|
Rikhter R-23
The Rikhter R-23 is an aircraft autocannon developed for the Soviet Air Force starting in the late 1950s. It was designed to be as short as possible to avoid problems found on high-speed aircraft when the guns were pointed into the airstream. The R-23 was a gas operated revolver cannon that used gas bled from holes in the barrel to provide the motive force. Firing up to 2,600 rpm, the R-23 was the fastest firing single-barrel cannon ever introduced into service. The R-23 took some time to develop, and was not used operationally until 1964. It was used only in the tail turret of the Tu-22, and experimentally on the Salyut 3 space station. Its role was taken over by the twin-barrel Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23. A modified version of the weapon was the only cannon to have been fired in space. Development In the late 1940s and the early 1950s tests with defensive bomber turret cannons resulted in problems caused by the air flow affecting the weapons' barrel. Among these were the wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afanasev Makarov AM-23
The Afanasev Makarov AM-23 is a Soviet designed aircraft autocannon that has been used in a number of aircraft in the Soviet Air Force. Its GRAU index was 9-A-036. It was often used in place of the earlier and slower-firing Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23. In 1953 the first strategic jet bomber, the Tu-16, was introduced into the Soviet Air Force. A new 23 mm cannon was needed for the defensive turrets of this bomber, which was supposed to be more compact and faster firing than the NR-23. The designers Nikolay M. Afanasev and Nikolay F. Makarov from the TsKB-14 design bureau scaled-up the A-12.7 12.7 mm machine gun to create a 23 mm aircraft cannon. The TKB-495 (TKB - ''Tool'skoye Konstrooktorskoye Byuro'' – Tula design bureau) achieved a maximum rate of 1,350 rounds per minute during the tests and in May 1954, roughly double that of the NR-23. It was officially renamed the AM-23 in honour of its designers. The Tu-16 bomber was armed with a total of seven AM-23 cannon. A sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Guns Of The Soviet Union
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocannons Of The Soviet Union
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary shells, as opposed to the smaller-caliber kinetic projectiles (bullets) fired by a machine gun. Autocannons have a longer effective range and greater terminal performance than machine guns, due to the use of larger/heavier munitions (most often in the range of , but bigger calibers also exist), but are usually smaller than tank guns, howitzers, field guns or other artillery. When used on its own, the word "autocannon" typically indicates a non-rotary weapon with a single barrel. When multiple rotating barrels are involved, such a weapon is referred to as a "rotary autocannon" or occasionally "rotary cannon", for short (particularly on aircraft). Autocannons are heavy weapons that are unsuitable for use by infantry. Due to the heavy weight and recoil, they are typically installed on fixed mounts, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Target Practice
In the military and in shooting, target practice are exercises in which weapons are shot at a target. The purpose of such exercises is to improve the aim or the weapons handling expertise of the person firing the weapon. Targets being shot at for practice include: * with handguns, rifles, and shotguns: shooting targets, * by air forces or air defense forces: target drones and target tugs, * by navies: seaborne targets. See also *Live fire exercise *Shooting range A shooting range, firing range, gun range or shooting ground is a specialized facility, venue or field designed specifically for firearm usage qualifications, training, practice or competitions. Some shooting ranges are operated by military ... References Military education and training Ammunition {{weapons-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Explosive Incendiary
In warfare, high-explosive incendiary (HEI) is a type of ammunition specially designed to impart energy and therefore damage to its target in one or both of two ways: via a high-explosive charge and/or via its incendiary (fire-causing) effects. Each round has both capabilities. HEI ammunition is fused either mechanically or chemically. The armor-piercing ability can vary widely, allowing for more focused fragmentation or larger scatter. History HEI ammunition was originally developed for use in large-caliber cannon, howitzer and naval artillery. Currently, HEI rounds are most commonly made in medium-caliber sizes of 20, 25, and 30 mm. They are fired from various platforms, including aircraft, anti-aircraft cannons, and anti-missile systems, as well as common battlefield howitzers, though the latter has gone through a recent decline in use. HEI ammunition has also been used on the battlefield against tanks and other armoured vehicles, but this has become impractical due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIM-23 Hawk
The Raytheon MIM-23 HAWK ("Homing all the way killer") is an American medium-range surface-to-air missile. It was designed to be a much more mobile counterpart to the MIM-14 Nike Hercules, trading off range and altitude capability for a much smaller size and weight. Its low-level performance was greatly improved over Nike through the adoption of new radars and a continuous wave semi-active radar homing guidance system. It entered service with the US Army in 1959. In 1971 it underwent a major improvement program as the Improved Hawk, or I-Hawk, which made several improvements to the missile and replaced all of the radar systems with new models. Improvements continued throughout the next twenty years, adding improved ECCM, a potential home-on-jam feature, and in 1995, a new warhead that made it capable against short-range tactical missiles. '' Jane's'' reported that the original system's single shot kill probability was 0.56; I-Hawk improved this to 0.85. Hawk was superseded b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomb Disposal
Bomb disposal is an explosives engineering profession using the process by which hazardous explosive devices are rendered safe. ''Bomb disposal'' is an all-encompassing term to describe the separate, but interrelated functions in the military fields of explosive ordnance disposal (EOD) and improvised explosive device disposal (IEDD), and the public safety roles of public safety bomb disposal (PSBD) and the bomb squad. History The first professional civilian bomb squad was established by Sir Vivian Dering Majendie. As a Major in the Royal Artillery, Majendie investigated an explosion on 2 October 1874 in the Regent's Canal, when the barge 'Tilbury', carrying six barrels of petroleum and five tons of gunpowder, blew up, killing the crew and destroying Macclesfield Bridge and cages at nearby London Zoo. In 1875, he framed The Explosives Act, the first modern legislation for explosives control. He also pioneered many bomb disposal techniques, including remote methods for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
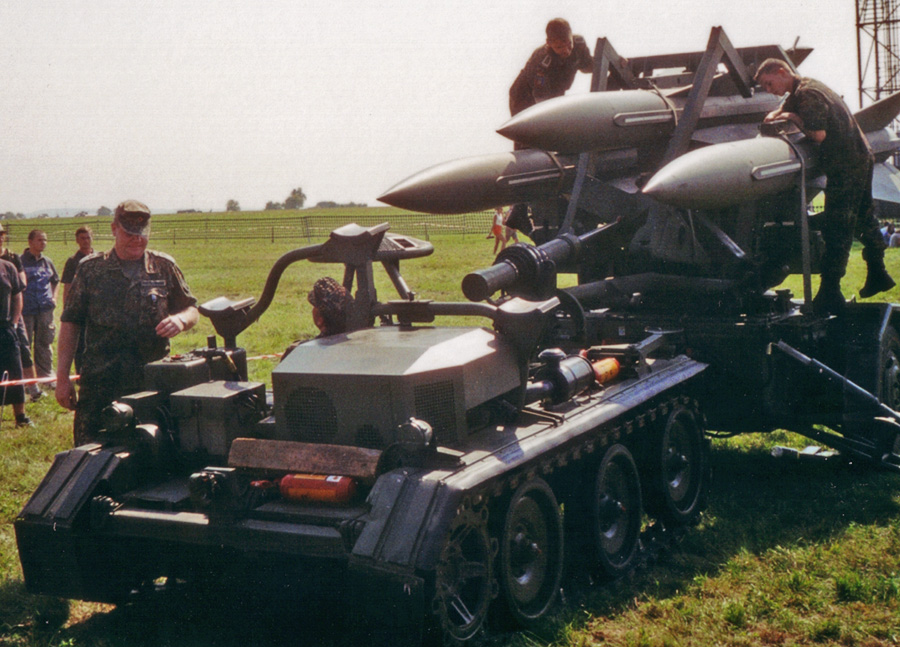
ZSU-23-4
The ZSU-23-4 "Shilka" is a lightly armored Soviet self-propelled, radar-guided anti-aircraft weapon system ( SPAAG). Etymology The acronym "ZSU" stands for ''Zenitnaya Samokhodnaya Ustanovka'' (russian: Зенитная Самоходная Установка), meaning "anti-aircraft self-propelled system"; the "23" signifies the bore diameter in millimeters; the "4" signifies the number of gun barrels. It is named after the Shilka River in Russia. Afghan soldiers nicknamed it the " sewing machine" due to the sound of firing guns. It is also referred to by its nickname of "Zeus", derived from the Russian acronym. History The previous Soviet self-propelled anti-aircraft gun ( SPAAG), the ZSU-57-2, was armed with two 57 mm autocannons; it was aimed optically using a basic tracking and lead calculating system. The ZSU-57-2 was not particularly successful despite its very powerful autocannons; given their large caliber, it could only carry 300 rounds, was inaccurate as it lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSh-30-1
The Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-30-1 (also known by the GRAU index designation 9A-4071K) is a 30 mm autocannon designed for use on Soviet and later Russian military aircraft, entering service in the early 1980s. Its current manufacturer is the Russian company JSC Izhmash. The name GSH-30-1 is formed from the surnames of the designers Gryazev (Грязев) and Shipunov (Шипунов), the caliber of 30 mm and the single-barrel design of the gun itself. Description The GSh-30-1 is a single-barreled, recoil operated autocannon weighing 46 kg (101 lb). Unlike many postwar cannons, it uses a short recoil action instead of a revolver cannon or Gatling gun mechanism. This results in a reduced rate of fire, but lower weight and bulk. The GSh-30-1 has a rate of fire of 1,800 rounds per minute, customarily limited to 1,500 rounds per minute to reduce barrel wear. Despite that, its barrel life is quite short: 2,000 rounds, with a continuous burst rated for 150 rounds. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primer (firearm)
In firearms and artillery, the primer () is the chemical and/or device responsible for initiating the propellant combustion that will push the projectiles out of the gun barrel. In early black powder guns such as muzzleloaders, the primer was essentially the same chemical as the main propellant (albeit usually in a finer-powdered form), but poured into an external flash pan, where it could be ignited by an ignition source such as a slow match or a flintlock though some muzzleloaders have primers like cap gun caps. This external powder was connected through a small opening at the rear of the gun barrel that led to the main charge within the barrel. As gunpowder will not burn when wet, this made it difficult (or even impossible) to fire these types of weapons in rainy or humid conditions. Modern primers, by contrast, are more specialized and distinct from the main propellant they are designed to ignite. They are of two types, those using shock-sensitive chemicals, and those relia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
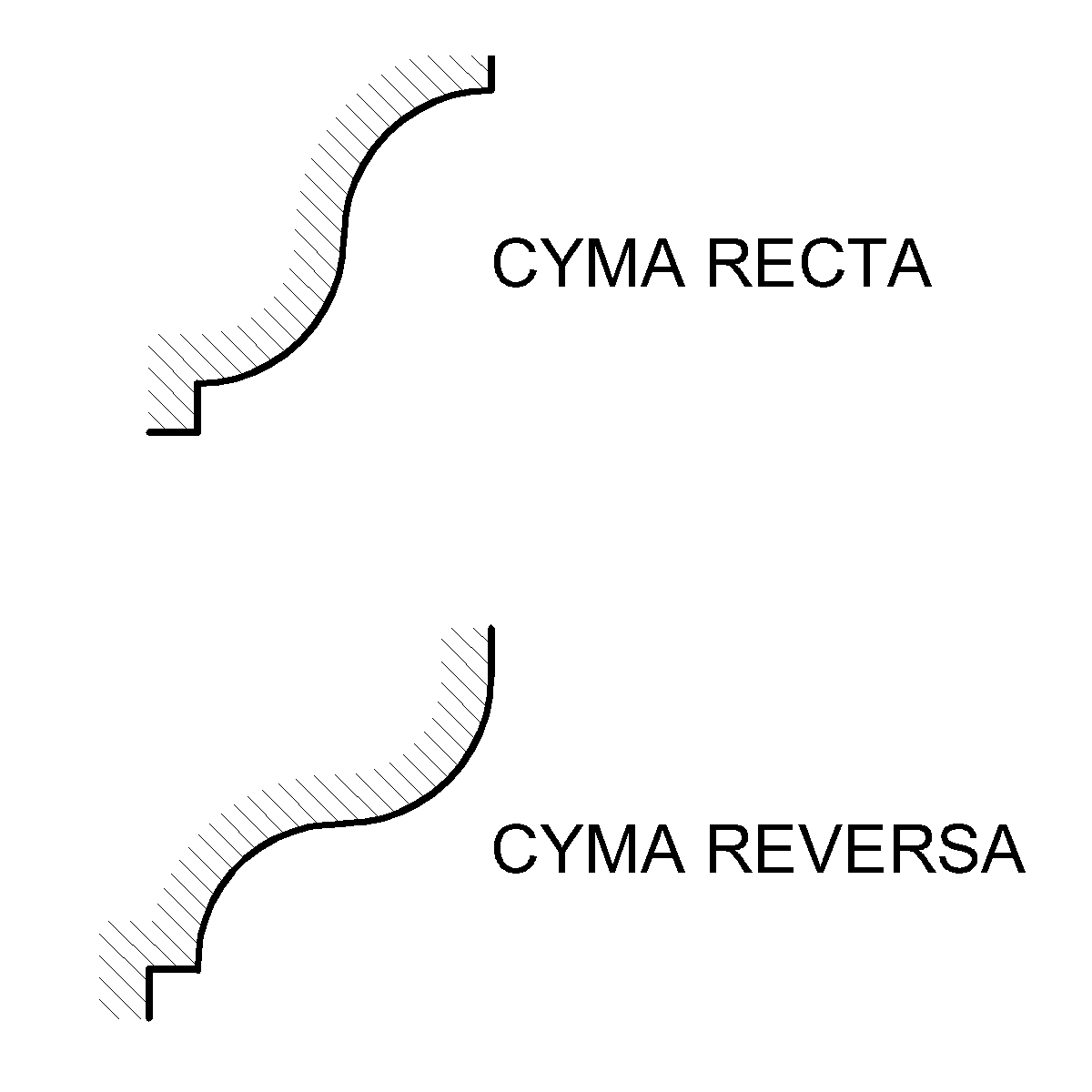
Ogee
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or ''vice versa'', have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions (and have tangents that are approximately parallel). First seen in textiles in the 12th century, the use of ogee elements—in particular, in the design of arches—has been said to characterise various Gothic and Gothic Revival architectural styles. The shape has many such uses in architecture from those periods to the present day, including in the ogee arch in these architectural styles, where two ogees oriented as mirror images compose the sides of the arch, and in decorative molding designs, where single ogees are common profiles (see opening i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)