17.5 mm film on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 17.5 mm film was a
17.5 mm film was a
Tracing 17.5mm practices in Germany in 1902–1908
A Brief History of Amateur Film Gauges and Related Equipment
Film formats {{Photo-stub
 17.5 mm film was a
17.5 mm film was a film gauge
Film gauge is a physical property of photographic or motion picture film stock which defines its width. Traditionally, the major movie film gauges are 8 mm, 16 mm, 35 mm, and 65/70 mm (in this case 65 mm for the negative and 70 mm f ...
for as many of eight types of motion picture film stock, generally created by splitting unperforated 35 mm film.
History
17.5 mm film was first documented in 1898 with the creation of the Birtac camera, and subsequently went through several different iterations up until the end ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, when Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
's 16 mm film
16 mm film is a historically popular and economical gauge of film. 16 mm refers to the width of the film (about inch); other common film gauges include 8 and 35 mm. It is generally used for non-theatrical (e.g., industrial, educ ...
and 8 mm film
8 mm film is a motion picture film format in which the film strip is wide. It exists in two main versions – the original standard 8 mm film, also known as regular 8 mm, and Super 8. Although both standard 8 mm and S ...
largely took its place in terms of popularity. In addition to original pioneering experiments, 17.5 mm film was used during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
to use existing 35 mm stock more economically. Afterward, this format continued to be used primarily in developing countries such as India, or for projects where usage of regular 35 mm film would have been too expensive.
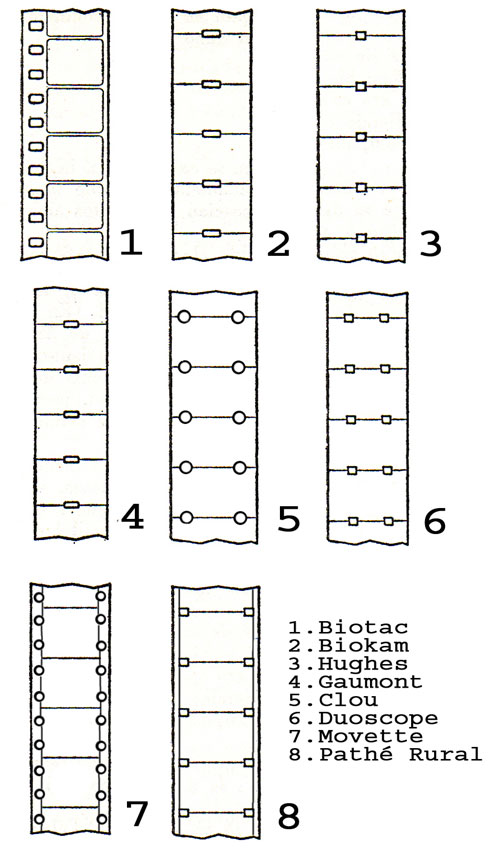
Partial list
Birtac
The British-American photographer and inventorBirt Acres
Birt Acres (23 July 1854 – 27 December 1918) was an American and British photographer and film pioneer. Among his contributions to the early film industry are the first working 35 mm camera in Britain (Wales), and ''Birtac'', the firs ...
split 35 mm film in half for his Birtac camera-projector in 1898. The film used had a single row of perforations running down the left side of the image, with two perforations per image. Historically, this is considered to be the first piece of motion picture equipment that utilized 17.5 film.
Biokam
Alfred Wrench andAlfred Darling
Alfred Darling (1862–1931) was an engineer and a key member of the loose association of early film pioneers dubbed the Brighton School by French film historian Georges Sadoul.
Biography
Darling began to manufacture film equipment at his engin ...
created second 17.5 mm format film in 1899 in London. The only differences between their and Acres' film was that their film had central perforations, and it could be utilized as a medium for still pictures as well. The Biokam camera, projector, and printer (all in one machine) was produced by the Warwick Trading Company
The Warwick Trading Company was a British film production and distribution company, which operated between 1898 and 1915.
History
The Warwick Trading Company had its origins in the London office of Maguire and Baucus, a firm run by two American ...
.
References
External links
Tracing 17.5mm practices in Germany in 1902–1908
A Brief History of Amateur Film Gauges and Related Equipment
Film formats {{Photo-stub