghanistan for fixing the limit of their respective spheres of influence. The single-page agreement, which contained seven short articles, was signed by Durand and Khan, agreeing not to exercise political interference beyond the frontier
A frontier is the political and geographical area near or beyond a boundary. A frontier can also be referred to as a "front". The term came from French in the 15th century, with the meaning "borderland"—the region of a country that fronts ...
line between Afghanistan and what was then the British Indian Empire
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himse ...
.
Shortly after the demarcation of the Durand Line, the British began connecting the region on its side of Durand line to the vast and expansive Indian railway network. Concurrently, the Afridi tribesmen began to rise up in arms against the British, creating a zone of instability between Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
and the Durand Line
The Durand Line ( ps, د ډیورنډ کرښه; ur, ), forms the Pakistan–Afghanistan border, a international land border between Pakistan and Afghanistan in South Asia. The western end runs to the border with Iran and the eastern end to th ...
. As a result, travel across the boundary was almost entirely halted, and the Pashtun tribes living under the British rule began to orient themselves eastward in the direction of the Indian railways. By the time of the India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
n independence movement
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
, prominent Pashtun nationalists such as Abdul Ghaffar Khan
Abdul Ghaffār Khān (; 6 February 1890 – 20 January 1988), also known as Bacha Khan () or Badshah Khan (), and honourably addressed as Fakhr-e-Afghan (), was a Pakistani Pashtun, independence activist, and founder of the Khudai Khidmatgar ...
advocated unity with the nearly formed Dominion of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and N ...
, and not a united Afghanistan – highlighting the extent to which infrastructure and instability began to erode the Pashtun self-identification with Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
. By the time of the Pakistan independence movement
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
, popular opinion among Pashtuns was in support of joining the Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of ...
.
Pakistan inherited the Durand Line agreement after its independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the stat ...
in 1947 but there has never been a formal agreement or ratification
Ratification is a principal's approval of an act of its agent that lacked the authority to bind the principal legally. Ratification defines the international act in which a state indicates its consent to be bound to a treaty if the parties inten ...
between Islamabad
Islamabad (; ur, , ) is the capital city of Pakistan. It is the country's ninth-most populous city, with a population of over 1.2 million people, and is federally administered by the Pakistani government as part of the Islamabad Capital ...
and Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into #Districts, 22 municipal dist ...
. The Afghan government has not formally accepted the Durand Line as the international border between the two states, claiming that the Durand Line Agreement has been void in the past. This complicated issue is very sensitive to both the countries. The Afghan government worried that if it ever ratified the agreement, it would've permanently divided the 50 million Pashtuns and thus create a backlash in Afghanistan. Pakistan felt that the border issue had been resolved before its birth in 1947. This unmanagable border has always served as the main trade route between Afghanistan and the South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
, especially for supplies into Afghanistan.
Shortly after Pakistan gained independence in 1947, Afghanistan crafted a two-fold strategy to destabilize the frontier regions
The Frontier Regions (often abbreviated as FR) of Pakistan were a group of small administrative units in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA), lying immediately to the east of the seven main tribal agencies and west of the settled distr ...
of Pakistan, in an attempt to take advantage of Pakistan's post-independence instability. Firstly, it strongly aligned itself with Pakistan's rival, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, and also the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
. Secondly, it politically and financially backed secessionist politicians in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the northwestern region of the country, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa ...
in the 1960s. In January 1950, the Afghan king, Mohammed Zahir Shah
Mohammed Zahir Shah (Pashto/Dari: , 15 October 1914 – 23 July 2007) was the last king of Afghanistan, reigning from 8 November 1933 until he was deposed on 17 July 1973. Serving for 40 years, Zahir was the longest-serving ruler of Afghanistan ...
, had an anti-Pakistan speech which was condemned by Pakistan's Liaquat Ali Khan
Liaquat Ali Khan ( ur, ; 1 October 1895 – 16 October 1951), also referred to in Pakistan as ''Quaid-e-Millat'' () or ''Shaheed-e-Millat'' ( ur, lit=Martyr of the Nation, label=none, ), was a Pakistani statesman, lawyer, political theoris ...
. A serious incident took place on September 30, 1950, when Pakistan claimed Afghan troops had crossed into their territory near the Bogra Pass
Bogra ( bn, বগুড়া), officially known as Bogura, is a major city located in Bogra District, Rajshahi Division, Bangladesh. The city is a major commercial hub in Northern Bangladesh. It is the second largest city in Rajshahi Divi ...
as a low-scale invasion. The Afghan government denied involvement, saying they were pro-Pashtunistan tribesmen. Zahir Shah mentioned in a 1952 speech the friendly feelings towards Pakistan, but that the Pashtunistan issue cannot be ignored. The 1954 military pact between Pakistan and the United States concerned Afghanistan and India, and it brought Afghanistan closer to the Soviet Union but whilst maintaining non-alignment.
The Afghan government denounced the merger of West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was ...
provinces, and on March 30, 1955, Afghan demonstrators attacked the Pakistani embassy and consulates in Kabul, Kandahar and Jalalabad. Pakistan retaliated by closing the border, an economic blockage. Diplomatic relations were restored in September. Again due to the Pashtunistan issue, the two countries accused each other of border mispractices in 1961. In August, the consulates in both countries closed and relations were broken in September 1961. The situation was not defused until about 1965.
Afghanistan's policies placed a severe strain upon Pakistan–Afghan relations in the 1960s, up until the 1970s, when the Pashtunistan movement largely subsided as the population came to identify with Pakistan; although, resentment against the Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
elite continued to develop. The Pashtun assimilation into the Pakistani state followed years of rising Pashtun influence in Pakistani politics and the nation's bureaucracy, culminating in Ayub Khan
Ayub Khan is a compound masculine name; Ayub is the Arabic version of the name of the Biblical figure Job, while Khan or Khaan is taken from the title used first by the Mongol rulers and then, in particular, their Islamic and Persian-influenced s ...
, Yahya Khan
General Agha Muhammad Yahya Khan , (Urdu: ; 4 February 1917 – 10 August 1980); commonly known as Yahya Khan, was a Pakistani military general who served as the third President of Pakistan and Chief Martial Law Administrator following his p ...
, Ishaq Khan – all Pashtuns, attaining leadership
Leadership, both as a research area and as a practical skill, encompasses the ability of an individual, group or organization to "lead", influence or guide other individuals, teams, or entire organizations. The word "leadership" often gets v ...
of Pakistan. The largest nationalist party of the time, the Awami National Party (ANP), dropped its secessionist agenda and embraced the Pakistani state, leaving only a small Pakhtunkhwa Millat Party to champion the cause of independence in relation to both Pakistan and Afghanistan. Despite the weaknesses of the early secessionist movement, this period in history continues to negatively influence Pakistani-Afghan relations in the 21st century, in addition to the province's politics.
Confederation proposal
In order to solve the disputes, mainly centered around the borders issue with the Durand line,Khurshid Mahmud Kasuri
Khurshid Mahmud Kasuri (Urdu: خورشيد محمود قصورى; born 18 June 1941), is a Pakistani politician and writer who served as the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Pakistan between November 2002 until November 2007. He is the Senior Ad ...
, a veteran diplomat who served as the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Pakistan (2002–2007), says that "at one time serious efforts were made at government level for a Pak-Afghan Confederation", precising that these initiatives were taken during the time of President Mohammed Daoud Khan
Mohammed Daoud Khan ( ps, ), also romanized as Daud Khan or Dawood Khan (18 July 1909 – 28 April 1978), was an Afghan politician and general who served as prime minister of Afghanistan from 1953 to 1963 and, as leader of the 1973 Afghan cou ...
, generally considered to be anti-Pakistan for his galvanization of the Pashtunistan
Pashtunistan ( ps, پښتونستان, lit=land of the Pashtuns) is a historical region in Central Asia and South Asia, inhabited by the indigenous Pashtun people of Afghanistan and western Pakistan. Wherein Pashtun culture, the Pashto language, ...
issue. Aslam Khattak
Muhammad Aslam Khan Khattak ( ps, محمد اسلم خان خټک) ( ur, محمد اسلم خان خٹک) (April 5, 1908 – October 10, 2008) was a Pakistani politician and diplomat
, a politician who also served as an ambassador to Afghanistan, talked about this process in his book ''A Pathan Odyssey'', and says that Prime Minister Malik Firoz Khan Noon
Sir Malik Feroz Khan Noon, ( ur, ملک فیروز خان نون; 7 May 18939 December 1970), best known as Feroze Khan, was a Pakistani politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Pakistan from 1957 until being removed wh ...
and President Iskandar Mirza both agreed with the plans, the former also agreeing to take King Zahir Shah
Mohammed Zahir Shah ( Pashto/ Dari: , 15 October 1914 – 23 July 2007) was the last king of Afghanistan, reigning from 8 November 1933 until he was deposed on 17 July 1973. Serving for 40 years, Zahir was the longest-serving ruler of Afghanista ...
"as the constitutional Head of State", proclaiming that "after all, for some time after independence, we had a Christian Queen (Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states durin ...
). Now, we would have a Muslim man!’." As per Kasuri, the United States supported the idea as well. He blames the failure of the project to the assassination of Daud Khan and the advent, in 1978, of the pro-Soviet PDPA PDPA can refer to:
*People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan – a communist party
* Personal Data Protection Act 2012 – a Singapore law governing the use and protection of personal data
*Professional Dart Players Association – a trade associ ...
party and Nur Muhammad Taraki
Nur Muhammad Taraki (; 14 July 1917 – 9 October 1979) was an Afghan revolutionary communist politician, journalist and writer. He was a founding member of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) who served as its General Secret ...
.
 Afghan scholar
Afghan scholar Hafizullah Emadi
Hafizullah Emadi is an Afghan author, independent scholar and works as a development consultant for international non-governmental organizations. Most recently, he lives in California and works in Kabul, Afghanistan.
Biography
He was born in ...
says that "the initial blueprint suggested that both sides would maintain their internal autonomy, but in the matter of defense, foreign policy, foreign trade and communication, there would be a central government. The prime minister would be by rotation." He also explains the failure of the proposition : Iskandar Mirza was replaced by General Ayub Khan
Muhammad Ayub Khan (Urdu: ; 14 May 1907 – 19 April 1974), was the second President of Pakistan. He was an army general who seized the presidency from Iskander Mirza in a coup in 1958, the first successful coup d'état in the country's h ...
, after a coup d'état in 1958, an ethnic Pashtun
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
who "regarded himself as the leader of the Pashtuns in Pakistan, and believed that the Pashtuns in Afghanistan should join Pakistan under his leadership" instead of a confederation. Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar (or Zulfiqar) Ali Bhutto ( ur, , sd, ذوالفقار علي ڀٽو; 5 January 1928 – 4 April 1979), also known as Quaid-e-Awam ("the People's Leader"), was a Pakistani barrister, politician and statesman who served as the fourth ...
rejected the idea because "an economically underdeveloped Afghanistan would not benefit Pakistan." In his diaries, in an observation dated to 9 January 1967, Ayub Khan noted that "it is people from the Punjab like Feroz Khan Noon and Amjad Ali who keep on emphasizing to me the need to make up with Afghanistan."
President Zia-ul-Haq
General Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq HI, GCSJ, ร.ม.ภ, ( Urdu: ; 12 August 1924 – 17 August 1988) was a Pakistani four-star general and politician who became the sixth President of Pakistan following a coup and declaration of martial ...
too was for such confederation. " Charles Wilson recalled a map that Zia had also shown to him in which overlay indicated the goal of a confederation embracing first Pakistan and Afghanistan and eventually Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
and Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
. Zia further explained about the Pakistan-Afghanistan confederation in which Pakistanis and Afghans could travel freely back and forth without passports." General Akhtar Abdur Rahman
Akhtar Abdur Rahman Khan NI(M), HI(M), TI(M), SBt (Urdu: اختر عبد الرحمن; 11 June 1924 – 17 August 1988), was a Pakistani senior army general who served as the 5th Chairman Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee of the Pakistan ...
, considered Zia's right-hand man and more importantly the DG-ISI (1979–1987), himself a Pashtun, "also shared Zia’s vision of a post-Soviet "Islamic Confederation" composed of Pakistan, Afghanistan, Kashmir and even the states of Soviet Central Asia."
Even more than a confederation, recently declassified CIA documents point out that, in 1954, the Afghan government approached the US in order to have a merger with Pakistan, being threatened by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
's economic envelopment. Pakistan's then Prime Minister Mohammad Ali Bogra
Sahibzada Syed Mohammad Ali Chowdhury ( bn, সৈয়দ মোহাম্মদ আলী চৌধুরী; Urdu: سید محمد علی چوہدری), more commonly known as Mohammad Ali Bogra ( bn, মোহাম্মদ আলী ...
was skeptical of a total merger, but the idea of a confederation in itself, on the other hand, was already floating around, as "the CIA report hinted that there had been some talk in Afghan and Pakistani official circles of some sort of confederation."
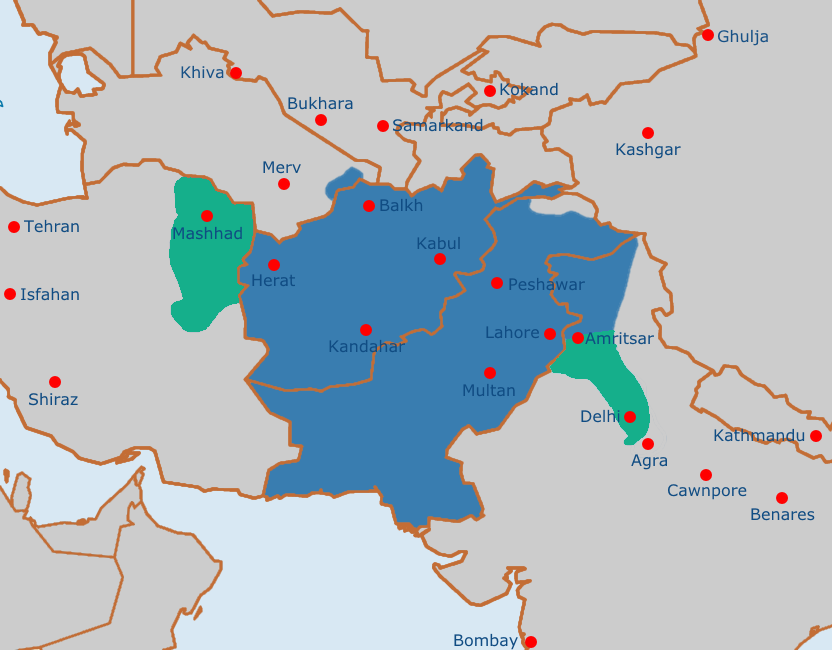
Some analysts have noted that present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan have already been amalgamated into a single geographical unit during the Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, د درانيانو ټولواکمني; fa, امپراتوری درانیان) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, د افغانان ټولواکمني, label=none; fa, امپراتوری افغان, label=none), also know ...
(1747–1826). For instance, scholar Muhammad Shamsuddin Siddiqi says that " Ahmed Shah's empire with its power base in Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
, and later transferred to Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into #Districts, 22 municipal dist ...
, incorporated Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
, Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
, Sind
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Baluchistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western Asia, Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian S ...
" and thus "the Durrani empire bears the closest resemblance to Pakistan", while others have noted that "since the Durrani Empire included the present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan, the forces of history, the principle of national self-determination, and the aspiration for the unity of Muslim ''Ummah
' (; ar, أمة ) is an Arabic word meaning "community". It is distinguished from ' ( ), which means a nation with common ancestry or geography. Thus, it can be said to be a supra-national community with a common history.
It is a synonym for ' ...
'' have all come into line", explaining the interconnected geopolitics of both countries, its latest example being the AfPak
AfPak (also spelled Af-Pak) was a neologism used within Foreign policy of the United States, United States foreign policy circles to designate Afghanistan and Pakistan as a single theatre of operations. Introduced in 2008, the neologism refle ...
doctrine, theorized under the Obama administration
Barack Obama's tenure as the 44th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 2009, and ended on January 20, 2017. A Democrat from Illinois, Obama took office following a decisive victory over Republican ...
from 2008 onward, concluding that Afghanistan and Pakistan should be the aim of common security policies considering their similarities.
Contemporary era
 Relations between Afghanistan and Pakistan began deteriorating again in the 1970s when Afghanistan hosted Pashtun-Baluch militants operating against Pakistan under the leadership of National Awami Party led by Abdul Wali Khan and in retaliation Pakistan started supporting Islamist movements against the progressive and Soviet-influenced Afghan government of
Relations between Afghanistan and Pakistan began deteriorating again in the 1970s when Afghanistan hosted Pashtun-Baluch militants operating against Pakistan under the leadership of National Awami Party led by Abdul Wali Khan and in retaliation Pakistan started supporting Islamist movements against the progressive and Soviet-influenced Afghan government of Mohammed Daoud Khan
Mohammed Daoud Khan ( ps, ), also romanized as Daud Khan or Dawood Khan (18 July 1909 – 28 April 1978), was an Afghan politician and general who served as prime minister of Afghanistan from 1953 to 1963 and, as leader of the 1973 Afghan cou ...
, and encouraged the Islamists to rise up against the government. The figures included Gulbuddin Hekmatyar
Gulbuddin Hekmatyar ( ps, ګلب الدين حكمتيار; born 1 August 1949) is an Afghan politician, former mujahideen leader and drug trafficker. He is the founder and current leader of the Hezb-e-Islami Gulbuddin political party, so calle ...
and Ahmad Shah Massoud
)
, branch = Jamiat-e Islami / Shura-e Nazar Afghan Armed Forces United Islamic Front
, serviceyears = 1975–2001
, rank = General
, unit =
, commands = Mujahideen commander during the Soviet–Afghan War ...
-both members of the Jamiat-e Islami
Jamayat-E-Islami (also rendered as Jamiat-e-Islami and Jamiati Islami; fa, جمعیت اسلامی افغانستان, lit=Islamic Society), sometimes shortened to Jamiat, is a predominantly Tajik political party in Afghanistan. It was origin ...
students' political society- and the Haqqanis. In April 1978, Afghan President
The president of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was constitutionally the head of state and head of government of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (2004–2021) and Commander-in-Chief of the Afghan Armed Forces.
On 15 August 2021, as th ...
Daoud Khan was assassinated in Kabul during the self-declared Marxist Saur Revolution
The Saur Revolution or Sowr Revolution ( ps, د ثور انقلاب; prs, إنقلاب ثور), also known as the April Revolution or the April Coup, was staged on 27–28 April 1978 (, ) by the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) ...
. This was followed by the execution of deposed
Deposition by political means concerns the removal of a politician or monarch.
ORB: The Online Reference for Med ...
Pakistani ORB: The Online Reference for Med ...
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar (or Zulfiqar) Ali Bhutto ( ur, , sd, ذوالفقار علي ڀٽو; 5 January 1928 – 4 April 1979), also known as Quaid-e-Awam ("the People's Leader"), was a Pakistani barrister, politician and statesman who served as the fourt ...
in April 1979 and the assassination of Afghan leader Nur Muhammad Taraki
Nur Muhammad Taraki (; 14 July 1917 – 9 October 1979) was an Afghan revolutionary communist politician, journalist and writer. He was a founding member of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) who served as its General Secret ...
in September 1979. After the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan in December 1979, the United States joined Pakistan to counter Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
influence and advance its own interests in the region. In turn, Afghan
Afghan may refer to:
*Something of or related to Afghanistan, a country in Southern-Central Asia
*Afghans, people or citizens of Afghanistan, typically of any ethnicity
**Afghan (ethnonym), the historic term applied strictly to people of the Pash ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
and Soviet intelligence agencies played their role by supporting al-Zulfikar
Al-Zulfiqar was a Pakistani left-wing Insurgency organization. It was formed in 1979 by Murtaza Bhutto and Shahnawaz Bhutto after their father, then-Prime Minister of Pakistan Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, was deposed in a military coup and execu ...
– a Pakistani leftist terrorist group responsible for the March 1981 hijacking of a Pakistan International Airlines
Pakistan International Airlines ( ur, ; abbreviated PIA, ur, ) is an international airline that serves as the national flag carrier of Pakistan under the administrative control of the Aviation Secretary of Pakistan, Secretary to the Governme ...
(PIA) plane. Al-Zulfiqar was a Pakistani left-wing organisation formed in 1977 by Mir Murtaza Bhutto
Ghulam Murtaza Bhutto (; 18 September 1954 – 20 September 1996) was a Pakistani politician and leader of al-Zulfiqar, a Pakistani left-wing militant organization. The son of Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, the former Prime Minister of Pakistan, he ear ...
, son of former Pakistani Prime Minister Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar (or Zulfiqar) Ali Bhutto ( ur, , sd, ذوالفقار علي ڀٽو; 5 January 1928 – 4 April 1979), also known as Quaid-e-Awam ("the People's Leader"), was a Pakistani barrister, politician and statesman who served as the fourt ...
. Its goal was to overthrow the military regime that ousted Bhutto. After March 1981 Al-Zulfiqar claimed no further attacks. The Bhutto family and Pakistani military dictator Zia-ul-Haq
General Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq HI, GCSJ, ร.ม.ภ, ( Urdu: ; 12 August 1924 – 17 August 1988) was a Pakistani four-star general and politician who became the sixth President of Pakistan following a coup and declaration of martial ...
shared a common enemy, as Zia was the one supporting attacks against the Afghan government.
 During the 1980s, the
During the 1980s, the Durand Line
The Durand Line ( ps, د ډیورنډ کرښه; ur, ), forms the Pakistan–Afghanistan border, a international land border between Pakistan and Afghanistan in South Asia. The western end runs to the border with Iran and the eastern end to th ...
was heavily used by Afghan refugees
Afghan refugees are citizens of Afghanistan who were compelled to abandon their country as a result of major wars, persecution, torture or genocide. The 1978 Saur Revolution followed by the 1979 Soviet invasion marked the first wave of interna ...
fleeing the Soviet occupation
During World War II, the Soviet Union occupied and annexed several countries effectively handed over by Nazi Germany in the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of 1939. These included the eastern regions of Poland (incorporated into two different ...
in Afghanistan, including a large number of Mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term t ...
insurgent groups who crossed back and forth. Pakistan became a major training ground for roughly 250,000 foreign mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term t ...
fighters who began crossing into Afghanistan on a daily basis to wage war against the communist Afghanistan and the Soviet forces. The mujahideen included not only locals but also Arabs and others from over 40 different Islamic nations. Many of these foreign fighters married local women and decided to stay in Pakistan, among them were radical Muslims such those of Saudi-led Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military targets in various countr ...
and Egyptian Muslim Brotherhood
The Society of the Muslim Brothers ( ar, جماعة الإخوان المسلمين'' ''), better known as the Muslim Brotherhood ( '), is a transnational Sunni Islamist organization founded in Egypt by Islamic studies, Islamic scholar and scho ...
as well as prisoners from Arab countries. Relations between the two countries remained hostile during the Soviet-Afghan War. Afghan leader Babrak Karmal
Babrak Karmal (Farsi/ Pashto: , born Sultan Hussein; 6 January 1929 – 1 or 3 December 1996) was an Afghan revolutionary and politician who was the leader of Afghanistan, serving in the post of General Secretary of the People's Democratic Pa ...
refused to improve relations with Pakistan due to their refusal to formally recognize the PDPA government.
Following the death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
of Pakistani President Zia-ul-Haq in 1988, U.S. State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other n ...
blamed the WAD (a KGB created Afghan secret intelligence agency) for terrorist attacks inside Pakistan in 1987 and 1988. With funds from the international community channeled through the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrati ...
(UNHCR), Pakistan hosted over 3 million Afghans at various refugee camp
A refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced people who have fled their home country, but camps are also made for internally displaced peo ...
s, mainly around Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the northwestern region of the country, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa ...
. The United States and others provided billions of dollars in humanitarian assistance to the refugees. There were no regular schools provided for the refugees but only madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated '' ...
s in which students were trained to become members of the Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state (polity), state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalism, Islamic fundamentalist, m ...
movement. When the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
began leaving Afghanistan, during the Presidency of Mohammad Najibullah
Mohammad Najibullah Ahmadzai (Pashto/ prs, محمد نجیبالله احمدزی, ; 6 August 1947 – 27 September 1996), commonly known as Dr. Najib, was an Afghan politician who served as the General Secretary of the People's Democratic Par ...
, the UNHCR and the international community assisted 1.5 million Afghan refugees in returning to Afghanistan. Pakistan were also thought to have played a part in the attempted coup in 1990 against Najibullah's government.
Although the victorious mujahideen formed a government in 1992 through the Peshawar Accords
On 24 April 1992, the Peshawar Accord was announced by several but not all Afghan mujahideen parties: Gulbuddin Hekmatyar, leader of Hezb-e Islami, had since March 1992 opposed these attempts at a coalition government.
The accord proclaimed an ...
, Pakistan remained unhappy with new leaders Rabbani and Massoud, including their foreign policy of maintaining friendly relations with India as during the communist era. Pushing for a "trusted" friendly government in Afghanistan, the Pakistani intelligence started funding Hekmatyar-the only mujahideen commander not to sign the Accords-to fight against the new Afghan government in hopes that he would win and install a new government. Through Pakistani funding, Hekmatyar's forces sieged Kabul city with thousands of rockets for three years, killing thousands. However, upon realizing that Hekmatyar was unable to take power in Kabul, Pakistan looked elsewhere. The Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state (polity), state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalism, Islamic fundamentalist, m ...
movement had just formed with the help of then-Pakistani Interior Minister, Naseerullah Babar, and the Pakistani intelligence threw its weight behind the new movement. Around September 1994, the Taliban movement captured the Afghan city of Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
and began its long conquest with help from Pakistan. The Taliban claimed that they wanted to clean Afghanistan from the warlords and criminals. According to Pakistan and Afghanistan expert Ahmed Rashid, "between 1994 and 1999, an estimated few Pakistanis volunteers trained and fought in Afghanistan" keeping the Taliban regime in power. The role of the Pakistani military during that time has been described by some international observers as a "creeping invasion" of Afghanistan. UN documents also reveal the role of Arab and Pakistani support troops in the Taliban massacre campaigns.
In late 1996, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
emerged and established close relations with neighbouring Pakistan. However, the relations began to decline when the Taliban refused to endorse the Durand Line despite pressure from Islamabad, arguing that there shall be no borders among Muslims.The Unholy Durand Line, Buffering the Bufferby Dr. G. Rauf Roashan. August 11, 2001. A discussion over the Durrand Line between the-then Taliban leader Mohammed Omar and Naseerullah Babar ended abruptly. Omar called Babar, who was an ethnic Pashtun, a traitor for saying that "all problems would be resolved" should the Durrand Line be recognised by the Taliban government. When the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan was toppled and the new Afghan government was formed, President Hamid Karzai began repeating the previous Taliban statement. The
Karzai administration
Hamid Karzai (; Pashto/ fa, حامد کرزی, , ; born 24 December 1957) is an Afghan statesman who served as the fourth president of Afghanistan from July 2002 to September 2014, including as the first elected president of the Islamic Republ ...
in Afghanistan has close relations with the Pakistan's Awami National Party
The Awami National Party (ANP; ur, , ps, اولسي ملي ګوند; lit. ''People's National Party'') is a Pashtun nationalist, secular and leftist political party in Pakistan. The party was founded by Abdul Wali Khan in 1986 and its cur ...
(ANP) and the Pakistan Peoples Party
The Pakistan People's Party ( ur, , ; PPP) is a centre-left, social-democratic political party in Pakistan. It is currently the third largest party in the National Assembly and second largest in the Senate of Pakistan. The party was founded i ...
(PPP). In 2006, Afghan President
The president of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was constitutionally the head of state and head of government of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (2004–2021) and Commander-in-Chief of the Afghan Armed Forces.
On 15 August 2021, as th ...
Hamid Karzai
Hamid Karzai (; Pashto/ fa, حامد کرزی, , ; born 24 December 1957) is an Afghan statesman who served as the fourth president of Afghanistan from July 2002 to September 2014, including as the first elected president of the Islamic Repub ...
warned that "Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and Pakistan and others are not fooling anyone" when it comes to interfering in his country.
The Durand Line border has been used in the last decade as the main supply route for NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
-led forces in Afghanistan as well as by Taliban insurgents and other militant groups who stage attacks inside Afghanistan. The American government decided to rely on drone attacks, which began to negatively affect the US-Pakistan relations.
 In 2007, Afghan intelligence captured Muhammad Hanif, the Taliban spokesman. During his interrogation which was recorded, Hanif claimed that the Taliban leader was being kept in
In 2007, Afghan intelligence captured Muhammad Hanif, the Taliban spokesman. During his interrogation which was recorded, Hanif claimed that the Taliban leader was being kept in Quetta
Quetta (; ur, ; ; ps, کوټه) is the tenth most populous city in Pakistan with a population of over 1.1 million. It is situated in south-west of the country close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is the capital of th ...
under the protection of the ISI. Pakistan denied the claims.
Relations have become more strained after the Afghan government began openly accusing Pakistan of using its ISI spy network in aiding the Taliban and other militants. Pakistan usually denies these allegations but has said in the past that it does not have full control of the actions of the ISI. There have been a number of reports about the Afghanistan–Pakistan skirmishes, which usually occur when army soldiers are in hot pursuit
Hot pursuit
Hot pursuit is a legal term.
Hot Pursuit may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''Hot Pursuit'' (1984 TV series), a 1984 NBC television series
* ''Hot Pursuit'' (2006 TV series), a 2006 Court TV television series
* ''Hot Pursuit ...
chasing insurgents who cross the border back and forth. This leads to tensions between the two states, especially after hearing reports of civilian casualties.
After the May 2011 death of Osama bin Laden
On May 2, 2011, Osama bin Laden, the founder and first leader of the Islamist militant group al-Qaeda, was shot several times and killed at his compound in the Pakistani city of Abbottabad, by United States Navy SEALs of the U.S. Naval Spe ...
in Pakistan, many prominent Afghan figures began being assassinated, including Mohammed Daud Daud, Ahmad Wali Karzai
Ahmed Wali Karzai ( ps, احمد ولي کرزی, , 1961 – 12 July 2011) was a politician in Afghanis ...
, Jan Mohammad Khan
Jan Mohammad Khan (died July 17, 2011) was a politician in Afghanistan, who served as Governor of Oruzgan Province from January 2002 to March 2006, member of the National Assembly, and a special adviser to President Hamid Karzai.
He was an el ...
, Ghulam Haider Hamidi
Ghulam Haider Hamidi ( ps, غلام حیدر حمیدی, also spelled Ghulam Haidar Hameedi and also known as Henry Hamidi; 1945 – 27 July 2011) was the Mayor of Kandahar in Afghanistan. his family fled to Pakistan, then to the United St ...
, Burhanuddin Rabbani and others. Also in the same year, the Afghanistan–Pakistan skirmishes intensified and many large scale attacks by the Pakistani-based Haqqani network took place across Afghanistan. This led to the United States warning Pakistan of a possible military action against the Haqqanis in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas
, conventional_long_name = Federally Administered Tribal Areas
, nation = Pakistan
, subdivision = Autonomous territory
, image_flag = Flag of FATA.svg
, image_coat = File:Coat of arms ...
. The U.S. blamed Pakistan's government, mainly Pakistani Army
The Pakistan Army (, ) is the land service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The roots of its modern existence trace back to the British Indian Army that ceased to exist following the Partition of British India, which occurred as a result ...
and its ISI spy network as the masterminds behind all of this. U.S. Ambassador to Pakistan, Cameron Munter, told Radio Pakistan that "the attack that took place in Kabul a few days ago, that was the work of the Haqqani network. There is evidence linking the Haqqani Network to the Pakistan government. This is something that must stop." Other top U.S. officials such as Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
and Leon Panetta
Leon Edward Panetta (born June 28, 1938) is an American Democratic Party politician who has served in several different public office positions, including Secretary of Defense, CIA Director, White House Chief of Staff, Director of the Office of ...
made similar statements. Despite all of this, Afghan President Hamid Karzai labelled Pakistan as Afghanistan's "twin brother".
After the May 2017 Kabul attack, the Afghan National Directorate of Security
The National Directorate of Security (NDS; ps, د ملي امنیت لوی ریاست; prs, ریاست عمومی امنیت ملی) was the national intelligence and security service of Afghanistan. The headquarters of the NDS was in Kabul, ...
(NDS) claimed that the blast was planned by the Afghan insurgent group Haqqani Network, and reiterated allegations that those elements had support and presence across the border in Pakistan. Afghan President Ashraf Ghani
Mohammad Ashraf Ghani Ahmadzai (born 19 May 1949) is an Afghan politician, academic, and economist who served as the president of Afghanistan from September 2014 until August 2021, when his government was overthrown by the Taliban.
Born in ...
stated that Pakistan has instigated an "undeclared war of aggression" against the country. Pakistan's Foreign Ministry In many countries, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the government department responsible for the state's diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral relations affairs as well as for providing support for a country's citizens who are abroad. The entit ...
spokesman, Nafees Zakaria rejected the Afghan allegations as "baseless".
In 2015, Inter-Services Intelligence
The Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI; ur, , bayn khadamatiy mukhabarati) is the premier intelligence agency of Pakistan. It is responsible for gathering, processing, and analyzing any information from around the world that is deemed relevant ...
and National Directorate of Security
The National Directorate of Security (NDS; ps, د ملي امنیت لوی ریاست; prs, ریاست عمومی امنیت ملی) was the national intelligence and security service of Afghanistan. The headquarters of the NDS was in Kabul, ...
inked a memorandum of understanding. Under the memorandum of understanding, both nations agreed to fight terrorism together and also to share intelligence information. On 16 May 2015, the Pakistani army
The Pakistan Army (, ) is the land service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The roots of its modern existence trace back to the British Indian Army that ceased to exist following the Partition of British India, which occurred as a result ...
launched an operation to save the life of an injured Afghan soldier on the Afghanistan side of the border. The soldier was injured in a clash with militants and he was evacuated by the Pakistan military. There have been instances where Afghan soldiers injured in fighting the militants near the Pakistan Afghanistan border are sent to Pakistan for treatment.
After fall of Kabul by Afghan Taliban, Pakistani PM Imran Khan describing it as Afghans breaking "the shackles of slavery". Although Pakistan still not officially recognition of the Taliban's Islamic Emirate, it launched a diplomatic effort urging the international community to engage with the Taliban, help ease Afghanistan's humanitarian crisis and prevent it from descending into chaos again. In December 2021, foreign ministers of the 56 nations belonging to the Organization of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
, along with Taliban delegates, gathered in Islamabad. The meeting focused on Afghanistan's humanitarian crisis. But Tehreek-e-Taliban Pakistan
The Pakistani Taliban (), formally called the Tehreek-e-Taliban-e-Pakistan (Urdu/ ps, , lit=Student Movement of Pakistan, TTP), is an umbrella organization of various Islamist armed militant groups operating along the Afghan–Pakistani bor ...
attacks lead to growing tension between the Afghan Taliban and Pakistan.
In April 2022, Islamabad urged Kabul "to secure Pak-Afghan Border region and take stern actions against the individuals involved in terrorist activities in Pakistan", and Pakistan Air Force
, "Be it deserts or seas; all lie under our wings" (traditional)
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = ...
conducted air raids across its border with Afghanistan, claiming to strike TTP militants operating in the porous border regions.
In late 2022, Pakistan's embassy in Kabul came under attack with gunfire wounding a Pakistani security guard, IS-K claims responsibility for the attack, Pakistan asked the attack to be thoroughly probed by Taliban authorities.
Afghan-Pak Transit Trade Agreement
In July 2010, a Memorandum of understanding (MoU) was reached between Pakistan and Afghanistan for the Afghan-Pak Transit Trade Agreement (APTTA), which was observed byU.S. Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
. The two states also signed an MoU for the construction of rail tracks in Afghanistan to connect with Pakistan Railways
Pakistan Railways ( ur, ) is the national, state-owned railway company of Pakistan. Founded in 1861 and headquartered in Lahore, it owns of track across Pakistan, stretching from Torkham to Karachi, offering both freight and passenger se ...
(PR), which has been in the making since at least 2005. In October 2010, the landmark APTTA agreement was signed by Pakistani Commerce Minister Makhdoom Amin Fahim
Makhdoom Muhammad Ameen Faheem ( ur, ; ''alt. spelling'': Amin Fahim; 4 August 1939 – 21 November 2015) was a Pakistani populist left-wing figure and a poet. He was the senior vice-chairman of Pakistan Peoples Party, chairman of Pakist ...
and Anwar ul-Haq Ahady, Afghan Ministry of Commerce. The ceremony was attended by Richard Holbrooke
Richard Charles Albert Holbrooke (April 24, 1941 – December 13, 2010) was an American diplomat and author. He was the only person to have held the position of Assistant Secretary of State for two different regions of the world (Asia from 1977 ...
, U.S. Special Representative for Afghanistan and Pakistan, and a number of foreign ambassadors, Afghan parliamentarians and senior officials. The APTTA allows Afghan trucks to drive inside Pakistan to the Wagah
Wagah ( ur, ) or Wagha (Shahmukhi pnb, ) is a village and union council (UC 181) located in the Wahga Zone near Lahore City District, Pakistan. The town is famous for the Wagah border ceremony and also serves as a goods transit terminal and ...
border with India, including to the port cities of Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
and Gwadar
Gwadar ( Balochi/ ur, ) is a port city with located on the southwestern coast of Balochistan, Pakistan. The city is located on the shores of the Arabian Sea opposite Oman. Gwadar is the 100th largest city of Pakistan, according to the 2017 ...
.
In November 2010, the two states formed a joint chamber of commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to ...
to expand trade relations and solve the problems traders face. The APTTA agreement has taken effect after several Afghan trucks delivered fruits from Afghanistan to the Wagah border with India in June 2011. With the completion of the APTTA, the United States and other NATO states are planning to revive the ancient Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
. This is to help the local economies of Afghanistan and Pakistan by connecting South Asia with Central Asia and the Middle East. The APTTA is intended to improve trade between the two countries but Pakistan often delays Afghan-bound containers, especially after the 2011 NATO attack in Pakistan
The 2011 NATO attack in Pakistan (also known as the Salala incident, Salala attack or 26/11 attacks) was a border skirmish that occurred when United States-led NATO forces engaged Pakistani security forces at two Pakistani military checkpo ...
.
In July 2012, Afghanistan and Pakistan agreed to extend APTTA to Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
in what will be the first step for the establishment of a North–South trade corridor. The proposed agreement will provide facilities to Tajikistan to use Pakistan's Gwadar and Karachi ports for its imports and exports while Pakistan will enjoy trade with Tajikistan under terms similar to the transit arrangement with Afghanistan. Trade between Pakistan and Afghanistan is expected to reach $5 billion by 2015. Afghanistan's economy is one of the fastest growing economies in the world. A 2012 World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
report added, "In contrast, Afghanistan’s economy grew robustly by about 11 percent mostly due to a good harvest."
Towards the end of the same year, both the governments of Afghanistan and Pakistan drafted plans to talk to the Taliban.
Cooperation between the two countries includes possible defence cooperation and intelligence sharing as well as further enhancing the two-way trade and abolishment of visas for diplomats from the two nations.
See also
*List of ambassadors of Afghanistan to Pakistan
The Afghan ambassador to Pakistan is the top-level diplomatic representative of Afghanistan in Pakistan. The ambassador is in charge of the Afghan embassy in Islamabad. It is politically an important Afghan diplomatic post, due to the Afghan ...
* Afghanistan–Pakistan sports rivalries
* Foreign relations of Afghanistan
* Foreign relations of Pakistan
The Islamic Republic of Pakistan maintains a large network of diplomatic relations across the world. Pakistan is the second largest Muslim- majority country in terms of population ( after Indonesia) and is the only Muslim majority nation to ...
* AfPak
AfPak (also spelled Af-Pak) was a neologism used within Foreign policy of the United States, United States foreign policy circles to designate Afghanistan and Pakistan as a single theatre of operations. Introduced in 2008, the neologism refle ...
* Durand Line
The Durand Line ( ps, د ډیورنډ کرښه; ur, ), forms the Pakistan–Afghanistan border, a international land border between Pakistan and Afghanistan in South Asia. The western end runs to the border with Iran and the eastern end to th ...
* Khyber Pass Economic Corridor
Khyber Pass Economic Corridor (KPEC) ( ur, ; ps, د خيبر دره اقتصادي دهلیز) is an infrastructure project that aims to expand Pakistan's economic connectivity with Afghanistan, and by extension Central Asia, via the Khyber Pass ...
* South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan ...
(SAARC)
References
Further reading
*Abbas, Hassan. ''The Taliban Revival: Violence and Extremism on the Pakistan-Afghanistan Frontier'' (Yale UP, 2014) * Gartenstein-Ross, Daveed, and Tara Vassefi. "The forgotten history of Afghanistan-Pakistan relations." ''Yale Journal of International Affairs'' 7 (2012): 38online
* Hussain, Rizwan. '' Pakistan and the Emergence of Islamic Militancy in Afghanistan'' (Ashgate, 2005)
excerpt
* Nadiri, Khalid Homayun. "Old Habits, New Consequences: Pakistan's Posture toward Afghanistan since 2001." ''International Security'' 39.2 (2014): 132–168
online
* Paliwal, Avinash. "Pakistan–Afghanistan Relations Since 2001." in ''Pakistan at the Crossroads'' ed by Christophe Jaffrelot; (Columbia UP, 2016) pp. 191–218. * Rashid, Ahmed. ''Pakistan on the Brink: The future of Pakistan, Afghanistan and the West'' (Penguin, 2012). * Raza, Muhammad Amjad, and Ghulam Mustufa. "Indo-Afghan Relations: Implications for Pakistan." ''Central Asia'' 84.Summer (2019): 53–79
online
* Shahrani, M Nazif, ed. ''Modern Afghanistan: The Impact of 40 Years of War'' (Indiana UP, 2018) * Siddique, Abubakar. ''The Pashtun Question The Unresolved Key to the Future of Pakistan and Afghanistan'' (Hurst, 2014) * Zahab, Mariam Abou, and Olivier Roy. ''Islamist Networks: The Afghan-Pakistan Connection'' (Columbia UP, 2004)
Former British Commander Cautions Taliban May Get Control of Pakistan Nuclear Weapons
Pakistan-Afghanistan Nuclear Sectarian Policy emerges after Benazir Bhutto Nuclear Sectarian policy with Iran leaks
Pakistan Ranked 1st in Muslim Countries Nuclear Business
Afghanistan-Pakistan Drug Sales in International Airports
{{DEFAULTSORT:Afghanistan-Pakistan relations
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
Bilateral relations of Pakistan