|
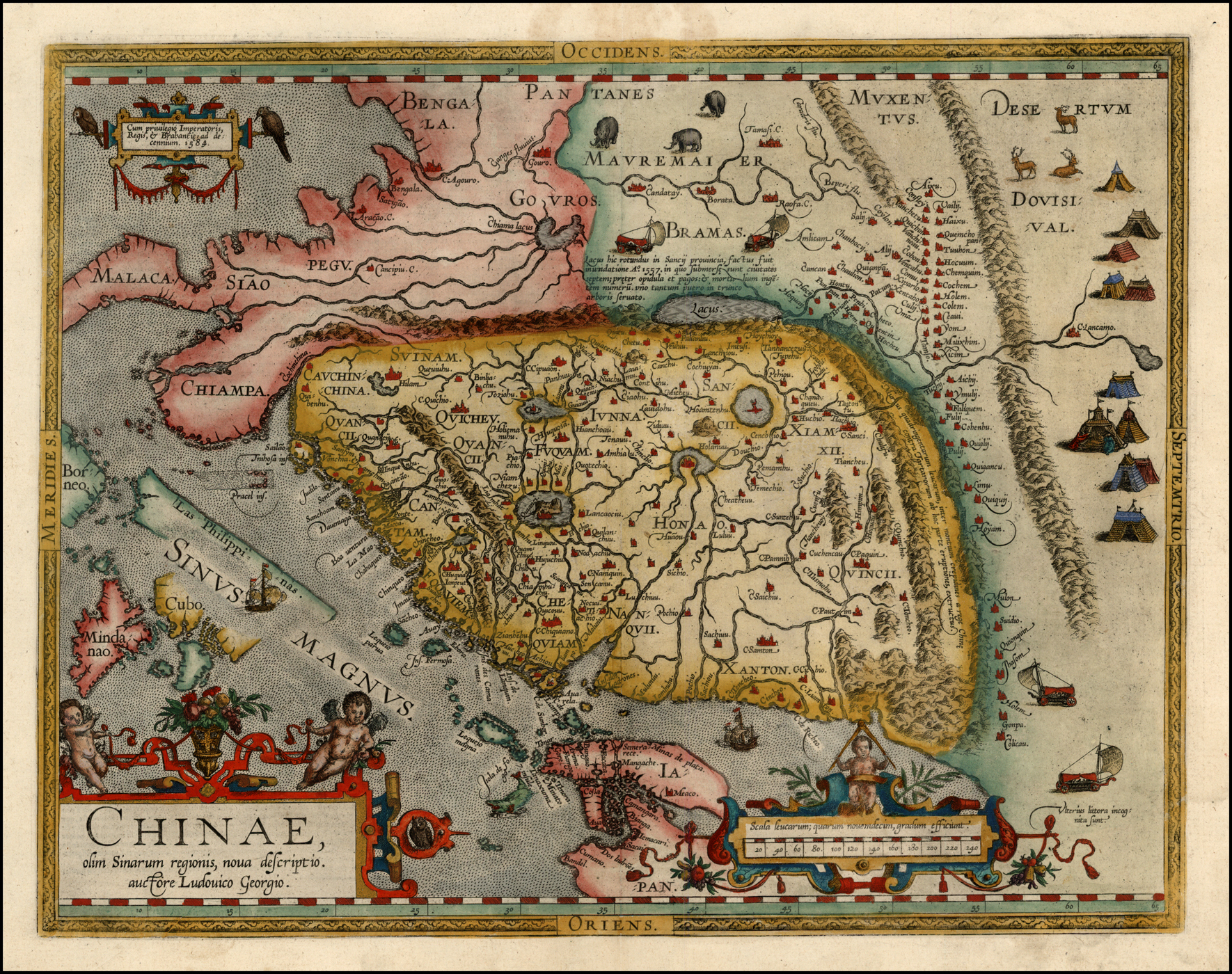
Zhu Quan
Zhu Quan (; 27 May 1378 – 12 October 1448), the Prince of Ning (), was a Chinese historian, military commander, musician, and playwright. He was the 17th son of the Hongwu Emperor of the Ming dynasty. During his life, he served as a military commander, feudal lord, historian, and playwright. He is also remembered as a great tea connoisseur, a zither player, and composer. Other names In addition to Prince of Ning, Zhu Quan was also known as the Strange Scholar of the Great Ming (, ''Da Ming Qi Shi''). As part of his Taoist attempts to avoid death, he adopted the aliases the Emaciated Immortal (, ''Qúxiān''), the "Master who Encompasses Emptiness" (, ''Hánxūzi''), "Taoist of the Mysterious Continent" or " Taoist of the Mysterious Island" (, ''Xuánzhōu Dàoren''), and "Perfected Gentleman of the Marvelous Way of the Unfathomable Emptiness of the Southern Pole" (, ''Nánjí Chōngxū Miàodào Zhēnjūn''). Biography Zhu Quan was initially a military commander in ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328 – 24 June 1398), personal name Zhu Yuanzhang (), courtesy name Guorui (), was the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty of China, reigning from 1368 to 1398. As famine, plagues and peasant revolts increased across China proper in the 14th century, Zhu Yuanzhang rose to command the Red Turban forces that conquered China proper, ending the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty and forcing the remnant Yuan court (known as Northern Yuan in historiography) to retreat to the Mongolian Plateau. Zhu claimed the Mandate of Heaven and established the Ming dynasty at the beginning of 1368 and occupied the Yuan capital, Khanbaliq (present-day Beijing), with his army that same year. Trusting only his family, he made his many sons feudal princes along the northern marches and the Yangtze valley.Chan Hok-lam.Legitimating Usurpation: Historical Revisions under the Ming Yongle Emperor (r. 14021424)". ''The Legitimation of New Orders: Case Studies in World His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. The city has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a total recorded population of 9,314,685 . Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949, and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's administrative structure, enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly less than that of a province. Nanjing has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanchang
Nanchang (, ; ) is the capital of Jiangxi Province, People's Republic of China. Located in the north-central part of the province and in the hinterland of Poyang Lake Plain, it is bounded on the west by the Jiuling Mountains, and on the east by Poyang Lake. Because of its strategic location connecting the prosperous East and South China, it has become a major railway hub in Southern China in recent decades. As the Nanchang Uprising in 1927 is distinctively recognized by the ruling Communist Party as "firing the first gunshot against the evil Nationalists", the current government has therefore named the city since 1949 "the City of Heroes", "the place where the People's Liberation Army was born", and the most widely known "place where the military banner of the People's Liberation Army was first raised". Nanchang is also a major city, appearing among the top 150 cities in the world by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index and home to Nanchang University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, which separates Shanghai and Ningbo. Hangzhou grew to prominence as the southern terminus of the Grand Canal and has been one of China's most renowned and prosperous cities for much of the last millennium. It is a major economic and e-commerce hub within China, and the second biggest city in Yangtze Delta after Shanghai. Hangzhou is classified as a sub-provincial city and forms the core of the Hangzhou metropolitan area, the fourth-largest in China after Guangzhou-Shenzhen Pearl River agglomeration, Shanghai-Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou conurbation and Beijing. As of 2019, the Hangzhou metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product ( nominal) of 3.2 trillion yuan ($486.53 billion), making it larger than the economy of Nigeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzhou
Suzhou (; ; Suzhounese: ''sou¹ tseu¹'' , Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Soochow, is a major city in southern Jiangsu province, East China. Suzhou is the largest city in Jiangsu, and a major economic center and focal point of trade and commerce. Administratively, Suzhou is a prefecture-level city with a population of 6,715,559 in the city proper, and a total resident population of 12,748,262 as of the 2020 census in its administrative area. The city jurisdiction area's north waterfront is on a lower reach of the Yangtze whereas it has its more focal south-western waterfront on Lake Tai – crossed by several waterways, its district belongs to the Yangtze River Delta region. Suzhou is now part of the Greater Shanghai metro area, incorporating most of Changzhou, Wuxi and Suzhou urban districts plus Kunshan and Taicang, with a population of more than 38,000,000 residents as of 2020. Its urban population grew at an unprecedented rate of 6.5% between 2000 and 2014, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (; pronounced ; 2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), personal name Zhu Di (), was the third Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 1424. Zhu Di was the fourth son of the Hongwu Emperor, the founder of the Ming dynasty. He was originally enfeoffed as the Prince of Yan () in May 1370,Chan Hok-lam.Legitimating Usurpation: Historical Revisions under the Ming Yongle Emperor (r. 14021424). ''The Legitimation of New Orders: Case Studies in World History''. Chinese University Press, 2007. . Accessed 12 October 2012. with the capital of his princedom at Beiping (modern Beijing). Zhu Di was a capable commander against the Mongols. He initially accepted his father's appointment of his eldest brother Zhu Biao and then Zhu Biao's son Zhu Yunwen as crown prince, but when Zhu Yunwen ascended the throne as the Jianwen Emperor and began executing and demoting his powerful uncles, Zhu Di found pretext for rising in rebellion against his nephew. Assisted in large part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ming
The ''History of Ming'' or the ''Ming History'' (''Míng Shǐ'') is one of the official Chinese historical works known as the ''Twenty-Four Histories''. It consists of 332 volumes and covers the history of the Ming dynasty from 1368 to 1644. It was written by a number of officials commissioned by the court of Qing dynasty, with Zhang Tingyu as the lead editor. The compilation started in the era of the Shunzhi Emperor and was completed in 1739 in the era of the Qianlong Emperor, though most of the volumes were written in the era of the Kangxi Emperor. The sinologist Endymion Wilkinson writes that the ''Mingshi'', the second longest of the ''Twenty-Four Histories'', after the '' History of Song'', is "generally reckoned to be one of the best of the ''Histories'' and one of the easiest to read." Background After the Qing dynasty had extended its rule into the Central Plain, in the second year of the Shunzhi Emperor, the Censor Zhao Jiding ( 趙繼鼎) was asked to compile the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beiping
"Beijing" is from pinyin ''Běijīng,'' which is romanized from , the Chinese name for this city. The pinyin system of transliteration was approved by the Chinese government in 1958, but little used until 1979. It was gradually adopted by various news organizations, governments, and international agencies over the next decade. Etymology The Chinese characters ("north") and ("capital") together mean the "Northern Capital". The name was first used during the reign of the Ming dynasty's Yongle Emperor, who made his northern fief a second capital, along with Nanjing (, the "Southern Capital"), in 1403 after successfully dethroning his nephew during the Jingnan Campaign. The name was restored in 1949 at the founding of the People's Republic of China. Peking Portugal was the first European country to contact China in modern times. In Portuguese, the city is called ''Pequim.'' This name appeared in the letters of Francis Xavier in 1552. It transferred to English as "Pekin" and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanhaiguan District
Shanhaiguan District (), formerly Shan-hai-kwan or Shan-hai-kuan, is a district of the city of Qinhuangdao, Hebei Province, China, named after the pass of the Great Wall within the district, Shanhai Pass. It is located east of the city centre. Administrative divisions There are five subdistricts, three towns, and one township, Bohai Township (), in the district. Subdistricts * Nanguan Subdistrict () * Dongjie Subdistrict () *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lulong County
Lulong County, formerly Yongping, is a county of Qinhuangdao City, in northeastern Hebei Province, China. Administrative divisions The county administers 6 towns and 6 townships. Towns: * Lulong (), Panzhuang (), Yanheying (), Shuangwang (), Liutiangezhuang (), Shimen () Townships: * Xiazhai Township (), Liujiaying Township (), Chenguantun Township (), Yinzhuang Township (), Gebo Township (), Mujing Township () Climate Transport * China National Highway 102 *China National Highway 205 China National Highway 205 (G205) runs from Shanhaiguan, Hebei Province to Shenzhen, Guangdong. It is 3,160 kilometres in length and runs south from Shanhaiguan towards Tianjin, Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu, Anhui, Zhejiang, Fujian, and ends in Gua ... * Beijing–Harbin Railway * Beijing–Qinhuangdao Railway * Datong–Qinhuangdao Railway * G1 Beijing–Harbin Expressway References External linksOfficial site of Lulong County [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Gao
Wu may refer to: States and regions on modern China's territory *Wu (state) (; och, *, italic=yes, links=no), a kingdom during the Spring and Autumn Period 771–476 BCE ** Suzhou or Wu (), its eponymous capital ** Wu County (), a former county in Suzhou * Eastern Wu () or Sun Wu (), one of the Three Kingdoms in 184/220–280 CE * Li Zitong (, died 622), who declared a brief Wu Dynasty during the Sui–Tang interregnum in 619–620 CE * Wu (Ten Kingdoms) (), one of the ten kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period 907–960 CE * Wuyue (), another of the ten kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period 907–960 CE * Wu (region) (), a region roughly corresponding to the territory of Wuyue ** Wu Chinese (), a subgroup of Chinese languages now spoken in the Wu region ** Wuyue culture (), a regional Chinese culture in the Wu region Language * Wu Chinese, a group of Sinitic languages that includes Shanghaiese People * Wu (surname) (or Woo), several di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)