Adolf Bastian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Adolf Philipp Wilhelm Bastian (26 June 18262 February 1905) was a 19th-century
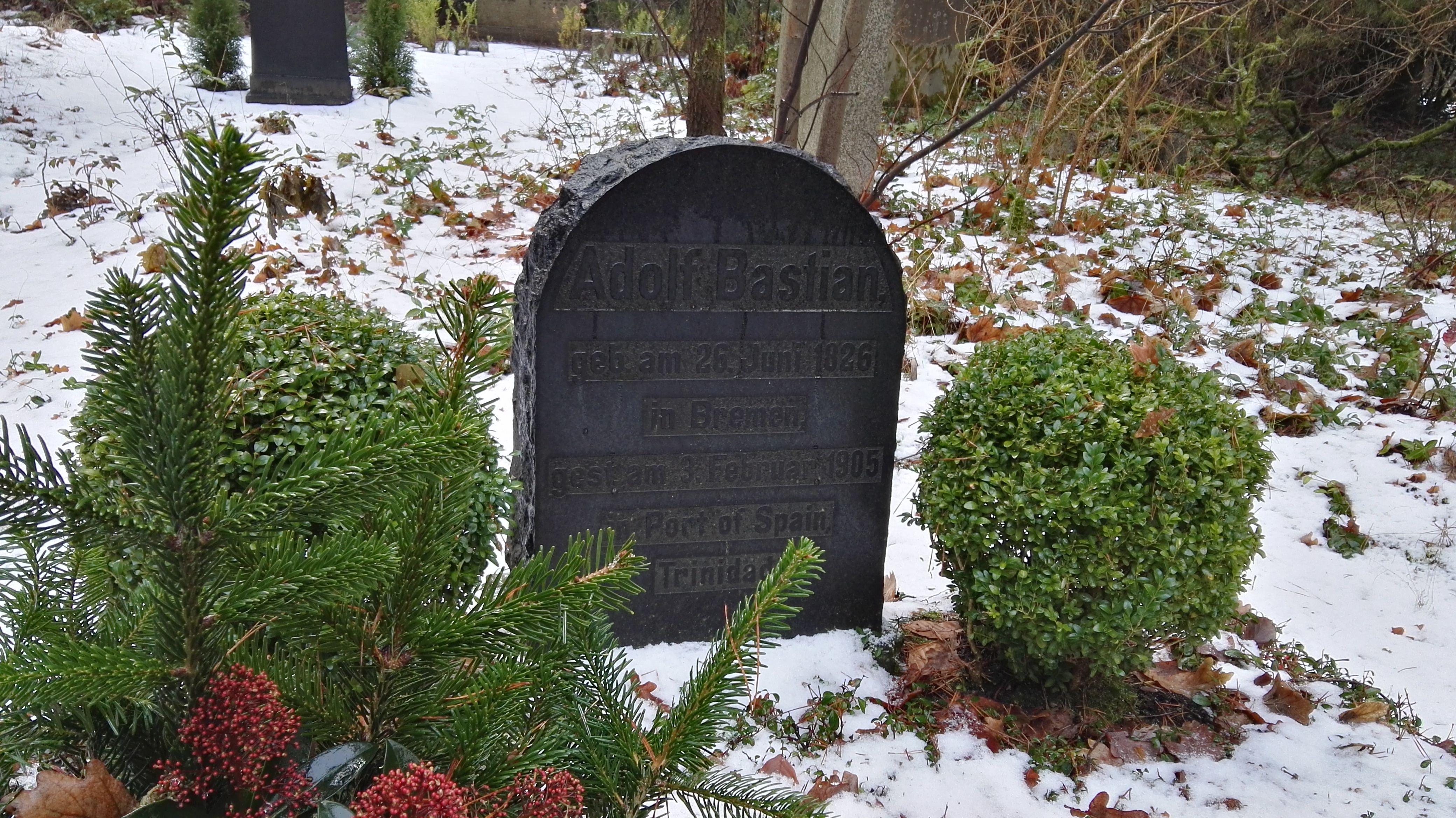 He moved to
He moved to
 In arguing for a "psychic unity of mankind," Bastian proposed a straightforward project for the long-term development of a science of human culture and consciousness.
He argued that the mental acts of all people everywhere on the planet are the products of physiological mechanisms characteristic of the human species.
Every human mind inherits a complement of species-specific "elementary ideas" (''Elementargedanken''), and hence the minds of all people, regardless of their race or culture, operate in the same way.
According to Bastian, the contingencies of geographic location and historical background create different local elaborations of the "elementary ideas"; these he called "folk ideas" (''Völkergedanken''). Bastian also proposed a "genetic principle" by which societies develop over the course of their history from exhibiting simple sociocultural institutions to becoming increasingly complex in their organization.
Through the accumulation of ethnographic data, we can study the psychological laws of mental development as they reveal themselves in diverse regions and under differing conditions. Although one is speaking with individual informants, Bastian held that the object of research is not the study of the individual per se, but rather the "folk ideas" or "collective mind" of a particular people.
The more one studies various peoples, Bastian thought, the more one sees that the historically conditioned "folk ideas" are of secondary importance compared with the universal "elementary ideas". The individual is like the cell in an organism, a social animal whose mind – its "folk ideas" – is influenced by its social background; and the "elementary ideas" are the ground from which these “folk ideas” develop. From this perspective, the social group has a kind of group mind, a "societal soul" (''Gesellschaftsseele''), in which the individual mind is embedded.
These ideas of Bastian's prefigured (and influenced) the later study of psychological archetypes,
In arguing for a "psychic unity of mankind," Bastian proposed a straightforward project for the long-term development of a science of human culture and consciousness.
He argued that the mental acts of all people everywhere on the planet are the products of physiological mechanisms characteristic of the human species.
Every human mind inherits a complement of species-specific "elementary ideas" (''Elementargedanken''), and hence the minds of all people, regardless of their race or culture, operate in the same way.
According to Bastian, the contingencies of geographic location and historical background create different local elaborations of the "elementary ideas"; these he called "folk ideas" (''Völkergedanken''). Bastian also proposed a "genetic principle" by which societies develop over the course of their history from exhibiting simple sociocultural institutions to becoming increasingly complex in their organization.
Through the accumulation of ethnographic data, we can study the psychological laws of mental development as they reveal themselves in diverse regions and under differing conditions. Although one is speaking with individual informants, Bastian held that the object of research is not the study of the individual per se, but rather the "folk ideas" or "collective mind" of a particular people.
The more one studies various peoples, Bastian thought, the more one sees that the historically conditioned "folk ideas" are of secondary importance compared with the universal "elementary ideas". The individual is like the cell in an organism, a social animal whose mind – its "folk ideas" – is influenced by its social background; and the "elementary ideas" are the ground from which these “folk ideas” develop. From this perspective, the social group has a kind of group mind, a "societal soul" (''Gesellschaftsseele''), in which the individual mind is embedded.
These ideas of Bastian's prefigured (and influenced) the later study of psychological archetypes,
polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
best remembered for his contributions to the development of ethnography
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject ...
and the development of anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
as a discipline. Modern psychology
Psychology is defined as "the scientific study of behavior and mental processes". Philosophical interest in the human mind and behavior dates back to the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Persia, Greece, China, and India.
Psychology as a field of ...
owes him a great debt, because of his theory of the ''Elementargedanke'', which led to Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, ph ...
's development of the theory of ''archetype
The concept of an archetype (; ) appears in areas relating to behavior, historical psychology, and literary analysis.
An archetype can be any of the following:
# a statement, pattern of behavior, prototype, "first" form, or a main model that ...
s''. His ideas had a formative influence on the "father of American anthropology" Franz Boas
Franz Uri Boas (July 9, 1858 – December 21, 1942) was a German-American anthropologist and a pioneer of modern anthropology who has been called the "Father of American Anthropology". His work is associated with the movements known as historical ...
, and he also influenced the thought of comparative mythologist
Comparative mythology is the comparison of myths from different cultures in an attempt to identify shared themes and characteristics.Littleton, p. 32 Comparative mythology has served a variety of academic purposes. For example, scholars have used ...
Joseph Campbell
Joseph John Campbell (March 26, 1904 – October 30, 1987) was an American writer. He was a professor of literature at Sarah Lawrence College who worked in comparative mythology and comparative religion. His work covers many aspects of the ...
.
Life
Bastian was born inBremen
Bremen ( Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state cons ...
, at the time a state of the German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, w ...
, into a prosperous bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. ...
German family of merchants.
His career at university was broad almost to the point of being eccentric. He studied law at the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg
}
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg, (german: Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg; la, Universitas Ruperto Carola Heidelbergensis) is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württember ...
, and biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
at what is today Humboldt University of Berlin
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (german: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a German public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin. It was established by Frederick William III on the initiative ...
, the Friedrich Schiller University of Jena
The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (german: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany.
The un ...
, and the University of Würzburg
The Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg (also referred to as the University of Würzburg, in German ''Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg'') is a public research university in Würzburg, Germany. The University of Würzburg is one of ...
. It was at this last university that he attended lectures by Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow (; or ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder ...
and developed an interest in what was then known as 'ethnology
Ethnology (from the grc-gre, ἔθνος, meaning 'nation') is an academic field that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology). ...
'. He finally settled on medicine and earned a degree from Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
in 1850.
Bastian became a ship's doctor and began an eight-year voyage that took him around the world. This was the first of what would be a quarter of a century of travels. He returned to Germany in 1859 and wrote a popular account of his travels along with an ambitious three-volume work entitled ''Man in History'', which became one of his most well-known works.
In 1861 he undertook a four-year trip to Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and his account of this trip, ''The People of East Asia'' ran to six volumes. when Bastian finally published the studies and observations during his ''Journey through Cambodia to Cochinchina'' in Germany in 1868 - told in detail but uninspiredly, above all without a single one of his drawings - this work hardly made an impression, while everyone was talking about Henri Mouhot's posthumous work with vivid descriptions of Angkor
Angkor ( km, អង្គរ , 'Capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura ( km, យសោធរបុរៈ; sa, यशोधरपुर),Headly, Robert K.; Chhor, Kylin; Lim, Lam Kheng; Kheang, Lim Hak; Chun, Chen. 1977. ''Cambodian-Engl ...
, ''Travels in the Central Parts of Indo-China, Siam, Cambodia and Laos'', published in 1864 through the Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical scien ...
.
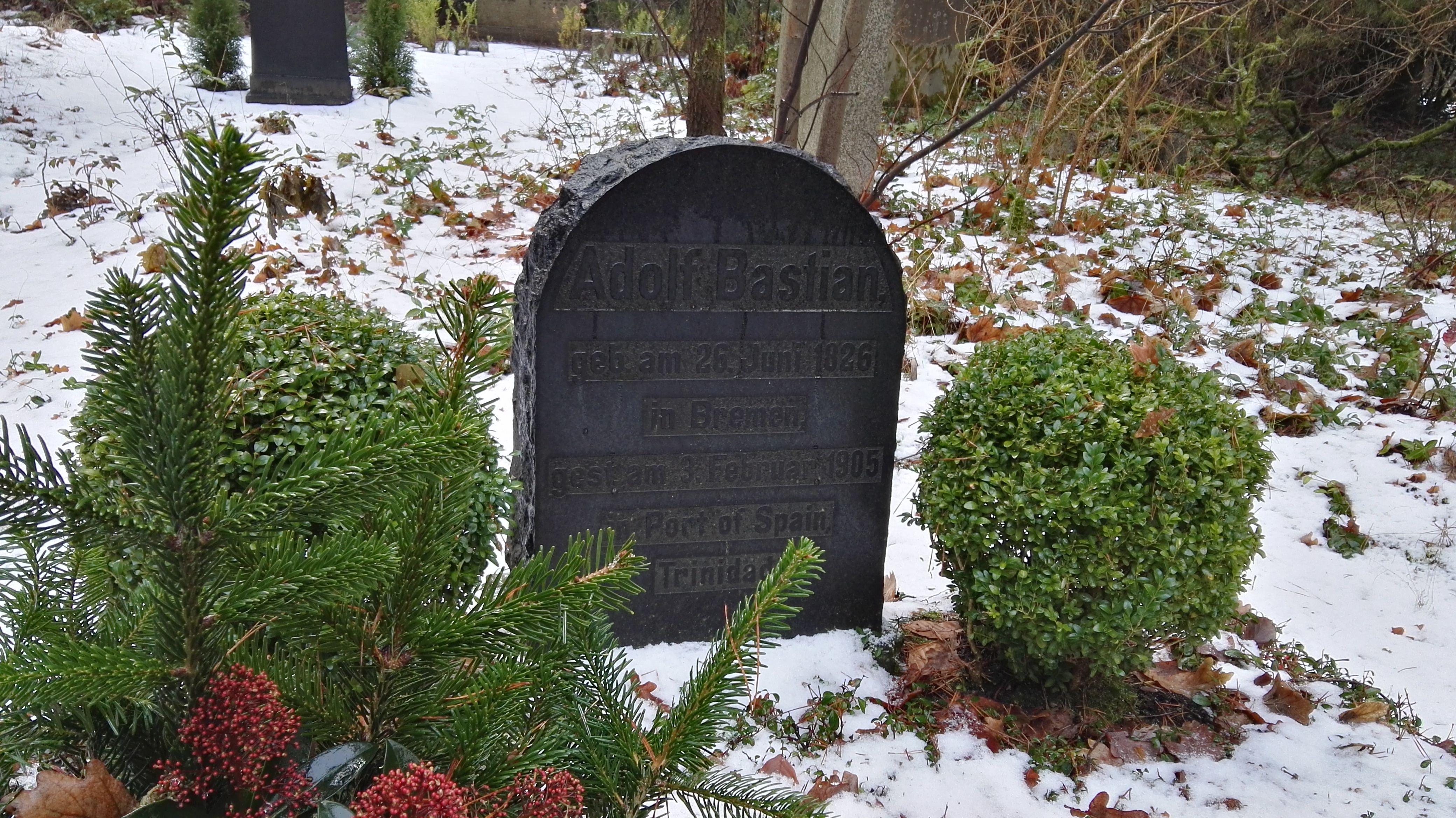 He moved to
He moved to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
in 1866, where he became a member of the Academy of Sciences Leopoldina
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (german: Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina – Nationale Akademie der Wissenschaften), short Leopoldina, is the national academy of Germany, and is located in Halle (Saale). Founded ...
in 1869. Together with Robert Hartmann (1832–1893), Bastian founded the ethnological and anthropological journal, ''Zeitschrift für Ethnologie'' (ZfE) in 1869. He also worked with Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow (; or ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder ...
to organize the Berlin Society for Anthropology, Ethnology, and Prehistory, which would use the ZfE as its main publication outlet.
In 1873, he was one of the founders and first director of the Ethnological Museum of Berlin, and served as its first director. Its collection of ethnographic artifacts became one of the largest in the world for decades to come. Among others who worked under him at the museum were the young Franz Boas
Franz Uri Boas (July 9, 1858 – December 21, 1942) was a German-American anthropologist and a pioneer of modern anthropology who has been called the "Father of American Anthropology". His work is associated with the movements known as historical ...
, who later founded the American school of ethnology, and Felix von Luschan
Felix Ritter von Luschan (11 August 1854 – 7 February 1924) was an Austrian doctor, anthropologist, explorer, archaeologist and ethnographer.
Life
Luschan was born the son of a lawyer in Hollabrunn, Lower Austria, and attended the Akademische ...
.
In the 1870s Bastian left Berlin and again traveled extensively in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
as well as the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
. He was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit ...
in 1886.
He died in Port of Spain
Port of Spain ( Spanish: ''Puerto España''), officially the City of Port of Spain (also stylized Port-of-Spain), is the capital of Trinidad and Tobago and the third largest municipality, after Chaguanas and San Fernando. The city has a muni ...
, Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
during one of these journeys in 1905.Works
* ''Travels in Burma in the Years 1861–1862'' * ''Travels in Siam in the Year 1863'' * ''Travels in China...'' *''Die deutsche Expedition an der Loango-Küste'' (1874) Bastian is remembered as one of the pioneers of the concept of the 'psychic unity of mankind' – the idea that all humans share a basic mental framework. This became the basis in other guises of 20th centurystructuralism
In sociology, anthropology, archaeology, history, philosophy, and linguistics, structuralism is a general theory of culture and methodology that implies that elements of human culture must be understood by way of their relationship to a broader s ...
, and influenced Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, ph ...
's idea of the collective unconscious
Collective unconscious (german: kollektives Unbewusstes) refers to the unconscious mind and shared mental concepts. It is generally associated with idealism and was coined by Carl Jung. According to Jung, the human collective unconscious is popula ...
. He also argued that the world was divided up into different 'geographical provinces' and that each of these provinces moved through the same stages of evolutionary development. According to Bastian, innovations and culture traits tended not to diffuse across areas. Rather, each province took its unique form as a result of its environment. This approach was part of a larger nineteenth century interest in the 'comparative method' as practiced by anthropologists such as Edward B. Tylor.
While Bastian considered himself to be extremely scientific, it is worth noting that he emerged from the naturalist tradition that was inspired by Johann Gottfried Herder
Johann Gottfried von Herder ( , ; 25 August 174418 December 1803) was a German philosopher, theologian, poet, and literary critic. He is associated with the Enlightenment, '' Sturm und Drang'', and Weimar Classicism.
Biography
Born in Mohr ...
and exemplified by figures such as Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister ...
. For him, empiricism
In philosophy, empiricism is an epistemological theory that holds that knowledge or justification comes only or primarily from sensory experience. It is one of several views within epistemology, along with rationalism and skepticism. Empir ...
meant a rejection of philosophy in favor of scrupulous observations. As a result, he remained hostile to Darwin's theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
(and its main German advocate, Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new s ...
), because the physical transformation of species had never been empirically observed, despite the fact that he posited a similar evolutionary development for human civilization. Daum, ''Wissenschaftspopularisierung'', p. 427. Additionally, he was much more concerned with documenting unusual civilizations before they vanished (presumably as a result of contact with Western civilization) than with the rigorous application of scientific observation. As a result, some have criticized his works for being disorganized collections of facts rather than coherently structured or carefully researched empirical studies.
 In arguing for a "psychic unity of mankind," Bastian proposed a straightforward project for the long-term development of a science of human culture and consciousness.
He argued that the mental acts of all people everywhere on the planet are the products of physiological mechanisms characteristic of the human species.
Every human mind inherits a complement of species-specific "elementary ideas" (''Elementargedanken''), and hence the minds of all people, regardless of their race or culture, operate in the same way.
According to Bastian, the contingencies of geographic location and historical background create different local elaborations of the "elementary ideas"; these he called "folk ideas" (''Völkergedanken''). Bastian also proposed a "genetic principle" by which societies develop over the course of their history from exhibiting simple sociocultural institutions to becoming increasingly complex in their organization.
Through the accumulation of ethnographic data, we can study the psychological laws of mental development as they reveal themselves in diverse regions and under differing conditions. Although one is speaking with individual informants, Bastian held that the object of research is not the study of the individual per se, but rather the "folk ideas" or "collective mind" of a particular people.
The more one studies various peoples, Bastian thought, the more one sees that the historically conditioned "folk ideas" are of secondary importance compared with the universal "elementary ideas". The individual is like the cell in an organism, a social animal whose mind – its "folk ideas" – is influenced by its social background; and the "elementary ideas" are the ground from which these “folk ideas” develop. From this perspective, the social group has a kind of group mind, a "societal soul" (''Gesellschaftsseele''), in which the individual mind is embedded.
These ideas of Bastian's prefigured (and influenced) the later study of psychological archetypes,
In arguing for a "psychic unity of mankind," Bastian proposed a straightforward project for the long-term development of a science of human culture and consciousness.
He argued that the mental acts of all people everywhere on the planet are the products of physiological mechanisms characteristic of the human species.
Every human mind inherits a complement of species-specific "elementary ideas" (''Elementargedanken''), and hence the minds of all people, regardless of their race or culture, operate in the same way.
According to Bastian, the contingencies of geographic location and historical background create different local elaborations of the "elementary ideas"; these he called "folk ideas" (''Völkergedanken''). Bastian also proposed a "genetic principle" by which societies develop over the course of their history from exhibiting simple sociocultural institutions to becoming increasingly complex in their organization.
Through the accumulation of ethnographic data, we can study the psychological laws of mental development as they reveal themselves in diverse regions and under differing conditions. Although one is speaking with individual informants, Bastian held that the object of research is not the study of the individual per se, but rather the "folk ideas" or "collective mind" of a particular people.
The more one studies various peoples, Bastian thought, the more one sees that the historically conditioned "folk ideas" are of secondary importance compared with the universal "elementary ideas". The individual is like the cell in an organism, a social animal whose mind – its "folk ideas" – is influenced by its social background; and the "elementary ideas" are the ground from which these “folk ideas” develop. From this perspective, the social group has a kind of group mind, a "societal soul" (''Gesellschaftsseele''), in which the individual mind is embedded.
These ideas of Bastian's prefigured (and influenced) the later study of psychological archetypes, comparative mythology
Comparative mythology is the comparison of myths from different cultures in an attempt to identify shared themes and characteristics.Littleton, p. 32 Comparative mythology has served a variety of academic purposes. For example, scholars have used ...
, cultural universals
A cultural universal (also called an anthropological universal or human universal) is an element, pattern, trait, or institution that is common to all known human cultures worldwide. Taken together, the whole body of cultural universals is known ...
and cross-cultural psychology
Cross-cultural psychology is the scientific study of human behavior and mental processes, including both their variability and invariance, under diverse cultural conditions. Through expanding research methodologies to recognize cultural variance i ...
.
Bastian believed that the "elementary ideas" are to be scientifically reconstructed from "folk ideas" as varying forms of collective representations (''Gesellschaftsgedanken'').
Because one cannot observe the collective representations per se, Bastian felt that the ethnographic project had to proceed through a series of five analytical steps (see Koepping, 1983):
:1. Fieldwork: Empirical description of cross-cultural data (as opposed to armchair philosophy; Bastian himself spent much of his adult life among non-European peoples).
:2. Deduction of collective representations: From cross-cultural data we describe the collective representations in a given society.
:3. Analysis of folk ideas: Collective representations are broken down into constituent folk ideas. Geographical regions often exhibit similar patterns of folk ideas – he called these “idea circles” which described the collective representations of particular regions.
:4. Deduction of elementary ideas: Resemblances between folk ideas and patterns of folk ideas across regions indicate underlying elementary ideas.
:5. Application of a scientific psychology: Study of elementary ideas defines the psychic unity of mankind, which is due to the underlying psychophysiological structure of the species – this study is to be accomplished by a truly scientific, cross-culturally grounded psychology.
Notes
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Bastian, Adolf 1826 births 1905 deaths Scientists from Bremen Writers from Bremen German anthropologists German ethnographers German ethnologists Heidelberg University alumni Humboldt University of Berlin alumni University of Jena alumni University of Würzburg alumni German male writers Members of the German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina Members of the American Philosophical Society German explorers of Africa