Abrictosaurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Abrictosaurus'' (; "wakeful lizard") is a
 Heterodontosaurids like ''Abrictosaurus'' were small, early ornithischians, named for their markedly heterodont dentition. They are best known for the large, canine-like tusks (often called '' caniniforms'') in both upper and lower jaws. There were no teeth in the front of the jaws, where a hard
Heterodontosaurids like ''Abrictosaurus'' were small, early ornithischians, named for their markedly heterodont dentition. They are best known for the large, canine-like tusks (often called '' caniniforms'') in both upper and lower jaws. There were no teeth in the front of the jaws, where a hard
 Both specimens of ''Abrictosaurus'' are housed in the collection of
Both specimens of ''Abrictosaurus'' are housed in the collection of 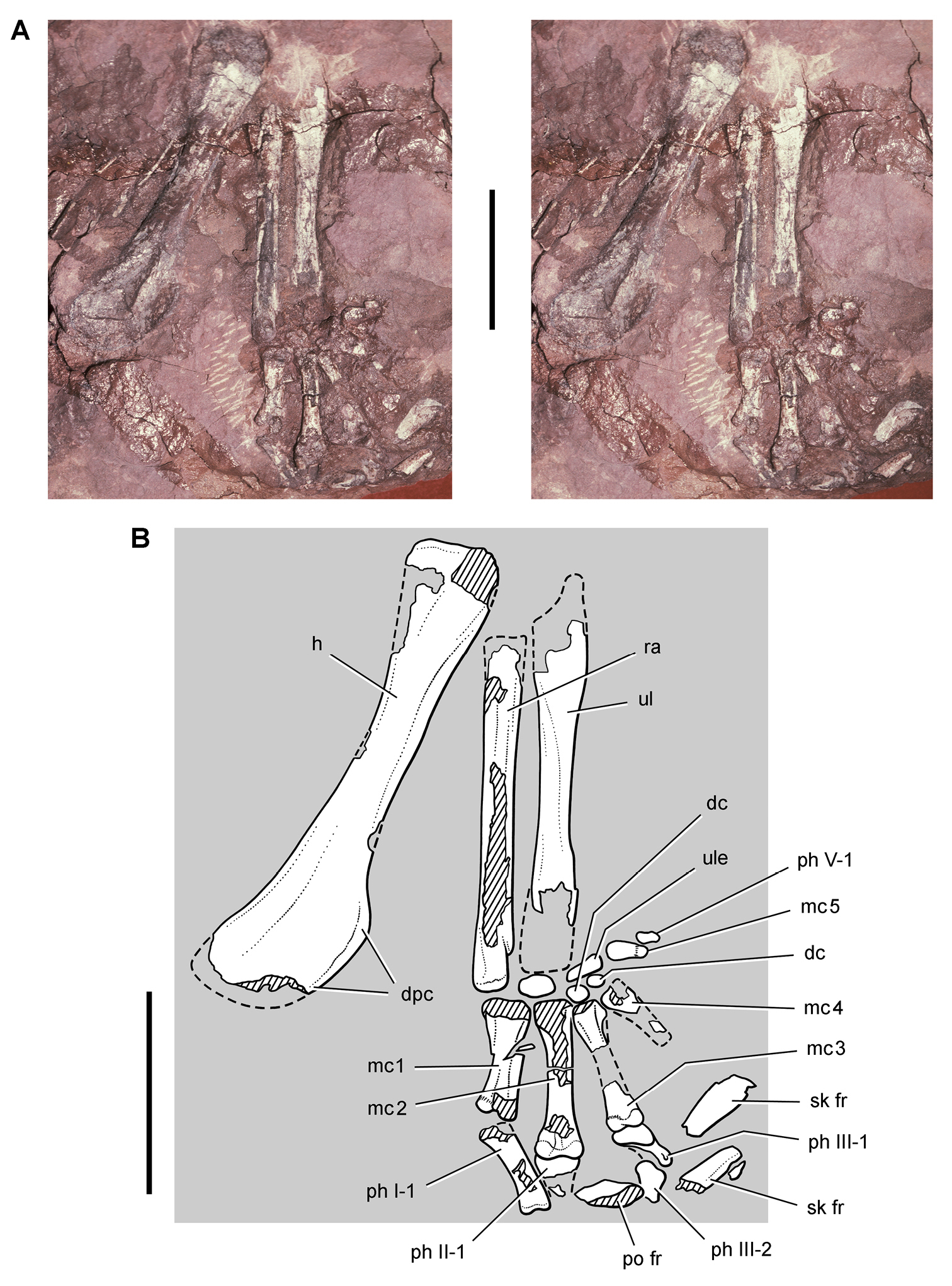 In 1975,
In 1975,
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of heterodontosaurid dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived during the Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic-J ...
in what is now in parts of southern Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
such as Lesotho and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
. It was a bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
herbivore or omnivore and was one of the most basal heterodontosaurids. It was approximately long and weighed between .
This dinosaur is known from the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
remains of only two individuals, found in the Upper Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, sout ...
of Qacha's Nek District in Lesotho and Cape Province
The Province of the Cape of Good Hope ( af, Provinsie Kaap die Goeie Hoop), commonly referred to as the Cape Province ( af, Kaapprovinsie) and colloquially as The Cape ( af, Die Kaap), was a province in the Union of South Africa and subsequen ...
in South Africa. The Upper Elliot is thought to date from the Hettangian and Sinemurian
In the geologic timescale, the Sinemurian is an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic Epoch or Series. It spans the time between 199.3 ± 2 Ma and 190.8 ± 1.5 Ma (million years ago). The Sinemurian is preceded by the Hettangian and ...
stages of the Early Jurassic Period, approximately 200 to 190 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago) ...
. This formation is thought to preserve sand dunes as well as seasonal floodplains
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
, in a semiarid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
environment with sporadic rainfall. Other dinosaurs found in this formation
Formation may refer to:
Linguistics
* Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes
* Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes
Mathematics and science
* Cave formation or speleothem, a secondar ...
include the theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
''Megapnosaurus
''Megapnosaurus'' (meaning "big dead lizard", from Greek μεγα = "big", 'απνοος = "not breathing", "dead", σαυρος = "lizard") is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago dur ...
'', the sauropodomorph
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had lon ...
''Massospondylus
''Massospondylus'' ( ; from Greek, (massōn, "longer") and (spondylos, "vertebra")) is a genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Early Jurassic. (Hettangian to Pliensbachian ages, ca. 200–183 million years ago). It was described by S ...
'', as well as other heterodontosaurids like ''Heterodontosaurus
''Heterodontosaurus'' is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic, 200–190 million years ago. Its only known member species, ''Heterodontosaurus tucki'', was named in 1962 based on a skull discovered in South ...
'' and ''Lycorhinus
''Lycorhinus'' is a genus of heterodontosaurid ornithischian dinosaur from the Early Jurassic (Hettangian to Sinemurian ages) strata of the Elliot Formation located in the Cape Province, South Africa.
Description
''Lycorhinus'', including the r ...
''. Remains of terrestrial
Terrestrial refers to things related to land or the planet Earth.
Terrestrial may also refer to:
* Terrestrial animal, an animal that lives on land opposed to living in water, or sometimes an animal that lives on or near the ground, as opposed to ...
crocodylomorphs, cynodonts and early mammals are also abundant.
Description
 Heterodontosaurids like ''Abrictosaurus'' were small, early ornithischians, named for their markedly heterodont dentition. They are best known for the large, canine-like tusks (often called '' caniniforms'') in both upper and lower jaws. There were no teeth in the front of the jaws, where a hard
Heterodontosaurids like ''Abrictosaurus'' were small, early ornithischians, named for their markedly heterodont dentition. They are best known for the large, canine-like tusks (often called '' caniniforms'') in both upper and lower jaws. There were no teeth in the front of the jaws, where a hard beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for foo ...
was used to crop vegetation. There were three premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
ry teeth, with the first two small and conical and the third enlarged to form the upper caniniform, counterpart to the even larger lower caniniform, which was the first dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
tooth. In the upper jaw, a large gap (or diastema
A diastema (plural diastemata, from Greek διάστημα, space) is a space or gap between two teeth. Many species of mammals have diastemata as a normal feature, most commonly between the incisors and molars. More colloquially, the condition ...
) accommodated the lower caniniform tooth and separated the premaxillary teeth from the wider chewing teeth of the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
. Similar teeth lined the remainder of the lower jaw.
''Abrictosaurus'' is usually considered the most basal member of the family Heterodontosauridae. ''Lycorhinus'' and ''Heterodontosaurus'' both had high-crowned cheek teeth, which overlapped each other in the jaw, forming a continuous chewing surface analogous
Analogy (from Greek ''analogia'', "proportion", from ''ana-'' "upon, according to" lso "against", "anew"+ ''logos'' "ratio" lso "word, speech, reckoning" is a cognitive process of transferring information or meaning from a particular subject ...
to those of Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
hadrosaurids. ''Abrictosaurus'' had more widely separated cheek teeth, with lower crowns, more similar to other early ornithischians. It has been suggested that ''Abrictosaurus'' lacked tusks and that this is another primitive feature. However, caniniforms were clearly present on one of the two specimens of ''Abrictosaurus''. The upper caniniform measured 10.5 millimeters (0.4 inches) high, while the lower reached 17 mm (0.67 in). These caniniforms were serrated only on the anterior surface, unlike those of ''Lycorhinus'' and ''Heterodontosaurus'', which were serrated on both anterior and posterior edges. ''Abrictosaurus'' also had smaller, less powerful forelimbs than ''Heterodontosaurus'' and one fewer phalanx bone
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bon ...
in both the fourth and fifth digits of the forelimb.
History and naming
 Both specimens of ''Abrictosaurus'' are housed in the collection of
Both specimens of ''Abrictosaurus'' are housed in the collection of University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
. The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of sever ...
specimen was discovered in Lesotho and consists of a partial skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
and skeleton (UCL B54). Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
Richard Thulborn, who first described the specimen in 1974, considered it a new species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of ''Lycorhinus'' and named it ''L. consors'', using the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word ' which means 'companion' or 'spouse'. As UCL B54 lacked the caniniforms which had been found in the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specime ...
, ''Lycorhinus angustidens'', Thulborn believed it to be female. Neither the skull nor the skeletons of ''Abrictosaurus'' have been fully described in the literature. A tooth from the latest Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
of Switzerland has been assigned to ''Abrictosaurus'' sp., but this has not been supported, as the specimen does not have unique characteristics of ''Abrictosaurus'', heterodontosaurids, or ornithischians in general.
 In 1975,
In 1975, James Hopson
James Allen Hopson (born 1935) is an American paleontologist and professor (now retired) at the University of Chicago. His work has focused on the evolution of the synapsids (a group of amniotes that includes the mammals), and has been focused ...
redescribed a fragmentary heterodontosaur skull (UCL A100) found in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
that Thulborn had previously assigned to ''Lycorhinus angustidens''. After showing that UCL A100 could not belong to ''L. angustidens'' but was instead more similar to UCL B54, Hopson erected a new genus to contain both specimens. The generic name ''Abrictosaurus'' (from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
' (') meaning 'wakeful' and (') meaning 'lizard') refers to Hopson's disagreement with Thulborn's hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obse ...
that heterodontosaurids underwent periods of aestivation ( hibernation during hot and/or dry seasons). The specific name was retained, creating the new binomial ''Abrictosaurus consors''. Despite Hopson's renaming, Thulborn continued to consider ''Lycorhinus angustidens'', ''Heterodontosaurus tucki'', and ''Abrictosaurus consors'' to be three species of the genus ''Lycorhinus''. Most paleontologists maintain all three genera separately, although there is no precise definition of a species or genus in paleontology.
Sexual dimorphism
The hypothesis ofsexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
in heterodontosaurids has long centered on ''Abrictosaurus''. Tusks are a sexually dimorphic trait in many modern mammals, including musk deer, walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
, Asian elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus ''Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in the no ...
s and many pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
, with tusks being present primarily in males. The lack of tusks in UCL B54 led to suggestions that it was female; perhaps even a female of another species. The discovery of caniniforms in UCL A100 showed that ''A. consors'' also has this 'male' characteristic, suggesting that it is at least a valid species in its own right. However, UCL B54 may actually be a juvenile, based on its short face and unfused sacral
Sacral may refer to:
*Sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property ...
(hip) vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
e. Therefore, the lack of tusks could be a juvenile trait instead of a secondary sexual characteristic
Secondary sex characteristics are features that appear during puberty in humans, and at sexual maturity in other animals. These characteristics are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a s ...
, weakening the case for sexual dimorphism.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q131598 Early Jurassic dinosaurs of Africa Heterodontosaurids Fossil taxa described in 1975 Taxa named by James Hopson Paleontology in Lesotho Ornithischian genera