|
Ethoprop
Ethoprophos (or ethoprop) is an organophosphate ester with the formula C8H19O2PS2. It is a clear yellow to colourless liquid that has a characteristic mercaptan-like odour. It is used as an insecticide and nematicide and it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Synthesis Ethoprop can be synthesised by reacting phosphoryl chloride with two equivalents of ''n''-propylmercaptan and one equivalent of sodium ethoxide. A second pathway is reacting ''n''-propylmercaptan and sodium ethoxide with phosphorus trichloride to yield ethoxy-bis(propylsulfanyl)phosphane, which can then be oxidized by hydrogen peroxide to yield the product. : : Applications Ethoprop is used as an insecticide against soil insects like wireworms and as a nematicide. It is used on different crops, ranging from potatoes, bananas, and sugarcane to ornamental plants and tobacco. Most of the ethoprop used in the United States is applied to potatoes. In the period of 1987 to 1996, an estimated total of 691,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethoprophos Synthesis 2
Ethoprophos (or ethoprop) is an organophosphate ester with the formula C8H19O2PS2. It is a clear yellow to colourless liquid that has a characteristic mercaptan-like odour. It is used as an insecticide and nematicide and it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Synthesis Ethoprop can be synthesised by reacting phosphoryl chloride with two equivalents of ''n''-propylmercaptan and one equivalent of sodium ethoxide. A second pathway is reacting ''n''-propylmercaptan and sodium ethoxide with phosphorus trichloride to yield ethoxy-bis(propylsulfanyl)phosphane, which can then be oxidized by hydrogen peroxide to yield the product. : : Applications Ethoprop is used as an insecticide against soil insects like wireworms and as a nematicide. It is used on different crops, ranging from potatoes, bananas, and sugarcane to ornamental plants and tobacco. Most of the ethoprop used in the United States is applied to potatoes. In the period of 1987 to 1996, an estimated total of 691,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethoprophos Synthesis 1
Ethoprophos (or ethoprop) is an organophosphate ester with the formula C8H19O2PS2. It is a clear yellow to colourless liquid that has a characteristic mercaptan-like odour. It is used as an insecticide and nematicide and it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Synthesis Ethoprop can be synthesised by reacting phosphoryl chloride with two equivalents of ''n''-propylmercaptan and one equivalent of sodium ethoxide. A second pathway is reacting ''n''-propylmercaptan and sodium ethoxide with phosphorus trichloride to yield ethoxy-bis(propylsulfanyl)phosphane, which can then be oxidized by hydrogen peroxide to yield the product. : : Applications Ethoprop is used as an insecticide against soil insects like wireworms and as a nematicide. It is used on different crops, ranging from potatoes, bananas, and sugarcane to ornamental plants and tobacco. Most of the ethoprop used in the United States is applied to potatoes. In the period of 1987 to 1996, an estimated total of 691,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercaptan
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the "smell of natural gas" is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' ( Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate group () bonds very stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esterase
An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis. A wide range of different esterases exist that differ in their substrate specificity, their protein structure, and their biological function. EC classification/list of enzymes * ''EC 3.1.1'': Carboxylic ester hydrolases ** Acetylesterase (EC 3.1.1.6), splits off acetyl groups *** Cholinesterase **** Acetylcholinesterase, inactivates the neurotransmitter acetylcholine **** Pseudocholinesterase, broad substrate specificity, found in the blood plasma and in the liver ** Pectinesterase (EC 3.1.1.11), clarifies fruit juices * ''EC 3.1.2'': Thiolester hydrolases ** Thioesterase *** Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 * ''EC 3.1.3'': Phosphoric monoester hydrolases ** Phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.x), hydrolyses phosphoric acid monoesters into a phosphate ion and an alcohol *** Alkaline phosphatase, removes phosphate groups from many types of molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route Of Administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body. Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. Common examples include oral and intravenous administration. Routes can also be classified based on where the target of action is. Action may be topical (local), enteral (system-wide effect, but delivered through the gastrointestinal tract), or parenteral (systemic action, but delivered by routes other than the GI tract). Route of administration and dosage form are aspects of drug delivery. Classification Routes of administration are usually classified by application location (or exposition). The route or course the active substance takes from application location to the location where it has its target effect is usually rather a matter of pharmacokinetics (concerning the processes of uptake, distribution, and elimination of drugs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
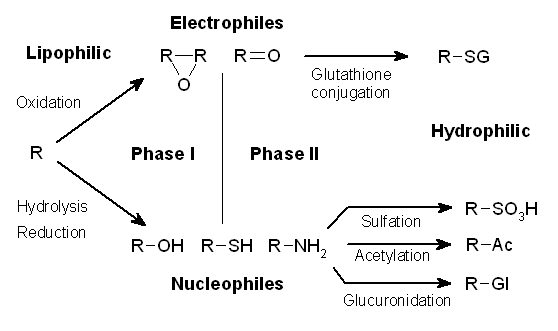
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is called pharmacokinetics. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important aspect of pharmacology and medicine. For example, the rate of metabolism determines the duration and intensity of a drug's pharmacologic action. Drug metabolism also affects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propyl Group
In organic chemistry, propyl is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is often represented in organic chemistry with the symbol Pr (not to be confused with the element praseodymium). An isomeric form of propyl is obtained by moving the point of attachment from a terminal carbon atom to the central carbon atom, named 1-methylethyl or isopropyl. To maintain four substituents on each carbon atom, one hydrogen atom has to be moved from the middle carbon atom to the carbon atom which served as attachment point in the ''n''-propyl variant, written as . Linear propyl is sometimes termed normal and hence written with a prefix ''n''- (i.e., ''n-''propyl), as the absence of the prefix ''n''- does not indicate which attachment point is chosen, i.e. absence of prefix does not automatically exclude the possibility of it being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings. Common side effects include a dry mouth, large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate. It should generally not be used in people with angle closure glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during pregnancy causes birth defects, that has not been well studied. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (a type of anticholinergic) that works by inhibiting the parasympathetic nervous system. Atropine occurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyspnoea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, interstitial lung disease, congestive heart failur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miosis
Miosis, or myosis (), is excessive constriction of the pupil. citing: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th ed. The opposite condition, , is the dilation of the pupil. is the condition of one being more dilated than the other. Causes Age * Senile miosis (a reduction in the size of a person's pupil in old age) ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system. The nicotinic receptors are considered cholinergic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)