1928 Summer Olympics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1928 Summer Olympics ( nl, Olympische Zomerspelen 1928), officially known as the Games of the IX Olympiad ( nl, Spelen van de IXe Olympiade) and commonly known as Amsterdam 1928, was an international multi-sport event that was celebrated from 28 July to 12 August 1928 in
 * For the first time, the parade of nations started with
* For the first time, the parade of nations started with  * The sponsor
* The sponsor
, sports-reference.com; retrieved 12 November 2015.
 Fourteen sports venues were used for the 1928 Summer Olympics. The Swim Stadium was demolished in 1929. The Het Kasteel football stadium was renovated in 1998–99. The Monnikenhuize stadium was demolished in 1950. The Schermzaal sports hall has also been demolished. The Olympic Stadium was renovated between 1996 and 2000, and is still in use. The Old Stadion was demolished in 1929 and replaced with housing in the Amsterdam area.
Fourteen sports venues were used for the 1928 Summer Olympics. The Swim Stadium was demolished in 1929. The Het Kasteel football stadium was renovated in 1998–99. The Monnikenhuize stadium was demolished in 1950. The Schermzaal sports hall has also been demolished. The Olympic Stadium was renovated between 1996 and 2000, and is still in use. The Old Stadion was demolished in 1929 and replaced with housing in the Amsterdam area.
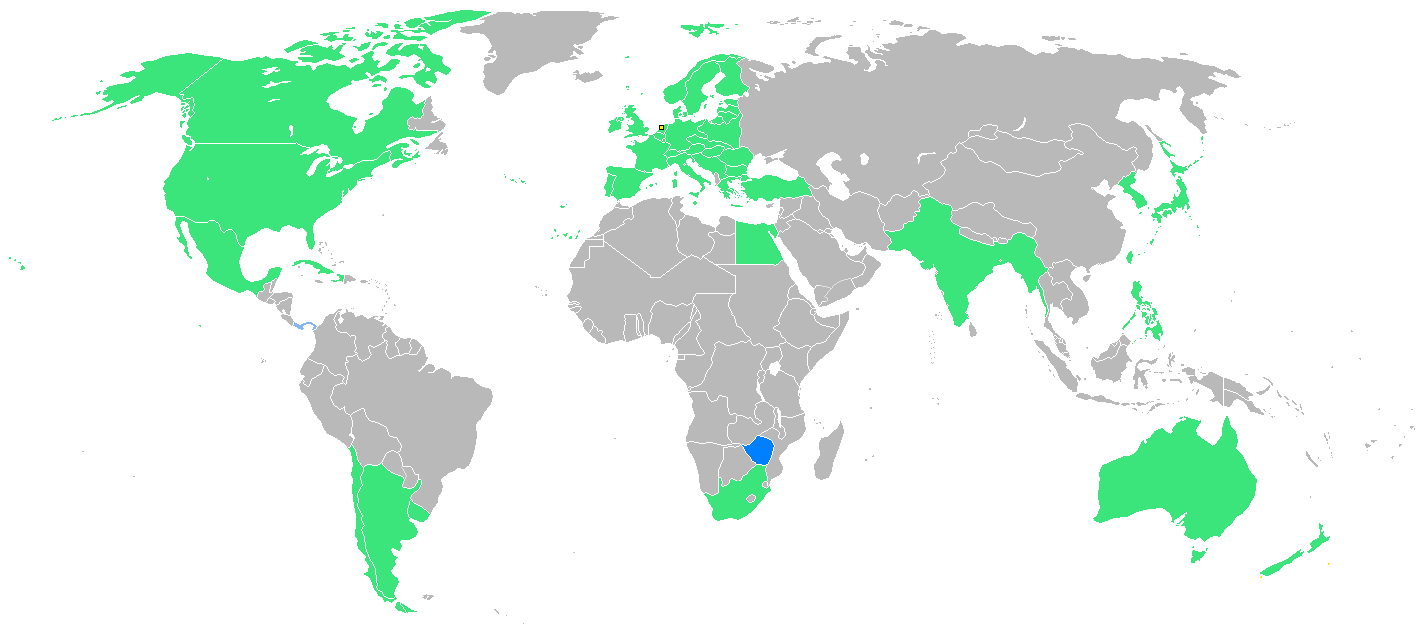
 A total of 46 nations were represented at the Amsterdam Games.
A total of 46 nations were represented at the Amsterdam Games.
The Ninth Olympiad. Amsterdam 1928. Official Report
Memorabilia of the Ninth Olympiad 1928 Amsterdam
{{Portal bar, 1920s, Olympics, Netherlands Summer Olympics, 1928 Amsterdam-Zuid
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
, Netherlands. The city of Amsterdam had previously bid for the 1920 and 1924 Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a multi ...
, but was obliged to give way to war-torn Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
for the 1920 Games and Pierre de Coubertin
Charles Pierre de Frédy, Baron de Coubertin (; born Pierre de Frédy; ...
's Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
for the 1924 Games.
The only other candidate city for the 1928 Olympics was Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world ...
, which would eventually be selected to host the Olympics four years later. In preparation for the 1932 Summer Olympics, the United States Olympic Committee reviewed the costs and revenue of the 1928 Games. The committee reported a total cost of US$1.183 million with receipts of US$1.165 million, giving a negligible loss of US$18,000, which was a considerable improvement over the 1924 Games.
The United States won the most gold and overall medals.
Host city selection
Dutch nobleman Frederik van Tuyll van Serooskerken first proposed Amsterdam as host city for theSummer Olympic Games
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
in 1912, even before the Netherlands Olympic Committee was established.
The Olympic Games were cancelled in 1916 due to World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
. In 1919, the Netherlands Olympic Committee abandoned the proposal of Amsterdam in favor of their support for the nomination of Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
as host city for the 1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
. In 1921, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
was selected for the 1924 Summer Olympics on the condition that the 1928 Summer Olympics would be organized in Amsterdam. This decision, supported by the Netherlands Olympic Committee, was announced by the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swis ...
(IOC) on 2 June 1921.
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world ...
bid for the 1928 Summer Olympics was without success in 1922 and again in 1923. The city was eventually selected as host city for the 1932 Summer Olympics, being the only bidder for that year.
Highlights
*These were the first Olympics to be organized under the IOC presidency ofHenri de Baillet-Latour
Henri de Baillet-Latour, Count of Baillet-Latour (1 March 1876 – 6 January 1942) was a Belgian aristocrat and the third president of the International Olympic Committee (IOC).
Early life
Henri de Baillet-Latour was born in Brussels, Belgium ...
.
* The Olympic Flame was lit for the first time for the duration of the Olympics, a tradition that continues to this day. The torch relay, however, would not take place until the 1936 Summer Olympics.
 * For the first time, the parade of nations started with
* For the first time, the parade of nations started with Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, which holds the origins of the Olympics, and ended with the host country, a tradition which has also continued ever since.
* The Games were officially opened by Prince Hendrik, consort of Queen Wilhelmina, who had authorized her husband to deputise for her. The Queen was unable to attend the opening ceremony as she was on holiday in Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
and did not want to disrupt her trip. This was the second time a head of state had not personally officiated at an Olympic opening ceremony
The Olympic Games ceremonies of the Ancient Olympic Games were an integral part of these Games; the modern Olympic games have opening, closing, and medal ceremonies. Some of the elements of the modern ceremonies date back to the Ancient Games from ...
(the first occasion being the 1904 Games in St. Louis, Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, which were officially opened by David R. Francis the Mayor of St. Louis). The Queen had initially refused to make an appearance at either the opening or closing ceremony; it is thought that she objected to the Netherlands hosting the 1928 Games as she considered the Olympics to be a demonstration of paganism. However, she returned from Norway before the conclusion of the Games, to be present at the closing ceremony, and she presented the first prizes at the prize distribution which was held immediately beforehand.
 * The sponsor
* The sponsor Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, or Coke, is a carbonated soft drink manufactured by the Coca-Cola Company. Originally marketed as a temperance bar, temperance drink and intended as a patent medicine, it was invented in the late 19th century by John Stith Pembe ...
made its first appearance at the Olympic Games.
* Many cars were expected for the Games, but Amsterdam had no more than 2,000 single car parking spaces. Consequently, a number of new parking sites were provided and a special parking symbol was launched to show foreign visitors where they could park. The white P on a blue background was to become the international traffic sign for parking, which is still used today.
* These Games were the first to bear the name "Summer Olympic Games", to distinguish them from the Winter Olympic Games.
* These Games were the first to feature a fixed schedule of sixteen days, which is still followed since 1984. In previous Olympics, competition had been stretched out over several months.
* Athletics
Athletics may refer to:
Sports
* Sport of athletics, a collection of sporting events that involve competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking
** Track and field, a sub-category of the above sport
* Athletics (physical culture), competi ...
events were held on a 400-meter track, later becoming the standard for athletics tracks.
* Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
returned to the Olympic Games for the first time since 1912, after being banned from the 1920 and 1924 Games. The German team finished second in the 1928 medal count.
* Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
would compete as a nation at the Summer Olympics for the last time until 1992, as a result of political problems and its occupation by the Soviet Union
* South American football made a definite breakthrough, as Uruguay retained its title by defeating Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
.
* India took its first ever gold medal in field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ...
, beginning a streak of six consecutive gold medals in the sport.
Athlete highlights
*Paavo Nurmi
Paavo Johannes Nurmi (; 13 June 1897 – 2 October 1973) was a Finnish middle-distance and long-distance runner. He was called the "Flying Finn" or the "Phantom Finn", as he dominated distance running in the 1920s. Nurmi set 22 official worl ...
of Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
won his ninth, and final, gold medal in the 10,000 m race.
* Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
athlete Percy Williams exceeded expectations by winning both the 100 m
The 100 metres, or 100-meter dash, is a sprint race in track and field competitions. The shortest common outdoor running distance, the dash is one of the most popular and prestigious events in the sport of athletics. It has been conteste ...
and 200 m
The 200 metres, or 200-meter dash, is a sprint running event. On an outdoor 400 metre racetrack, the race begins on the curve and ends on the home straight, so a combination of techniques is needed to successfully run the race. A slightl ...
sprint events.
* Crown Prince Olav
Olav V (; born Prince Alexander of Denmark; 2 July 1903 – 17 January 1991) was the King of Norway from 1957 until his death in 1991.
Olav was the only child of King Haakon VII of Norway and Maud of Wales. He became heir apparent to the Nor ...
, who would later become King of Norway; won a gold medal in the 6 meter sailing event.
* Pat O'Callaghan won the first ever medal for a newly independent Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, taking gold in the hammer throw
The hammer throw is one of the four throwing events in regular track and field competitions, along with the discus throw, shot put and Javelin throw, javelin.
The "hammer" used in this sport is not like any of the tools also called by that na ...
.
* Mikio Oda of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
won the triple jump event with a result of , becoming the first gold medalist from an Asian country.
* Betty Robinson
Elizabeth R. Schwartz (née Robinson; August 23, 1911 – May 18, 1999) was an American athlete and winner of the first Olympic 100 metres for women.
Early life
Robinson was born in Riverdale, Illinois. She was a student at Thornton Township H ...
of USA won the women's 100 metres in a world record time of 12.2 seconds. She was still just 16 years of age at the time.
* Algerian-born marathon runner Boughera El Ouafi
Ahmed Boughèra El Ouafi ( ar, أحمد بوقرة الوافي; 15 October 1898 – 18 October 1959) was an Algerian athlete during the time of the French occupation of Algeria. In 1928, he won the Olympic gold medal in the marathon.
Biog ...
won a gold medal for France in the men's marathon.
* Johnny Weissmuller, who later appeared in several Tarzan
Tarzan (John Clayton II, Viscount Greystoke) is a fictional character, an archetypal feral child raised in the African jungle by the Mangani great apes; he later experiences civilization, only to reject it and return to the wild as a heroic adv ...
movies, won two gold medals in swimming: an individual gold in the men's 100 m freestyle, and a team gold in the men's 4 x 200 m freestyle relay.Johnny Weissmuller profile, sports-reference.com; retrieved 12 November 2015.
Sports
During the 1928 Summer Olympics, there were 14 sports, 20 disciplines and 109 events in the tournament. In parentheses is the number of events per discipline. Women'sathletics
Athletics may refer to:
Sports
* Sport of athletics, a collection of sporting events that involve competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking
** Track and field, a sub-category of the above sport
* Athletics (physical culture), competi ...
and team gymnastics
Gymnastics is a type of sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, dedication and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, s ...
debuted at these Olympics, in spite of criticism. Five women's athletics events were added: 100 meters, 800 meters, high jump, discus, and 400 meter hurdles. In protest of the limited number of events, British women athletes, boycotted the Games. Halina Konopacka
Halina Konopacka (Leonarda Kazimiera Konopacka-Matuszewska-Szczerbińska) (26 February 1900 – 28 January 1989) was a Polish athlete. She won the discus throw event at the 1928 Summer Olympics, defeating American silver medal winner Lillian Cop ...
of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
became the first female Olympic track and field champion. Reports that the 800 meter run ended with several of the competitors being completely exhausted were widely (and erroneously) circulated. As a result, the IOC decided that women were too frail for long-distance running, and women's Olympic running events were limited to 200 meters until the 1960s.
Tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball cov ...
disappeared from the program, only to reappear in 1968 as a demonstration sport.
Demonstration sports
*Kaatsen
Frisian handball ( fry, keatsen; nl, kaatsen) is a traditional Frisian sport, related to American handball and fives, that is most commonly practiced by people from the northern Dutch province of Friesland (''Fryslân''). It is believed to be ...
* Korfball
* Lacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensiv ...
These Games also included art competitions in five categories: architecture, painting, sculpture, literature, and poetry. However, the IOC no longer considers these to be official medal events, so the medals awarded are not included in today's Olympic medal counts.
Venues
 Fourteen sports venues were used for the 1928 Summer Olympics. The Swim Stadium was demolished in 1929. The Het Kasteel football stadium was renovated in 1998–99. The Monnikenhuize stadium was demolished in 1950. The Schermzaal sports hall has also been demolished. The Olympic Stadium was renovated between 1996 and 2000, and is still in use. The Old Stadion was demolished in 1929 and replaced with housing in the Amsterdam area.
Fourteen sports venues were used for the 1928 Summer Olympics. The Swim Stadium was demolished in 1929. The Het Kasteel football stadium was renovated in 1998–99. The Monnikenhuize stadium was demolished in 1950. The Schermzaal sports hall has also been demolished. The Olympic Stadium was renovated between 1996 and 2000, and is still in use. The Old Stadion was demolished in 1929 and replaced with housing in the Amsterdam area.
Participating nations

 A total of 46 nations were represented at the Amsterdam Games.
A total of 46 nations were represented at the Amsterdam Games. Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
, and Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
) competed at the Olympic Games for the first time. Germany returned after having been banned in 1920 and 1924.
Number of athletes by National Olympic Committees
Medal count
These are the top ten nations that won medals at the 1928 Games.Poster
The official poster for the Games displaying a running man in a white shirt was designed by Jos Rovers however the IOC never succeeded in obtaining the copyright of the image. The IOC used a different poster, with theGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
text ''Olympische Spiele'', and an athlete partly covered in the Dutch national flag, holding a peace leaf in his hand. The poster was made for a German book about the Amsterdam Olympics.
Last surviving competitor
The last living competitor of the 1928 Summer Olympics wasClara Marangoni
Carla Marangoni, better known as Clara Marangoni (13 November 1915 – 18 January 2018), was an Italian gymnast who competed in the 1928 Summer Olympics. She was born in Pavia as "Carla," but she is usually (mistakenly) mentioned in the offici ...
, a member of the silver medal-winning Italian gymnastic team who had been twelve years old during the Olympics. Marangoni died 18 January 2018, at the age of 102 as the oldest living Olympic medalist at the time of her death.
See also
References
External links
*The Ninth Olympiad. Amsterdam 1928. Official Report
Memorabilia of the Ninth Olympiad 1928 Amsterdam
{{Portal bar, 1920s, Olympics, Netherlands Summer Olympics, 1928 Amsterdam-Zuid
Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
1920s in Amsterdam
Olympic Games in the Netherlands
Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
Summer Olympics by year
Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...