Α-Neurotoxin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
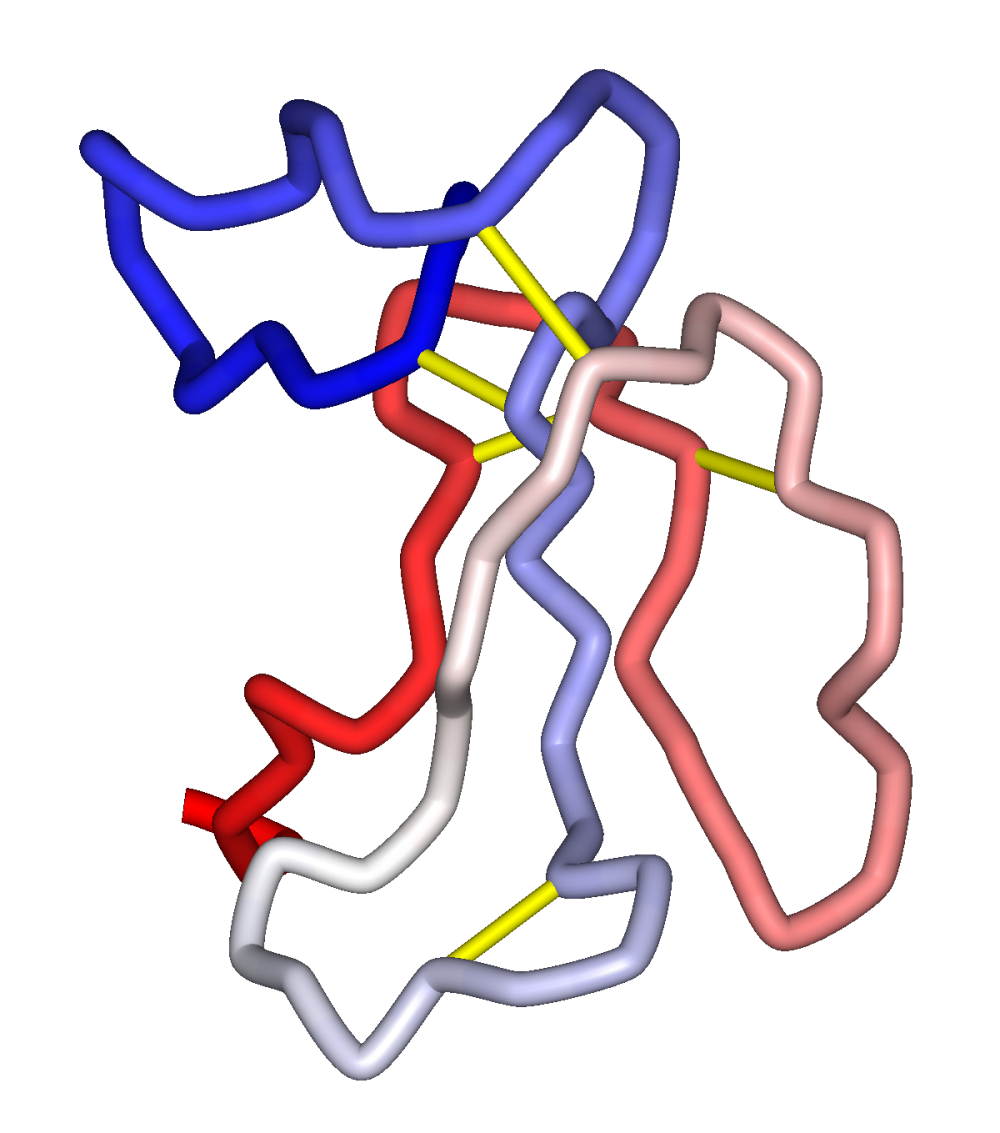 α-Neurotoxins are a group of neurotoxic
α-Neurotoxins are a group of neurotoxic
 α-Neurotoxins are a group of neurotoxic
α-Neurotoxins are a group of neurotoxic peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
...
s found in the venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a st ...
of snakes in the families Elapidae
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydoce ...
and Hydrophiidae
Hydrophiinae is a subfamily of venomous snakes in the family Elapidae. It contains most sea snakes and many genera of venomous land snakes found in Australasia, such as the taipans (''Oxyuranus''), tiger snakes (''Notechis''), brown snakes (''P ...
. They can cause paralysis, respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise ...
, and death. Members of the three-finger toxin
Three-finger toxins (abbreviated 3FTx) are a protein superfamily of small toxin proteins found in the venom of snakes. Three-finger toxins are in turn members of a larger superfamily of three-finger protein domains which includes non-toxic prote ...
protein family, they are antagonists
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist.
Etymology
The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, ri ...
of post-synaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral ner ...
s (nAChRs) in the neuromuscular synapse that bind competitively and irreversibly, preventing synaptic acetylcholine (ACh) from opening the ion channel. Over 100 α-neurotoxins have been identified and sequenced.
History
The term α-neurotoxin was coined by C.C. Chang, who designated the postsynaptic bungarotoxin with the α- prefix because it happened to be slowest moving of the bungarotoxins under starch zone electrophoresis. The "α-" prefix subsequently came to connote any toxins with postsynaptic action. Members of this group are sometimes referred to as "curaremimetics" due to the similarity of their effects with the plantalkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
curare
Curare ( /kʊˈrɑːri/ or /kjʊˈrɑːri/; ''koo-rah-ree'' or ''kyoo-rah-ree'') is a common name for various alkaloid arrow poisons originating from plant extracts. Used as a paralyzing agent by indigenous peoples in Central and South ...
.
As more snake venoms were characterized, many were found to contain homologous nAChR-antagonist proteins. These came to be collectively known as the snake venom α-neurotoxins.
General structure
All α-neurotoxins share thethree-finger toxin
Three-finger toxins (abbreviated 3FTx) are a protein superfamily of small toxin proteins found in the venom of snakes. Three-finger toxins are in turn members of a larger superfamily of three-finger protein domains which includes non-toxic prote ...
tertiary structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may i ...
, consisting of a small globular
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member ...
core containing four disulfide bond
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
s, three loops or "fingers", and a C-terminal tail.
The class can be divided into two groups distinguished by length; short-chain neurotoxins have 60-62 residues and only the four core disulfide bonds characteristic of the fold, while long-chain neurotoxins have 66 or more residues, often including a longer C-terminus, and an additional disulfide bond in the second "finger" loop. These classes have significant sequence homology and share the same three-dimensional structure, but have differing specificities and kinetics of association/dissociation with the receptor. Localized mobility at the tips of fingers I and II is essential for binding. Accordingly, mutation of these residues produces large effects on binding. The additional disulfide bond in the second loop of the long-chain forms is likewise thought to influence binding specificity. Although both short and long-chain neurotoxins bind the same site on their target receptors, short-chain neurotoxins do not potently block α7 homo-oligomeric neuronal AChRs, while long-chain neurotoxins do. α-bungarotoxin and α-cobratoxin are both long-type.
Functions
''For specifics, see α-Bungarotoxin andnicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral ner ...
''
α-Neurotoxins antagonistically bind tightly and noncovalently to nAChRs of skeletal muscles, thereby blocking the action of ACh at the postsynaptic membrane, inhibiting ion flow and leading to paralysis. nAChRs contain two binding sites for snake venom neurotoxins. Some computational studies of the mechanism of inhibition using normal mode dynamics suggest that a twist-like motion caused by ACh binding may be responsible for pore opening, and that this motion is inhibited by toxin binding.
Evolution
Although three-finger protein domains are widespread, three-finger toxins appear only in snakes, and are particularly enriched inelapid
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydoce ...
s. There is evidence that alpha-neurotoxins have evolved rapidly and are subject to positive selection, possibly due to an evolutionary arms race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an ongoing struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes, phenotypic and behavioral traits that develop escalating adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling an ...
with prey species.
Snake nAchRs have specific sequence features that render them poor binding partners for alpha-neurotoxins. Some mammalian lineages also display mutations conferring resistance to alpha-neurotoxins; such resistance is believed to have evolved convergently at least four times in mammals, reflecting two different biochemical mechanisms of adaptation. The introduction of glycosylation sites on the receptor, resulting in steric hindrance
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
at the neurotoxin binding site, is a well-characterized resistance mechanism found in mongoose
A mongoose is a small terrestrial carnivorous mammal belonging to the family Herpestidae. This family is currently split into two subfamilies, the Herpestinae and the Mungotinae. The Herpestinae comprises 23 living species that are native to so ...
s, while the honey badger
The honey badger (''Mellivora capensis''), also known as the ratel ( or ), is a mammal widely distributed in Africa, Southwest Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. Because of its wide range and occurrence in a variety of habitats, it is liste ...
, domestic pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
, and hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introductio ...
lineages replace aromatic amino acid
An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromatic ring.
Among the 20 standard amino acids, the following are classically considered aromatic: phenylalanine, tryptophan and tyrosine. Although histidine contains an aromatic ring, ...
s with charged residues; at least in some lineages, these molecular adaptations likely reflect predation on venomous snakes.
References
{{Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators Neurotoxins Nicotinic antagonists Venomous snakes