Administrative division of Second Polish Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Subdivisions of the Second Polish Republic became an issue immediately after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in 1918. The
Subdivisions of the Second Polish Republic became an issue immediately after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in 1918. The


 Subdivisions of the Second Polish Republic became an issue immediately after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in 1918. The
Subdivisions of the Second Polish Republic became an issue immediately after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in 1918. The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
had been partitioned in the late 18th century. Various parts of new Polish territory had belonged to different administrative structures of Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
, Imperial Germany
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditar ...
and Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.
In 1919 the first voivodeships
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
of interwar Poland were created; in addition, the capital of Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
had a status of an independent city-voivodeship. In the years 1919–1921 additional voivodeships were created, as borders of Poland were still fluid, with events such as the Silesian Uprisings
The Silesian Uprisings (german: Aufstände in Oberschlesien, Polenaufstände, links=no; pl, Powstania śląskie, links=no) were a series of three uprisings from August 1919 to July 1921 in Upper Silesia, which was part of the Weimar Republic ...
in the West and Polish-Soviet War in the East. Eventually by 1921 Poland would have 15 voivodeships, Warsaw capital city-voivodeship and the Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
(the system known as 15+1+1). Additionally, creation of the new Sandomierz Voivodeship
Sandomierz Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo Sandomierskie, la, Palatinatus Sandomirensis) was a unit of administration and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. It was part of the Lesser Polan ...
was planned for late 1939.
The lower level of administration, below voivodeships, were powiat
A ''powiat'' (pronounced ; Polish plural: ''powiaty'') is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture ( LAU-1, formerly NUTS-4) in other countries. The term "''powiat ...
s (counties). They were subject to several reforms, particularly in early and late 1930s. Below them were gminas and gromada
Gromada is a Polish word meaning "gathering", "group", or "assembly". In the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the term referred to a village organization which embraced all the inhabitants of a village and acted as a local authority, as well a ...
s. Shortly before the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, in April 1939, Poland had 264 powiats, 611 urban and 3195 rural gminas and 40533 gromads.
The division was based on the three-tier system. On the lowest rung were the ''gminy'', which were little more than local town and village governments. These were then grouped together into ''powiaty'' which were then arranged into ''województwa''.
On April 1, 1938, borders of several western Voivodeships changed considerably. For more information, see Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938
{{cleanup, reason=Polish words should be translated or linked to an explanatory article, or capitalized if they are proper nouns, and linked to the English Wikipedia article about them., date=March 2019
On 1 April 1938, borders of several western a ...
.
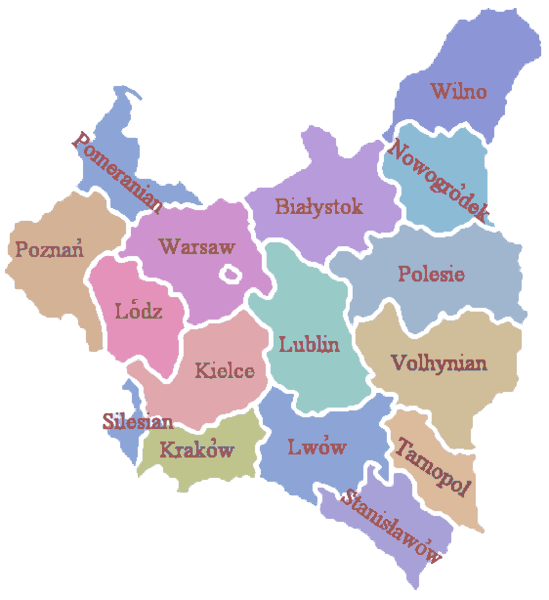
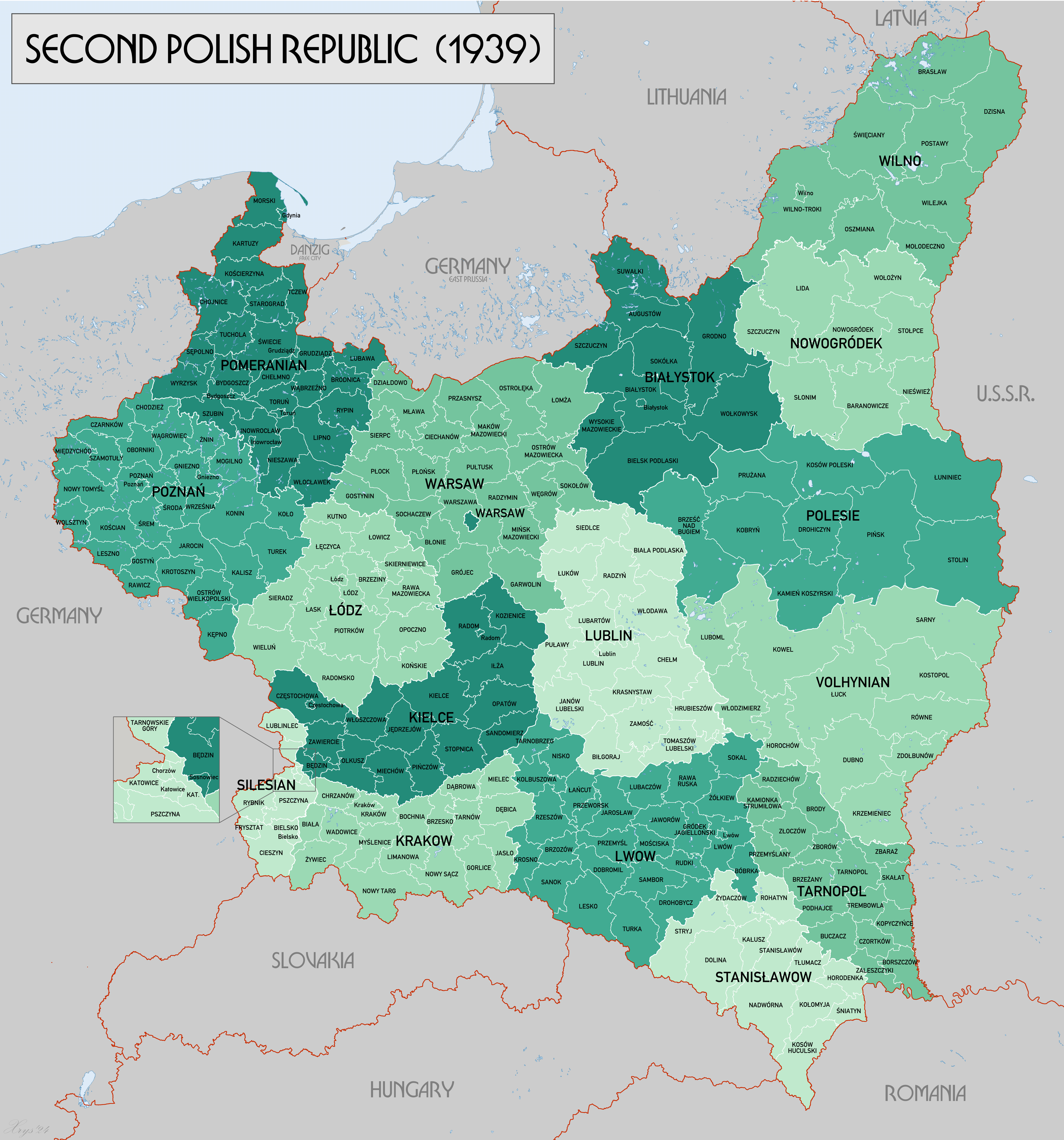
Polish Voivodeships 1919–1939
Total number of Voivodeships - 16, plus the capital city of Warsaw, which was regarded as a separate unit.Biggest Voivodeships (as for August 1, 1939)
* Polesie Voivodeship - area 36 668 km² * Volhynian Voivodeship - area 35 754 km² * Warszawa Voivodeship - area 31 656 km²Smallest Voivodeships (as for August 1, 1939)
* miasto stołeczne Warszawa (the capital city of Warsaw) - area 141 km² * Silesian Voivodeship - area 5 122 km² * Tarnopol Voivodeship - area 16 533 km²Most populous Voivodeships
* Lwów Voivodeship - pop. 3 126 300, * Kielce Voivodeship - pop. 2 671 000, * Łódź Voivodeship - pop. 2 650 100.Least populous Voivodeships
* Nowogródek Voivodeship - pop. 1 057 200, * Polesie Voivodeship - pop. 1 132 200, * miasto stołeczne Warszawa (the capital city of Warsaw) - pop. 1 179 500.Polish Counties 1919–1939
Total number of counties (as for August 1, 1939) - 264, including 23 urban counties.Biggest counties (as for August 1, 1939)
*Wilno
Vilnius ( , ; see also #Etymology and other names, other names) is the capital and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the munic ...
– Troki
Trakai (; see names section for alternative and historic names) is a historic town and lake resort in Lithuania. It lies west of Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. Because of its proximity to Vilnius, Trakai is a popular tourist destination. ...
county (area 5 967 km²),
* Łuniniec county (area 5 722 km²),
* Kowel
Kovel (, ; pl, Kowel; yi, קאוולע / קאוולי ) is a city in Volyn Oblast (province), in northwestern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Kovel Raion (district). Population:
Kovel gives its name to one of the oldest runi ...
county (area 5 682 km²).
Smallest counties (as for August 1, 1939)
* Warszawa-Srodmiescie (mid-Warsaw) (area 10 km²), * city ofBielsko
Bielsko (german: Bielitz, cs, Bílsko) was until 1950 an independent town situated in Cieszyn Silesia, Poland. In 1951 it was joined with Biała Krakowska to form the new town of Bielsko-Biała. Bielsko constitutes the western part of that to ...
(area 10 km²),
* city of Gniezno
Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...
(area 18 km²).
Most populous counties
* city ofŁódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of cant ...
county (pop. 604 600),
* Warszawa-North county (pop. 478 200),
* Katowice county, (pop. 357 300).
Least populous counties
* city of Bielsko county, (pop. 25 400), * city of Gniezno, (pop. 30 700), *Międzychód
Międzychód (, german: Birnbaum) is a town in Greater Poland Voivodeship, Poland, the administrative seat of Międzychód County. It is located on the southern shore of the Warta river, about west of Poznań. Population is 10,915 (2009).
His ...
county, (pop. 31 000).
Sources
* Mały rocznik statystyczny 1939, Nakładem Głównego Urzędu Statystycznego, Warszawa 1939 (Concise Statistical Year-Book of Poland, Warsaw 1939). {{Administrative division of Poland Second Polish Republic Former subdivisions of Poland it:Seconda Repubblica di Polonia#Divisione amministrativa e geografia