AT91SAM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Atmel ARM-based processors are microcontrollers and
/ref> ** Cortex-M3 (MCU) (ARMv7-M Harvard architecture) *** SAM3U (2009) *** SAM3S (2009) *** SAM3N (2010) *** SAM3A (2012) *** SAM3X (2012) ** Cortex-M4 (MCU) (ARMv7E-M Harvard architecture) *** SAM4S (2011) *** SAM4L (2012) *** SAM4E (2013) series based on the ARM Cortex-M4F, first Atmel MCU that has a FPU (Floating-Point Unit).Press Release; Atmel; January 14, 2013.
/ref> *** SAM4N (2013) *** SAM4C (2014) dual-corePress Release; Atmel; August 12, 2014.
/ref> *** SAM G51/53 (2014) based on the ARM Cortex-M4F.Press Release; Atmel; January 7, 2014.
/ref> *** SAM G54/55 (2015) based on the ARM Cortex-M4F.Press Release; Atmel; January 5, 2015.
/ref> ** Cortex-A5 (MPU) (ARMv7-A architecture) *** SAMA5D3 series, (2013) Atmel announced the SAMA5D3 series based on the ARM Cortex-A5, which is the first Atmel chip with a Cortex-A5 core. *** SAMA5D4 (2014)Press Release; Atmel; October 1, 2014.
/ref> *** SAMA5D2 series (2015)Press Release; Atmel; September 14, 2015.
/ref> ** Cortex-M0+ (MCU)in the SAM D20 (2013) (ARMv6-M architecture) – In June 2013, Atmel announced the SAMD20 series based on the ARM Cortex-M0+.Press Release; Atmel; June 17, 2013.
/ref> ** Cortex-M7 (MCU) (ARMv7-M architecture) *** SAMS70 series, (2015) Atmel announced the SAM S70 series based on the ARM Cortex-M7.Press Release; Atmel; July 15, 2015.
/ref> *** SAME70 series, (2015) Atmel announced the SAM S70 series based on the ARM Cortex-M7. *** SAMV70 series, (2015) Atmel announced the SAM S70 series based on the ARM Cortex-M7, which is the first Atmel chip automotive grade with a Cortex-M7 core.Press Release; Atmel; Jan 6, 2015.
/ref>
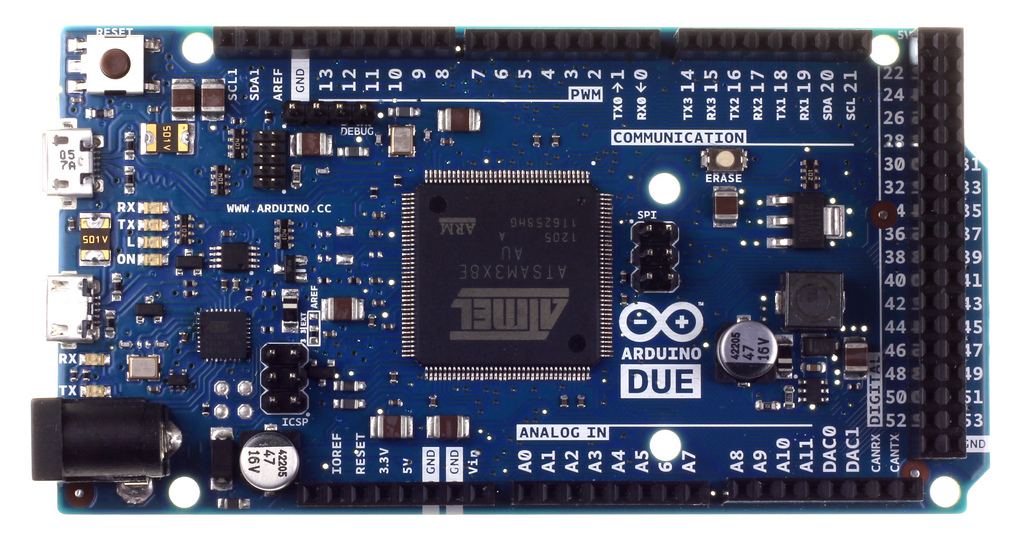 In 2009 Atmel announced the ATSAM3U line of flash-based microcontrollers based on the
In 2009 Atmel announced the ATSAM3U line of flash-based microcontrollers based on the
SAM3A
SAM3N
SAM3S
– reduce power consumption
SAM3U
– high-speed USB
SAM3X
– the ''
SAM4C
– ARM Cortex-M4/M4F dual-core, which includes FPU
SAM4E18-16 series
– ARM Cortex-M4F core, which includes FPU
SAM4L
– ARM Cortex-M4 core
SAM4N
– ARM Cortex-M4 core, pin-to-pin compatibility with SAM4S, SAM3S, SAM3N, SAM7S devices
SAM4S
– ARM Cortex-M4 core
SAMG5x
– ARM Cortex-M4F core, which includes FPU, ATSAMG55 for 120 MHz CPU speed.
SAMD5x
- Latest ARM Cortex-M4F core, which includes FPU and Integrated Security including Symmetric (AES) and Asymmetric (ECC) Encryption, Public Key Exchange Support(PUKCC), TRNG and SHA based memory Integrity checker.
SAME5x
- Same with D5x plus Ethernet MAC and CAN-FD networking peripherals. Both SAMD5x-E5x series integrate many similar peripherals for ex Timers and Sercoms for UART, I2C, SPI etc from ATSAMD2x and ATSAMC2x M0+ series thus is easier to upgrade to M4F Core MCUs.
SAMS70
– general purpose high performance MCU
SAME70
– connectivity high performance MCU
SAMV70, SAMV71
– automotive high performance MCU
SAM7L
– low power operation
SAM7S
– USB and other peripherals. SAM7S 64-pin chips are compatible with SAM4S, SAM4N SAM3S, SAM3N families.
SAM7SE
– USB, external memory support, and other peripherals
SAM7X
– Ethernet, USB, CAN, and other peripherals
SAM7XC
-–cryptographic extensions (notably AES support) to AT91SAM7X chips
SAM9G25
SAM9G45
SAM9X35
SAM9XE512
SAM9260
SAMA5D2
– 10/100 Ethernet, CAN, LCD, ClassD audio, QSPI, USB HSIC, Raw Bayer Image Sensor Interface, LPDDR3/LPDDR2/LPDDR/DDR2, up to 10 UART ;SAMA5D3
SAMA5D31
– 10/100 Ethernet, LCD
SAMA5D33
– Gigabit Ethernet, LCD
SAMA5D34
– Gigabit Ethernet, LCD, dual CAN
SAMA5D35
– no LCD, dual CAN, one Gigabit Ethernet + one 10/100 Ethernet
SAMA5D36
– LCD, dual CAN, one Gigabit Ethernet + one 10/100 Ethernet ;SAMA5D4
SAMA5D4
– 528 MHz (840 DMIPS), Neon, 128 KB L2 cache, video decoder, LCD, Ethernet
Arduino Due
with 84 MHz Atmel ATSAM3X8E (
Arduino Zero
with 48 MHz Atmel ATSAMD21G18 (
Arduino MKR1000
with 48 MHz Atmel ATSAMW25 (
Rascal
with 400 MHz Atmel AT91SAM9G20 (
Crossware – Development Suite for ARM
;Linux * Buildroot * Openembedded * meta-atmel Yocto compliant layer
Crossware Jaguar
Atmel AT91 ARM Microcontroller Forum
{{DEFAULTSORT:At91sam ARM-based processors ARM architecture
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
s integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s, by Microchip Technology (previously Atmel
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included mi ...
), that are based on various 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calculati ...
ARM processor cores, with in-house designed peripherals and tool support.
Overview
ARM licenses the core design for a series of 32-bit processors. ARM does not manufacture any complete silicon products, just intellectual property (IP). The ARM processors areRISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set comp ...
(reduced instruction set computing). This is similar to Microchip’s AVR 8-bit products, a later adoption of RISC architecture. Whereas the AVR architecture used Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data. It contrasts with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and data share the same memory and pathway ...
exclusively, some ARM cores are Harvard (Cortex-M3) and others are Von Neumann architecture
The von Neumann architecture — also known as the von Neumann model or Princeton architecture — is a computer architecture based on a 1945 description by John von Neumann, and by others, in the '' First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC''. T ...
(ARM7TDMI).
Semiconductor companies such as Microchip take the ARM cores, which use a consistent set of instructions and register naming, and add peripheral circuits such as ADCs (analog to digital converters), clock management, and serial communications such as USART, SPI, I2C, CAN, LIN, USB, Ethernet, and LCD, Camera or Touch controllers. Microchip made efforts to adapt advanced peripherals and power management that used very little power and can operate independently without having the CPU core powered up (sleepwalking). They also provided for DMA between external interfaces and memories increasing data throughput with minimal processor intervention.
Microchip sells both MCUs (microcontroller units) that have internal Flash memory, and MPUs (microprocessor units) that use external memory. In addition to the chips themselves, Microchip offers demo boards, both on its website, and through distribution channels such as Digi-key, Farnell, Ineltek, Arrow, Avnet, Future Electronics, and Mouser.
Some of the Microchip ARM-based products are meant for specific applications, such as their SAM4CP that is used in smart-grid energy meters.
History
* 1995 sign ARM ARM7TDMI "Thumb" core license agreement (ARMv4T Von Neumann architecture) (an MPU core Atmel made into MCU) ** AT91M40800 (1998) ** AT91M42800A ** AT91M55800A ** AT91R40008 ** AT91FR40162 (2002) ** SAM7S/SE ** SAM7X/XC ** SAM7L * 1995 sign ARM920T/ARM9TDMI (MPU) core license agreement (ARMv4T Von Neumann architecture) ** AT91RM9200 (2003) * 2000 sign ARM926EJ/ARM9E (MPU) core license agreement (ARMv5 architecture) ** AT91SAM9260 (2006) ** AT91SAM9263 (2007) ** SAM9XE (2008) ** SAM9N/CN, ** SAM9R (2009) ** SAM9G (2009) ** SAM9X ** SAM9M (2010) * 2004 sign ARM1176JZ-S core license agreement (not used in Atmel parts) * 2008 sign Cortex license agreement with ARM Holdings.Press Release; Atmel; February 4, 2013./ref> ** Cortex-M3 (MCU) (ARMv7-M Harvard architecture) *** SAM3U (2009) *** SAM3S (2009) *** SAM3N (2010) *** SAM3A (2012) *** SAM3X (2012) ** Cortex-M4 (MCU) (ARMv7E-M Harvard architecture) *** SAM4S (2011) *** SAM4L (2012) *** SAM4E (2013) series based on the ARM Cortex-M4F, first Atmel MCU that has a FPU (Floating-Point Unit).Press Release; Atmel; January 14, 2013.
/ref> *** SAM4N (2013) *** SAM4C (2014) dual-corePress Release; Atmel; August 12, 2014.
/ref> *** SAM G51/53 (2014) based on the ARM Cortex-M4F.Press Release; Atmel; January 7, 2014.
/ref> *** SAM G54/55 (2015) based on the ARM Cortex-M4F.Press Release; Atmel; January 5, 2015.
/ref> ** Cortex-A5 (MPU) (ARMv7-A architecture) *** SAMA5D3 series, (2013) Atmel announced the SAMA5D3 series based on the ARM Cortex-A5, which is the first Atmel chip with a Cortex-A5 core. *** SAMA5D4 (2014)Press Release; Atmel; October 1, 2014.
/ref> *** SAMA5D2 series (2015)Press Release; Atmel; September 14, 2015.
/ref> ** Cortex-M0+ (MCU)in the SAM D20 (2013) (ARMv6-M architecture) – In June 2013, Atmel announced the SAMD20 series based on the ARM Cortex-M0+.Press Release; Atmel; June 17, 2013.
/ref> ** Cortex-M7 (MCU) (ARMv7-M architecture) *** SAMS70 series, (2015) Atmel announced the SAM S70 series based on the ARM Cortex-M7.Press Release; Atmel; July 15, 2015.
/ref> *** SAME70 series, (2015) Atmel announced the SAM S70 series based on the ARM Cortex-M7. *** SAMV70 series, (2015) Atmel announced the SAM S70 series based on the ARM Cortex-M7, which is the first Atmel chip automotive grade with a Cortex-M7 core.Press Release; Atmel; Jan 6, 2015.
/ref>
Products
Microcontrollers
Microcontrollers have internal program memory as well as the conventional internal registers and RAM. Microchip ARM MCUs range from the SAM D10 series with as few as 14 pins, to the 144-pin SAM S70 and SAM E70 products. The SAM4S, SAM4N, SAM3S, SAM3N, SAM7S (64-pin) families have pin-compatible IC footprints, except for USB device, though they are not voltage level compatible.SAM C
The Atmel C family was launched in May 2015. Based on Cortex-M0+, pin and code compatible with the SAM D and SAM L series, with wide operating voltage ranges (2.7–5.5 V), CAN bus, and up to 12 DMA controller channels.SAM D
The SAM D (ATSAMD) family from Microchip consists of four different sub series (SAM D10, SAM D11, SAM D20, SAM D21). The devices are all based on theARM Cortex-M0+
The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Holdings. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though ...
processor and offer different pin, memory, and feature combinations. The devices are pin- and code-compatible and share peripherals like the Event System and the SERCOM module for reconfigurable multiplexed serial communication
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits a ...
ports. The Arduino Zero board uses an ATSAMD21G18 chip.
The SAM D5X/E5X and SAM D51 feature the 32-bit Cortex-M4F.
SAM L
SAM 3
 In 2009 Atmel announced the ATSAM3U line of flash-based microcontrollers based on the
In 2009 Atmel announced the ATSAM3U line of flash-based microcontrollers based on the ARM Cortex-M3
The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Holdings. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though ...
processor, as a higher end evolution of the SAM7 microcontroller products. They have a top clock speed in the range of 100 MHz, and come in a variety of flash sizes. In the summer 2009 these parts were still sampling, and a development board had recently been made available.
In December 2009, the ATSAM3S line was announced. This features several enhancements for lower power operation and bill of materials cost reduction.
Market watchers observe that these Cortex-M3 products are competition for Atmel's own AVR32
AVR32 is a 32-bit RISC microcontroller architecture produced by Atmel. The microcontroller architecture was designed by a handful of people educated at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, including lead designer Øyvind Strøm a ...
UC3A products. Both are microcontrollers with largely identical peripherals and other hardware technology, flash-based, similar clock speeds, and with dense 16/32 bit RISC instruction sets.
SAM3A
SAM3N
SAM3S
– reduce power consumption
SAM3U
– high-speed USB
SAM3X
– the ''
Arduino Due This is a non-exhaustive list of Arduino boards and compatible systems. It lists boards in these categories:
* Released under the official Arduino name
* Arduino "shield" compatible
* Development-environment compatible
* Based on non-Atmel processor ...
'' board uses the Atmel SAM3X8E microcontroller
SAM 4
The ATSAM4 is based on the ARM Cortex-M4 core. The SAM4E includes a FPU ( Floating-Point Unit). The SAM4C includes a dual-core ARM Cortex-M4 (one core with a FPU). 1 August 2017, the ATSAMD5x and ATSAME5x family was announced. This features several enhancements for lower power operation and more peripherals, Ethernet and CANBUS-FD in SAME5x seriesSAM4C
– ARM Cortex-M4/M4F dual-core, which includes FPU
SAM4E18-16 series
– ARM Cortex-M4F core, which includes FPU
SAM4L
– ARM Cortex-M4 core
SAM4N
– ARM Cortex-M4 core, pin-to-pin compatibility with SAM4S, SAM3S, SAM3N, SAM7S devices
SAM4S
– ARM Cortex-M4 core
SAMG5x
– ARM Cortex-M4F core, which includes FPU, ATSAMG55 for 120 MHz CPU speed.
SAMD5x
- Latest ARM Cortex-M4F core, which includes FPU and Integrated Security including Symmetric (AES) and Asymmetric (ECC) Encryption, Public Key Exchange Support(PUKCC), TRNG and SHA based memory Integrity checker.
SAME5x
- Same with D5x plus Ethernet MAC and CAN-FD networking peripherals. Both SAMD5x-E5x series integrate many similar peripherals for ex Timers and Sercoms for UART, I2C, SPI etc from ATSAMD2x and ATSAMC2x M0+ series thus is easier to upgrade to M4F Core MCUs.
SAM x70
These are based on the ARM Cortex-M7 core.SAMS70
– general purpose high performance MCU
SAME70
– connectivity high performance MCU
SAMV70, SAMV71
– automotive high performance MCU
Legacy
=AT91SAM7
= There are a wide variety of AT91 flash-based microcontrollers, based on ARM7TDMI cores. These chips have a top clock speed in the range of 60 MHz, and come with a variety of flash sizes and peripheral sets.SAM7L
– low power operation
SAM7S
– USB and other peripherals. SAM7S 64-pin chips are compatible with SAM4S, SAM4N SAM3S, SAM3N families.
SAM7SE
– USB, external memory support, and other peripherals
SAM7X
– Ethernet, USB, CAN, and other peripherals
SAM7XC
-–cryptographic extensions (notably AES support) to AT91SAM7X chips
Microprocessors
AT91SAM9
The AT91SAM9XE flash-based microcontrollers are based on the ARM926ej-s cores. They have a top clock speed in the range of 200 up to 400 MHz, and come with a variety of flash sizes. They somewhat resemble flash-equipped AT91SAM9260 chips. Microchip introduced the AT91SAM9 processors (using the ARM926ej-s core, with the ARMv5TEJ architecture) as its first broad market follow on to the highly successful AT91RM9200 processor. These processors improved on that predecessor by using less power, incorporating a newer and more powerful ARM core, and providing a variety of chips with different peripheral sets. While most are clocked at up to about 200 MHz, some can run at twice that speed. Processors include:SAM9G25
SAM9G45
SAM9X35
SAM9XE512
SAM9260
SAMA5
This series is based on the ARM Cortex-A5 core. ;SAMA5D2SAMA5D2
– 10/100 Ethernet, CAN, LCD, ClassD audio, QSPI, USB HSIC, Raw Bayer Image Sensor Interface, LPDDR3/LPDDR2/LPDDR/DDR2, up to 10 UART ;SAMA5D3
SAMA5D31
– 10/100 Ethernet, LCD
SAMA5D33
– Gigabit Ethernet, LCD
SAMA5D34
– Gigabit Ethernet, LCD, dual CAN
SAMA5D35
– no LCD, dual CAN, one Gigabit Ethernet + one 10/100 Ethernet
SAMA5D36
– LCD, dual CAN, one Gigabit Ethernet + one 10/100 Ethernet ;SAMA5D4
SAMA5D4
– 528 MHz (840 DMIPS), Neon, 128 KB L2 cache, video decoder, LCD, Ethernet
Smart Energy
* SAM 4C/CMArduino boards
;OfficialArduino Due
with 84 MHz Atmel ATSAM3X8E (
ARM Cortex-M3
The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Holdings. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though ...
core).
Arduino Zero
with 48 MHz Atmel ATSAMD21G18 (
ARM Cortex-M0+
The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Holdings. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though ...
core).
Arduino MKR1000
with 48 MHz Atmel ATSAMW25 (
ARM Cortex-M0+
The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Holdings. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though ...
core).
;Shield Compatible
* Shield-compatiblRascal
with 400 MHz Atmel AT91SAM9G20 (
ARM926EJ-S
ARM9 is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Holdings for microcontroller use. The ARM9 core family consists of ARM9TDMI, ARM940T, ARM9E-S, ARM966E-S, ARM920T, ARM922T, ARM946E-S, ARM9EJ-S, ARM926EJ-S, ARM968E-S, ARM996H ...
core).
Atmel boards
* Xplained Pro * Xplained * SAM W21 * SAMA5Development tools
Cortex-M
IDE
Integrated development environments: ;Windows * Microchip - MPLAB and Atmel Studio 7 * IAR – Embedded Workbench for ARMCrossware – Development Suite for ARM
;Linux * Buildroot * Openembedded * meta-atmel Yocto compliant layer
Debuggers
* Atmel-ICE * JTAG-ICE * Segger J-LinkCrossware Jaguar
Documentation
The amount of documentation for all ARM chips is daunting, especially for newcomers. The documentation for microcontrollers from past decades would easily be inclusive in a single document, but as chips have evolved so has the documentation grown. The total documentation is especially hard to grasp for all ARM chips since it consists of documents from the IC manufacturer (for example,Microchip
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
) and documents from CPU core vendor ( ARM Holdings).
A typical top-down documentation tree is: manufacturer website, manufacturer marketing slides, manufacturer datasheet for the exact physical chip, manufacturer detailed reference manual that describes common peripherals and aspects of a physical chip family, ARM core generic user guide, ARM core technical reference manual, ARM architecture reference manual that describes the instruction set(s).
;Documentation tree (top to bottom):
# Microchip Microcontrollers and Microprocessors website
# Microchip ARM-series marketing slides
# Microchip ARM-chip datasheet
# ARM core website
# ARM core generic user guide
# ARM core technical reference manual
# ARM architecture reference manual
Microchip has additional documents, such as: evaluation board user manuals, application notes, getting started guides, software library documents, errata, and more. See External Links
An internal link is a type of hyperlink on a web page to another page or resource, such as an image or document, on the same website or domain.
Hyperlinks are considered either "external" or "internal" depending on their target or destination ...
section for links to official Microchip and ARM documents.
See also
*ARM architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured ...
, List of ARM microprocessor cores
This is a list of central processing units based on the ARM family of instruction set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA), also called computer architecture, is an abstract model of a computer. A device that executes i ...
, ARM Cortex-M
* Microcontroller, List of common microcontrollers
* Embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded ...
, Single-board microcontroller
A single-board microcontroller is a microcontroller built onto a single printed circuit board. This board provides all of the circuitry necessary for a useful control task: a microprocessor, I/O circuits, a clock generator, RAM, stored progr ...
* Interrupt, Interrupt handler, Comparison of real-time operating systems
* JTAG
JTAG (named after the Joint Test Action Group which codified it) is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.
JTAG implements standards for on-chip instrumentation in electronic design aut ...
, SWD
References
Further reading
External links
; Microcontrollers, Digital Signal Controllers and Microprocessors official documents * ;ARM official documents ;OtherAtmel AT91 ARM Microcontroller Forum
{{DEFAULTSORT:At91sam ARM-based processors ARM architecture