|
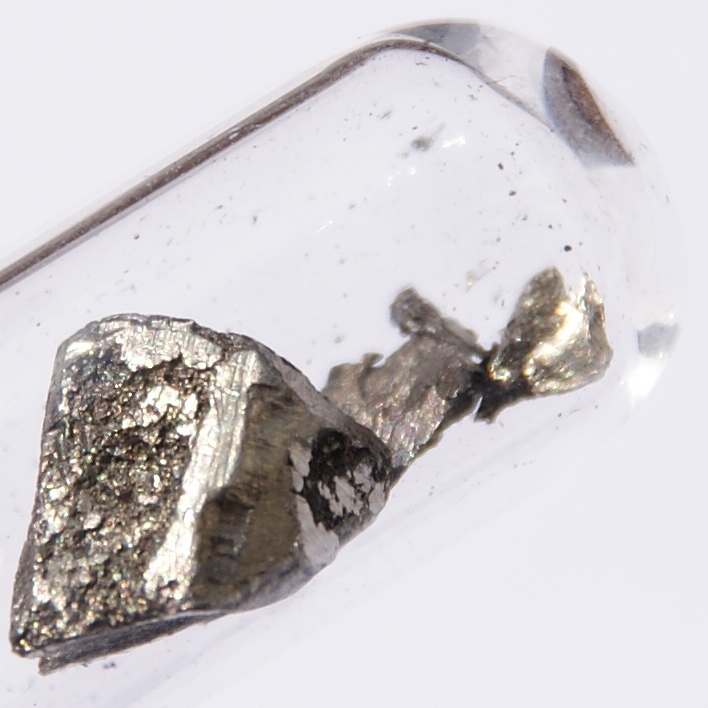
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with the symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a " rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in combination with lanthanide elements in rare-earth minerals, and is never found in nature as a free element. 89Y is the only stable isotope, and the only isotope found in the Earth's crust. The most important uses of yttrium are LEDs and phosphors, particularly the red phosphors in television set cathode ray tube displays. Yttrium is also used in the production of electrodes, electrolytes, electronic filters, lasers, superconductors, various medical applications, and tracing various materials to enhance their properties. Yttrium has no known biological role. Exposure to yttrium compounds can cause lung disease in humans. The element is named after ''ytterbite'', a mineral first identified in 1787 by the chemist Carl Axel Arrhenius. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 3 Element
Group 3 is the first group of transition metals in the periodic table. This group is closely related to the rare-earth elements. Although some controversy exists regarding the composition and placement of this group, it is generally agreed among those who study the matter that this group contains the four elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lutetium (Lu), and lawrencium (Lr); this composition has also been suggested by a 2021 IUPAC provisional report studying the problem. The group is also called the scandium group or scandium family after its lightest member. The chemistry of the group 3 elements is typical for early transition metals: they all essentially have only the group oxidation state of +3 as a major one, and like the preceding main-group metals are quite electropositive and have a less rich coordination chemistry. Due to the effects of the lanthanide contraction, yttrium and lutetium are very similar in properties. Yttrium and lutetium have essentially the chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare-earth Element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides ( yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties. These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously. These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yttrium, are often collectively known as the rare-earth elements or rare-earth metals. The informal chemical symbol Ln is used in general discussions of lanthanide chemistry to refer to any lanthanide. All but one of the lanthanides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 4f electron shell. There is some dispute on whether lanthanum or lutetium is a d-block element, but lutetium is usually considered so by those who study the matter; it is included due to its chemical similarities with the other 14. All lanthanide elements form trivalent cations, Ln3+, whose chemistry is largely determined by the ionic radius, which decreases steadily from lanthanum to lutetium. These elements are called lanthanides because the ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period 5 Element
The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fifth period contains 18 elements, beginning with rubidium and ending with xenon. As a rule, period 5 elements fill their 5s shells first, then their 4d, and 5p shells, in that order; however, there are exceptions, such as rhodium. Physical properties This period contains technetium, one of the two elements until lead that has no stable isotopes (along with promethium), as well as molybdenum and iodine, two of the heaviest elements with a known biological role, and Niobium has the largest magnetic known penetration depth of all the elements. Zirconium is one of the main components of zircon crystals, currently the oldest known minerals in the earth's crust. Many later transition m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the Lanthanides. It was discovered in 1879 by spectral analysis of the minerals euxenite and gadolinite from Scandinavia. Scandium is present in most of the deposits of rare-earth and uranium compounds, but it is extracted from these ores in only a few mines worldwide. Because of the low availability and difficulties in the preparation of metallic scandium, which was first done in 1937, applications for scandium were not developed until the 1970s, when the positive effects of scandium on aluminium alloys were discovered, and its use in such alloys remains its only major application. The global trade of scandium oxide is 15–20 tonnes per year. The properties of scandium compounds are intermediate between those of aluminium and yttrium. A diagonal relationship exists between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadolinite
Gadolinite, sometimes known as ytterbite, is a silicate mineral consisting principally of the silicates of cerium, lanthanum, neodymium, yttrium, beryllium, and iron with the formula . It is called gadolinite-(Ce) or gadolinite-(Y), depending on the prominent composing element (Y if yttrium predominates, and Ce if cerium). It may contain 35.5% yttria sub-group rare earths, 2.2% ceria earths, as much as to 11.6% BeO, and traces of thorium. It is found in Sweden, Norway, and the US (Texas and Colorado). Characteristics Gadolinite is fairly rare and typically occurs as well-formed crystals. It is nearly black in color and has a vitreous luster. The hardness is between 6.5 and 7 on the Mohs scale, and the specific gravity is between 4.0 and 4.7. It fractures in a conchoidal pattern and streaks grayish-green. It was also thought to exhibit pyrognomic properties, as it can emit visible light when heated to relatively low temperatures, but the scientific consensus is that this is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances ( collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort puls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, the usual oxidation state is +3. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although it is classified as a rare earth element, lanthanum is the 28t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, and cathodoluminescent substances which glow when struck by an electron beam ( cathode rays) in a cathode-ray tube. When a phosphor is exposed to radiation, the orbital electrons in its molecules are excited to a higher energy level; when they return to their former level they emit the energy as light of a certain color. Phosphors can be classified into two categories: fluorescent substances which emit the energy immediately and stop glowing when the exciting radiation is turned off, and phosphorescent substances which emit the energy after a delay, so they keep glowing after the radiation is turned off, decaying in brightness over a period of milliseconds to days. Fluorescent materials are used in applications in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutetium
Lutetium is a chemical element with the symbol Lu and atomic number 71. It is a silvery white metal, which resists corrosion in dry air, but not in moist air. Lutetium is the last element in the lanthanide series, and it is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Lutetium is generally considered the first element of the 6th-period transition metals by those who study the matter, although there has been some dispute on this point. Lutetium was independently discovered in 1907 by French scientist Georges Urbain, Austrian mineralogist Baron Carl Auer von Welsbach, and American chemist Charles James. All of these researchers found lutetium as an impurity in the mineral ytterbia, which was previously thought to consist entirely of ytterbium. The dispute on the priority of the discovery occurred shortly after, with Urbain and Welsbach accusing each other of publishing results influenced by the published research of the other; the naming honor went to Urbain, as he had publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Axel Arrhenius
Carl Axel Arrhenius (29 March 1757 – 20 November 1824) was an officer in the Swedish army as well as an amateur geologist and chemist. He is best known for his discovery of the mineral ytterbite (later called gadolinite) in 1787. The discovery of ytterbite was the first step in identifying an entire group of previously unknown elements, the rare earths. Eight stable rare earth elements were eventually extracted from ytterbite: terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, and yttrium. Early life Arrhenius was born in Stockholm on 29 March 1757 to Jakob Larsson Arrhenius and Brita Sofia Georgii. In 1796 he married Gustafva von Bilang. Career Arrhenius became a lieutenant of the Svea Artillery Regiment of the Swedish army, the regiment being stationed in Vaxholm. As an artillery officer, Arrhenius was assigned to study the characteristics of gunpowder at the Swedish Royal Mint's (Kungliga Myntet) laboratory. Being taught to test gunp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
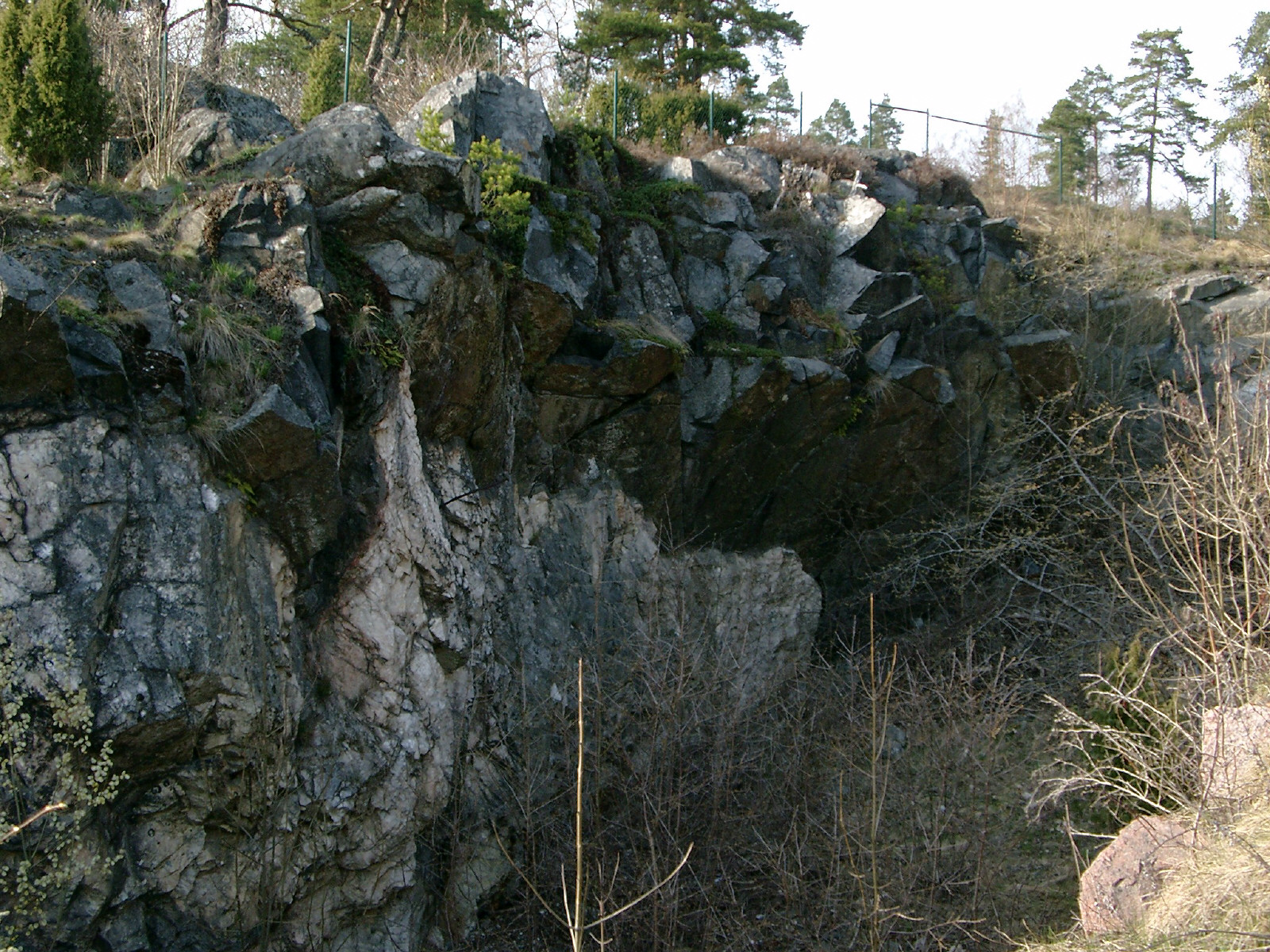
Ytterby
Ytterby () is a village on the Swedish island of Resarö, in Vaxholm Municipality in the Stockholm archipelago. Today the residential area is dominated by suburban homes. The name of the village translates to "outer village". Ytterby is perhaps most famous for being the single richest source of elemental discoveries in the world; the chemical elements yttrium (Y), terbium (Tb), erbium (Er), and ytterbium (Yb) are all named after Ytterby, while four more elements were first discovered there. Mine Quartz was mined in the area beginning in the 1600s for the ironworks in Uppland. Feldspar was mined for local porcelain manufacture, such as Gustavsberg, and the porcelain trade with Britain and Poland. The mine is likely the first feldspar mine in Sweden, starting in 1790. Feldspar mining was likely sporadic and based on manufacture demand. This demand took off in the 1860s, leading to deeper mining efforts at Ytterby. The mine became one of the most productive quartz and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





-244305.jpg)
