0-4-0 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Under the

 The
The
 In 1847, the government of the
In 1847, the government of the
 In September 1859 Messrs. E. & J. Pickering, contractors to the Cape Town Railway and Dock Company for the construction of the Cape Town-Wellington railway line, imported a small broad gauge 0-4-0 side-tank steam locomotive from England for use during the construction of the railway. This was the first locomotive in South Africa. In 1874 the locomotive was rebuilt to a 0-4-2T configuration before it was shipped to
In September 1859 Messrs. E. & J. Pickering, contractors to the Cape Town Railway and Dock Company for the construction of the Cape Town-Wellington railway line, imported a small broad gauge 0-4-0 side-tank steam locomotive from England for use during the construction of the railway. This was the first locomotive in South Africa. In 1874 the locomotive was rebuilt to a 0-4-2T configuration before it was shipped to  The first railway locomotive to run in revenue earning service in South Africa was a small broad gauge 0-4-0WT well tank engine named ''Natal'', manufactured by Carrett, Marshall and Company of Leeds. It made its inaugural run from Market Square to Point station in Durban during the official opening of the first operating railway in South Africa on Tuesday, 26 June 1860.The South African Railways - Historical Survey (Editor George Hart, Publisher Bill Hart, Sponsored by Dorbyl Ltd, Circa 1978, pp. 6-8.)
In 1865, the
The first railway locomotive to run in revenue earning service in South Africa was a small broad gauge 0-4-0WT well tank engine named ''Natal'', manufactured by Carrett, Marshall and Company of Leeds. It made its inaugural run from Market Square to Point station in Durban during the official opening of the first operating railway in South Africa on Tuesday, 26 June 1860.The South African Railways - Historical Survey (Editor George Hart, Publisher Bill Hart, Sponsored by Dorbyl Ltd, Circa 1978, pp. 6-8.)
In 1865, the
 * In 1873 and 1874, three Cape gauge saddle-tank locomotives, built by
* In 1873 and 1874, three Cape gauge saddle-tank locomotives, built by  * In 1889 the ''Nederlandsche-Zuid-Afrikaansche Spoorwegmaatschappij'' (NZASM) obtained its first six locomotives for use on the new line which was being constructed from
* In 1889 the ''Nederlandsche-Zuid-Afrikaansche Spoorwegmaatschappij'' (NZASM) obtained its first six locomotives for use on the new line which was being constructed from  * In 1902 the Harbours Department of the Natal Government placed a single saddle-tank locomotive in service as harbour shunter in Durban Harbour. It was built by Hudswell, Clarke and named Congella.
* In 1903, a single 0-4-0ST locomotive, built by New Lowca Engineering, was delivered to the Port Elizabeth Harbour Board.
* After the Harbour Boards were disbanded, some locomotives entered SAR harbour service as previously owned. Two locomotives named ''Stormberg'' and ''Thebus'' were originally built by
* In 1902 the Harbours Department of the Natal Government placed a single saddle-tank locomotive in service as harbour shunter in Durban Harbour. It was built by Hudswell, Clarke and named Congella.
* In 1903, a single 0-4-0ST locomotive, built by New Lowca Engineering, was delivered to the Port Elizabeth Harbour Board.
* After the Harbour Boards were disbanded, some locomotives entered SAR harbour service as previously owned. Two locomotives named ''Stormberg'' and ''Thebus'' were originally built by  * In 1907, the Central South African Railways also acquired a single self-contained Railmotor with a 0-4-0T+4 wheel arrangement.''CSAR General Manager's Reports'', Extracts from the CSAR General Manager's Reports for 1906, 1907, 1908 & 1909.
* In 1929, the South African Railways acquired a single self-contained Clayton railmotor with a 0-4-0+4 wheel arrangement for low-volume passenger service. The vehicle was a vertical boilered steam locomotive with a passenger coach which was an integral part of the locomotive itself.''Clayton Steam Rail Coach - From the Dave Rhind Collection'', Railway History Group of South Africa, Pinelands, Cape Town.
* In 1941, long after the Harbour Boards had ceased to exist, a contractor's locomotive which had been imported c. 1939 for use on the Foreshore land reclamation project in Cape Town was bought by the SAR for use as dock shunter in Table Bay Harbour. It had been built in 1909 by
* In 1907, the Central South African Railways also acquired a single self-contained Railmotor with a 0-4-0T+4 wheel arrangement.''CSAR General Manager's Reports'', Extracts from the CSAR General Manager's Reports for 1906, 1907, 1908 & 1909.
* In 1929, the South African Railways acquired a single self-contained Clayton railmotor with a 0-4-0+4 wheel arrangement for low-volume passenger service. The vehicle was a vertical boilered steam locomotive with a passenger coach which was an integral part of the locomotive itself.''Clayton Steam Rail Coach - From the Dave Rhind Collection'', Railway History Group of South Africa, Pinelands, Cape Town.
* In 1941, long after the Harbour Boards had ceased to exist, a contractor's locomotive which had been imported c. 1939 for use on the Foreshore land reclamation project in Cape Town was bought by the SAR for use as dock shunter in Table Bay Harbour. It had been built in 1909 by
/ref>
 Between 1886 and 1888, three well-tank condensing locomotives were placed in service by the Cape Copper Mining Company on its
Between 1886 and 1888, three well-tank condensing locomotives were placed in service by the Cape Copper Mining Company on its  In 1900 the British War Office placed two Sirdar class 0-4-0T tank steam locomotives in service on a narrow gauge line near Germiston in the ''Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek'', where the Royal Engineers had established a siege park during the
In 1900 the British War Office placed two Sirdar class 0-4-0T tank steam locomotives in service on a narrow gauge line near Germiston in the ''Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek'', where the Royal Engineers had established a siege park during the
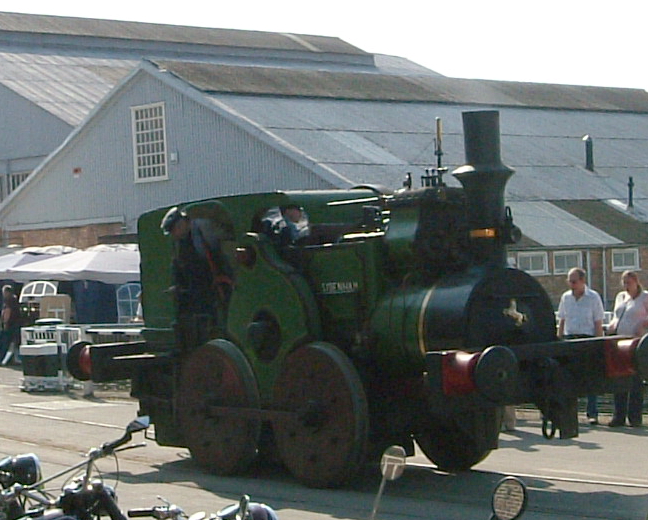 The tank engine versions of the wheel arrangement began to appear in the United Kingdom in the early 1850s, with the first significant class being six saddle tanks designed by Robert Sinclair for the
The tank engine versions of the wheel arrangement began to appear in the United Kingdom in the early 1850s, with the first significant class being six saddle tanks designed by Robert Sinclair for the 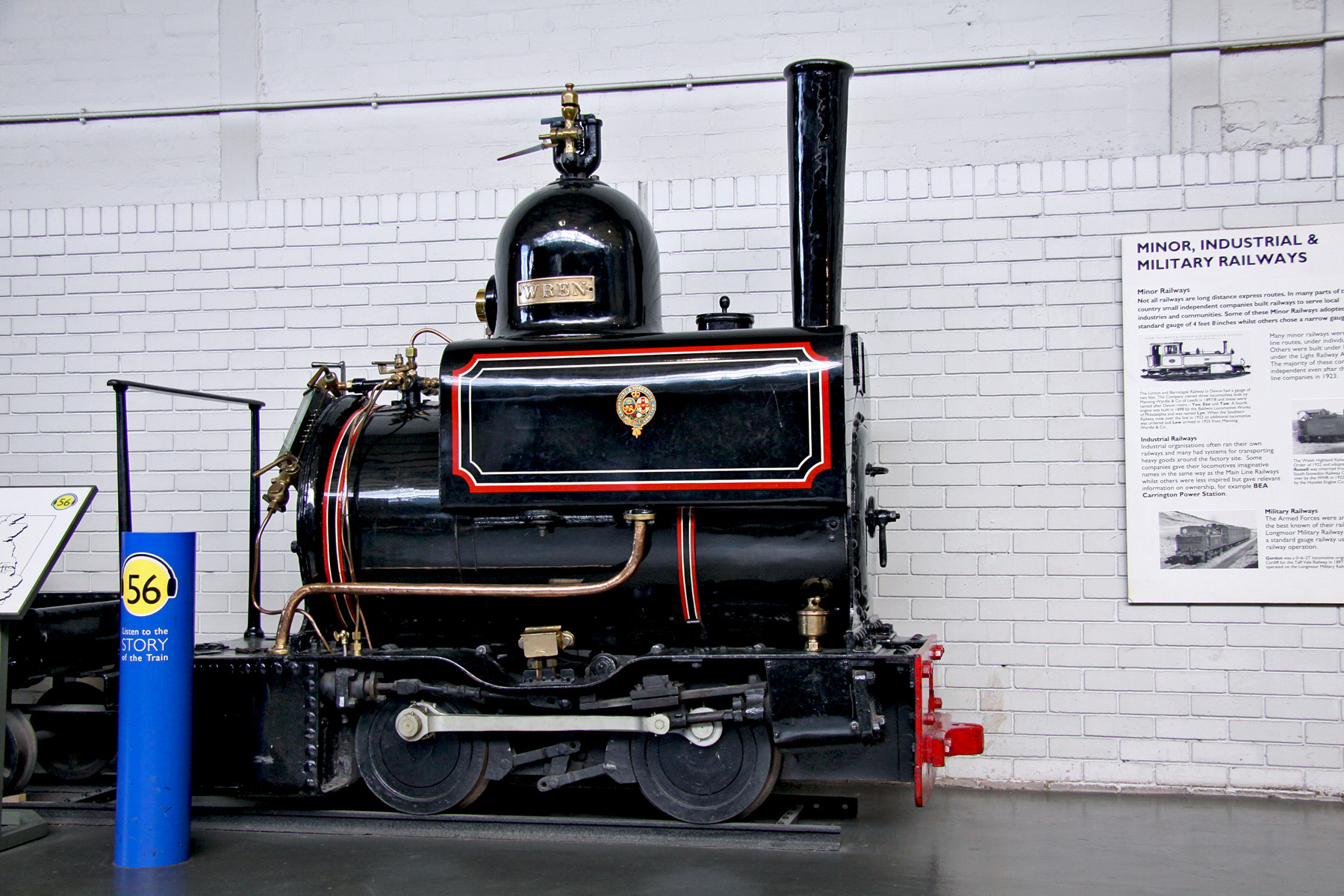 By 1860 the type was very popular and it continued to be built in significant numbers for both mainline and
By 1860 the type was very popular and it continued to be built in significant numbers for both mainline and
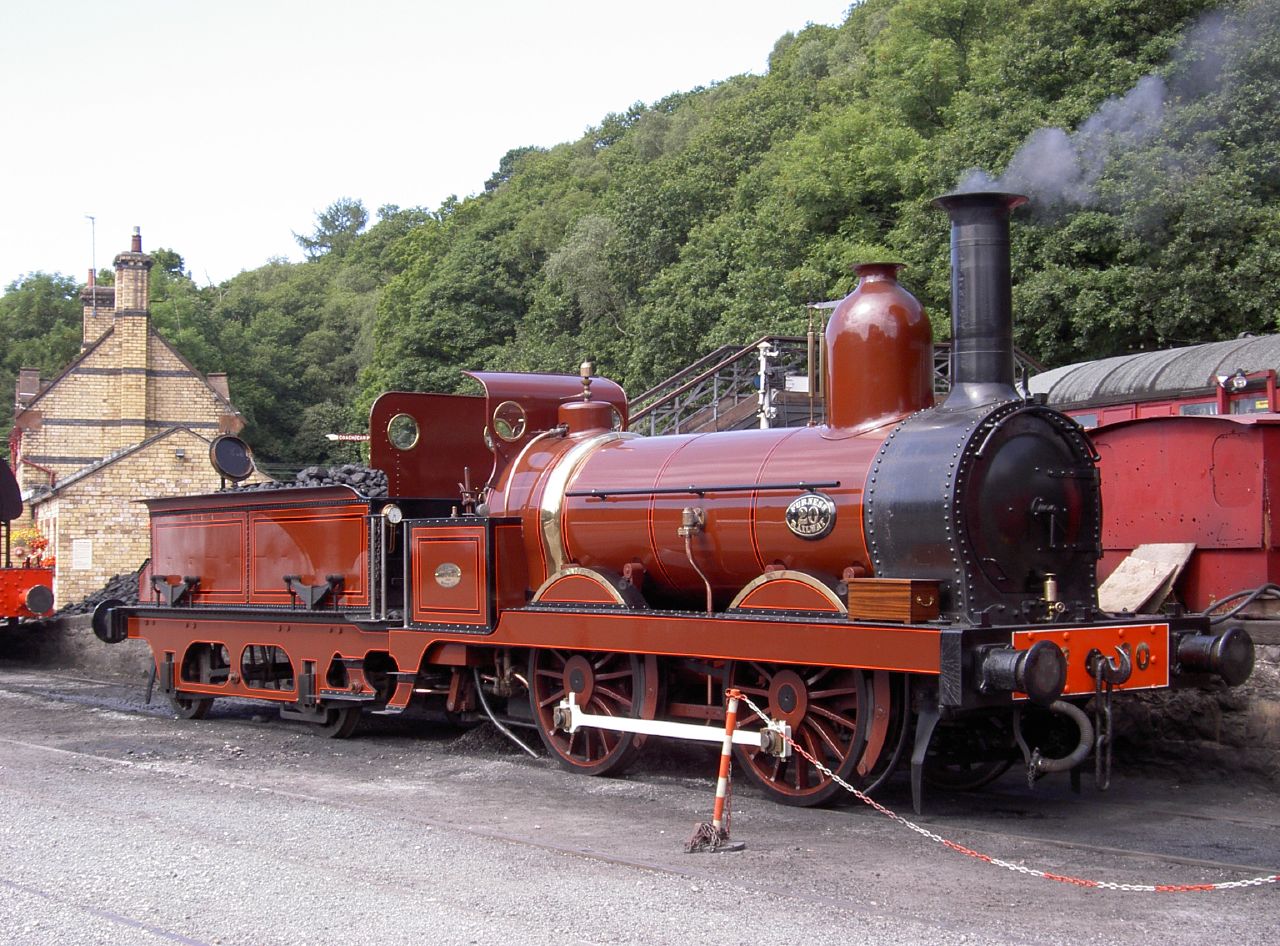 During the 1840s, the wheel arrangement was widely used by
During the 1840s, the wheel arrangement was widely used by
 An early example of the 0-4-0 vertical boiler type was the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad's ''
An early example of the 0-4-0 vertical boiler type was the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad's ''
 The wheel arrangement was also used on a number of small 0-4-0DM
The wheel arrangement was also used on a number of small 0-4-0DM
Whyte notation
Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth cen ...
for the classification of steam locomotives, represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven. The wheels on the earliest four-coupled locomotives were connected by a single gear wheel
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic p ...
, but from 1825 the wheels were usually connected with coupling rod
A coupling rod or side rod connects the driving wheels of a locomotive. Steam locomotives in particular usually have them, but some diesel and electric locomotives, especially older ones and shunters, also have them. The coupling rods transfer t ...
s to form a single driven set.
The notation 0-4-0T indicates a tank locomotive
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locom ...
of this wheel arrangement on which its water and fuel is carried on board the engine itself, rather than in an attached tender.
In Britain, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod-coupled driving wheels.
Under the UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Cre ...
used in Europe and, in more recent years, in simplified form in the United States, a 0-4-0 is classified as B (German and Italian) if the axles are connected by side rods or gearing and 020 (French), independent of axle motoring. The UIC's Bo classification for electric and diesel-electric locomotives indicates that the axles are independently motored, which would be under the Whyte notation.
Overview
The term ''Four-coupled'' is often used for 0-4-0 locomotives. ''Four-wheeled'' is also sometimes used, but this term can also encompass other wheel arrangements, for example Stephenson's Rocket which was an 0-2-2 four-wheeled locomotive. 0-4-0 locomotives were built astank locomotive
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locom ...
s as well as tender locomotives
A tender or coal-car (US only) is a special rail vehicle hauled by a steam locomotive containing its fuel (wood, coal, oil or torrefied biomass) and water. Steam locomotives consume large quantities of water compared to the quantity of fuel, s ...
. The former were more common in Europe and the latter in the United States, except in the tightest of situations such as that of a shop switcher, where overall length was a concern. The earliest 0-4-0 locomotives were tender engines and appeared as early as c. 1802. The 0-4-0 tank engine
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locomo ...
s were introduced in the early 1850s. The type was found to be so useful in many locations that they continued to be built for more than a century and existed until the end of the steam era.

Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
's ''Coalbrookedale'' (1802), ''Pen-y-Darren'' (1804) and ''Newcastle'' (1805) locomotives were of the 0-4-0 type, although in their cases the wheels were connected by a single gear wheel. The first 0-4-0 to use coupling rods was Locomotion No. 1
''Locomotion'' No. 1 (originally named ''Active'') is an early steam locomotive that was built in 1825 by the pioneering railway engineers George and Robert Stephenson at their manufacturing firm, Robert Stephenson and Company. It became th ...
, built by Robert Stephenson and Company
Robert Stephenson and Company was a locomotive manufacturing company founded in 1823 in Forth Street, Newcastle upon Tyne in England. It was the first company in the world created specifically to build railway engines.
Famous early locomoti ...
for the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. Stephenson also built the Lancashire Witch
''Lancashire Witch'' was an early steam locomotive built by Robert Stephenson and Company in Newcastle-upon-Tyne in 1828. It was a development of ''Locomotion''.
Description
''Lancashire Witch'' was an 0-4-0 locomotive with rear mounted cy ...
in 1828, and Timothy Hackworth
Timothy Hackworth (22 December 1786 – 7 July 1850) was an English steam locomotive engineer who lived in Shildon, County Durham, England and was the first locomotive superintendent of the Stockton and Darlington Railway.
Youth and early wor ...
built Sans Pareil
''Sans Pareil'' is a steam locomotive built by Timothy Hackworth which took part in the 1829 Rainhill Trials on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, held to select a builder of locomotives. The name is French and means 'peerless' or 'with ...
which ran at the Rainhill Trials in 1829. The latter two locomotives later worked on the Bolton and Leigh Railway
The Bolton and Leigh Railway (B&LR) was the first public railway in Lancashire, it opened for goods on 1 August 1828 preceding the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) by two years. Passengers were carried from 1831. The railway operated inde ...
.
A four-wheeled configuration, where all the wheels are driving wheels, uses all the locomotive's mass for traction but is inherently unstable at speed. The type was therefore mainly used for switchers (United States) and shunter
A switcher, shunter, yard pilot, switch engine, yard goat, or shifter is a small railroad locomotive used for manoeuvring railroad cars inside a rail yard in a process known as ''switching'' (US) or ''shunting'' (UK). Switchers are not inten ...
s (United Kingdom). Because of the lack of stability, tender engines of this type were only built for a few decades in the United Kingdom. They were built for a longer period in the United States.
The possible tractive effort
As used in mechanical engineering, the term tractive force can either refer to the total traction a vehicle exerts on a surface, or the amount of the total traction that is parallel to the direction of motion.
In railway engineering, the term t ...
of an 0-4-0 within normal axle load limits was not enough to move large loads. By 1900, they had therefore largely been superseded for most purposes by locomotives with more complex wheel arrangements. They nevertheless continued to be used in situations where tighter radius curves existed or the shorter length was an advantage. Thus, they were commonly employed in dockyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance ...
work, industrial tramways, or as shop switchers.
The wheel arrangement was also used on specialised types such as fireless locomotive
A fireless locomotive is a type of locomotive which uses reciprocating engines powered from a reservoir of compressed air or steam, which is filled at intervals from an external source. They offer advantages over conventional steam locomotives of ...
s, crane tank
A crane tank (CT) is a steam locomotive fitted with a crane for working in railway workshops, docksides, or other industrial environments. The crane may be fitted at the front, centre or rear.
The 'tank' in its name refers to water tanks mount ...
s, tram engine
A tram engine is a steam locomotive specially built, or modified, to run on a street, or roadside, tramway track.
Legal requirements
In the steam locomotive era, tram engines had to comply with certain legal requirements, although these varie ...
s and geared steam locomotives. It was also widely used on narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
railways.
Usage
Australia
In New South Wales,Dorrigo Steam Railway and Museum
The Dorrigo Steam Railway & Museum in Dorrigo, New South Wales, Australia is a large, privately owned collection of railway vehicles and equipment from the railways of New South Wales, covering both Government and private railways. The collect ...
has preserved twelve 0-4-0 steam locomotives and eight 0-4-0 diesel locomotives, a total of twenty examples, all on the one site.
Austria
In Tyrol,Achensee Railway
The Achensee Railway (german: Achenseebahn, ) is a long metre gauge railway running between Jenbach () and Seespitz () on Achensee, Lake Achen in state of Tyrol, Tyrol (Austria). Within its length it rises some in height, with the steeper sect ...
operates three 0-4-0 geared steam cog locomotives on their 1 meter narrow gauge tourist railway and has one on display. The locomotives were originally built by Wiener Lokomotivfabrik, but one has been rebuilt from scavenged parts.
Angola
 The
The Catumbela
Catumbela is a city and municipality of the Benguela province in Angola. The municipality had a population of 175,805 in 2014.
History
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the Portuguese built ''Forte de São Pedro'' to establish themselv ...
Sugar Estate in Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
operated a narrow gauge line on the estate. One of their locomotives, Rührthaler Maschinen-Fabrik 963 of 1929, was later rebuilt with a diesel engine.
Finland
Finland had the E1 and Vk4 classes with an 0-4-0 wheel arrangement. The E1 was a class of only two locomotives, numbered 76 and 77. The Vk4 was also a class of only two locomotives, built byBorsig Lokomotiv Werke (AEG)
The rail vehicle factory in Hennigsdorf, Germany, was founded in 1910 by AEG. Locomotive production began in 1913, and in the 1930s absorbed the work of the August Borsig locomotive factory, being renamed the Borsig Lokomotiv Werke GmbH until 19 ...
of Germany in 1910. The Vk4s were used at a fortress, and were eventually also used in dismantling the fortress, after which one locomotive went into industrial use and was scrapped in 1951. The other was sold to the Finnish Railways
VR-Group Plc ( fi, VR-Yhtymä Oyj, sv, VR-Group Abp), commonly known as VR, is a government-owned railway company in Finland. VR's most important function is the operation of Finland's passenger rail services with 250 long-distance and 800 co ...
and nicknamed ''Leena''. It became No. 68 and is now the oldest working broad gauge locomotive in Finland, being preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum
The Finnish Railway Museum ( fi, Suomen Rautatiemuseo) is located in Hyvinkää, Finland. It was founded in 1898 and located in Helsinki. The museum was moved to Hyvinkää in 1974.
The museum is on the original station and yard site of the Han ...
.
Indonesia
The Semarang-Cheribon Stoomtram Maatschappij (SCS) imported 27 standard gauge 0-4-0T locomotives of the B52 class between 1908 and 1911, originally to operate services from Kalibrodi- Semarang to Tanggung and Yogyakarta. They were built bySächsische Maschinenfabrik
The Sächsische Maschinenfabrik in Chemnitz was one of the most important engineering companies in Saxony in the second half of the 19th century and the first two decades of the 20th century. Including its various predecessor businesses, the firm ...
in Chemnitz, Germany. They were a modern locomotive design for the time, equipped with a superheater.
The largest allocation of B52 class locomotives was in Tegal, Central Java for services to Purwokerto. Some were later converted to tram engines and worked in Tegal and Purwokerto.
All 27 locomotives were in existence at the end of 1960, but by 1970 only 15 units remained. Two locomotives have been preserved, B5212 at the Taman Mini Indonesia Indah
Taman Mini "Indonesia Indah" (literally ''"Beautiful Indonesia" Mini Park''—the apostrophes are in the name—abbreviated as TMII) is a culture-based recreational area located in East Jakarta, Indonesia. Since July 2021, it is operated by the G ...
Museum of Transport and B5210 at the Ambarawa
Ambarawa is a town (and administratively, a district of the Semarang Regency) located between the city of Semarang and Salatiga in Central Java, Indonesia. Administratively, it is bordered by the districts of Banyubiru to the south, Jambu to the ...
Railway Museum.
New Zealand
The NZR A class of 1873 consisted of three engine types of similar specification but differing detail. They were British and New Zealand-built and several were preserved.Philippines
The only examples of this type in the Philippines were the five ''Manila'' class light-duty tank locomotives built byHunslet Engine Company
The Hunslet Engine Company is a locomotive-building company, founded in 1864 in Hunslet, England. It manufactured steam locomotives for over 100 years and currently manufactures diesel shunting locomotives. The company is part of Ed Murray & So ...
for the Manila Railway. They were ordered in 1885 for the Tranvía
The tranvía was a streetcar system that served Manila and its surrounding cities during the early years of the 20th century.
History
Prior to the tranvia, modes of street transportation in Manila are mostly horse-drawn, consisting of the ''c ...
system until they were used on the '' Ferrocarril de Manila a Dagupan'' in the 1890s. After being retired from the Manila Railroad in 1927, ''Manila'' was sold to the newly-formed Central Azucarrera de Tarlac, where it was made into a tank-tender locomotive until the 1980s. The locomotive was scrapped by 1991.
South Africa
Brunel gauge
 In 1847, the government of the
In 1847, the government of the Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with t ...
established harbour boards at its three major ports, Table Bay
Table Bay (Afrikaans: ''Tafelbaai'') is a natural bay on the Atlantic Ocean overlooked by Cape Town (founded 1652 by Van Riebeeck) and is at the northern end of the Cape Peninsula, which stretches south to the Cape of Good Hope. It was named b ...
, Port Elizabeth and East London. While railway lines were laid at all these harbours, trains were for the most part initially hauled by oxen or mules. The first steam locomotives to see service at these harbours were Brunel gauge engines which were placed in service on breakwater construction at Table Bay Harbour in 1862 and East London Harbour in 1874.
* At Table Bay Harbour a third Brunel gauge 0-4-0T locomotive was acquired from Fletcher, Jennings & Co. in 1874 to haul tip-wagons from the Victoria Basin excavation site to the breakwater which was being constructed simultaneously. Table Bay Harbour construction locomotives
* The East London Harbour's construction locomotives were 0-4-0 vertical boiler engines, similar in appearance to the American Grasshopper type. Four of them were acquired from Alexander Chaplin & Co. between 1873 and 1880, although the first one was only placed in service in 1874. John Middleton on vertical boiler locomotives in South Africa
* A fourth locomotive was added at Table Bay Harbour in 1879, a 0-4-0 well-tank engine, also built by Fletcher, Jennings.
* Three 0-4-0 saddle-tank locomotives entered breakwater construction service in Table Bay Harbour, two in 1881 and one more in 1893, built by Black, Hawthorn & Co.Classification of S.A.R. Engines with Renumbering Lists, issued by the Chief Mechanical Engineer’s Office, Pretoria, January 1912, pp. 2, 17. (Reprinted in April 1987 by SATS Museum, R.3125-6/9/11-1000)
Standard gauge
 In September 1859 Messrs. E. & J. Pickering, contractors to the Cape Town Railway and Dock Company for the construction of the Cape Town-Wellington railway line, imported a small broad gauge 0-4-0 side-tank steam locomotive from England for use during the construction of the railway. This was the first locomotive in South Africa. In 1874 the locomotive was rebuilt to a 0-4-2T configuration before it was shipped to
In September 1859 Messrs. E. & J. Pickering, contractors to the Cape Town Railway and Dock Company for the construction of the Cape Town-Wellington railway line, imported a small broad gauge 0-4-0 side-tank steam locomotive from England for use during the construction of the railway. This was the first locomotive in South Africa. In 1874 the locomotive was rebuilt to a 0-4-2T configuration before it was shipped to Port Alfred
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ha ...
, where it served as construction locomotive on the banks of the Kowie river and was nicknamed ''Blackie''. It has been declared a heritage object and was plinthed in the main concourse of Cape Town station.''Blackie'', Article by D. Littley, SA Rail September–October 1989, Published by RSSA, p. 133.
 The first railway locomotive to run in revenue earning service in South Africa was a small broad gauge 0-4-0WT well tank engine named ''Natal'', manufactured by Carrett, Marshall and Company of Leeds. It made its inaugural run from Market Square to Point station in Durban during the official opening of the first operating railway in South Africa on Tuesday, 26 June 1860.The South African Railways - Historical Survey (Editor George Hart, Publisher Bill Hart, Sponsored by Dorbyl Ltd, Circa 1978, pp. 6-8.)
In 1865, the
The first railway locomotive to run in revenue earning service in South Africa was a small broad gauge 0-4-0WT well tank engine named ''Natal'', manufactured by Carrett, Marshall and Company of Leeds. It made its inaugural run from Market Square to Point station in Durban during the official opening of the first operating railway in South Africa on Tuesday, 26 June 1860.The South African Railways - Historical Survey (Editor George Hart, Publisher Bill Hart, Sponsored by Dorbyl Ltd, Circa 1978, pp. 6-8.)
In 1865, the Natal Railway Company
The Natal Railway Company was formed in January 1859 for the construction of a railway in Durban.
The Natal Railway Company made use of broad gauge. The was only adopted in Natal in 1876 when the Natal Government Railways was established.
Th ...
obtained a saddle-tank locomotive with a wheel arrangement from Kitson and Company
Kitson and Company was a locomotive manufacturer based in Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Early history
The company was started in 1835 by James Kitson at the Airedale Foundry, off Pearson Street, Hunslet, with Charles Todd as a part ...
. This was the Natal Railway's second locomotive and was named ''Durban''.''It’s a Puzzlement'', Article by Bruno Martin, SA Rail December 1990, pp. 214-215.
In 1878, while construction work by the Kowie Harbour Improvement Company was underway at Port Alfred, the Cape Government Railways
The Cape Government Railways (CGR) was the government-owned railway operator in the Cape Colony from 1874 until the creation of the South African Railways (SAR) in 1910.
History Private railways
The first railways at the Cape were privately own ...
acquired one broad gauge (Saddle Tank) locomotive named ''Aid'' from Fox, Walker and Company of Bristol for use as construction locomotive on the east bank of the Kowie river.
Cape gauge
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a number of 0-4-0 tank- and saddle-tank locomotives were imported into South Africa, many of them for use in harbours. Many of these locomotives came intoSouth African Railways
Transnet Freight Rail is a South African rail transport company, formerly known as Spoornet. It was part of the South African Railways and Harbours Administration, a state-controlled organisation that employed hundreds of thousands of people ...
(SAR) stock in 1912, but were never classified.
 * In 1873 and 1874, three Cape gauge saddle-tank locomotives, built by
* In 1873 and 1874, three Cape gauge saddle-tank locomotives, built by Manning Wardle
Manning Wardle was a steam locomotive manufacturer based in Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Precursor companies
The city of Leeds was one of the earliest centres of locomotive building; Matthew Murray built the first commercially s ...
, were placed in service by the Cape Government Railways
The Cape Government Railways (CGR) was the government-owned railway operator in the Cape Colony from 1874 until the creation of the South African Railways (SAR) in 1910.
History Private railways
The first railways at the Cape were privately own ...
, two on the Midland System in 1873 and the third on the Western System in 1874. They were the first Cape gauge locomotives to enter service in South Africa.''C.G.R. Numbering Revised'', Article by Dave Littley, SA Rail May–June 1993, pp. 94-95.
* In 1874, a third saddle-tank locomotive, also built by Manning Wardle, was delivered to the Midland System of the CGR in Port Elizabeth. The locomotive was of a smaller design than the earlier locomotives of 1873.''Railway History of South Africa no. 2 - Early Locomotives of the Cape Government Railway'', Article by Leith Paxton, The Uloliwe, Vol 4 no 1, January 2013, pp. 62-63.
* Between 1875 and 1882, six saddle-tank locomotives with domeless boilers and three with domes were placed in service on all three systems of the CGR. They were all designated First Class when a classification system was adopted.
* In 1881, two Cape gauge saddle tank locomotives with a 0-4-0 wheel arrangement were placed in service by Teague and Company, who operated Teague's Tramway at the Kimberley diamond mine. In 1885 one was sold to the mine and the other to the CGR for use during the construction of a temporary rail bridge across the Orange River at Norvalspont. In the process the CGR locomotive, nicknamed ''Coffee Pot'', became the first locomotive to run across the border between the Cape Colony and the Orange Free State. John Middleton on the Coffee Pot
* Thirteen saddle-tank locomotives were acquired by the Table Bay Harbour Board from Black, Hawthorn and Company, Chapman and Furneaux and Hawthorn Leslie and Company
R. & W. Hawthorn, Leslie and Company, Limited, usually referred to as Hawthorn Leslie, was a shipbuilder and locomotive manufacturer. The company was founded on Tyneside in 1886 and ceased building ships in 1982.
History
The company was formed ...
between 1881 and 1904. Eleven survived to come into SAR stock in 1912, but were not included in the renumbering schedules or classified.
Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Dem ...
to Boksburg
Boksburg is a city on the East Rand of Gauteng province of South Africa. Gold was discovered in Boksburg in 1887. Boksburg was named after the State Secretary of the South African Republic, W. Eduard Bok. The Main Reef Road linked Boksburg ...
, one 13 Tonner and five very similar 14 Tonners.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1944). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter IV - The N.Z.A.S.M.''. South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, October 1944. pp. 761-764.
* In 1889 and 1890 the NZASM obtained three 10 Tonner tramway locomotives for use on the new line from Johannesburg to Boksburg which became known as the Randtram line.
* In 1891 five saddle-tank locomotives were imported, built by Neilson and Company
Neilson and Company was a locomotive manufacturer in Glasgow, Scotland.
The company was started in 1836 at McAlpine Street by Walter Neilson and James Mitchell to manufacture marine and stationary engines. In 1837 the firm moved to Hyde Park ...
for the Natal Government Railways
The Natal Government Railways (NGR) was formed in January 1877 in the Colony of Natal.
In 1877, the Natal Government Railways acquired the Natal Railway Company for the sum of £40,000, gaining the line from the Point to Durban and from Durban ...
(NGR). One was later sold to the Pretoria-Pietersburg Railway (PPR), where it was named ''Natal'', while two more went to the Durban Harbour. The remaining two were later included in the NGR's Class K. In 1912, four of these locomotives survived, including the ex-PPR locomotive, to be taken onto the SAR roster as obsolete unclassified locomotives.
* Between 1894 and 1902 eight saddle-tank locomotives were acquired by the Port Elizabeth Harbour Board for shunting service at the Port Elizabeth Harbour, four built by Black, Hawthorn in 1894 and 1895, two by Chapman and Furneaux in 1900 and two by Hudswell, Clarke in 1902.
 * In 1902 the Harbours Department of the Natal Government placed a single saddle-tank locomotive in service as harbour shunter in Durban Harbour. It was built by Hudswell, Clarke and named Congella.
* In 1903, a single 0-4-0ST locomotive, built by New Lowca Engineering, was delivered to the Port Elizabeth Harbour Board.
* After the Harbour Boards were disbanded, some locomotives entered SAR harbour service as previously owned. Two locomotives named ''Stormberg'' and ''Thebus'' were originally built by
* In 1902 the Harbours Department of the Natal Government placed a single saddle-tank locomotive in service as harbour shunter in Durban Harbour. It was built by Hudswell, Clarke and named Congella.
* In 1903, a single 0-4-0ST locomotive, built by New Lowca Engineering, was delivered to the Port Elizabeth Harbour Board.
* After the Harbour Boards were disbanded, some locomotives entered SAR harbour service as previously owned. Two locomotives named ''Stormberg'' and ''Thebus'' were originally built by Hudswell Clarke
Hudswell, Clarke and Company Limited was an engineering and locomotive building company in Jack Lane, Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
History
The company was founded as Hudswell and Clarke in 1860. In 1870 the name was changed to Hud ...
for the South African Public Works Department in 1903. They were acquired by the SAR in 1916, but were named instead of being classified and numbered.
* The CGR acquired a single self-contained Railmotor with a 0-4-0T+4 wheel arrangement for low-volume passenger service. The railmotor was a 0-4-0 side-tank locomotive with a passenger coach as an integral part of the locomotive itself, with a four-wheeled bogie under the coach end.Metropolitan Amalgamated Railway Carriage and Wagon Company Ltd drawing no. 12640
Orenstein & Koppel
Orenstein & Koppel (normally abbreviated to "O&K") was a major Germany, German engineering company specialising in railway vehicles, escalators, and heavy equipment. It was founded on April 1, 1876 in Berlin by Benno Orenstein and Arthur Koppel. ...
and on the SAR it was numbered SAR-H&NW no. 69.Railway History Group of Southern Africa, Bulletin no. 114, January 2013: Notes on Cape Town Harbour Extension Contracts, by John Middleton/ref>
Narrow gauges
 Between 1886 and 1888, three well-tank condensing locomotives were placed in service by the Cape Copper Mining Company on its
Between 1886 and 1888, three well-tank condensing locomotives were placed in service by the Cape Copper Mining Company on its Namaqualand Railway
The Namaqualand Railway was a narrow gauge railway operating between Port Nolloth and O'okiep in the Namaqualand region of the former Cape Colony in South Africa. It was originally a mule-drawn railway built to provide an outlet for the copper ...
between Port Nolloth and O'okiep
Okiep is a small town in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, and was in the 1870s ranked as having the richest copper mine in the world. The town is on the site of a spring that was known in the Khoekhoe language of the Nama people as ''U ...
in the Cape Colony. They were the first condensing steam locomotives to enter service in South Africa. They were later rebuilt as conventional well-tank locomotives.
In 1899, Rand Mines acquired two narrow gauge tank steam locomotives from Avonside Engine Company and in 1900 a similar locomotive was delivered to Reynolds Brothers Sugar Estates in Natal. In 1915, when an urgent need arose for additional narrow gauge locomotives in German South West Africa during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, these three locomotives were purchased second-hand by the South African Railways.
 In 1900 the British War Office placed two Sirdar class 0-4-0T tank steam locomotives in service on a narrow gauge line near Germiston in the ''Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek'', where the Royal Engineers had established a siege park during the
In 1900 the British War Office placed two Sirdar class 0-4-0T tank steam locomotives in service on a narrow gauge line near Germiston in the ''Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek'', where the Royal Engineers had established a siege park during the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
. The locomotives were built by Kerr, Stuart and Company
Kerr, Stuart and Company Ltd was a locomotive manufacturer in Stoke-on-Trent, England.
History
It was founded in 1881 by James Kerr as "James Kerr & Company", and became "Kerr, Stuart & Company" from 1883 when John Stuart was taken on as a ...
. At the end of the war, the two Sirdar locomotives were sold to a farmer, who used them on a firewood line between Pienaarsrivier and Pankop, until the line and locomotives were taken over by the Central South African Railways
The Central South African Railways (CSAR) was from 1902 to 1910 the operator of public railways in the Transvaal Colony and Orange River Colony in what is now South Africa. During the Anglo-Boer War, as British forces moved into the territory of ...
(CSAR). In 1912, when these locomotives were assimilated into the SAR, they were renumbered with an "NG" prefix to their numbers. When a system of grouping narrow gauge locomotives into classes was eventually introduced by the SAR somewhere between 1928 and 1930, they were designated .Kerr, Stuart and Company works list
In 1902, the CGR placed a single narrow gauge tank steam locomotive in service on the Avontuur branch, built by Manning Wardle
Manning Wardle was a steam locomotive manufacturer based in Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Precursor companies
The city of Leeds was one of the earliest centres of locomotive building; Matthew Murray built the first commercially s ...
, classified Type C and named ''Midget''. In 1912, this locomotive was assimilated into the South African Railways and renumbered. It was sold to the West Rand Consolidated Mines near Krugersdorp in 1921.
A single small five-ton locomotive, built by Krauss & Company, was purchased by the CGR c. 1903 and placed in service as construction engine on the narrow gauge Avontuur
Avontuur is a town situated in the Garden Route District Municipality in the Western Cape province of South Africa. The town is located 13km south-east of Uniondale on an intersection of the R339 and R62 regional routes.
History
The name is A ...
branch out of Port Elizabeth.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1944). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter II - The Cape Government Railways'' (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, April 1944. pp. 254-255.
United Kingdom
Tank locomotives
Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was a major Scottish railway company. It was formed in the early 19th century with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh an ...
.
 By 1860 the type was very popular and it continued to be built in significant numbers for both mainline and
By 1860 the type was very popular and it continued to be built in significant numbers for both mainline and industrial railway
An industrial railway is a type of railway (usually private) that is not available for public transportation and is used exclusively to serve a particular industrial, logistics, or military site. In regions of the world influenced by British ra ...
s, almost to the end of steam traction. Hudswell Clarke
Hudswell, Clarke and Company Limited was an engineering and locomotive building company in Jack Lane, Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
History
The company was founded as Hudswell and Clarke in 1860. In 1870 the name was changed to Hud ...
were supplying industrial saddle tanks until at least 1947, and both Barclay and Robert Stephenson and Hawthorns
Robert Stephenson and Hawthorns Ltd (RSH) was a locomotive builder with works in North East England.
History
The company was formed in September 1937 when Robert Stephenson and Company, which was based in Darlington, took over the locomotive ...
until 1949.
An interesting variation on this theme were the traction engine
A traction engine is a steam engine, steam-powered tractor used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin ''tractus'', meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any t ...
-based railway locomotives built by Aveling and Porter
Aveling and Porter was a British agricultural engine and steamroller (road roller) manufacturer. Thomas Aveling and Richard Thomas Porter entered into partnership in 1862, and developed a steam engine three years later in 1865. By the ear ...
.
The last British Railways 0-4-0ST dock shunters were built by Horwich Works
Horwich Works was a railway works built in 1886 by the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (LYR) in Horwich, near Bolton, in North West England when the company moved from its original works at Miles Platting, Manchester.
Buildings
Horwich Works ...
as late as 1955 and survived until 1966.
A locomotive based on these also appears in one of ''Mario Kart 8
is a 2014 kart racing game developed and published by Nintendo for the Wii U. It features the ''Mario Kart'' series' game mechanics, in which players drive go-karts using ''Mario'' franchise characters in various race formats. Items placed a ...
s Rainbow Road tracks.
Tender locomotives
 During the 1840s, the wheel arrangement was widely used by
During the 1840s, the wheel arrangement was widely used by Edward Bury
Edward Bury (22 October 1794 – 25 November 1858) was an English locomotive manufacturer. Born in Salford, Lancashire, he was the son of a timber merchant and was educated at Chester.
Career
By 1823 he was a partner in Gregson and Bury's ste ...
on the bar-framed locomotives built for the London and Birmingham Railway
The London and Birmingham Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom, in operation from 1833 to 1846, when it became part of the London and North Western Railway (L&NWR).
The railway line which the company opened in 1838, betw ...
. However, with the exception of a few isolated examples used by the smaller companies such as the Cambrian Railways, the Furness Railway
The Furness Railway (Furness) was a railway company operating in the Furness area of Lancashire in North West England.
History
Formation
In the early 1840s, the owners of iron ore mines in the Furness district of Lancashire became interested i ...
and the Taff Vale Railway
The Taff Vale Railway (TVR) was a standard gauge railway in South Wales, built by the Taff Vale Railway Company to serve the iron and coal industries around Merthyr Tydfil and to connect them with docks in Cardiff. It was opened in st ...
, and four examples built by Edward Fletcher (engineer)
Edward Fletcher (1807 – 21 December 1889) was an English engineer, and locomotive superintendent of the North Eastern Railway (NER). He was born at Elsdon in Northumberland.
Career
He was apprenticed to George Stephenson beginning in ...
of the North Eastern Railway between 1854 and 1868, the 0-4-0 tender locomotive had been largely superseded on Britain's mainline railways by 1850.Bertram Baxter, British Locomotive Catalogue 1825-1923, Vol.1, Moorland Publishing Company, 1977. .
United States
Tank locomotives
 An early example of the 0-4-0 vertical boiler type was the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad's ''
An early example of the 0-4-0 vertical boiler type was the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad's ''Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
'' No. 2, built in 1832 by Phineas Davis Phineas Davis (January 27, 1792 – September 27, 1835) was a well-known clockmaker and inventor who designed and built the first practical American coal-burning railroad locomotive.
Early life and career
Davis was born in Warner, New Hampshi ...
and Israel Gartner. In the United States, the 0-4-0 tank locomotive was principally used for industrial railway
An industrial railway is a type of railway (usually private) that is not available for public transportation and is used exclusively to serve a particular industrial, logistics, or military site. In regions of the world influenced by British ra ...
purposes.
Tender locomotives
In the United States, the ''Best Friend of Charleston
The ''Best Friend of Charleston'' was a steam-powered railroad locomotive widely considered the first locomotive to be built entirely within the United States for revenue service. It produced the first locomotive boiler explosion in the United St ...
'' was the first locomotive to be built entirely within the United States. It was built in 1830 for the South Carolina Canal and Rail Road Company
The South Carolina Canal and Rail Road Company was a railroad in South Carolina that operated independently from 1830 to 1844. One of the first railroads in North America to be chartered and constructed, it provided the first steam-powered, schedu ...
by the West Point Foundry
The West Point Foundry was a major American ironworking and machine shop site in Cold Spring, New York, operating from 1818 to about 1911. Initiated after the War of 1812, it became most famous for its production of Parrott rifle artillery and ot ...
of New York.
The ''John Bull
John Bull is a national personification of the United Kingdom in general and England in particular, especially in political cartoons and similar graphic works. He is usually depicted as a stout, middle-aged, country-dwelling, jolly and matter- ...
'' was built by Robert Stephenson and Company
Robert Stephenson and Company was a locomotive manufacturing company founded in 1823 in Forth Street, Newcastle upon Tyne in England. It was the first company in the world created specifically to build railway engines.
Famous early locomoti ...
for the Camden and Amboy Railroad
The United New Jersey Railroad and Canal Company (UNJ&CC) was a railroad company which began as the important Camden & Amboy Railroad (C&A), whose 1830 lineage began as one of the eight or ten earliest permanent North AmericanList of Earliest Am ...
in New Jersey in 1831, but was later rebuilt as a 2-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and no trailing wheels.
The notation 2-4-0T indi ...
.
The Pennsylvania Railroad kept producing classes long after all other major railroads had abandoned development of the type, building their final '' A5s'' class into the 1920s. The ''A5s'' was a monster among , larger than many designs, with modern features found on few others of its type, such as superheating, power reverse On a steam locomotive, the reversing gear is used to control the direction of travel of the locomotive. It also adjusts the cutoff of the steam locomotive.
Reversing lever
This is the most common form of reverser. It consists of a long lever moun ...
, and piston valves
Piston valves are one form of valve used to control the flow of steam within a steam engine or locomotive. They control the admission of steam into the cylinders and its subsequent exhausting, enabling a locomotive to move under its own power ...
. The Pennsy continued to build the type because it had a large amount of confined and tight industrial track, more than most other railroads had.
0-4-0 Diesel locomotives
 The wheel arrangement was also used on a number of small 0-4-0DM
The wheel arrangement was also used on a number of small 0-4-0DM diesel-mechanical
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels ...
shunters produced by John Fowler & Co. and other builders in the 1930s and earlier. Similarly, it was perpetuated on a number of diesel-mechanical and diesel-hydraulic
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels ...
classes between 1953 and 1960 (see the List of British Rail modern traction locomotive classes
This article lists every locomotive allocated a TOPS classification and all modern traction (e.g. diesel, electric, gas turbine, petrol) stock used on the mainline network since 1948 (i.e. British Railways and post-privatisation).
Diesel locomot ...
). Many of these were later sold for industrial use.
There are 0-4-0DE diesel-electric locomotives too, although small in number. The smallest diesel switchers, such as the EMD Model 40, were of this arrangement.
0-4-0 diesel-mechanical shunters are also Polish PKP class SM02 and PKP class SM03 and narrow gauge WLs40/50.
References
{{Whyte types 4,0-4-0