|
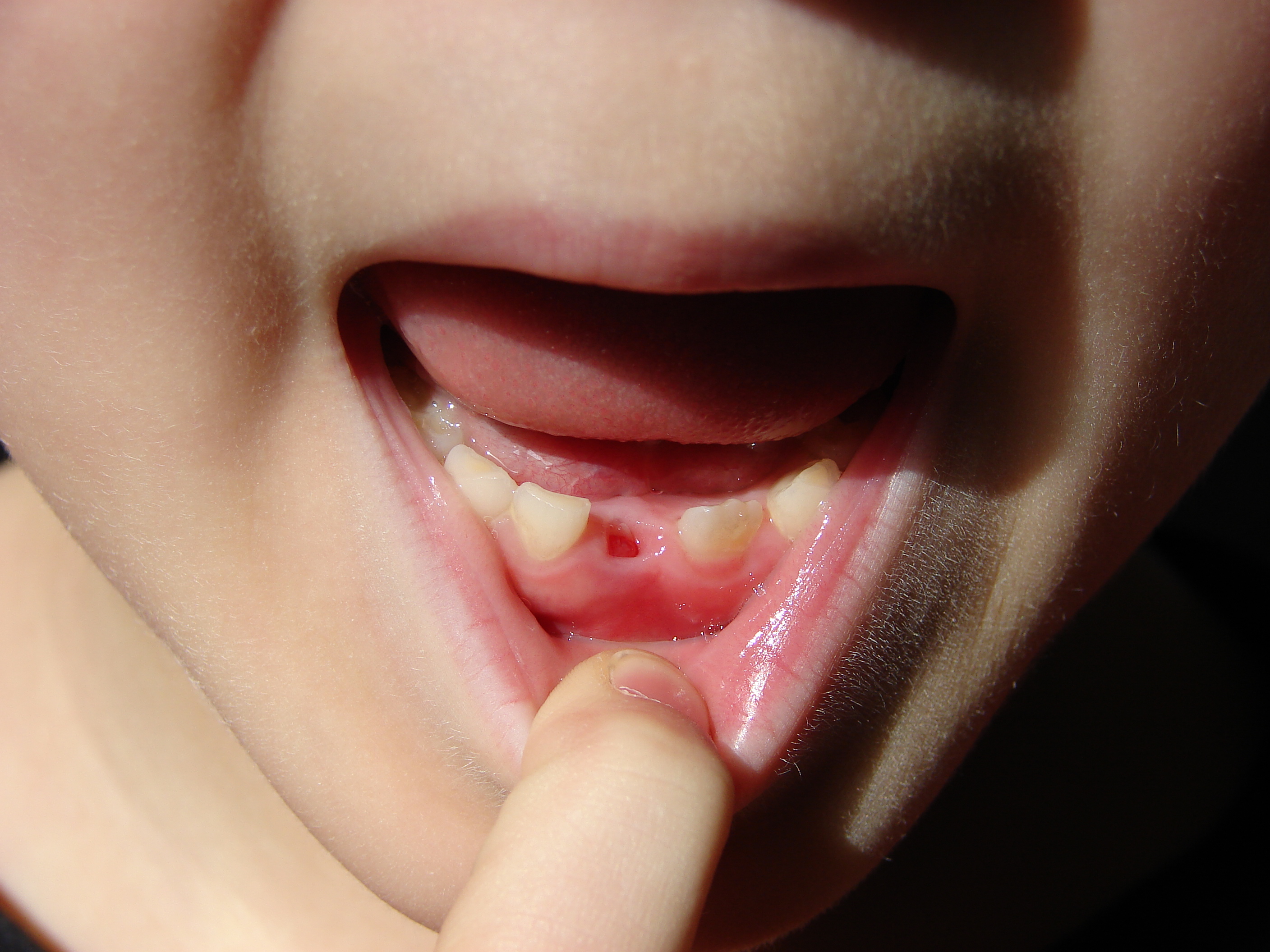
Deciduous Dentition
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Fehrenbach, MJ and Popowics, T. (2026). ''Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy'', 6th edition, Elsevier, page 287–296. are the first set of teeth in the growth and development of humans and other diphyodonts, which include most mammals but not elephants, kangaroos, or manatees, which are polyphyodonts. Deciduous teeth develop during the embryonic stage of development and erupt (break through the gums and become visible in the mouth) during infancy. They are usually lost and replaced by permanent teeth, but in the absence of their permanent replacements, they can remain functional for many years into adulthood. Development Formation Primary teeth start to form during the embryonic phase of human life. The development of primary teeth starts at the sixth week of tooth development as the dental lamina. This process starts at the midline and then spreads b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diphyodont
A diphyodont is any animal with two sets of teeth, initially the ''deciduous'' set and consecutively the '' permanent'' set. Most mammals are diphyodonts—as to chew their food they need a strong, durable and complete set of teeth. Diphyodonts contrast with ''polyphyodonts'', whose teeth are constantly replaced. Diphyodonts also differ from '' monophyodonts'', which are animals who have only one set of teeth that does not change over a long period of growth. In diphyodonts, the number of teeth that are replaced varies from species to species. In humans, a set of twenty deciduous teeth, or "milk teeth", are replaced by a completely new set of thirty-two adult teeth. In some cases hypodontia or hyperdontia occurs, the latter in cleidocranial dysostosis and Gardner's syndrome. In the hare the anterior incisors are not replaced but the posterior smaller incisors are replaced. Not much is known about the developmental mechanisms regulating diphyodont replacement. The house shre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maxillary Second Molar
The maxillary second molar is the tooth located distally (away from the midline of the face) from both the maxillary first molars of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both maxillary third molars. This is true only in permanent teeth. In deciduous (baby) teeth, the maxillary second molar is the last tooth in the mouth and does not have a third molar behind it. The function of this molar is similar to that of all molars in regard to grinding being the principal action during mastication, commonly known as chewing. There are usually four cusps on maxillary molars, two on the buccal (side nearest the cheek) and two palatal (side nearest the palate). There are great differences between the deciduous In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ... ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mastication
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is comminution, crushed and ground by the teeth. It is the first step in the process of digestion, allowing a greater surface area for digestive enzymes to break down the foods. During the mastication process, the food is positioned by the cheek and tongue between the teeth for grinding. The muscles of mastication move the jaws to bring the teeth into intermittent contact, repeatedly occlusion (dentistry), occluding and opening. As chewing continues, the food is made softer and warmer, and the enzymes in saliva begin to break down carbohydrates in the food. After chewing, the food (now called a Bolus (digestion), bolus) is swallowed. It enters the esophagus and via peristalsis continues on to the stomach, where the next step of digestion occurs. Increasing the number of chews per bite stimulates the production of digestive enzymes and peptides and has been shown to increase diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT) by activating the sympa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exfoliation (botany)
Exfoliation (from the term "foliate", meaning “related to leaves”) means the removal or loss of leaves from a plant. It is used both to describe the loss of a leaves as a natural part of a plant's life cycle (such as in the case of deciduous trees which lose their leaves in the autumn) or because of some trauma or outside cause (such as dehydration, an infestation of caterpillars or hurricane A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its ...-force winds). In arboriculture, the term “exfoliating bark” describes the natural process and condition of the bark peeling-away from a tree trunk, typically in large pieces that remain partially attached to the trunk until such time as they are completely detached by the elements or the eventual and subsequent exfoliation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Odontoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated protein and mineral at a molecular level by secreting acid and a collagenase, a process known as ''bone resorption''. This process also helps regulate the level of blood calcium. Osteoclasts are found on those surfaces of bone that are undergoing resorption. On such surfaces, the osteoclasts are seen to be located in shallow depressions called ''resorption bays (Howship's lacunae)''. The resorption bays are created by the erosive action of osteoclasts on the underlying bone. The border of the lower part of an osteoclast exhibits finger-like processes due to the presence of deep infoldings of the cell membrane; this border is called ''ruffled border''. The ruffled border lies in contact with the bone surface within a resorption bay. The periph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Root Resorption
Resorption of the root of the tooth, or root resorption, is the progressive loss of dentin and cementum by the action of odontoclasts. Root resorption is a normal physiological process that occurs in the exfoliation of the primary dentition. However, pathological root resorption occurs in the permanent or secondary dentition and sometimes in the primary dentition. Causes While resorption of bone is a normal physiological response to stimuli throughout the body, root resorption in permanent dentition and sometimes in the primary dentition is pathological. The root is protected internally (endodontium) by pre-dentin and externally on the root surface by cementum and the periodontal ligament. Chronic stimuli that damage these protective layers expose underlying dentin to the action of osteoclasts. Root resorption most commonly occurs due to inflammation caused by pulp necrosis, trauma, periodontal treatment, orthodontic tooth movement and tooth whitening. Less common causes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos, anteaters and other animals in the order Edentata have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisors are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar Tooth (human), teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the Canine tooth, canine and Molar (tooth), molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per dental terminology#Quadrant, quadrant in the permanent teeth, permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two Cusp (dentistry), cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie Posterior (anatomy), posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular Second Molar
The mandibular second molar is the tooth located distally (away from the midline of the face) from both the mandibular first molars of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular third molars. This is true only in permanent teeth. The function of this molar is similar to that of all molars in regard to grinding being the principal action during mastication, commonly known as chewing. Though there is more variation between individuals than that of the first mandibular molar, there are usually four cusps on mandibular second molars: two on the buccal (side nearest the cheek) and two lingual (side nearest the tongue). There are great differences between the deciduous (baby) mandibular molars and those of the permanent mandibular molars, even though their function is similar. The permanent mandibular molars are not considered to have any teeth that precede them. Despite being named molars, the deciduous molars are followed by permanent premolars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
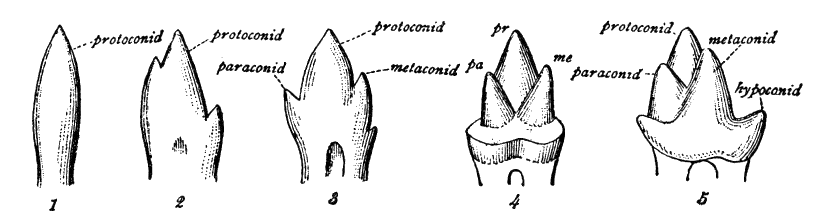
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |