|
Íslendingabók
''Íslendingabók'' (, Old Norse pronunciation: , ''Book of Icelanders''; ) is a historical work dealing with early Icelandic history. The author was an Icelandic priest, Ari Þorgilsson, working in the early 12th century. The work originally existed in two different versions but only the younger one has survived. The older contained information on Norwegian kings, made use of by later writers of kings' sagas. The priest Jón Erlendsson in Villingaholt (died 1672) in the service of bishop Brynjólfur Sveinsson made two copies of Íslendingabók (now AM 113 a fol and AM 113 b fol at the Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies in Reykjavík), the latter one because the bishop was unhappy with the first version. The original copied from is assumed to have dated to ca. 1200. It was lost in the course of the late 17th century, and when Árni Magnússon looked for it, it had disappeared without a trace. Style and sources ''Íslendingabók'' is a concise work which relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Íslendingabók - AM 113 A Fol
''Íslendingabók'' (, Old Norse pronunciation: , ''Book of Icelanders''; ) is a historical work dealing with early Icelandic history. The author was an Icelandic priest, Ari Þorgilsson, working in the early 12th century. The work originally existed in two different versions but only the younger one has survived. The older contained information on Norwegian kings, made use of by later writers of kings' sagas. The priest Jón Erlendsson in Villingaholt (died 1672) in the service of bishop Brynjólfur Sveinsson made two copies of Íslendingabók (now AM 113 a fol and AM 113 b fol at the Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies in Reykjavík), the latter one because the bishop was unhappy with the first version. The original copied from is assumed to have dated to ca. 1200. It was lost in the course of the late 17th century, and when Árni Magnússon looked for it, it had disappeared without a trace. Style and sources ''Íslendingabók'' is a concise work which relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Íslendingabók
''Íslendingabók'' (, Old Norse pronunciation: , ''Book of Icelanders''; ) is a historical work dealing with early Icelandic history. The author was an Icelandic priest, Ari Þorgilsson, working in the early 12th century. The work originally existed in two different versions but only the younger one has survived. The older contained information on Norwegian kings, made use of by later writers of kings' sagas. The priest Jón Erlendsson in Villingaholt (died 1672) in the service of bishop Brynjólfur Sveinsson made two copies of Íslendingabók (now AM 113 a fol and AM 113 b fol at the Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies in Reykjavík), the latter one because the bishop was unhappy with the first version. The original copied from is assumed to have dated to ca. 1200. It was lost in the course of the late 17th century, and when Árni Magnússon looked for it, it had disappeared without a trace. Style and sources ''Íslendingabók'' is a concise work which relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic History
The recorded history of Iceland began with the settlement by Viking explorers and the people they enslaved from the east, particularly Norway and the British Isles, in the late ninth century. Iceland was still uninhabited long after the rest of Western Europe had been settled. Recorded settlement has conventionally been dated back to 874, although archaeological evidence indicates Gaelic monks from Ireland, known as papar according to sagas, had settled Iceland earlier. The land was settled quickly, mainly by Norwegians who may have been fleeing conflict or seeking new land to farm. By 930, the chieftains had established a form of governance, the ''Althing'', making it one of the world's oldest parliaments. Towards the end of the tenth century, Christianity came to Iceland through the influence of the Norwegian king Olaf Tryggvason. During this time, Iceland remained independent, a period known as the Old Commonwealth, and Icelandic historians began to document the nation's h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Iceland
The recorded history of Iceland began with the settlement by Viking explorers and the people they enslaved from the east, particularly Norway and the British Isles, in the late ninth century. Iceland was still uninhabited long after the rest of Western Europe had been settled. Recorded settlement has conventionally been dated back to 874, although archaeological evidence indicates Gaelic monks from Ireland, known as papar according to sagas, had settled Iceland earlier. The land was settled quickly, mainly by Norwegians who may have been fleeing conflict or seeking new land to farm. By 930, the chieftains had established a form of governance, the ''Althing'', making it one of the world's oldest parliaments. Towards the end of the tenth century, Christianity came to Iceland through the influence of the Norwegian king Olaf Tryggvason. During this time, Iceland remained independent, a period known as the Old Commonwealth, and Icelandic historians began to document the nation's hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harald I Of Norway
Harald Fairhair no, Harald hårfagre Modern Icelandic: ( – ) was a Norwegian king. According to traditions current in Norway and Iceland in the eleventh and twelfth centuries, he reigned from 872 to 930 and was the first King of Norway. Supposedly, two of his sons, Eric Bloodaxe and Haakon the Good, succeeded Harald to become kings after his death. Much of Harald's biography is uncertain. A couple of praise poems by his court poet Þorbjörn Hornklofi survive in fragments, but the extant accounts of his life come from sagas set down in writing around three centuries after his lifetime. His life is described in several of the Kings' sagas, none of them older than the twelfth century. Their accounts of Harald and his life differ on many points, but it is clear that in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries Harald was regarded as having unified Norway into one kingdom. Since the nineteenth century, when Norway was in a personal union with Sweden, Harald has become a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Iceland
The recorded history of Iceland began with the settlement by Viking explorers and the people they enslaved from the east, particularly Norway and the British Isles, in the late ninth century. Iceland was still uninhabited long after the rest of Western Europe had been settled. Recorded settlement has conventionally been dated back to 874, although archaeological evidence indicates Gaelic monks from Ireland, known as papar according to sagas, had settled Iceland earlier. The land was settled quickly, mainly by Norwegians who may have been fleeing conflict or seeking new land to farm. By 930, the chieftains had established a form of governance, the ''Althing'', making it one of the world's oldest parliaments. Towards the end of the tenth century, Christianity came to Iceland through the influence of the Norwegian king Olaf Tryggvason. During this time, Iceland remained independent, a period known as the Old Commonwealth, and Icelandic historians began to document the nation's h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ari Þorgilsson
Ari Þorgilsson (1067–1148 AD; Old Norse: ; Modern Icelandic: ; also anglicized Ari Thorgilsson) was Iceland's most prominent medieval chronicler. He was the author of ''Íslendingabók'', which details the histories of the various families who settled Iceland. He is typically referred to as Ari the Wise (''Ari hinn fróði''), and according to Snorri Sturluson was the first to write history in Old Norse. Ari was a part of the Haukdælir family clan and studied in the school in Haukadalur as a student of Teitur Ísleifsson (the son of Ísleifur Gissurarson, first bishop of Iceland). There he became acquainted with Classical education Classical education may refer to: *''Modern'', educational practices and educational movements: **An education in the Classics, especially in Ancient Greek and Latin **Classical education movement, based on the trivium (grammar, logic, rhetoric) an .... His writings clearly indicate that he was familiar with Latin chronicler traditions, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose is the prevention of resources being spent on weak or disabled offspring. Unwanted infants were normally abandoned to die of exposure, but in some societies they were deliberately killed. Infanticide is now widely illegal, but in some places the practice is tolerated or the prohibition is not strictly enforced. Most Stone Age human societies routinely practiced infanticide, and estimates of children killed by infanticide in the Mesolithic and Neolithic eras vary from 15 to 50 percent. Infanticide continued to be common in most societies after the historical era began, including ancient Greece, ancient Rome, the Phoenicians, ancient China, ancient Japan, Aboriginal Australia, Native Americans, and Native Alaskans. Infanticide became forbidden in Europe and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Úlfljótr
Úlfljótr (Old Norse: ; Modern Icelandic: ) brought law to Iceland and is regarded by some as Iceland's first ''lawspeaker''. In around 927-930 AD Úlfljótr was sent to Norway by a group of chieftains to study law and culture and bring back to Iceland sufficient understanding to help establish Iceland's legal framework and form of government. And while he was in Norway, where he stayed for around three years, Grímur Geitskor, Úlfljótr's half-brother, made a survey of Iceland to find the best place for the establishment of the Althing The Alþingi (''general meeting'' in Icelandic, , anglicised as ' or ') is the supreme national parliament of Iceland. It is one of the oldest surviving parliaments in the world. The Althing was founded in 930 at (" thing fields" or "assemb .... Úlfljótr is commemorated with the first law enacted at the Alþing, Úlfljót's Law, with the lake Úlfljótsvatn and by the '' Úlfljótur Law Review''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
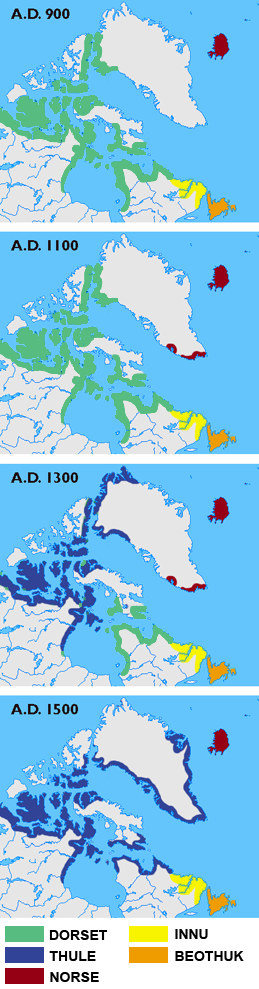
Skræling
''Skræling'' (Old Norse and Icelandic: ''skrælingi'', plural ''skrælingjar'') is the name the Norse Greenlanders used for the peoples they encountered in North America (Canada and Greenland). In surviving sources, it is first applied to the Thule people, the proto-Inuit group with whom the Norse coexisted in Greenland after about the 13th century. In the sagas, it is also used for the peoples of the region known as Vinland whom the Norse encountered and fought during their expeditions there in the early 11th century. Etymology The word is most likely related to the Old Norse word , meaning "dried skin", in reference to the animal pelts worn by the Inuit. William Thalbitzer (1932: 14) speculated that might have been derived from the Old Norse verb , meaning "bawl, shout, or yell". In modern Icelandic, means "barbarian", whereas the Danish descendant, , means "weakling". The term is thought to have first been used by in his work , also called ''The Book of the Icelanders' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Árni Magnússon Institute For Icelandic Studies
The Árni Magnússon Institute for Icelandic Studies ( is, Stofnun Árna Magnússonar í íslenskum fræðum ) is an institute of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Iceland which conducts research in Icelandic and related academic studies, in particular the Icelandic language and Icelandic literature, to disseminate knowledge in those areas, and to protect and develop the collections that it possesses or those placed in its care. It is named after Árni Magnússon, a 17th–18th century collector of medieval Icelandic manuscripts. The Árni Magnússon Institute () was an academic institute located in Reykjavík, Iceland. The institute had the task of preserving and studying mediaeval Icelandic manuscripts containing Landnáma, Heimskringla and the Icelandic sagas. On 1 September 2006, this institute was merged with the Icelandic Language Institute, the University of Iceland Institute of Lexicography, the Sigurður Nordal Institute, and the Place-Name Institute of Ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Þorgeirr Ljósvetningagoði
Thorgeir Ljosvetningagodi Thorkelsson ( ; Modern Icelandic: ; born c. 940) was a lawspeaker in Iceland's Althing from 985 to 1001. In the year 999 or 1000, Iceland's legislative assembly was debating which religion they should practice: Norse paganism or Christianity. Thorgeir, himself a pagan priest and chieftain (a '' gothi''), decided in favour of Christianity after a day and a night of silent meditation under a fur blanket, thus averting potentially disastrous civil conflict. Under the compromise, pagans could still practice their religion in private and several of the old customs were retained. After his decision, Thorgeir himself converted to Christianity. Thorgeir's story is preserved in Ari Thorgilsson's ''Íslendingabók''. References External linksChristianity from a site on the Icelandic parliament. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ljosvetningagodi, Thorgeir Lawspeakers Converts to Christianity from pagan religions Thorgeir Ljosvetningagodi 940s births 11th-century deaths Year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |