|
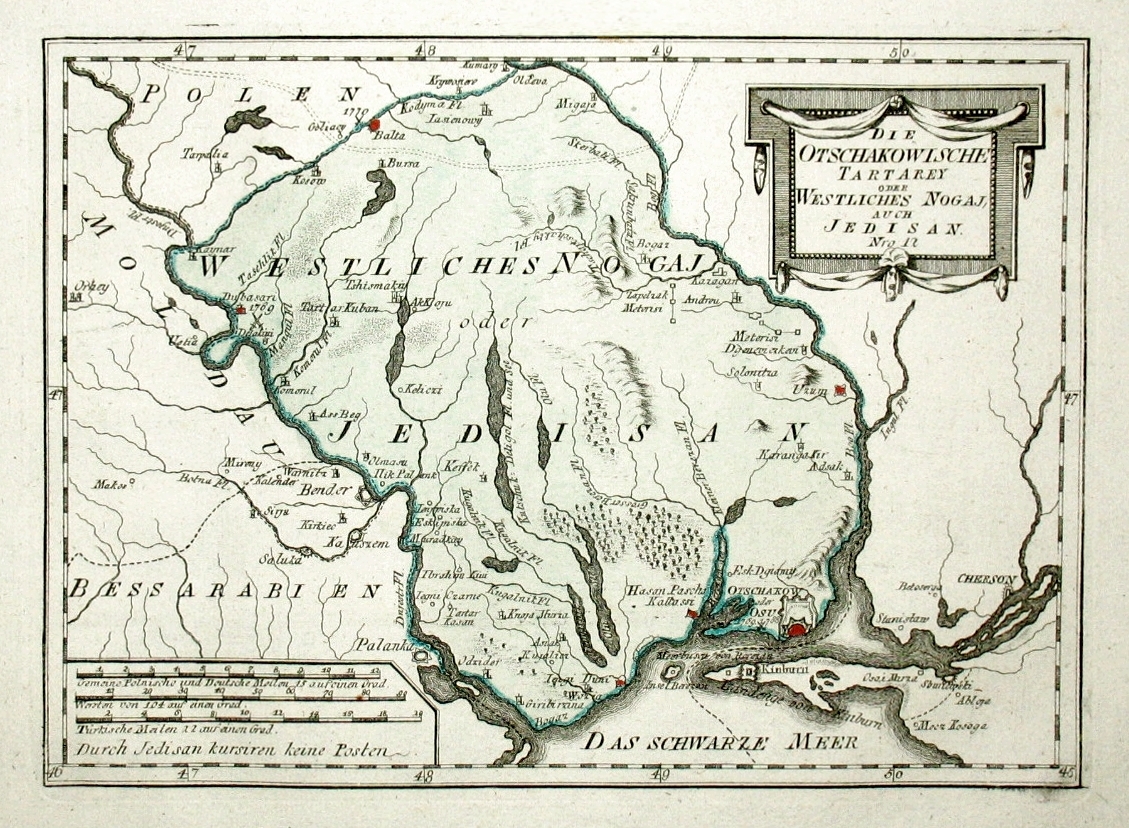
Yedisan
Yedisan (also ''Jedisan'' or ''Edisan''; tr, Yedisan; uk, Єдисан; ro, Edisan; russian: Едисан) was a conditional name for Özi așaSancağı (Ochakiv Sanjak) of Silistra Eyalet, a territory located in today's Southern Ukraine between the Dniester and the Southern Bug (Boh), which was placed by the Ottomans under the control of the Nogai Horde in the 17th and 18th centuries and was named after one of the Nogai Hordes. In the Russian Empire, it was referred to as Ochakov Oblast, while the Ottoman Turks called it simply Özü after the city of Ochakiv which served as its administrative center. Another named used was Western Nogai. Geographically, it was the western part of the so-called Wild Fields that sprawled to the north of the Black Sea between the Dniester and Dnieper rivers. It lies east of Budjak and Bessarabia, south of Podolia and Zaporizhzhia, and west of Taurida. Since the mid-20th century, the territory has been divided between southwestern Ukraine an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yedisan
Yedisan (also ''Jedisan'' or ''Edisan''; tr, Yedisan; uk, Єдисан; ro, Edisan; russian: Едисан) was a conditional name for Özi așaSancağı (Ochakiv Sanjak) of Silistra Eyalet, a territory located in today's Southern Ukraine between the Dniester and the Southern Bug (Boh), which was placed by the Ottomans under the control of the Nogai Horde in the 17th and 18th centuries and was named after one of the Nogai Hordes. In the Russian Empire, it was referred to as Ochakov Oblast, while the Ottoman Turks called it simply Özü after the city of Ochakiv which served as its administrative center. Another named used was Western Nogai. Geographically, it was the western part of the so-called Wild Fields that sprawled to the north of the Black Sea between the Dniester and Dnieper rivers. It lies east of Budjak and Bessarabia, south of Podolia and Zaporizhzhia, and west of Taurida. Since the mid-20th century, the territory has been divided between southwestern Ukraine an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nogai Horde
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds constituted a core of the Nogai Horde. In the 13th century, the leader of the Golden Horde, Nogai Khan, a direct descendant of Genghis Khan through Jochi, formed an army of the Manghits joined by numerous Turkic tribes. A century later the Nogays were led by Edigu, a commander of Manghit paternal origin and Jochid maternal origin, who founded the Nogai dynasty. In 1557, Nogai ''Nur-al-Din'' Qazi Mirza quarreled with Ismael Beg and founded the Lesser Nogai Horde on the steppe of the North Caucasus. The Nogais north of the Caspian were thereafter called the Great Nogai Horde. In the early 17th century, the Horde broke down further under the onslaught of the Kalmyks. The Nogais north of the Black Sea were nominally subject to the Crimean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silistra Eyalet
The Eyalet of Silistra or Silistria ( ota, ایالت سیلیستره; ''Eyālet-i Silistre''), later known as Özü Eyalet ( ota, ایالت اوزی; ''Eyālet-i Özi'') meaning Province of Ochakiv was an ''eyalet'' of the Ottoman Empire along the Black Sea littoral and south bank of the Danube River in southeastern Europe. The fortress of Akkerman was under the eyalet's jurisdiction. Its reported area in the 19th century was . History The Eyalet of Silistra was formed in 1593 as beylerbeylik of Özi (Ukrainian: Očakiv) Nejat Göyünç, Osmanlı Devleti'nde Tașra Teșkilâtı (Tanzimat'a Kadar), ''Osmanlı'', Cilt 6: Teșkilât, Yeni Türkiye Yayınları, Ankara, 1999, , p. 78. from territory of the former Principality of Karvuna, later Dobruja, Silistra was originally the Silistra Sanjak of Rumelia Eyalet. It was named after Silistra, since its governor often resided in this Danubian fortress. Around 1599, it was expanded and raised to the level of an eyalet likely as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine II Of Russia
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes , house = , father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst , mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp , birth_date = , birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst , birth_place = Stettin, Pomerania, Prussia, Holy Roman Empire(now Szczecin, Poland) , death_date = (aged 67) , death_place = Winter Palace, Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire , burial_date = , burial_place = Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg , signature = Catherine The Great Signature.svg , religion = Catherine II (born Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power following the overthrow of her husband, Peter III. Under her long reign, inspired by the ideas of the Enlightenment, Russia experienced a renaissance of culture and sciences, which led to the founding of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khadjibey
Khadjibey ( tr, Hacıbey) was a fortress and a haven by the Gulf of Odesa, in the location of the modern city of Odesa, Ukraine. Other known spellings include Khadzhibey, Khadjibei, Hajibey, Khacdjibei, Hacıbey, Hocabey, Gadzhibei, Chadžibėjus, Codjabey, Kachybey, Kotsiubey, Kotsiubiiv. By one hypothesis, it was named after Hacı I Giray. Polish historian suggested the connection of the name of the fortress with the Polish roots linking it with the surname Kociuba, an opinion criticized by . Nadler suggested that a Tatar settlement existed on the site by 14th century but was ceded in the early 15th century to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. An early mention of a "port Kaczubyeiow" dated by 1415 is given by Jan Długosz in his ''Historiae Polonicae''.Jan Długosz, ''Historiae Polonicae''p 367*''Quote'': "Wladislaus antem Poloniae Rex, necessitati corum satagens pia commiseratione succurere, petitam frumenti quantitatem dat et largitur, et in portu suo Regio Kaczubyeiow, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochakiv
Ochakiv, also known as Ochakov ( uk, Оча́ків, ; russian: Очаков; crh, Özü; ro, Oceacov and ''Vozia'', and Alektor ( in Greek), is a small city in Mykolaiv Raion, Mykolaiv Oblast (region) of southern Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Ochakiv urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: For many years the city fortress served as a capital of the Ottoman province (eyalet). Geography The city is located at the mouth of Dnieper, on the banks of the Dnieper-Bug Estuary. Between the Cape of Ochakiv (northern bank) and the Kinburn spit (southern bank) there are only . The Ochakiv and Kinburn fortresses controlled the entrance to Dnieper and Bug. History Establishment and names The strip of land on which Ochakov is located was inhabited by Thracians and Scythians in ancient times. It was known as a part of Great Scythia. In the 7th and 6th centuries BC, Greek colonists had founded a commercial colony town, named Alektor, near the Thracian c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Fields
The Wild Fields ( uk, Дике Поле, translit=Dyke Pole, russian: Дикое Поле, translit=Dikoye Polye, pl, Dzikie pola, lt, Dykra, la, Loca deserta or , also translated as "the wilderness") is a historical term used in the Polish–Lithuanian documents of the 16th to 18th centuries to refer to the Pontic steppe in the territory of present-day Eastern and Southern Ukraine and Western Russia, north of the Black Sea and Azov Sea. According to Ukrainian historian Vitaliy Shcherbak the term appeared sometime in the 15th century for territory between the Dniester and mid-Volga when colonization of the region by Zaporozhian Cossacks started.Shcherbak, V. Wild Field (ДИКЕ ПОЛЕ)'. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. 2004 Shcherbak notes that the term's contemporaries, such as Michalo Lituanus, Blaise de Vigenère, and Józef Wereszczyński,Sas, P. Duchy of the Zaporizhian Host, the project of Józef Wereszczyński (КНЯЗІВСТВО ВІЙСЬКО ЗАПОР� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Bug
, ''Pivdennyi Buh'' , name_etymology = , image = Sunset S Bug Vinnitsa 2007 G1.jpg , image_size = 270 , image_caption = Southern Bug River in the vicinity of Vinnytsia, Ukraine , map = PietinisBugas.png , map_size = 270px , map_caption = Southern Bug through Ukraine , pushpin_map = , pushpin_map_size = , pushpin_map_caption= , subdivision_type1 = Country , subdivision_name1 = Ukraine , subdivision_type2 = , subdivision_name2 = , subdivision_type3 = Oblast , subdivision_name3 = , subdivision_type4 = , subdivision_name4 = , subdivision_type5 = , subdivision_name5 = , length = , width_min = , width_avg = , width_max = , depth_min = , depth_avg = , depth_max = , discharge1_location= , discharge1_min = , discharge1_avg = 108 m3/s , discharge1_max = , source1 = , source1_location = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporozhian Host
Zaporozhian Host (or Zaporizhian Sich) is a term for a military force inhabiting or originating from Zaporizhzhia, the territory beyond the rapids of the Dnieper River in what is Central Ukraine today, from the 15th to the 18th centuries. These include: * Zaporozhian Cossacks, generally * Zaporozhian Sich, a semi-autonomous Cossacks' polity in the 16th–18th centuries * Registered Cossacks, Zaporizhian warriors who were recorded as cossacks in official registries of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth between 1572 and 1699 * Cossack Hetmanate The Cossack Hetmanate ( uk, Гетьманщина, Hetmanshchyna; or ''Cossack state''), officially the Zaporizhian Host or Army of Zaporizhia ( uk, Військо Запорозьке, Viisko Zaporozke, links=no; la, Exercitus Zaporoviensis) ..., a Cossack state between 1649 and 1764 {{SIA Early Modern history of Ukraine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Language
Ukrainian ( uk, украї́нська мо́ва, translit=ukrainska mova, label=native name, ) is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family. It is the native language of about 40 million people and the official state language of Ukraine in Eastern Europe. Written Ukrainian uses the Ukrainian alphabet, a variant of the Cyrillic script. The standard Ukrainian language is regulated by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (NANU; particularly by its Institute for the Ukrainian Language), the Ukrainian language-information fund, and Potebnia Institute of Linguistics. Comparisons are often drawn to Russian, a prominent Slavic language, but there is more mutual intelligibility with Belarusian,Alexander M. Schenker. 1993. "Proto-Slavonic," ''The Slavonic Languages''. (Routledge). pp. 60–121. p. 60: " hedistinction between dialect and language being blurred, there can be no unanimity on this issue in all instances..."C.F. Voegelin and F.M. Voegeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity. From the 10th–17th centuries, the land was ruled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( ota, باب عالی, Bāb-ı Ālī or ''Babıali'', from ar, باب, bāb, gate and , , ), was a synecdoche for the central government of the Ottoman Empire. History The name has its origins in the old practice in which the ruler announced his official decisions and judgements at the gate of his palace. This was the practice in the Byzantine Empire and it was also adopted by Ottoman Turk sultans since Orhan I, and therefore the palace of the sultan, or the gate leading to it, became known as the "High Gate". This name referred first to a palace in Bursa, Turkey. After the Ottomans had conquered Constantinople, now Istanbul, the gate now known as the Imperial Gate ( tr, Bâb-ı Hümâyûn), leading to the outermost courtyard of the Topkapı Palace, first became known as the "High Gate", or the "Sublime Porte". When Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent sealed an alliance with King Francis I of France in 1536, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)