|
Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint of Lebanon's Mediterranean coast. Beirut has been inhabited for more than 5,000 years, and was one of Phoenicia's most prominent city states, making it one of the oldest cities in the world (see Berytus). The first historical mention of Beirut is found in the Amarna letters from the New Kingdom of Egypt, which date to the 14th century BC. Beirut is Lebanon's seat of government and plays a central role in the Lebanese economy, with many banks and corporations based in the city. Beirut is an important seaport for the country and region, and rated a Beta + World City by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. Beirut was severely damaged by the Lebanese Civil War, the 2006 Lebanon War, and the 2020 massive explosion in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lies to its west across the Mediterranean Sea; its location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has contributed to its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious diversity. It is part of the Levant region of the Middle East. Lebanon is home to roughly six million people and covers an area of , making it the second smallest country in continental Asia. The official language of the state is Arabic, while French is also formally recognized; the Lebanese dialect of Arabic is used alongside Modern Standard Arabic throughout the country. The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back over 7000 years, predating recorded history. Modern-day Lebanon was home to the Phoenicians, a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law School Of Beirut
The law school of Berytus (also known as the law school of Beirut) was a center for the study of Roman law in classical antiquity located in Berytus (modern-day Beirut, Lebanon). It flourished under the patronage of the Roman emperors and functioned as the Roman Empire's preeminent center of jurisprudence until its destruction in AD 551. The law schools of the Roman Empire established organized repositories of imperial constitutions and institutionalized the study and practice of jurisprudence to relieve the busy imperial courts. The archiving of imperial constitutions facilitated the task of jurists in referring to legal precedents. The origins of the law school of Beirut are obscure, but probably it was under Augustus in the first century. The earliest written mention of the school dates to 238–239 AD, when its reputation had already been established. The school attracted young, affluent Roman citizens, and its professors made major contributions to the Codex of Justinian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
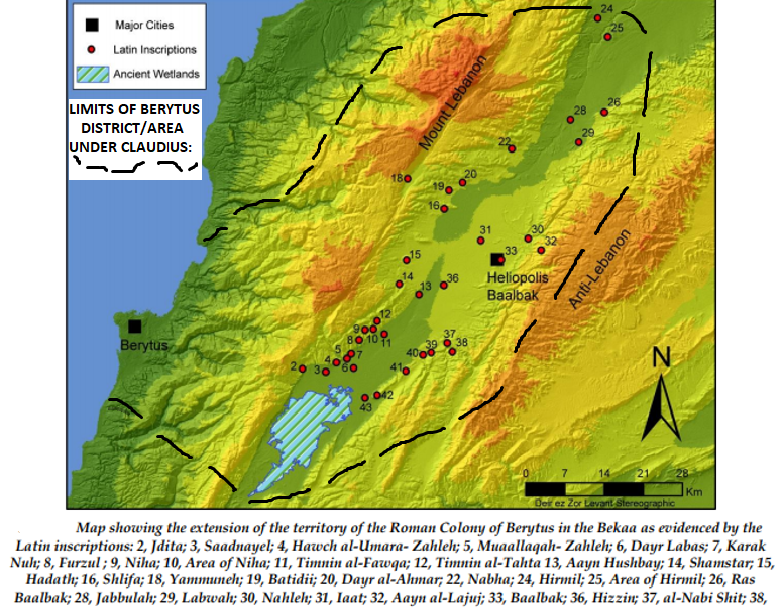
Berytus
) or Laodicea in Canaan (2nd century to 64 BCE) , image = St. George's Cathedral, Beirut.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = Roman ruins of Berytus, in front of Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral in modern-day Beirut , map = , map_type = Lebanon , map_alt = , map_size = 270 , coordinates = , altitude_m = , altitude_ref = , relief = , gbgridref = , map_dot_label = , location = Beirut, Lebanon , region = , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , volume = , diameter = , circumference = , height = , builder = , material = , built = Roman republic (merchants from early Laodicea/Berytus recorded by 110–109 BCE) , abandoned = , epochs = Roman and Early Byzantine/late antiquity; previous port dating back to Iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
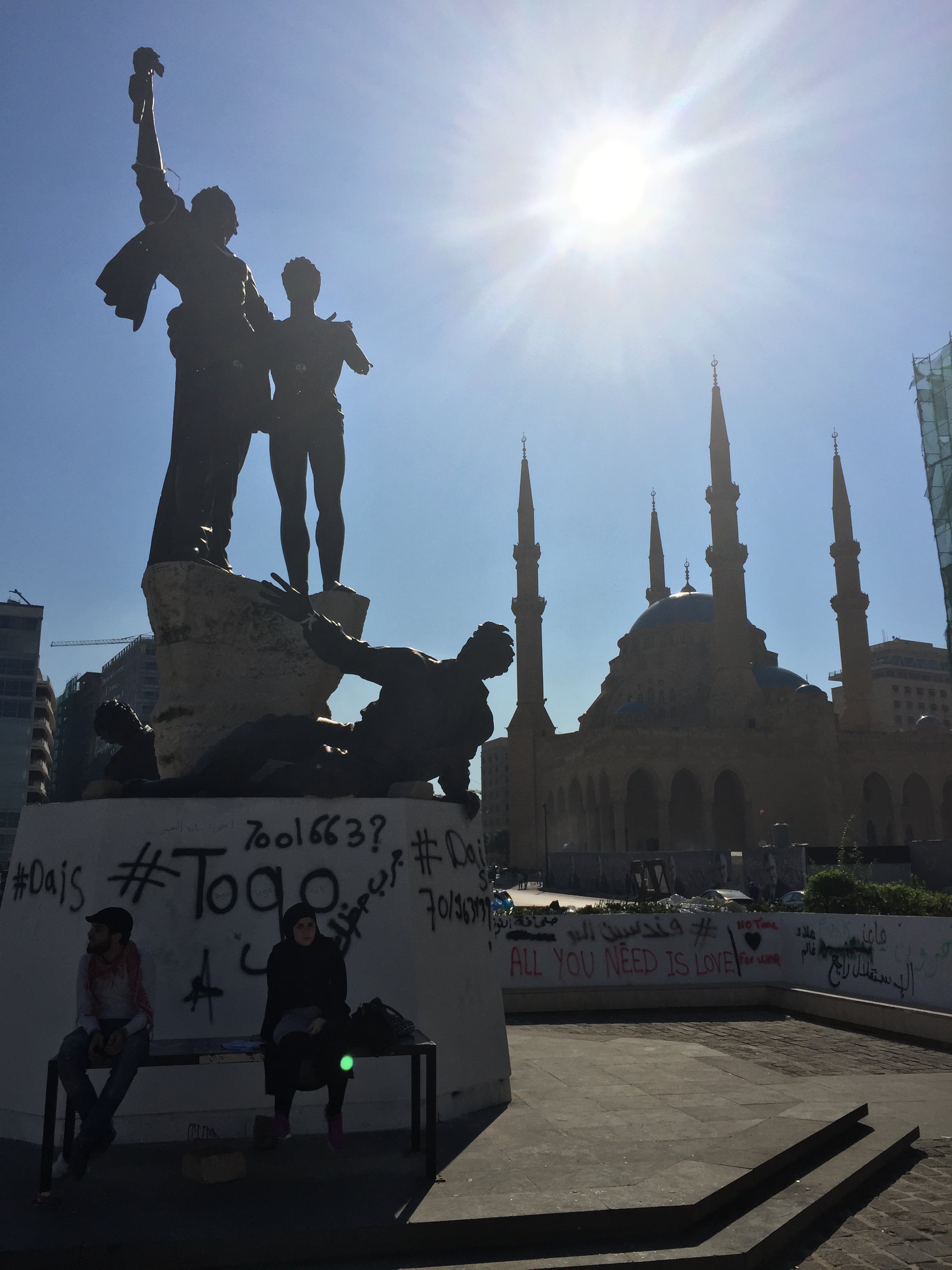
Martyrs' Square, Beirut
Martyrs' Square ( ; french: Place des Martyrs), historically known as "Al Burj" or "Place des Cannons", is the historical central public square of Beirut, Lebanon. Like the Martyr's Square in Damascus, it is named after the 6 May 1916 executions ordered by Djemal Pasha during World War I. Overview In 1931, the historic square took its name to commemorate the martyrs executed there under Ottoman rule. In the 1950s, the square became a popular venue for cinemas and coffee-houses. During the Lebanese Civil War, it was part of the demarcation line that divided the city in half. Construction Initially named ''Sahat al-Burj'', the Municipality of Beirut modernized the square in 1878 as the main meeting place of the city. Beshara Effendi designed a garden with fountain and kiosks, overlooked by the Petit Serail - the seat of Beirut’s governor general – as well as public buildings and souks. After that, the square underwent a lot of transformations until 1931, where it took the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maronite Cathedral Of Saint George, Beirut
Saint George Maronite Cathedral ( ar, كاتدرائية مار جرجس للموارنة) is the cathedral of the Maronite Catholic Archeparchy of Beirut, Archdiocese of the city of Beirut, Lebanon. Its construction, with a Neoclassical facade, interior and plan inspired by the Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore, began in 1884 and ended in 1894. The cathedral was heavily hit and shelled during the Lebanese civil war and was plundered and defaced. A number of works of art that were looted have since been recovered, including the famous painting by Eugène Delacroix representing Saint George, the patron saint of the cathedral and of the Archdiocese of the city of Beirut. The cathedral was restored after the end of the hostilities and was re-inaugurated by the Maronite Patriarch Nasrallah Boutros Sfeir on 24 April 2000. Construction The Cathedral of Saint George was built by Monsignor Joseph Debs, the Archbishop of Beirut, on the site of an earlier church that was also dedicated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammad Al-Amin Mosque
The Mohammad Al-Amin Mosque ( ar, 1=جامع محمد الأمين), also referred to as the Blue Mosque, is a Sunni Muslim mosque located in downtown Beirut, Lebanon. In the 19th century, a Zawiya (prayer corner) was built on this site. Decades of preparation to obtain sufficient land adjacent to the old Zawiya led finally to the building of the new mosque. It was inaugurated in 2008. Construction The Mohammad Al-Amin mosque is the biggest mosque in Lebanon. In the initial steps of building this mosque, Hariri endured many obstacles such as rights of property and funding the actual building. In preparation for the mosque, panels were placed which signified that a mosque was going to be built. Soon after the Lebanon Civil War, very little was left. Following a donation by late Prime Minister Rafic Hariri, the foundation stone for the Mohammad Al-Amin Mosque was laid in November 2002. The design is evocative of the Ottomans’ monumental architecture: with a built area coverin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beirut Governorate
Beirut Governorate ( ar, محافظة بيروت, ; french: Gouvernorat de Beyrouth) is a Lebanese governorate that consists of one district and one city, Beirut, which is also its capital, and the capital of Lebanon. The area of this governorate is 19.8 km2 (without suburbs); despite its small size, it is considered the most important region in Lebanon because of its economic, political, cultural, and social activity. The governor of the Beirut Governate is Greek Orthodox according to tradition, while the mayor of the City of Beirut is Sunni Muslim. Beirut is known to be the most religiously diverse city in the Middle East. There are about 2.5 million people in Beirut and its suburbs (Greater Beirut). Cities * Beirut (Greater Beirut Greater Beirut ( ar, بيروت الكبرى; french: Grand Beyrouth) is the urban agglomeration comprising the city of Beirut (Beirut Governorate) and the adjacent municipalities over the Mount Lebanon Governorate. It does not constitute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Beirut
Greater Beirut ( ar, بيروت الكبرى; french: Grand Beyrouth) is the urban agglomeration comprising the city of Beirut (Beirut Governorate) and the adjacent municipalities over the Mount Lebanon Governorate. It does not constitute a single administrative unit. Greater Beirut geographically stretches south to the Damour River in the Chouf District until it reaches the "Nahr al-Kalb" river in the Keserwan District in the north. It also comprises many towns and cities in the mountains in the Aley District, Baabda District and Metn District Districts, most notably being the cities of Baabda, Beit Mery, Bchamoun and Mtaileb. The conurbation spreads south, east, and north of Beirut city. To the west, the Eastern Mediterranean Sea serves as a natural boundary. Demographics Greater Beirut is equally split between Christians and Muslims: * West Beirut is predominantly Sunni (30%). * South Beirut is predominantly Shia (15%). * East and North Beirut are predominantly Chris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sursock Museum
The Sursock Museum ( ar, قصر سرسق), which is officially known as the Nicolas Ibrahim Sursock Museum, is a modern art and contemporary art museum in Beirut, Lebanon. History In 1912, the wealthy and prominent Lebanese aristocrat Nicolas Ibrahim Sursock built the private villa that now houses the museum. He decreed in his will that the villa be transformed into a museum. When he died in 1952, he bequeathed the villa to the city of Beirut.Daratalfunun.org The museum opened in 1961, directed by Amine Beyhum, with an exhibit of works of contemporary Lebanese artists, setting a precedent for cultural events in Beirut. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raouché
Raouché () is a residential and commercial neighborhood in Beirut, Lebanon. It is known for its upscale apartment buildings, numerous restaurants, and cliff-side cafés that line Avenue de Paris, which forms part of the Corniche Beirut. The corniche or the wide, seaside sidewalk of Avenue de Paris is popular on weekends and evenings where strollers and joggers crowd the pavements. Off the coast of Raouché, there is a natural landmark called the Pigeons' Rock (also known as the Rock of Raouché). Located at Beirut's westernmost tip, the two huge rock formations, which stand like gigantic sentinels, are a popular destination for locals and visitors alike. Raouché also is claimed to be the remains of a sea monster the Greek hero Perseus killed to save Andromeda. The stone is rock as Perseus used Medusa’s head on the monster to turn it into stone. Etymology Some historians believe that the word "raouché" derives from the Aramaic word ''rosh'' or Arabic word ''ras'', both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marwan Abboud
Marwan Abboud ( ar, مروان عبود; born 25 August 1969) is a Lebanese politician and judge, who was appointed governor of Beirut in June 2020. He was in office as governor during the 2020 Beirut explosion, and broke down in tears on television, calling it "a national catastrophe". He was previously President of the Supreme Disciplinary Authority Supreme may refer to: Entertainment * Supreme (character), a comic book superhero * ''Supreme'' (film), a 2016 Telugu film * Supreme (producer), hip-hop record producer * "Supreme" (song), a 2000 song by Robbie Williams * The Supremes, Motown- ..., appointed to the role on 14 November 2012. He had responsibility for reviewing allegations of corruption among civil servants. References 1969 births People from Batroun District Living people Lebanese politicians Lebanese judges {{Lebanon-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

