Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
and largest city of
Ghana, located on the southern coast at the
Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is i ...
, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the
Accra Metropolitan District
The Accra Metropolitan District is one of the 254 Metropolitan, Municipal and Districts in Ghana, and among the 26 such districts in the Greater Accra Region with a population of 284,124 as of 2021. As of March 2018, it spans an area of approxi ...
, , had a population of 284,124 inhabitants, and the larger
Greater Accra Region, , had a population of 5,455,692
inhabitants.
In common usage, the name "Accra" often refers to the territory of the Accra Metropolitan District as it existed before 2008, when it covered .
[Sum of the land areas of ]Accra Metropolitan District
The Accra Metropolitan District is one of the 254 Metropolitan, Municipal and Districts in Ghana, and among the 26 such districts in the Greater Accra Region with a population of 284,124 as of 2021. As of March 2018, it spans an area of approxi ...
, Ablekuma Central Municipal District
Ablekuma Central Municipal District is one of the twenty-nine districts in Greater Accra Region, Ghana. Originally it was formerly part of the then-larger Accra Metropolitan District
The Accra Metropolitan District is one of the 254 Metropolit ...
, Ablekuma North Municipal District
Ablekuma North Municipal District is one of the twenty-nine districts in Greater Accra Region, Ghana. Originally it was formerly part of the then-larger Accra Metropolitan District in 1988, until a small portion of the district was split off to ...
, Ablekuma West Municipal District
Ablekuma West Municipal District is one of the twenty-nine districts in Greater Accra Region, Ghana.https://mofep.gov.gh/sites/default/files/composite-budget/2020/GR/Ablekuma-West.pdf Originally it was formerly part of the then-larger Accra Metro ...
, Ayawaso Central Municipal District, Ayawaso East Municipal District
Ayawaso East Municipal District is one of the twenty-nine districts in Greater Accra Region, Ghana.https://mofep.gov.gh/sites/default/files/composite-budget/2019/GR/Ayawaso-East.pdf Originally it was formerly part of the then-larger Accra Metro ...
, Ayawaso North Municipal District, Ayawaso West Municipal District
Ayawaso West Municipal District is one of the twenty-nine districts in Greater Accra Region, Ghana.https://mofep.gov.gh/sites/default/files/composite-budget/2019/GR/Ayawaso-West.pdf Originally it was formerly part of the then-larger Accra Metr ...
, Korle Klottey Municipal District
Korle-Klottey Municipal District is one of the twenty-nine districts in Greater Accra Region, Ghana. Originally it was formerly part of the then-larger Accra Metropolitan District in 1988, until a small portion of the district was split off to ...
, Krowor Municipal District, La Dadekotopon Municipal District, Ledzokuku Municipal District
Ledzokuku Municipal District is one of the twenty-nine districts in Greater Accra Region, Ghana. Originally it was formerly part of the defunct Ledzokuku-Krowor Municipal District on 29 February 2008 (which was created from Accra Metropolitan D ...
, and Okaikoi North Municipal District, as per the 2021 census, page 80
This territory has since been split into 13
Districts of Ghana, local government districts: 12 independent municipal districts (total area: 179.0 km²) and the reduced Accra Metropolitan District (20.4 km²), which is the only district within the capital to be granted city status. This territory of 199.4 km² contained 1,782,150 inhabitants at the 2021 census, and serves as the capital of Ghana, while the district under the jurisdiction of the Accra Metropolitan Assembly proper (20.4 km²) is distinguished from the rest of the capital as the "City of Accra".
Formed from the merger of distinct settlements around British
Fort James, Dutch
Fort Crêvecoeur (Ussher Fort), and Danish
Fort Christiansborg
Osu Castle (also known as Fort Christiansborg or the Castle) is a castle located in Osu, Ghana on the coast of the Gulf of Guinea in Africa.
A substantial fort was built by Denmark-Norway in the 1660s, thereafter the fort changed ownersh ...
as
Jamestown,
Usshertown, and
Christiansborg respectively, Accra served as the capital of the British
Gold Coast between 1877 and 1957 and has since transitioned into a modern metropolis. The capital's architecture reflects this history, ranging from 19th-century
colonial architecture to modern
skyscrapers and apartment blocks.
Accra is the
Greater Accra Region's economic and administrative hub, and serves as the anchor of the larger
Greater Accra Metropolitan Area (GAMA), which is inhabited by about 4 million people, making it the
thirteenth-largest metropolitan area in Africa. In 2020, the
Globalization and World Cities Research Network
The Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) is a think tank that studies the relationships between world cities in the context of globalization. It is based in the geography department of Loughborough University in Leicestershir ...
think tank
A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, military, technology, and culture. Most think tanks are non-govern ...
designated Accra as a "Gamma −" level
global city, indicating a growing level of international influence and connectedness.
Etymology
The word ''Accra'' is derived from the
Akan word ''Nkran'' meaning "ants", a reference to the numerous anthills seen in the countryside around Accra. The name specifically refers to
soldier ants, and was applied to both the town and people by the
Twi speakers.
The name of Accra in the local
Ga language
Ga is a Kwa language spoken in Ghana, in and around the capital Accra. There are also some speakers in Togo, Benin and Western Nigeria. It has a phonemic distinction between three vowel lengths.
Classification
Ga is a Kwa language, part ...
is ''Ga'' or ''Gaga'', the same name as that of the
Ga people and a
cognate with ''Nkran''. The word is sometimes rendered with the nasalised vowels as ''Gã'' or ''Gãgã''. Historian
Carl Christian Reindorf
Carl Christian Reindorf (31 May 1834 – 1 July 1917) was a Euro-African-born pioneer historian, teacher, farmer, trader, physician and pastor who worked with the Basel Mission on the Gold Coast. He wrote '' The History of the Gold Coast and ...
confirmed this etymology, proposing a link between the martial qualities and migratory behaviour of the local ants and those of the Ga people. The link between the
ethnonym and ants was explicitly reflected in the recognition of anthills as sacred places. Often ringed by sacred fences (''aklabatsa''), the tall red mounds dotting Accra's hinterland were seen as microcosms of human community and as nodal points between the known world and the world of the dead.
While the Ga used the reference to the invasive species of dark-red swarming ants to connote military prowess and their ancient conquest of
Guang speakers residing in the Accra Plains, the Akan-speaking appropriation and translation of this metaphor had a less than generous meaning. Instead of viewing Ga speakers as a formidable military force, the Akan-speaking term "''Nkran''" cast Ga peoples as pests or nuisances to be controlled or exterminated.
The name ''Ga'' is actually a cognate of the name ''Akan'', one of a few words in which corresponds to in Akan. ''Ga'' also gave its name to the
Ga districts surrounding Accra.
The spelling ''Accra'' was given to ''Nkran'' by
Europeans.
An earlier spelling used by the
Danes was ''Akra.''
History
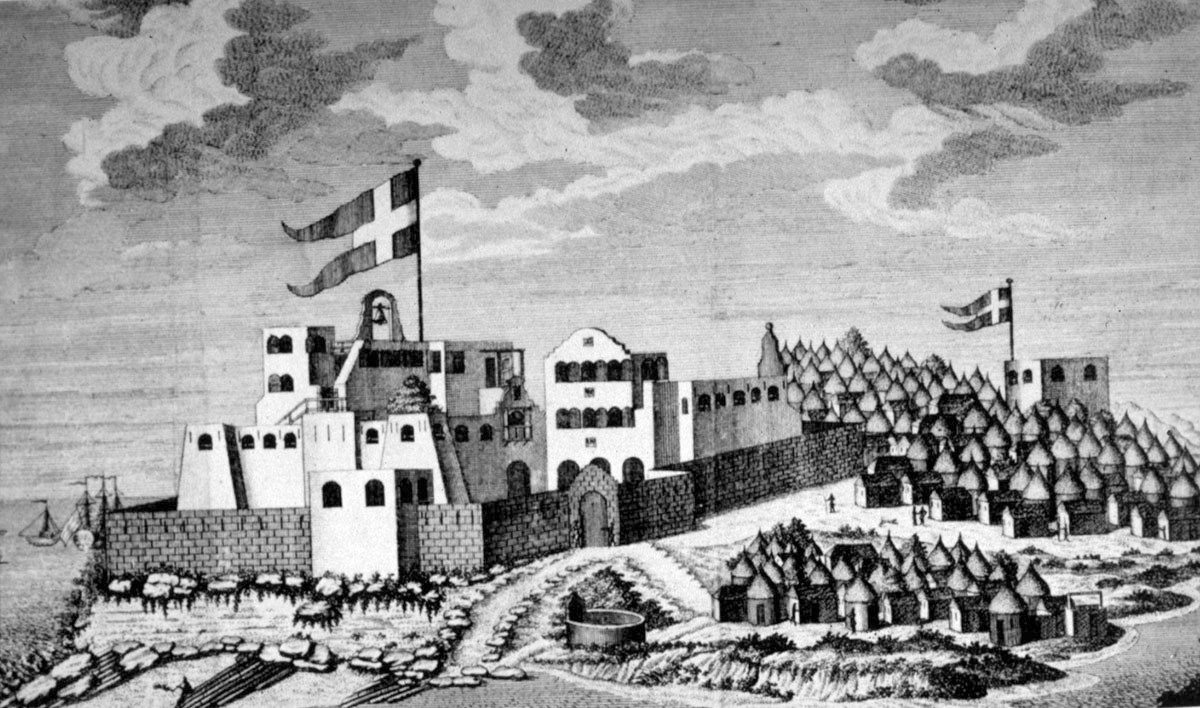
The main
Ga group known as the Tumgwa Were led by Ayi Kushie arrived by sea. When the Guan (
Larteh
Larteh is a language of southeastern Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast ...
s) on the coast saw them on their canoes at sea, they looked like ants. Hence, the Lartehs refer to them as Nkran (ants). Nkran was later corrupted by the
Danes to Akra, then to present-day Accra. ''Nkran'' in the
Ga language
Ga is a Kwa language spoken in Ghana, in and around the capital Accra. There are also some speakers in Togo, Benin and Western Nigeria. It has a phonemic distinction between three vowel lengths.
Classification
Ga is a Kwa language, part ...
is ''Gaga'', thus they also started calling themselves Ga. Due to their sheer numbers, the indigenous Lartehs thus relocated to the
Akuapem ridge.
Initially, Accra was not the most prominent trading centre; the trade hubs of the time were the ports at
Ada
Ada may refer to:
Places
Africa
* Ada Foah, a town in Ghana
* Ada (Ghana parliament constituency)
* Ada, Osun, a town in Nigeria
Asia
* Ada, Urmia, a village in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran
* Ada, Karaman, a village in Karaman Province, T ...
and
Prampram
Prampram is a coastal town in the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. The town is located in the Ningo Prampram District.
Prampram (Gbugbla), the capital of Ningo-Prampram, is 15 minutes' drive from the port city of Tema and 45 minutes from Accra, th ...
, along with the inland centres of
Dodowa and
Akuse
Akuse is a town in the Lower Manya Krobo district of the Eastern Region of Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the sout ...
. The Dutch built the nearby outposts of
Ussher Fort
Ussher Fort is a fort in Accra, Ghana. It was built by the Dutch in 1649 as Fort Crèvecœur, and is a day's march from Elmina and to the east of Accra on a rocky point between two lagoons. It was one of three forts that Europeans built in the reg ...
while the British and the Swedes built James Fort and Christiansborg castles, respectively. By the 17th century, Portugal, France and Denmark, had constructed forts in the city.
Britain gradually acquired the interests of all other countries beginning in 1851, when Denmark sold
Christiansborg (which they had acquired from the Swedes) and their other forts to the British. The Netherlands was the last to sell out, in 1871. In 1873, after decades of tension between the British and
Ashantis, the British captured
Kumasi, destroying portions of the city. The British then captured Accra in 1874, and in 1877, at the end of the second
Anglo-Asante War, Accra replaced
Cape Coast as the capital of the British
Gold Coast. This decision was made because Accra had a drier climate relative to Cape Coast. Until this time, the settlement of Accra was confined between Ussher Fort to the east and the
Korle Lagoon to the west.
As the newly established Gold Coast's administrative functions were moved to Accra (1877), an influx of British colonial administrators and European settlers grew around the Christiansborg (modern Osu, Ministries, Ridge, Labone, and Cantonments) began, and the city began to expand to accommodate the new residents. Victoriaborg was formed in the late 19th century as an exclusively European residential neighbourhood, located to the east of the city limits of the time. The boundaries of Accra were further stretched in 1908. This expansion entailed the creation of a native-only neighbourhood, intended to accommodate members of the native population as a means of relieving congestion problems in the overcrowded city centre.
Adabraka
Adabraka is a town in the Korley Klottey Municipal Assembly, a Municipality of the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. It was the first and the most posh neighborhood in Ghana during the British era.
Education
Adabraka was known for the O'Reilly ...
was thus established to the north of the city.
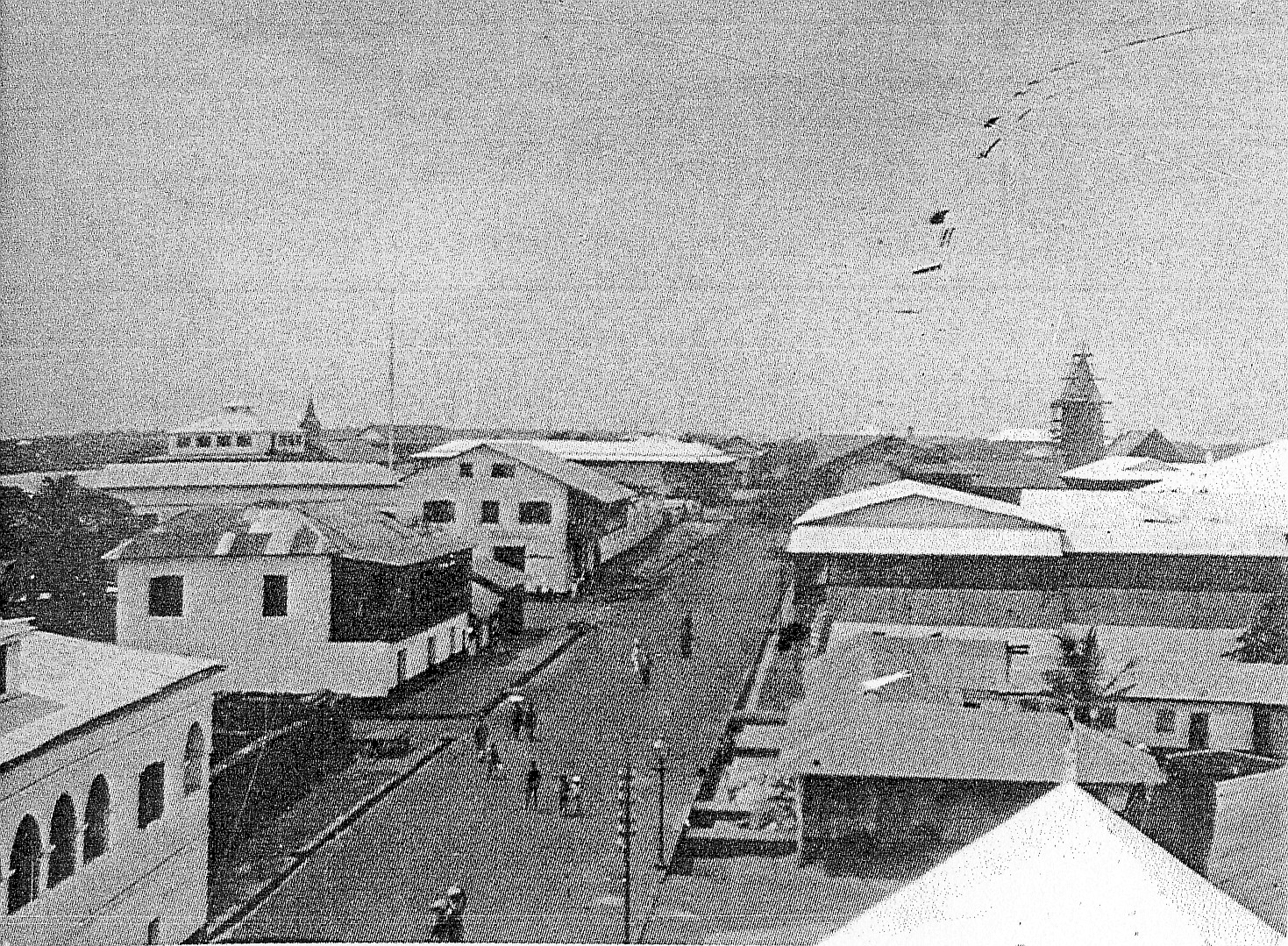

One of the most influential decisions in the history of the city was that of building the Accra-Kumasi railway in 1908. This was to connect Accra, the country's foremost port at that time, with Ghana's main
cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter an ...
-producing regions. In 1923, the railway was completed, and by 1924, cocoa was Ghana's largest export.
The colonial era heavily influenced the shape that Accra took during this period. For example, the
segregation of European and African neighbourhoods was mandated by law until 1923, and all new buildings were required to be built out of stone or concrete. Despite these regulations, European settlers in the Gold Coast were very hesitant to invest any large amount of money into the city to maintain its infrastructure or improve public works. This did not change until the governorship of
Sir Frederick Gordon Guggisberg during which period the three separate settlements (Osu, La and Jamestown) merged to become modern Accra. Guggisberg's administration laid out the present grid networked neighborhoods of Tudu, Adabraka and Asylum Down.
Among the achievements of Guggisberg was the building of a bridge across the Korle Lagoon in 1923, which opened the land west of the lagoon for settlement. Guggisberg also oversaw the building of a major hospital (Korle-Bu) and secondary school (Achimota). Such improvements led to an increase in Accra's population due to the
migration of rural dwellers into the city, and the immigration of increasing numbers of British businessmen and administrators.
After World War II

In the years following
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the neighbourhoods of Ridge and Cantonments were planned as low-density developments for Europeans, while many rural migrants settled in neighbourhoods which had not yet been incorporated into Accra's municipal boundary, such as Nima and surrounding areas. Thus, the development of these neighbourhoods was unregulated by the government, creating a crowded and jumbled
shanty-town landscape.
Another area of Accra that took shape at this time was the central business district (CBD). More administrative buildings were built on High Street, forming a massive judicial/administrative complex. Additionally, the expansion of the economy led to many more commercial buildings being built in the CBD.
In 1944, Accra's city planner Maxwell Fry devised a town plan, which was revised in 1958 by B.D.W. Treavallion and Alan Flood. Although the Fry/Trevallion plan was never followed through, it illustrated the British vision of how Accra should develop.
Fry/Treavallion plan
In the Fry/Treavallion plan, a reorganisation of the CBD was called for, as well as the development of the coastal region of the city. To reorganise the CBD, the planners decided to superimpose a tight street grid north of Fort Ussher.
To the east of this newly organised CBD, the planners hoped to preserve a broad, open space for a restaurant, country club, and
polo and
cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
fields. Additionally, the British planners intended to build large numbers of public squares, fountains, and ornamental pools and statues throughout the city, as well as a vast Parliament Complex in the city centre. Lastly, the Fry/Treavallion plan included plans to make the coastal region an extension of the exclusive European neighbourhood of Victoriaborg, and to create a recreational preserve for the elite. However, the
British Gold Coast ended before the Fry/Treavallion plan was enacted.
Nkrumah Plan

When
Kwame Nkrumah became Ghana's first postindependence
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
in 1957, he created his own plan for Accra's development. Instead of creating spaces to serve the elite, Nkrumah sought to create spaces to inspire pride and nationalism in his people and people throughout Africa.
Rather than creating ornamental fountains and a large Parliament complex, Nkrumah decided to build landmarks such as Independence Square, the State House, and the Organisation of African Unity building, and to refurbish Christianborg Castle. Nkrumah decided to leave the Atlantic coastal region undeveloped, so as to not detract attention from the Community Centre or Independence Square, lending both spaces symbolic significance. The Nkrumah plan did not emphasise order nearly as much as the Fry/Treavallion plan did; whereas the British plan strove to lessen crowding in the commercial district and help relieve the overcrowding of neighbourhoods bordering the CBD, the Nkrumah plan allowed for continued compression of commercial establishments into the CBD, as well as increased migration into Jamestown.
The modern city is centred on the original British, Danish, and Dutch forts and their surrounding communities:
Jamestown near the British
James Fort,
Osu near the Danish fort of
Christiansborg (now
Osu Castle), and
Ussherstown near the Dutch
Ussher fort
Ussher Fort is a fort in Accra, Ghana. It was built by the Dutch in 1649 as Fort Crèvecœur, and is a day's march from Elmina and to the east of Accra on a rocky point between two lagoons. It was one of three forts that Europeans built in the reg ...
.
Tourist attractions include the National Museum of Ghana, the Ghana Academy of Arts and Sciences, the National Archives of Ghana and Ghana's central library, the National Theatre, the Accra Centre for National Culture, and the
Jamestown Lighthouse
The Jamestown lighthouse is located in the Jamestown neighbourhood of Accra, Ghana. The structure was originally built in the 1930s, replacing an earlier lighthouse that had been built in 1871.
It consists of a stone tower with lantern and gal ...
.
The
Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
,
Supreme Court of Ghana
The Supreme Court of Ghana is the highest judicial body in Ghana. Ghana's 1992 constitution guarantees the independence and separation of the Judiciary from the Legislative and the Executive arms of government.1992 Constitution Article 125( ...
,
Black Star Square
Black Star Square, also known as Independence Square, is a public square in Accra, Ghana, bordered by the Accra Sports Stadium and the Kwame Nkrumah Memorial Park. The square often hosts the annual independence celebrations as well as other nati ...
and the
Bank of Ghana are also located in Accra.
The city is also a transportation hub, home to the
Kotoka International Airport
Kotoka International Airport is an international airport in Accra, the capital of Ghana. The airport is operated by Ghana Airports Company Limited (GACL), which has its offices on the airport property. It is the sole international airport in ...
, and railway links to
Tema,
Sekondi-Takoradi and
Kumasi. Accra has become a location for national and international business conferences, such as the BarCamp Ghana series, organised by GhanaThink Foundation.
Geography
Owing to its location in the
Dahomey Gap
In West Africa, the Dahomey Gap refers to the portion of the Guinean forest-savanna mosaic that extends all the way to the coast in Benin, Togo, and Ghana, thus separating the forest zone that covers much of the south of the region into two separat ...
, where the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean coast runs parallel to the prevailing moist monsoonal winds, Accra features a very marginal
hot semi-arid climate (
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
: BSh) that borders on a
tropical wet and dry climate (
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
: Aw/As). The average annual rainfall is about 730 mm, which falls primarily during Ghana's two rainy seasons. The chief rainy season begins in April and ends in mid-July, whilst a weaker second rainy season occurs in October. Rain usually falls in short intensive storms and causes local flooding in which drainage channels are obstructed.
Very little variation in temperature occurs throughout the year. The mean monthly temperature ranges from in August (the coolest) to in March (the hottest), with an annual average of . The "cooler" months tend to be more
humid than the warmer months. As a result, during the warmer months and particularly during the windy
harmattan season, the city experiences a breezy "dry heat" that feels less warm than the "cooler" but more humid rainy season.
As a coastal city, Accra is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change and sea level rise, with population growth putting increasing pressure on the coastal areas. Drainage infrastructure is particularly at risk, which has profound implications for people's livelihoods, especially in informal settlements. Inadequate planning regulation and law enforcement, as well as perceived corruption in government processes, lack of communication across government departments and lack of concern or government co-ordination with respect to building codes are major impediments to progressing the development of Accra's drainage infrastructure, according to the
Climate & Development Knowledge Network
The Climate and Development Knowledge Network (CDKN) works to enhance the quality of life for the poorest and most vulnerable to climate change. CDKN does this by combining research, advisory services and knowledge management in support of local ...
.
As Accra is close to the
equator, the daylight hours are practically uniform during the year. Relative humidity is generally high, varying from 65% in the midafternoon to 95% at night. The predominant wind direction in Accra is from the WSW to NNE sectors. Wind speeds normally range between 8 and 16 km/h. High wind gusts occur with
thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are some ...
s, which generally pass in
squalls along the coast.
The maximum wind speed record in Accra is 107.4 km/h (58 knots). Strong winds associated with thunderstorm activity often cause damage to property by removing roofing material. Several areas of Accra experience microclimatic effects. Low-profile
drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
s with a north–south orientation are not as well ventilated as those oriented east–west.
Air is often trapped in pockets over the city, and an insulation effect can give rise to a local increase in air temperature of several degrees. This occurs most notably in the Accra Newtown sports complex areas.
Administration
The administration of Accra occurs at two levels. Strategic initiatives, such as the urban transportation project, are coordinated between district authorities, while local administration is carried out by local government authorities, which are responsible for most local services, such as local planning, local roads and refuse collection within their area of jurisdiction.

The former territory of the Accra Metropolitan District, ,
as it existed before 2008, is now divided into 13 separate local government districts, all governed as municipal assemblies with their own town hall and a municipal executive appointed by the president of the republic. Each municipal assembly is responsible for most local services, such as local planning and refuse collection. The reduced
Accra Metropolitan District
The Accra Metropolitan District is one of the 254 Metropolitan, Municipal and Districts in Ghana, and among the 26 such districts in the Greater Accra Region with a population of 284,124 as of 2021. As of March 2018, it spans an area of approxi ...
(also referred to as City of Accra), , once comprised the entirety of Accra until the Ledzokuku, Krowor, La Dadekotopon, Ablekuma North, Ablekuma Central, Ablekuma West, Ayawaso East, Ayawaso North, Ayawaso Central, Ayawaso West, Okaikwei North, and Korley Kottey districts were carved out as separate municipal districts between 2008 and 2019.
Districts
Accra Metropolitan District (City of Accra)
The Accra Metropolitan District is one of the 13 local government districts that contains the historic center and the primary central business district (CBD) of Accra. To promote efficiency in the administrative machinery and also meet the ever pressing demands for amenities and essential services, the district is divided into the Ashiedu Keteke, Okaikoi South, and Ablekuma South sub-metropolitan districts.
The Accra Metropolitan Assembly, which governs the City of Accra within the boundaries of the
Accra Metropolitan District
The Accra Metropolitan District is one of the 254 Metropolitan, Municipal and Districts in Ghana, and among the 26 such districts in the Greater Accra Region with a population of 284,124 as of 2021. As of March 2018, it spans an area of approxi ...
, is led by a Metropolitan Chief Executive who is appointed by the
President of the Republic of
Ghana. The
Mayor of Accra is
Mohammed Adjei Sowah, who was appointed by President
Nana Akufo-Addo
Nana Addo Dankwa Akufo-Addo ( ; born 29 March 1944) is a Ghanaian politician who has served as the president of Ghana since 7 January 2017. In 2020, he was re-elected for his second term, which will end on 6 January 2025. Akufo-Addo previously ...
and approved unanimously by the AMA on 23 March 2017.
The Ablekuma South sub-metropolitan district covers an area of and is bordered by the Ablekuma Central and Ablekuma North Municipal Assemblies, and the Ashiedu Keteke sub-metropolitan district. It includes 5 electoral areas: Korle Gonno, Korlebu, Chorkor, Mamprobi, and New Mamprobi.
Communities within the Okaikoi South sub-metropolitan district include Darkuman, New Fadama, Kaneshie, Bubiashie, and Avenor. The sub-metro has 8 electoral areas namely Awudome, Goten, Kaatsean, Mukose, Bubuashie, Bubui, Avenor and Kaneshie.
The Ashiedu Keteke sub-metropolitan district covers the Central Business District (CBD) and as such the hub of major commercial activities within the Metropolis. Majr markets include Makola, Agbogbloshie, and Kwasiodwaso. There are 8 electoral areas namely Ngleshie, Mudor, Kinka, Nmlitsagonno, Amamomo, Korle Wonkon, and Korle Dudor.
Ledzekuku Municipal District
The Ledzekuku Municipal District, with its administrative capital at
Teshie
Teshie is a coastal town in the Ledzokuku Municipal District, a district in the Greater Accra Region of southeastern Ghana. Teshie is the ninth most populous settlement in Ghana, with a population of 171,875 people.
Politics
Teshie is in th ...
, covers an estimated area of .
Krowor Municipal District
The Krowor Municipal District was carved out of the Ledzokuku-Krowor Municipal District in 2018. Its administrative capital is
Nungua.
La Dadekotopon Municipal District
The La Dadekotopon Municipal District, with its administrative capital at La, was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District in 2012. The Kotoka International Airport, Airport City, Accra Mall, and the US Embassy are located within the district, which covers an area of
Other communities within this district include Cantonments, Labone, and Burma Camp.
Ablekuma North Municipal District
The Ablekuma North Municipal District was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District in 2018 with an administrative capital at
Darkuman Kokompe.
Ablekuma Central Municipal District
The Ablekuma Central Municipal District covers a total land area of .
Its administrative capital is
Lartebiokorshie
Lartebiokoshie is a town in the Ablekuma Central Municipal Assembly, a district of the Greater Accra Region of Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guin ...
.
Ablekuma West Municipal District
The Ablekuma West Municipal District was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District in 2018 and its administrative capital is
Dansoman
Dansoman is a suburban town in the Greater Accra Region of Ghana, located near Accra and Takoradi district of the Accra Metropolitan Area. The town is known for being one of the largest estates in West Africa.
History
The town was founded by the ...
.
Ayawaso East Municipal District
The Ablekuma East Municipal District was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District in 2018 and its administrative capital is
Nima.
Ayawaso North Municipal District
The Ablekuma North Municipal District was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District in 2018 and its administrative capital is
Accra Newtown
Accra New Town is a town in the Accra Metropolitan district, a district of the Greater Accra Region of Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the ...
.
Ayawaso Central Municipal District
The Ayawaso Central Municipal District was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District with an administrative capital being
Kokomlemle.
Ayawaso West Municipal District
The Ayawaso Central Municipal District was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District and its administrative capital is
Dzorwulu.
Okaikwei North Municipal District
Korley Kottey Municipal District
The Korley Klottey Municipal District was carved out of the Accra Metropolitan District in 2019 and covers an area of
Some of the communities within the district include Osu, Ringway Estates, Asylum Down, North Ridge, West Ridge, Ministries, Gold Coast City, North Adabraka, and Tudu. There are 9 electoral areas namely Osu Doku, Ringway Estates, Kinkawe, Osu Alata, Asylum Down, North Adabraka, Tudu, Odorna/Sahara, and Official Town.
Cityscape
Accra Central
The Ring Road, extending from the Korle Lagoon in the west, north to Kwame Nkrumah Circle, following east to the juncture of Independence Avenue, and continuing on to
Osu, forms a ring around the oldest districts of Accra, and separates central Accra from the outlying suburbs.
Central Accra includes the CBD, which consists of the historic districts of
Usshertown, Tudu,
Victoriaborg,
West Ridge, and
East Ridge, as well as the historic residential districts of
Jamestown,
Adabraka
Adabraka is a town in the Korley Klottey Municipal Assembly, a Municipality of the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. It was the first and the most posh neighborhood in Ghana during the British era.
Education
Adabraka was known for the O'Reilly ...
, Asylum Down,
North Ridge and
Christiansborg/Osu.
Although satellite business districts such as the Airport City have been established across the city, Central Accra remains the administrative and cultural centre of Accra, hosting government ministries, hotels, businesses, and financial institutions.
Central Accra's principal attractions include the
Kwame Nkrumah Mausoleum
The Kwame Nkrumah Mausoleum and memorial park is located in downtown Accra, the capital of Ghana.
History
It is dedicated to the prominent Ghanaian President Kwame Nkrumah
Kwame Nkrumah (born 21 September 190927 April 1972) was a Ghan ...
, the
National Museum,
Independence Square, the
National Theatre, and the
Ohene Djan Stadium.
Accra North
Northern Accra is a residential and business district. The area contains the "37" Military Hospital,
The Flagstaff House
Golden Jubilee House, or Jubilee House, is the presidential palace in Accra that serves as a residence and office to the President of Ghana. Jubilee House is built on the site of a building that was constructed and used for administrative pur ...
, several foreign
embassies,
Achimota School
Achimota School ( /ɑːtʃimoʊtɑː/ ), formerly Prince of Wales College and School at Achimota, later Achimota College, now nicknamed Motown, is a co-educational boarding school located at Achimota in Accra, Greater Accra, Ghana. The school w ...
, Achimota Golf Park, and the
University of Ghana's Legon campus, which serves as Accra's northern boundary.
Geographically, the areas north of Ring Road West and Central, east of Winneba/Graphic Road, west of Liberation Road, and the districts just north and south of the Kwame Nkrumah motorway are regarded as Northern Accra. Some areas North of Accra include, Ashongnman, Madina, Haatso, North and West Legon and others
Accra East
Eastern Accra is largely residential and geographically north of Ring Road East, stretching as far north as Kwame Nkrumah Motorway; the district is bordered to the west by Liberation Road.
Accra West
Western Accra is largely a residential and business area. Whilst geographically less expansive than the northern and eastern reaches of the city as a result of the large saltponds of Tettegu and Aplaku, it nonetheless boasts one of Accra's most important landmarks, the
Korle Bu Teaching Hospital
Korle-Bu Teaching Hospital (KBTH) is a public teaching hospital located in the Ablekuma South Metropolitan District in Accra, Ghana. It is the only public tertiary hospital in the southern part of the country. It is a teaching hospital affiliate ...
.
Geographically, the areas west of Ring Road West, extending as far west as the saltponds and south of Graphic Road, are considered Accra West.
Demographics
The period between 1960 and 1970 saw rapid industrialisation and expansion in Accra's manufacturing and commercial sectors. This contributed to high
rural-urban migration
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly the ...
to the city, and consequently a high population growth rate. The stagnation of the Ghanaian economy during the 1970s slowed the growth of Accra's population, as shown by the falling growth rate of the 1970–1984 intercensal years. Later, however, the decline in agriculture in rural communities in Ghana and rising industrialisation in urban regions, coupled with the late-1980s boom in the
service sector, once again propelled immigration to Accra. The primacy of the Accra Metropolitan Area as the Greater Accra region's administrative, educational, industrial and commercial centre continues to be the major force for its population growth, with immigration contributing to over 35% of the Accra's population growth.
Distribution and density
The gross density of population for the Accra Metropolitan Area in 2000 was 10.03 persons per hectare, compared to 6.23 per hectare in 1970. The highest densities were recorded in the Accra Metropolitan Assembly, with an overall average of 69.3 persons per hectare. At the community level, densities exceeding 250 persons per hectare occurred mostly in the immigrant and depressed areas in the oldest parts of Accra, such as Accra New Town, Nima, Jamestown and Usshertown. In higher-income areas, densities ranged between 17.5 and 40 persons per hectare.
Population distribution by age and gender
Accra's population is a very youthful one, with 56% of the population being under 24 years of age. This predominance of young people is not expected to decline in the foreseeable future. Fifty-one percent (51%) of the population are females, and the remaining 49% males. This gives a males-to-females ratio of 1:1.04. The greater number of females is a reflection of the nationwide trend, where the estimated ratio of males to females is 1:1.03.
Migration
Decentralisation is expected to reduce the migration rates in Accra. An assessment of the extent of migration to Accra, based on present locality and gender, reveals that 45% of residents in Accra are African immigrants from countries across the African continent.
Housing

Parts of Central Accra comprise a mixture of very low-density development with under-used service infrastructure on the one hand, high-density development and overstretched infrastructure services on the other. The growth of Accra has led to the neglect of some of the old settlements, whilst efforts are being made to provide the newly developing suburban areas with services and infrastructure to cater for the needs of the middle-income earners. Peripheral residential development in Accra barely has sufficient infrastructure to support it. There are also large numbers of uncompleted houses, interspersed with pockets of undeveloped land, which are often subject of litigation, due to the inability of organisations and individuals who own them to complete or develop them due to lack of funds. Housing can be grouped into three broad categories: the low-income, middle-income and high-income areas. The low-income housing areas comprise Osu, Jamestown, Adedenkpo, Chorkor, La, Teshie, Nungua, Sukura, Kwashieman, Odorkor, Bubiashie, Abeka, Nima, Maamobi and Chorkor. Altogether, these areas accommodate about 58% of Accra's total population. Most of Accra's informal businesses are located in low-income areas.
Almost all low-income areas are built up with little room for expansion. This is particularly so in the areas of the inner city. The middle-income areas of Accra are predominantly populated by Ghanaian citizens and business, administrative and professional families. Much of the housing in these areas has been provided by state, parastatal and private sector organisations and individuals. The middle-income areas include Dansoman Estates, North Kaneshie Estates, Asylum Down, Kanda Estates, Abelempke, Achimota, Adenta and Tesano. Usually, these areas, unlike the low-income areas, are planned developments, but are in need of infrastructure services. Building materials and general housing conditions are of better quality. The middle-income group comprises 32% of the city's population of which are Ghanaian citizens make up. The high-income areas provide housing for the remaining 10% of the population of which Ghanaian citizens also make up. They include areas like North Ridge and West Ridge, Ringway Estates, north Labone Estates, Airport Residential Area, Roman Ridge, East Legon.
These areas are all planned and have well developed infrastructure with spacious and landscaped ground in sharp contrast with, particularly, the low-income areas. Buildings are usually built with
sandcrete blocks, and have walls and roofed with aluminium, or
asbestos roofing sheets. There are also high-income peripheral areas like Haatso, Kwabenya, Pokuase, Adenta, Taifa, Mallam, where development of engineering infrastructure is not yet complete. These areas developed ahead of infrastructure, however the Achimota-Ofankor
controlled-access highway was scheduled to open in May 2012,
dual carriageway road construction was also due to be completed in 2012. In total, 84.4% of all houses in the Accra Metropolitan Area have their outside walls made up of cement. Similarly, houses found within Accra have 99.2% of their floor materials made up of cement.
Economy
In 2008, the
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
estimated that Accra's economy only constituted around
US$3 billion of Ghana's total gross domestic product (GDP). The economically active population of Accra is estimated to be 823,327.

Accra is a centre for manufacturing, marketing, finance, insurance, and transportation. Its financial sector incorporates a central bank, nine commercial banks (with 81 branches), four development banks (with 19 branches), four merchant banks (with seven branches), three discount houses, one home finance mortgage bank, multiple
building societies,
Ghana Stock Exchange,
foreign exchange bureaus, finance houses, insurance companies, insurance brokerage firms, two savings and loans companies, and numerous real estate developers, with industrial sites and residential developments. The road network in the Accra Metropolitan Area totals in length.
There are over 50,506 identified residential properties in Accra, and about 4,054 commercial/industrial/mixed properties, with a total rateable value of GH¢13,849,014.
There are also supermarkets, 36 facilities for both on–street and off-
street parking, and shopping malls, as well as several facilities for sports and recreation.
Sectors of the economy
The sectors of Accra's economy consist of the primary, secondary (manufacturing, electricity, gas, water, construction) and tertiary sectors (supermarkets, shopping malls, hotel, restaurant, transportation, storage, communication, financial intermediation, real estate service, public administration, education, health and other social services). The tertiary service sector is the city's largest, employing about 531,670 people. The second-largest, the secondary sector, employs 22.34% of the labour force, or around 183,934 people. 12.2% of the city's workforce are reportedly unemployed, totalling around 114,198 people.
Primary sector

Accra's smallest economic sector, the primary sector, employs approximately 91,556 people. The predominant economic activities are
fishery and
urban agriculture
Urban agriculture, urban farming, or urban gardening is the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. It encompasses a complex and diverse mix of food production activities, including fisheries and ...
, with fishery accounting for 78% of production labour. Urban agriculture in Accra centres on the growth of vegetables, several crops and poultry. The
fishery industry is the most important sub-sector, with 10% of the catch being exported and the rest consumed locally. The industry is characterised by extreme seasonableness, operating primarily between June and September. Although most deep-water Atlantic fishing around Accra takes place in the June–September period, fishery operations take place close to the shore throughout the year, and there are clear indications of the
depletion of fish stocks in the near future. Fishing operations are most prominent at the Jamestown, La, Teshie, Nungua and Chorkor fishing shores.
Education
Pre-school
Pre-school comprises nursery and kindergarten. In 2001, there were 7,923 children (3,893 girls and 4,030 boys) in
pre-schools in Accra. In 2010, the enrolment rate at Pre-school was 98%.
Pre-schools are regulated by the Ministry of Employment and Social Welfare, and are mostly privately owned and operated. In 2001, there were 62 government-owned pre-schools in the Accra metropolis.
Primary school
Primary school enrolment of girls is higher than that of boys.
In 2010, the enrollment rate at primary school level was 95%.
Junior high school (JHS)
The Junior High School is part of Ghana's basic education program. Its nationwide implementation began on 29 September 1987.
In the 2001/2002 academic year, 61,080 pupils had enrolled in Accra, representing 57.17% of the 129,467 school-age 12–to-14-year-olds. In 2010, the enrolment rate at Junior high school level was 95%.
The ratio of girls is also higher at this level.
Senior high school (SHS)
The transition rate between junior high and senior high school increased from 30 per cent in 1990 to 50 per cent in 2001. The number of students grew by 23,102 between 1990 and 2005, an increase of about 2,310 a year, since 2010 the senior high school enrolment rate has been 95%.
Ghana International School
Ghana International School is a coeducational international school located at Cantonment, Accra Ghana. Ghana International School has an enrollment of diverse backgrounds. The student population derives from many countries and cultural orientatio ...
(GIS), a private non-profit
A-Level school founded in 1955 for children from ages 3–18, is located in Accra's Cantonments. Abelemkpe is the home of
Lincoln Community School, a private, non-profit
International Baccalaureate (IB) school for students aged 3–18, established in 1968. The
American International School and
Abundant Grace Academy are also situated in Accra.
A number of notable public secondary schools lie on the outskirts of Accra:
Achimota School
Achimota School ( /ɑːtʃimoʊtɑː/ ), formerly Prince of Wales College and School at Achimota, later Achimota College, now nicknamed Motown, is a co-educational boarding school located at Achimota in Accra, Greater Accra, Ghana. The school w ...
, commonly referred to as "Motown", which was founded in 1924 and opened in 1927; the
Accra Academy
Accra Academy is a non-denominational day and boarding boys' school. It is located at Bubuashie near Kaneshie in the Greater Accra Region. The school was established as a private secondary educational institution in 1931 and gained the status o ...
ranked in top ten high schools in Africa, known as "Accra Aca"; the
Presbyterian Boys' Secondary School in
Legon, commonly known as "Presec";
Wesley Grammar School
Wesley Grammar School is a co-ed school, founded in 1956, in Accra, Ghana. Wesley Grammar School is located in Dansoman in the Greater Accra region. The Wesley Grammer is a missionary school. Though it is under Ghana Education Service it manage by ...
– WESS-G Dansoman,
St. Mary's Senior High School commonly referred to as "Merriez"- is a well-known girls' boarding school in Ghana;
St. Thomas Aquinas Senior High School, commonly known as "Quinas";
Accra High School
Accra High School is a Senior High school located in Accra, Ghana in West Africa. It initially started as a Boys School.
History
Accra High School was founded by the late Rev. James Thomas Roberts on 17 August 1923. The school, was located at b ...
commonly known as ("Ahisco");
West Africa Secondary School
West Africa Senior High School (WASS) is a second-cycle institution located at Adenta in the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. The school is a government assisted, mixed day and non-denominational institution providing a three-year senior high sch ...
, commonly known as "WASS"; the
Accra Girls' Senior High School, commonly known as "Agiss";
Kaneshie Secondary Technical School
Kaneshie is a suburb in the Accra Metropolitan district, a district of the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. The name was derived from a word in the Ga-Adangbe , that is "Kane Shie Shie", meaning "under the lamp" referring to its beginnings as a nig ...
("
Kateco"); the Armed Forces Secondary Technical; and St. John's
Grammar School
A grammar school is one of several different types of school in the history of education in the United Kingdom and other English-speaking countries, originally a school teaching Latin, but more recently an academically oriented secondary school ...
; among others.
Universities
The
University of Ghana is located north of the city centre at
Legon. A number of other public and private universities and
tertiary institution
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including uni ...
s have since been founded in Accra, some of which are listed below.
Healthcare
Hospitals
See
List of hospitals in the Greater Accra Region.
Environment
Water
As a growing city, Accra has a water supply and scarcity challenge.
Water access uses a patchwork of different delivery processes.
Pollution
Accra as a rapidly growing city, with lots of vehicles and other urban pollution sources, has also an increasing amount of air pollution and
plastic pollution
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are cate ...
. Accra's urban ecosystem has been a site of dumping by international waste networks, with the
Agbogbloshie
Agbogbloshie is a nickname of a commercial district on the Korle Lagoon of the Odaw River, near the center of Accra, Ghana's capital city in the Greater Accra region. Near the slum called "Old Fadama", the Agbogbloshie site became known as a ...
suburb known for its highly toxic e-waste recycling sites, and the
Kantamanto Market as handling an overwhelming flow of used
fast fashion from other parts of the world.
Both sites are sources of pollution and trash for other parts of the urban ecosystem.
Air pollution varies seasonally, but the average measure PM
2.5 average concentration of 49.5 μg/m
3. Live monitoring of air pollution is done at 3 sites in the city of Accra. A 2021 review by the
Environmental Protection Agency in Ghana found that the levels were well exceeding both national and international standards for health.
Plastic management is also an increasing challenge. Use of plastic water bottles,
water sachets and other packaging for food safety, as well as increased use of plastic during events like COVID-19.
The beaches around Accra have significant plastic pollution, and surrounding fisheries are heavily impacted by plastics.
Multiple non-profit organizations have been formed to collect the plastic and an increasingly growing network of recyclers and informal waste recovery networks.
However, activists and researchers largely attribute the issue to upstream use of plastics.
Green spaces
Rapidly growing population and construction within the city has been resulting in a reduction in
Urban green space. A 2021 study of low income communities in the city found increasing concern and desire among these communities for urban green spaces for recreation and health. A 2018 study of greenspaces in the city, found the ones that do exist are important for mammal biodiversity in the city.
Transportation
Accra is on the Atlantic coast but it has not served as a port city since the 1950s. Instead, the Port of
Tema, about 29 km to the east along the Atlantic coast, was developed for deepwater shipping to and from Ghana as it can accommodate larger ships; the port opened in 1961. Tema is part of the metropolitan area of Accra.
Transport within Accra includes roads and rails, and an international airport
Rapid transit
There are Public Transports from Accra to major cities such as
Kumasi;
Tamale,
Mim, Ahafo
Mim is a city in the Asunafo North Municipal District in the Ahafo Region of Ghana. It is a nodal town between Sunyani and Goaso via the N12 Highway. The distance from Mim to Sunyani is 64 km whilst that of Mim to Goaso is 14 km.
Mim ...
;
Cape Coast,
Sunyani;
Takoradi;
Tema;
Ho;
Wa;
Bolgatanga;
Elubo;
Aflao,
Techiman
Techiman is a city and is the capital of Techiman Municipal and Bono East Region of Ghana. Techiman is a leading market town in South Ghana. Techiman is one of the two major cities and settlements of Bono East region. Techiman is home to ...
;
In 2003, the
Metro Mass Transit Service, was inaugurated in Accra as a more comfortable and cheaper alternative to the trotro.
Accra is served by the
Aayalolo
Aayololo is a Bus Rapid Transit System, was inaugurated on the 25th of November 2016, in Ghana which is operational in Accra the Capital. Bus Rapid Transit system are special because particular lines are dedicated for the buses which allows them ...
bus system, which was inaugurated in November 2016. It was initially planned as a
bus rapid transit with dedicated lanes, but because these lanes were not provided it was renamed
Quality Bus System (QBS).
An agreement was signed in 2019 to build a five line, , automated, elevated light railway metro system called
Accra Skytrain. As of 2021 construction has not commenced on the $2.6 billion project. The government said in February 2021 it intends to proceed with the project which will developed under a
build-own-operate A project delivery method is a system used by an agency or owner for organizing and financing design, construction, operations, and maintenance services for a structure or facility by entering into legal agreements with one or more entities or parti ...
concession by private South African firm.
Accra is connected by railway line to
Kumasi and
Takoradi.
There is a suburban railway line from
Accra Central Station to
Tema.
Aviation
Accra is served by
Kotoka International Airport
Kotoka International Airport is an international airport in Accra, the capital of Ghana. The airport is operated by Ghana Airports Company Limited (GACL), which has its offices on the airport property. It is the sole international airport in ...
, which has both civil and military uses. Located from downtown Accra, the airport handles all of the city's
scheduled passenger services. There are plans to build a second airport to relieve the aviation pressure on the Kotoka International Airport. This new airport will be located at Prampram in Accra and will be constructed by China Airport Civil Construction. This plan was still under review in 2020, as additional runways at Kotoka are in consideration as an alternative to a new international airport.
Taxis

Accra has an extensive
taxi network and numerous
taxi rank
A taxi, also known as a taxicab or simply a cab, is a type of vehicle for hire with a driver, used by a single passenger or small group of passengers, often for a non-shared ride. A taxicab conveys passengers between locations of their choice ...
s, but most taxis lack a meter system, so price negotiation is required between the passenger and driver. Metered taxis do operate in the city, but tend to be more expensive. Taxis in Ghana are painted in two colours: the four bumpers
fenders are yellow/orange, and the rest of the car is in a colour of the operator's choice.
Tro tros and buses
By far the most common form of transport in Accra, ''
tro tros'' (minibuses or cargo vans modified for passenger transport) is the third biggest, and second most efficient and cost-effective way of getting around the city. The buses are typically minibuses or vans. Some of the most popular models used as tro tros are Nissan Urvan 15-seaters and Mercedes Benz Sprinter or D 309 vans. Trotros are typically decorated with decals such as flags of various countries or (local and international) soccer teams, popular sayings, proverbs (in English or local languages) or Bible verses. Trotros pick up and offload passengers at designated bus stops along their regular routes. Tro tros will also usually offload at undesignated locations along the route, by passenger request. Most routes commence and terminate at large urban transport terminals such as the Neoplan station or the
Achimota Transport Terminal
Achimota Transport Terminal was inaugurated in December, 2009, with the aim of reducing congestion on the Accra-Nsawam road.
The terminal can accommodate 800 vehicles and includes other facilities such as a police station and a clinic. It was st ...
.
Sport
 Football
Football is the most popular sport in Accra. The most famous football club in the city is
Accra Hearts of Oak
Accra Hearts of Oak Sporting Club, commonly referred to as Hearts of Oak or just Hearts, is a professional sports club based in Accra ( Greater Accra), Ghana. Founded in 1911, the club is the oldest surviving football club in Ghana and its tra ...
, whose main rivals are
Asante Kotoko
Asante Kotoko Sporting Club, simply known as Asante Kotoko, is a professional football club founded on 31 August 1935 and based in Kumasi in the Ashanti Region of Ghana. Nicknamed the ''Porcupine Warriors'', they compete in the Ghana Premier Lea ...
of
Kumasi. The Accra Sports Stadium is home to the Hearts of Oak, and a host venue of the
Black Stars, the national football team of Ghana. In 2008, the
Accra Sports Stadium
The Accra Sports Stadium, formerly named the Ohene Djan Stadium, is a multi-use stadium (40,000-capacity, all-seater) located in Accra. Ghana, mostly used for association football matches. It is also used for rugby union.
Overview
The stadium wa ...
hosted nine matches in the
2008 African Cup of Nations.
Another notable club is
Accra Lions FC, which also plays in the
Accra Sports Stadium
The Accra Sports Stadium, formerly named the Ohene Djan Stadium, is a multi-use stadium (40,000-capacity, all-seater) located in Accra. Ghana, mostly used for association football matches. It is also used for rugby union.
Overview
The stadium wa ...
.
Accra is home to the
Right to Dream Academy, which gives young Ghanaians a chance at a career in professional football. Many of the academy's alumni, including
Chicago Fire's David Accam
David Accam (born 28 September 1990) is a Ghanaian professional association football, footballer who plays as a Midfielder#Winger, winger for Finnish club FC Inter Turku, Inter Turku. He has won 11 caps for the Ghana national football team, Ghan ...
,
Helsingborg's Ema Boateng,
Halmstad's King Gyan and
Manchester City's Godsway Donyoh
Godsway Donyoh (born 14 October 1994) is a Ghanaian professional Association football, footballer who plays as a Striker (association football), striker for Apollon Limassol FC, Apollon Limassol in the Cypriot First Division.
Career Mancheste ...
and
Enock Kwakwa, as well as Ghanaian national team players,
Brimah Razak,
Harrison Afful
Harrison Afful (born 24 July 1986) is a Ghanaian professional footballer who plays as a fullback for Charlotte FC and the Ghana national team. He appeared previously for Feyenoord Academy, Espérance de Tunis, Columbus Crew, and Charlotte FC ...
,
John Boye
John Boye (born 23 April 1987) is a Ghanaian professional footballer who plays as a defender.
Club career
Early career
Born in Accra, Boye began his career with Schwepps' youth academy, where he played alongside Mohammed Iddi, he then later ...
,
Jonathan Mensah,
Mohamed Awal,
Yaw Frimpong
Yaw Frimpong (born 4 December 1986, in Accra) is a Ghanaian professional footballer.
Career
He began his career in Feyenoord Academy, was 2005 promoted to first team, on 15 November 2008 was on trial at Sweden side Helsingborgs IF, later joined ...
,
Mohammed Rabiu,
Paul de Vries,
Seidu Bancey
Seidu Bancey (born 15 May 1990) is a professional footballer who plays as a striker for ES Zarzis in Tunisia.
Club career
Bancey signed for Ebusua Dwarfs in the 2010–2011 season and played for the club until the end of the 2011–2012 seas ...
,
Mahatma Otoo
Mahatma Osumanu Otoo (born 6 February 1992) is a Ghanaian professional footballer who plays as a forward. He was the 2012–13 Ghana Premier League top scorer with 20 goals. Otoo played for Sogndal from 2013 to 2017, scoring 31 goals in 93 appe ...
,
Asamoah Gyan,
Latif Mohammed,
Yahaya Mohamed,
Theophilus Annorbaah,
Michael Essien,
Yussif Raman Chibsah,
Kwadwo Asamoah,
Joshua Otoo,
Nuru Sulley,
David Addy
David Nii Addy (born 21 February 1990) is a Ghanaian footballer.
Club career
Randers
In Summer 2008, Addy made his first international move to Europe, from a Ghanaian Club – International Allies FC being signed by Danish SAS Ligaen club R ...
,
Jerry Akaminko,
Daniel Opare and
Foli Adade, were also born in Accra.
Boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
is also popular, with many former world champions coming out of Ghana, including
Azumah Nelson
Azumah Nelson (born 19 July 1958) is a Ghanaian former professional boxer who competed from 1979 to 2008. He was a two-weight world champion, having held the WBC featherweight title from 1984 to 1987 and the WBC super-featherweight title tw ...
,
Joshua Clottey
Joshua Clottey (born October 6, 1977) is a Ghanaian former professional boxer who competed from 1995 to 2019, and held the IBF welterweight title from 2008 to 2009. As an amateur, he competed at the 1994 Commonwealth Games. At the peak of his car ...
, and
Ike Quartey.
Accra will host the
2023 African Games.
Places of worship
File:Anglican Holy Trinity Cathedral Accra.jpg, Holy Trinity Cathedral (Church of the Province of West Africa
The Church of the Province of West Africa is a province of the Anglican Communion, covering 17 dioceses in eight countries of West Africa, specifically in Cameroon, Cape Verde, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Senegal and Sierra Leone. Ghana is the ...
)
File:Christ the King Parish in Accra.jpg, Christ the King Parish in Accra (Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
)
File:All Saints church Accra Adabraka.jpg, All Saints church in Adabraka
Adabraka is a town in the Korley Klottey Municipal Assembly, a Municipality of the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. It was the first and the most posh neighborhood in Ghana during the British era.
Education
Adabraka was known for the O'Reilly ...
File:Accra Wesley Cathedral 2.jpg, alt=, Accra Wesley Cathedral is one of the oldest church buildings in Ghana
File:St. Augustine Anglican Church.jpg, alt=, The St. Augustine Anglican Church is located in Sahara, Dansoman
File:Anglican Diocese of Accra.jpg, alt=, Anglican Diocese of Accra - ST. Mary the Virgin Church
Among the
places of worship, they are predominantly
Christian churches and temples :
Church of the Province of West Africa
The Church of the Province of West Africa is a province of the Anglican Communion, covering 17 dioceses in eight countries of West Africa, specifically in Cameroon, Cape Verde, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Senegal and Sierra Leone. Ghana is the ...
(
Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is the third largest Christian communion after the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. Founded in 1867 in London, the communion has more than 85 million members within the Church of England and other ...
),
Presbyterian Church of Ghana,
Evangelical Presbyterian Church, Ghana (
World Communion of Reformed Churches),
Ghana Baptist Convention
The Ghana Baptist Convention is a Baptist Christian denomination in Ghana. It is affiliated with the Baptist World Alliance. The headquarters is in Accra.
History
The Ghana Baptist Convention has its origins in a Baptist mission of Nigerian Ba ...
(
Baptist World Alliance),
Lighthouse Chapel International
The United Denominations Originating from the Lighthouse Group of Churches (formerly Lighthouse Chapel International) is a Pentecostal Christian denomination founded in 1987 by Dag Heward-Mills and headquartered in Accra, Ghana.
Beliefs
The ...
,
Church of Pentecost
The Church of Pentecost is a Pentecostal denomination that originates from Ghana. The Church currently has a presence in more than 135 countries globally. Its current Chairman, who happens to be its highest officer worldwide, is Apostle Eric N ...
,
Assemblies of God,
Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Accra
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Accra covers the Greater Accra Region and parts of the Volta Region. There are 62 parishes and rectories. The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Accra ( la, Accraën(sis)) is the Metropolitan See for the ecclesiastic ...
(
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
). There are also
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
mosques.
Notable places of worship in the city include the
Holy Trinity Cathedral,
Wesley Methodist Cathedral,
Ebenezer Presbyterian Church, Osu
The Ebenezer Presbyterian Church, formerly known as the Basel Mission Church, Christiansborg, is a historic Protestant church located in the suburb of Osu in Accra, Ghana. The church was founded by the Basel Evangelical Missionary Society in 1 ...
,
Holy Spirit Cathedral, the
Ghana National Mosque
The Ghana National Mosque is a mosque in Ghana. It is the second largest mosque in West Africa.
The mosque was built at a cost of $10 million. It was funded by the Turkish Hudai Foundation in Accra with the support of the Turkish government.
T ...
, the
Madina Mosque
Medina Mosque or Madina Mosque may refer to:
* Al-Masjid al-Nabawi in Medina, Saudi Arabia
* Madina Mosque (Accra), Ghana
* Madina Mosque (Barbados)
* Madina Mosque (Bengal), in the Nizamat Fort Campus in Murshidabad, West Bengal, India
* Madina ...
, and the Mormon
Accra Ghana Temple
The Accra Ghana Temple is the 117th operating temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church).
History
The building of the Accra Ghana Temple was announced on February 16, 1998. Years before the temple was announced, LDS C ...
.
Culture
 Tourism in Ghana
Tourism in Ghana accounted for 1,087,000 international tourist arrivals in 2011.
Accra is the Greater Accra region's tourist hub, sporting a wide variety of hotels, monuments, museums and nightclubs. The city has three
five-star hotel
Hotel ratings are often used to classify hotels according to their quality. From the initial purpose of informing travellers on basic facilities that can be expected, the objectives of hotel rating have expanded into a focus on the hotel experi ...
s: the Labadi Beach Hotel, the La Palm Royal Beach Hotel and the Movenpick Ambassador Hotel. The Golden Tulip Hotel and Novotel Accra, located in Accra's central business district, are both ranked four stars. There are numerous three-star hotels, including the Hotel Wangara, Hotel Shangri-La and Erata Hotel, as well as many budget hotels. The
Accra International Conference Centre and other meeting facilities provide venues for conference tourism.
[Touring Ghana – Greater Accra Region](_blank)
. touringghana.com.
The Du Bois Centre houses a research library and gallery of manuscripts, as well as the graves of its namesake, the scholar
W.E.B. Du Bois
William Edward Burghardt Du Bois ( ; February 23, 1868 – August 27, 1963) was an American-Ghanaian sociologist, socialist, historian, and Pan-Africanist civil rights activist. Born in Great Barrington, Massachusetts, Du Bois grew up i ...
, and his wife
Shirley Graham Du Bois. The
Kwame Nkrumah Mausoleum
The Kwame Nkrumah Mausoleum and memorial park is located in downtown Accra, the capital of Ghana.
History
It is dedicated to the prominent Ghanaian President Kwame Nkrumah
Kwame Nkrumah (born 21 September 190927 April 1972) was a Ghan ...
is the resting place of Ghana's first President,
Kwame Nkrumah, who oversaw the Gold Coast's independence from Britain and was a leading exponent of
Pan-Africanism.
The
National Theatre in Accra, home of the
National Symphony Orchestra Ghana
The National Symphony Orchestra Ghana (NSO Ghana) is the national symphony orchestra of Ghana. NSO Ghana was founded in 1959 by order of Kwame Nkrumah, and established by Philip Gbeho (who had composed the Ghanaian national anthem in 1957), toge ...
Accra furthermore hosts the
National Museum,
National Theatre, with its distinctive modern
Chinese architecture
Chinese architecture ( Chinese:中國建築) is the embodiment of an architectural style that has developed over millennia in China and it has influenced architecture throughout Eastern Asia. Since its emergence during the early ancient era, t ...
.
The city's foremost historical site is the Jamestown area, which contains the
Ussher Fort
Ussher Fort is a fort in Accra, Ghana. It was built by the Dutch in 1649 as Fort Crèvecœur, and is a day's march from Elmina and to the east of Accra on a rocky point between two lagoons. It was one of three forts that Europeans built in the reg ...
and
James Fort, and
Osu Castle (also known as
Christiansborg), built by Danish settlers in the 17th century.
Other sites of note include the
Jubilee House
Golden Jubilee House, or Jubilee House, is the presidential palace in Accra that serves as a residence and office to the President of Ghana. Jubilee House is built on the site of a building that was constructed and used for administrative pur ...
(the office of the
Government of Ghana
The Government of Ghana was created as a parliamentary democracy, followed by alternating military and civilian governments in Ghana. In January 1993, military government gave way to the Fourth Republic after presidential and parliamentary elec ...
and the
President of Ghana
The president of the Republic of Ghana is the elected head of state and head of government of Ghana, as well as commander-in-chief of the Ghana Armed Forces. The current president of Ghana is Nana Akufo-Addo, who won the 2020 presidential ...
), the
Parliament House of Ghana
The Parliament House of Ghana is the official seat of the Speaker of Parliament of the country and also serves as Parliament of Ghana. It also has offices which serve temporal offices of certain members of parliament. It was designed by Kwame ...
, the
Ghana-India Kofi Annan Centre of Excellence in ICT
The Ghana-India Kofi Annan Centre of Excellence in ICT is Ghana's first Advanced Information Technology Institute (AITI) l. It was established in 2003, through a partnership between the Government of Ghana and the Government of India.
The cent ...
, the
Black Star Square
Black Star Square, also known as Independence Square, is a public square in Accra, Ghana, bordered by the Accra Sports Stadium and the Kwame Nkrumah Memorial Park. The square often hosts the annual independence celebrations as well as other nati ...
,
Accra Sports Stadium
The Accra Sports Stadium, formerly named the Ohene Djan Stadium, is a multi-use stadium (40,000-capacity, all-seater) located in Accra. Ghana, mostly used for association football matches. It is also used for rugby union.
Overview
The stadium wa ...
, and the Accra Centre for National Culture. The Accra-based
African Fashion Foundation supports the
African fashion industry, especially the fashion industry in
Ghana.
Accra has an Atlantic beachfront and the most popular of the city's beaches is
Labadi Beach, along with Kokrobite Beach, which is located west of Accra. The
beachfront area also houses the Academy of African Music and Arts.
Ghana's film industry is growing. Its first documentary addressing the impacts of climate change premiered in Accra on October 14, 2022. ''The Ghana Youth Film Program'' is a compilation film of 12 documentary short films made youth from across Ghana aged 18 to 30. It will participate in the United Nations climate summit, COP27, November 9, 2022.
Twin towns – sister cities
Accra has four official
sister cities, as recognised by
Sister Cities International
Sister Cities International (SCI) is a nonprofit citizen diplomacy network that creates and strengthens partnerships between communities in the United States and those in other countries, particularly through the establishment of " sister citie ...
:
UNESCO World Book
In October 2022, Accra was named as the
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) world book capital for 2023.
See also
*
2015 Accra explosion
On June 3, 2015, an explosion and a fire occurred at a petrol station in Ghana's capital city Accra, killing over 250 people.
Explosion
The GOIL station, near Kwame Nkrumah Interchange in the city's downtown area, was being used as a shelter ...
*
Atomic Junction Gas Explosion
*
List of people from Accra
This is a list of notable people who were born or have lived in Accra, Ghana.
Born in Accra 1901–1970
* Gottlieb Ababio Adom (1904–1979), educator, journalist, editor and Presbyterian clergyman
* Joseph Arthur Ankrah (1915–1992), 2n ...
References
Bibliography
External links
"Accra Night Life Still Dey Pap" Afrosages.com, 22 January 2020
{{Authority control
Capitals in Africa
Dutch Gold Coast
Former Danish colonies
Former Dutch colonies
Former Portuguese colonies
Populated coastal places in Ghana
Populated places established in the 15th century
Populated places in the Greater Accra Region
Portuguese Gold Coast
Port cities in Africa
Regional capitals in Ghana
1961 establishments in Ghana
 The main Ga group known as the Tumgwa Were led by Ayi Kushie arrived by sea. When the Guan (
The main Ga group known as the Tumgwa Were led by Ayi Kushie arrived by sea. When the Guan ( One of the most influential decisions in the history of the city was that of building the Accra-Kumasi railway in 1908. This was to connect Accra, the country's foremost port at that time, with Ghana's main
One of the most influential decisions in the history of the city was that of building the Accra-Kumasi railway in 1908. This was to connect Accra, the country's foremost port at that time, with Ghana's main  In the years following
In the years following  When Kwame Nkrumah became Ghana's first postindependence
When Kwame Nkrumah became Ghana's first postindependence  The former territory of the Accra Metropolitan District, , as it existed before 2008, is now divided into 13 separate local government districts, all governed as municipal assemblies with their own town hall and a municipal executive appointed by the president of the republic. Each municipal assembly is responsible for most local services, such as local planning and refuse collection. The reduced
The former territory of the Accra Metropolitan District, , as it existed before 2008, is now divided into 13 separate local government districts, all governed as municipal assemblies with their own town hall and a municipal executive appointed by the president of the republic. Each municipal assembly is responsible for most local services, such as local planning and refuse collection. The reduced  Parts of Central Accra comprise a mixture of very low-density development with under-used service infrastructure on the one hand, high-density development and overstretched infrastructure services on the other. The growth of Accra has led to the neglect of some of the old settlements, whilst efforts are being made to provide the newly developing suburban areas with services and infrastructure to cater for the needs of the middle-income earners. Peripheral residential development in Accra barely has sufficient infrastructure to support it. There are also large numbers of uncompleted houses, interspersed with pockets of undeveloped land, which are often subject of litigation, due to the inability of organisations and individuals who own them to complete or develop them due to lack of funds. Housing can be grouped into three broad categories: the low-income, middle-income and high-income areas. The low-income housing areas comprise Osu, Jamestown, Adedenkpo, Chorkor, La, Teshie, Nungua, Sukura, Kwashieman, Odorkor, Bubiashie, Abeka, Nima, Maamobi and Chorkor. Altogether, these areas accommodate about 58% of Accra's total population. Most of Accra's informal businesses are located in low-income areas.
Almost all low-income areas are built up with little room for expansion. This is particularly so in the areas of the inner city. The middle-income areas of Accra are predominantly populated by Ghanaian citizens and business, administrative and professional families. Much of the housing in these areas has been provided by state, parastatal and private sector organisations and individuals. The middle-income areas include Dansoman Estates, North Kaneshie Estates, Asylum Down, Kanda Estates, Abelempke, Achimota, Adenta and Tesano. Usually, these areas, unlike the low-income areas, are planned developments, but are in need of infrastructure services. Building materials and general housing conditions are of better quality. The middle-income group comprises 32% of the city's population of which are Ghanaian citizens make up. The high-income areas provide housing for the remaining 10% of the population of which Ghanaian citizens also make up. They include areas like North Ridge and West Ridge, Ringway Estates, north Labone Estates, Airport Residential Area, Roman Ridge, East Legon.
These areas are all planned and have well developed infrastructure with spacious and landscaped ground in sharp contrast with, particularly, the low-income areas. Buildings are usually built with sandcrete blocks, and have walls and roofed with aluminium, or asbestos roofing sheets. There are also high-income peripheral areas like Haatso, Kwabenya, Pokuase, Adenta, Taifa, Mallam, where development of engineering infrastructure is not yet complete. These areas developed ahead of infrastructure, however the Achimota-Ofankor controlled-access highway was scheduled to open in May 2012, dual carriageway road construction was also due to be completed in 2012. In total, 84.4% of all houses in the Accra Metropolitan Area have their outside walls made up of cement. Similarly, houses found within Accra have 99.2% of their floor materials made up of cement.
Parts of Central Accra comprise a mixture of very low-density development with under-used service infrastructure on the one hand, high-density development and overstretched infrastructure services on the other. The growth of Accra has led to the neglect of some of the old settlements, whilst efforts are being made to provide the newly developing suburban areas with services and infrastructure to cater for the needs of the middle-income earners. Peripheral residential development in Accra barely has sufficient infrastructure to support it. There are also large numbers of uncompleted houses, interspersed with pockets of undeveloped land, which are often subject of litigation, due to the inability of organisations and individuals who own them to complete or develop them due to lack of funds. Housing can be grouped into three broad categories: the low-income, middle-income and high-income areas. The low-income housing areas comprise Osu, Jamestown, Adedenkpo, Chorkor, La, Teshie, Nungua, Sukura, Kwashieman, Odorkor, Bubiashie, Abeka, Nima, Maamobi and Chorkor. Altogether, these areas accommodate about 58% of Accra's total population. Most of Accra's informal businesses are located in low-income areas.
Almost all low-income areas are built up with little room for expansion. This is particularly so in the areas of the inner city. The middle-income areas of Accra are predominantly populated by Ghanaian citizens and business, administrative and professional families. Much of the housing in these areas has been provided by state, parastatal and private sector organisations and individuals. The middle-income areas include Dansoman Estates, North Kaneshie Estates, Asylum Down, Kanda Estates, Abelempke, Achimota, Adenta and Tesano. Usually, these areas, unlike the low-income areas, are planned developments, but are in need of infrastructure services. Building materials and general housing conditions are of better quality. The middle-income group comprises 32% of the city's population of which are Ghanaian citizens make up. The high-income areas provide housing for the remaining 10% of the population of which Ghanaian citizens also make up. They include areas like North Ridge and West Ridge, Ringway Estates, north Labone Estates, Airport Residential Area, Roman Ridge, East Legon.
These areas are all planned and have well developed infrastructure with spacious and landscaped ground in sharp contrast with, particularly, the low-income areas. Buildings are usually built with sandcrete blocks, and have walls and roofed with aluminium, or asbestos roofing sheets. There are also high-income peripheral areas like Haatso, Kwabenya, Pokuase, Adenta, Taifa, Mallam, where development of engineering infrastructure is not yet complete. These areas developed ahead of infrastructure, however the Achimota-Ofankor controlled-access highway was scheduled to open in May 2012, dual carriageway road construction was also due to be completed in 2012. In total, 84.4% of all houses in the Accra Metropolitan Area have their outside walls made up of cement. Similarly, houses found within Accra have 99.2% of their floor materials made up of cement.
 Accra is a centre for manufacturing, marketing, finance, insurance, and transportation. Its financial sector incorporates a central bank, nine commercial banks (with 81 branches), four development banks (with 19 branches), four merchant banks (with seven branches), three discount houses, one home finance mortgage bank, multiple building societies, Ghana Stock Exchange, foreign exchange bureaus, finance houses, insurance companies, insurance brokerage firms, two savings and loans companies, and numerous real estate developers, with industrial sites and residential developments. The road network in the Accra Metropolitan Area totals in length.
There are over 50,506 identified residential properties in Accra, and about 4,054 commercial/industrial/mixed properties, with a total rateable value of GH¢13,849,014. There are also supermarkets, 36 facilities for both on–street and off- street parking, and shopping malls, as well as several facilities for sports and recreation.
Accra is a centre for manufacturing, marketing, finance, insurance, and transportation. Its financial sector incorporates a central bank, nine commercial banks (with 81 branches), four development banks (with 19 branches), four merchant banks (with seven branches), three discount houses, one home finance mortgage bank, multiple building societies, Ghana Stock Exchange, foreign exchange bureaus, finance houses, insurance companies, insurance brokerage firms, two savings and loans companies, and numerous real estate developers, with industrial sites and residential developments. The road network in the Accra Metropolitan Area totals in length.
There are over 50,506 identified residential properties in Accra, and about 4,054 commercial/industrial/mixed properties, with a total rateable value of GH¢13,849,014. There are also supermarkets, 36 facilities for both on–street and off- street parking, and shopping malls, as well as several facilities for sports and recreation.
 Accra's smallest economic sector, the primary sector, employs approximately 91,556 people. The predominant economic activities are fishery and
Accra's smallest economic sector, the primary sector, employs approximately 91,556 people. The predominant economic activities are fishery and  Accra has an extensive taxi network and numerous
Accra has an extensive taxi network and numerous  Football is the most popular sport in Accra. The most famous football club in the city is
Football is the most popular sport in Accra. The most famous football club in the city is  Tourism in Ghana accounted for 1,087,000 international tourist arrivals in 2011.
Accra is the Greater Accra region's tourist hub, sporting a wide variety of hotels, monuments, museums and nightclubs. The city has three
Tourism in Ghana accounted for 1,087,000 international tourist arrivals in 2011.
Accra is the Greater Accra region's tourist hub, sporting a wide variety of hotels, monuments, museums and nightclubs. The city has three