|
Zhao Erfeng
Zhao Erfeng (1845–1911), courtesy name Jihe, was a late Qing Dynasty official and Han Chinese bannerman, who belonged to the Plain Blue Banner. He was an assistant amban in Tibet at Chamdo in Kham (eastern Tibet). He was appointed in March, 1908 under Lien Yu, the main amban in Lhasa. Formerly Director-General of the Sichuan-Hubei Railway and acting viceroy of Sichuan province, Zhao was the much-maligned Chinese general of the late imperial era who led military campaigns throughout Kham, earning himself the nickname "the Butcher of Kham"Tsering Shakya"The Thirteenth Dalai Lama, Tubten Gyatso"Treasury of Lives, accessed May 11, 2021 and "Zhao the Butcher" (). Amban of Tibet Zhao Erfeng crushed the Tibetan Lamas and their monasteries in the 1905 Tibetan Rebellion in Yunnan and Sichuan, he then crushed the rebels at the siege of Chantreng (now Xiangcheng County, Sichuan) which lasted from 1905 to 1906. The Tibetan Lamas had revolted against Qing rule, killing Chinese gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
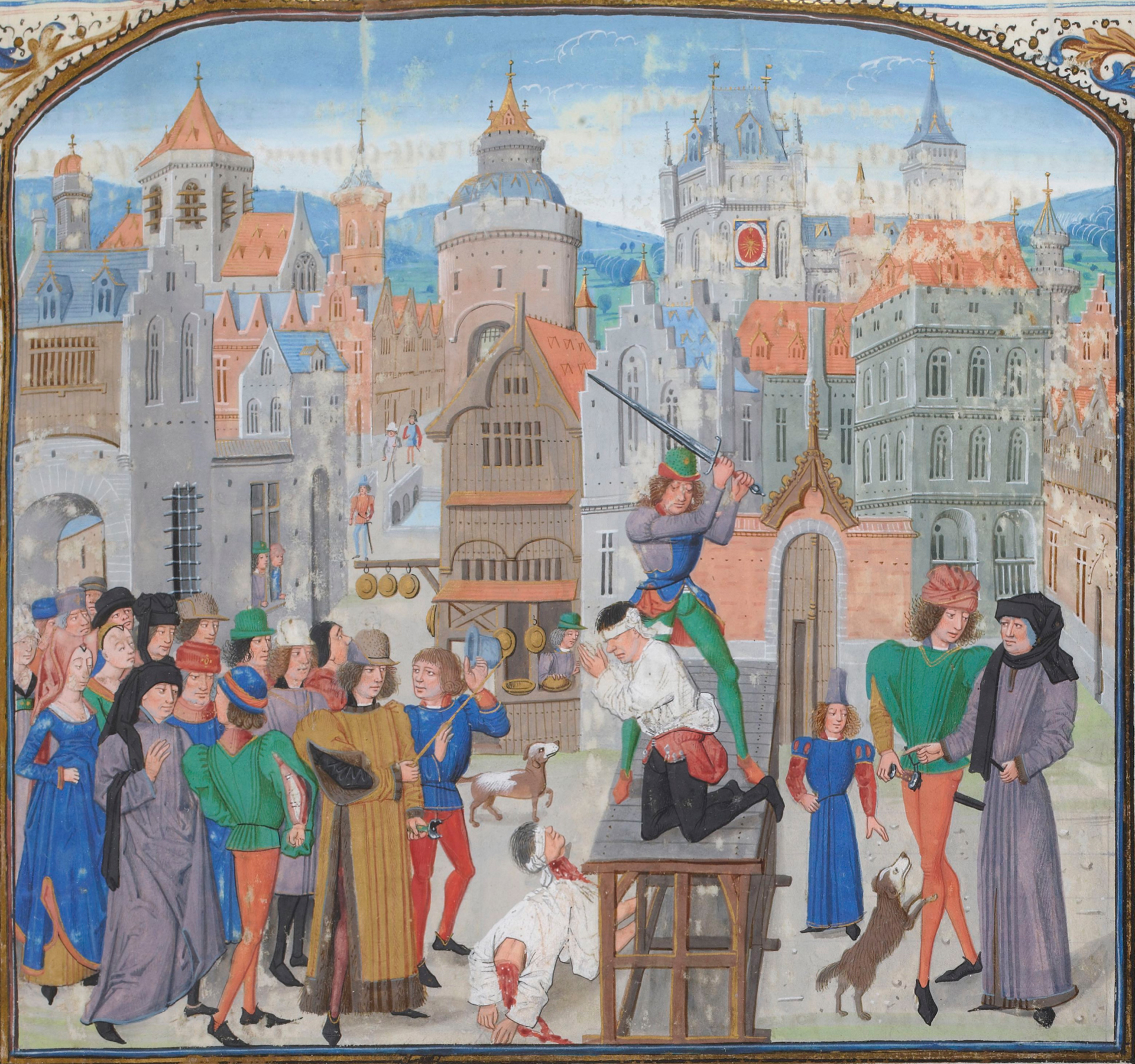
Decapitation
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the involuntary functions that are needed for the body to function. The term ''beheading'' refers to the act of deliberately decapitating a person, either as a means of murder or as an execution; it may be performed with an axe, sword, knife, machete or by mechanical means such as a guillotine or chainsaw. An executioner who carries out executions by beheading is sometimes called a headsman. Accidental decapitation can be the result of an explosion, a car or industrial accident, improperly administered execution by hanging or other violent injury. Suicide by decapitation is rare but not unknown. The national laws of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Qatar permit beheading; however, in practice, Saudi Arabia is the only country that continues to behead i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham presently covers a land area distributed between five regions in China, most of it in Tibet Autonomous Region and Sichuan, with smaller portions located within Qinghai, Gansu and Yunnan provinces. Densely forested with grass plains, its convergence of six valleys and four rivers supported independent Kham polities of Tibetan warrior kingdoms together with Tibetan Buddhist monastic centers.Jann Ronis"An Overview of Kham (Eastern Tibet) Historical Polities" The University of Virginia The early trading route between Central Tibet and China traveled through Kham, and Kham is said to be the inspiration for Shangri-La in James Hilton's novel. Settled as Tibet's eastern frontier in the 7th century, King Songtsen Gampo built temples along its e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuchang Uprising
The Wuchang Uprising was an armed rebellion against the ruling Qing dynasty that took place in Wuchang (now Wuchang District of Wuhan), Hubei, China on 10 October 1911, beginning the Xinhai Revolution that successfully overthrew China's last imperial dynasty. It was led by elements of the New Army, influenced by revolutionary ideas from Tongmenghui. The uprising and the eventual revolution directly led to the downfall of the Qing dynasty with almost three centuries of imperial rule, and the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC), which commemorates the anniversary of the uprising's starting date of 10 October as the National Day of the Republic of China. The uprising originated from popular unrest about a railway crisis, and the planning process took advantage of the situation. On 10 October 1911, the New Army stationed in Wuchang launched an assault on the residence of the Viceroy of Huguang. The viceroy Ruicheng quickly fled from the residence, and the revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuchang District
Wuchang forms part of the urban core of and is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China. It is the oldest of the three cities that merged into modern-day Wuhan, and stood on the right (southeastern) bank of the Yangtze River, opposite the mouth of the Han River. The two other cities, Hanyang and Hankou, were on the left (northwestern) bank, separated from each other by the Han River. The name "Wuchang" remains in common use for the part of urban Wuhan south of the Yangtze River. Administratively, however, it is split between several districts of the City of Wuhan. The historic center of Wuchang lies within the modern Wuchang District, which has an area of and a population of 1,003,400. Other parts of what is colloquially known as Wuchang are within Hongshan District (south and south-east) and Qingshan District (north-east). Presently, on the right bank of the Yangtze, it borders the districts of Qingshan (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Suyin
Rosalie Matilda Kuanghu Chou (; 12 September 1917 or 1916 – 2 November 2012) was a Chinese-born Eurasian physician and author better known by her pen name Han Suyin (). She wrote in English and French on modern China, set her novels in East and Southeast Asia, and published autobiographical memoirs which covered the span of modern China. These writings gained her a reputation as an ardent and articulate supporter of the Chinese Communist Revolution. She lived in Lausanne, Switzerland, for many years until her death. Biography Han Suyin was born in Xinyang, Henan, China. Her father was a Belgian-educated Chinese engineer, Chou Wei (; pinyin: Zhōu Wěi), of Hakka heritage, while her mother was Flemish. She began work as a typist at Peking Union Medical College in 1931, not yet 15 years old. In 1933 she was admitted to Yenching University where she felt she was discriminated against as a Eurasian. In 1935 she went to Brussels to study medicine. In 1938 she returned to Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
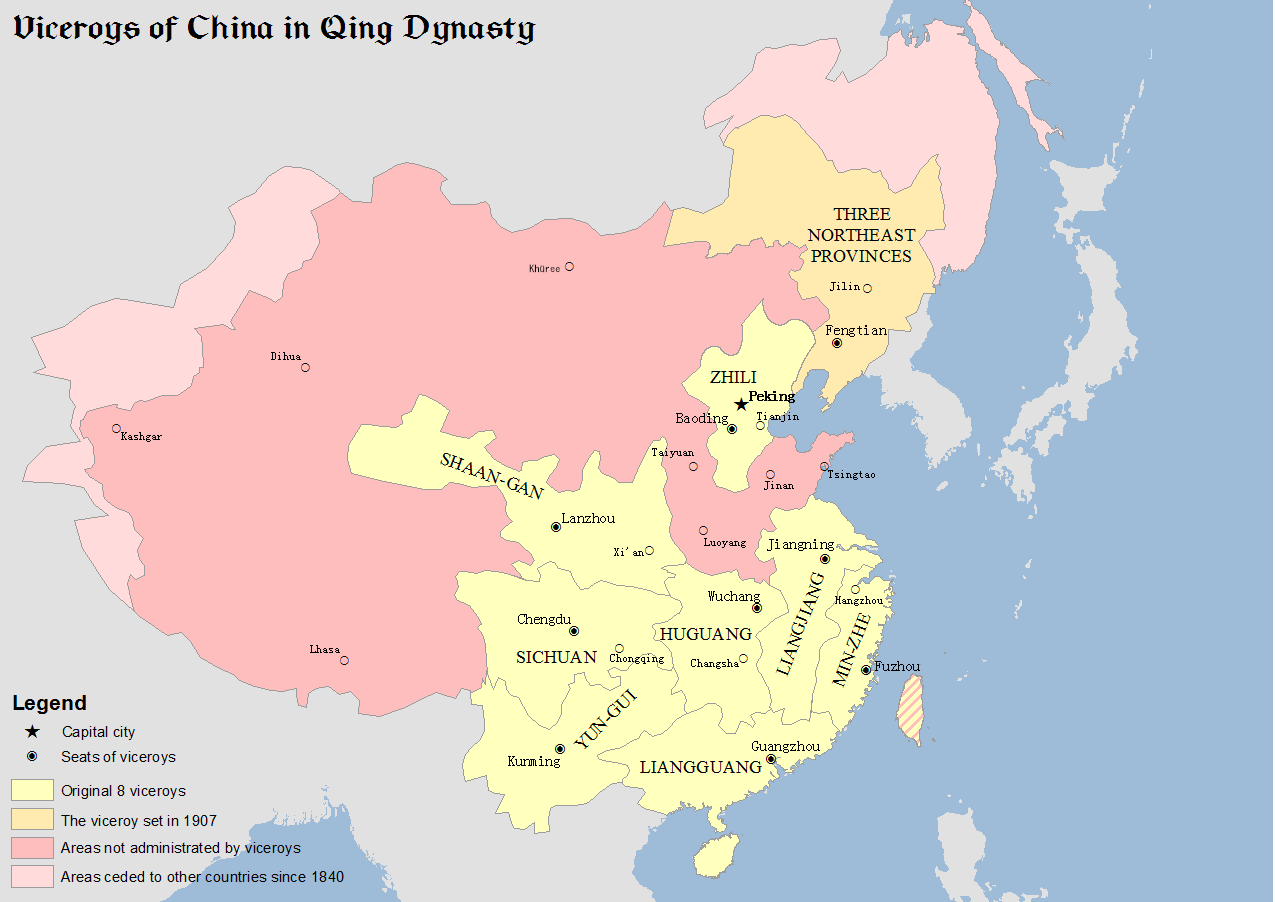
Viceroy Of Sichuan
The Viceroy of Sichuan, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Sichuan Province and the Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. As its name suggests, the Viceroy of Sichuan had control over Sichuan (Szechuan) Province, as well as modern Chongqing Municipality, which was split off in 1997. History The origins of the Viceroy of Sichuan trace back to 1644, during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, with the creation of the office of the Provincial Governor of Sichuan (四川巡撫). Its headquarters were in Chengdu. In 1645, the Qing government created the Viceroy of Huguang-Sichuan with Luo Xiujin (羅繡錦) as the first Viceroy overseeing both Huguang (present-day Hubei and Hunan) and Sichuan provinces. In 1653, Sichuan was placed under the jurisdiction of the Viceroy of the Three Borders in Shaanxi, which was subsequently renamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Younghusband
Lieutenant Colonel Sir Francis Edward Younghusband, (31 May 1863 – 31 July 1942) was a British Army officer, explorer, and spiritual writer. He is remembered for his travels in the Far East and Central Asia; especially the 1904 British expedition to Tibet, led by himself, and for his writings on Asia and foreign policy. Younghusband held positions including British commissioner to Tibet and President of the Royal Geographical Society. Early life Francis Younghusband was born in 1863 at Murree, British India (now Pakistan), to a British military family, being the brother of Major-General George Younghusband and the second son of Major-General John W. Younghusband and his wife Clara Jane Shaw. Clara's brother, Robert Shaw, was a noted explorer of Central Asia. His uncle Lieutenant-General Charles Younghusband CB FRS, was a British Army officer and meteorologist. As an infant, Francis was taken to live in England by his mother. When Clara returned to India in 1867 she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potala
The Potala Palace is a ''dzong'' fortress in Lhasa, Tibet. It was the winter palace of the Dalai Lamas from 1649 to 1959, has been a museum since then, and a World Heritage Site since 1994. The palace is named after Mount Potalaka, the mythical abode of the bodhisattva Avalokiteśvara. The 5th Dalai Lama started its construction in 1645Laird, Thomas. (2006). ''The Story of Tibet: Conversations with the Dalai Lama'', pp. 175. Grove Press, New York. . after one of his spiritual advisers, Konchog Chophel (died 1646), pointed out that the site was ideal as a seat of government, situated as it is between Drepung and Sera monasteries and the old city of Lhasa.Karmay, Samten C. (2005). "The Great Fifth", p. 1. Downloaded as a pdf file on 16 December 2007 from It may overlay the remains of an earlier fortress called the White or Red Palace on the site, built by Songtsen Gampo in 637. The building measures east-west and north-south, with sloping stone walls averaging thick, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Expedition To Tibet
The British expedition to Tibet, also known as the Younghusband expedition, began in December 1903 and lasted until September 1904. The expedition was effectively a temporary invasion by British Indian Armed Forces under the auspices of the Tibet Frontier Commission, whose purported mission was to establish diplomatic relations and resolve the dispute over the border between Tibet and Sikkim.Landon, P. (1905). ''The Opening of Tibet'' Doubleday, Page & Co, New York. In the nineteenth century, the British had conquered Burma and Sikkim, with the whole southern flank of Tibet coming under the control of the British Indian Empire. Tibet ruled by the Dalai Lama under the Ganden Phodrang government was a Himalayan state under the suzerainty of the Chinese Qing dynasty until the 1911 Revolution, after which a period of de facto Tibetan independence (1912-1951) followed. The invasion was intended to counter the Russian Empire's perceived ambitions in the East and was initiated lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelug
240px, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Bodhgaya (India).">Bodh_Gaya.html" ;"title="Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya">Bodhgaya (India). The Gelug (, also Geluk; "virtuous")Kay, David N. (2007). ''Tibetan and Zen Buddhism in Britain: Transplantation, Development and Adaptation,'' p. 39. Routledge. is the newest of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. It was founded by Je Tsongkhapa (1357–1419), a Tibetan people, Tibetan philosopher, Vajrayana, tantric yogi and lama and further expanded and developed by his disciples (such as Khedrup Je, Gyaltsap Je and Gendün Drubpa). The Gelug school is alternatively known as New Kadam (''bKa’-gdams gsar-pa''), since it sees itself as a continuation of the Kadam tradition of Atisha (c. 11th century). Furthermore, it is also called the Ganden school, after the first monastery established by Tsongkhapa. The Ganden Tripa ("Ganden Throne Holder") is the of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiangcheng County, Sichuan
Xiangcheng County (; ) is a county in the west of Sichuan Province, China, bordering Yunnan province to the south. It is under the administration of the Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, often shortened to Ganzi Prefecture, is an autonomous prefecture in the western arm of Sichuan province, China, bordering Yunnan to the south, the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west, and Gansu to the north .... Climate Terrain maps NH-47-11 Taocheng China.jpg, NH 47-11 (Taocheng) NH-47-15 Tejung China.jpg, NH 47-15 (Tejung) References External links * Populated places in the Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture County-level divisions of Sichuan {{Sichuan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |