|
Yamen
A ''yamen'' (''ya-men''; ; Manchu: ''yamun'') was the administrative office or residence of a local bureaucrat or mandarin in imperial China. A ''yamen'' can also be any governmental office or body headed by a mandarin, at any level of government: the offices of one of the Six Ministries is a ''yamen'', but so is a prefectural magistracy. The term has been widely used in China for centuries, but appeared in English during the Qing dynasty. Overview Within a local ''yamen'', the bureaucrat administered the government business of the town or region. Typical responsibilities of the bureaucrat includes local finance, capital works, judging of civil and criminal cases, and issuing decrees and policies. Typically, the bureaucrat and his immediate family would live in a residence attached to the ''yamen''. This was especially so during the Qing dynasty, when imperial law forbade a person from taking government office in his native province. ''Yamen''s varied greatly in size de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kowloon Walled City
Kowloon Walled City was an ungoverned and densely populated ''de jure'' Imperial Chinese enclave within the boundaries of Kowloon City, British Hong Kong. Originally a Chinese military fort, the walled city became an enclave after the New Territories were leased to the United Kingdom by China in 1898. Its population increased dramatically following the Japanese occupation of Hong Kong during World War II. By 1990, the walled city contained 50,000 residents within its borders. From the 1950s to the 1970s, it was controlled by local triads and had high rates of prostitution, gambling, and drug abuse. In January 1987, the Hong Kong government announced plans to demolish the walled city. After an arduous eviction process, and the transfer of ''de jure'' sovereignty of the enclave from China to Britain, demolition began in March 1993 and was completed in April 1994. Kowloon Walled City Park opened in December 1995 and occupies the area of the former walled city. Some histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin (bureaucrat)
A mandarin () was a bureaucrat scholar in the history of China, Korea and Vietnam. The term is generally applied to the officials appointed through the imperial examination system; it sometimes includes the eunuchs also involved in the governance of the above realms. History and use of the term The English term comes from the Portuguese ''mandarim'' (spelled in Old Portuguese as ''mandarin,'' ). The Portuguese word was used in one of the earliest Portuguese reports about China: letters from the imprisoned survivors of the Tomé Pires' embassy, which were most likely written in 1524, and in Castanheda's ''História do descobrimento e conquista da Índia pelos portugueses'' (c. 1559). Matteo Ricci, who entered mainland China from Portuguese Macau in 1583, also said the Portuguese used the word. The Portuguese word was thought by many to be related to ''mandador'' ("one who commands") and ''mandar'' ("to command"), from Latin ''mandare''. Modern dictionaries, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty Taiwan Provincial Administration Hall
The Guest House of Imperial Envoys Museum () is the former site of the Qing dynasty government yamen that ruled Taiwan. The building is located at Taipei Botanical Garden in Zhongzheng District, Taipei. The building is the only office of the Qing dynasty remaining in Taiwan. History The hall was built in 1882, late in the Qing period. Function The building served as the residential quarters for Qing government officials in Taipei on their inspection visits to Taiwan. Transportation The building is accessible within walking distance South from Xiaonanmen Station of the Taipei Metro. See also * List of tourist attractions in Taiwan * Taiwan under Qing Dynasty rule Taiwan under Qing rule refers to the rule of the Qing dynasty over the island of Taiwan from 1683 to 1895. The Qing dynasty sent an army led by general Shi Lang and defeated the Ming loyalist Kingdom of Tungning in 1683. Taiwan was formally annex ... References 1882 establishments in China Buildings and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureaucracy
The term bureaucracy () refers to a body of non-elected governing officials as well as to an administrative policy-making group. Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected officials. Today, bureaucracy is the administrative system governing any large institution, whether publicly owned or privately owned. The public administration in many jurisdictions and sub-jurisdictions exemplifies bureaucracy, but so does any centralized hierarchical structure of an institution, e.g. hospitals, academic entities, business firms, professional societies, social clubs, etc. There are two key dilemmas in bureaucracy. The first dilemma revolves around whether bureaucrats should be autonomous or directly accountable to their political masters. The second dilemma revolves around bureaucrats' behavior strictly following the law or whether they have leeway to determine appropriate solutions for varied circumstances. Various comment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taipei
Taipei (), officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Located in Northern Taiwan, Taipei City is an enclave of the municipality of New Taipei City that sits about southwest of the northern port city of Keelung. Most of the city rests on the Taipei Basin, an ancient lakebed. The basin is bounded by the relatively narrow valleys of the Keelung and Xindian rivers, which join to form the Tamsui River along the city's western border. The city of Taipei is home to an estimated population of 2,646,204 (2019), forming the core part of the Taipei–Keelung metropolitan area, which includes the nearby cities of New Taipei and Keelung with a population of 7,047,559, the 40th most-populous urban area in the world—roughly one-third of Taiwanese citizens live in the metro district. The name "Taipei" can refer either to the whole metropolitan area or just the city itself. Taipei has been the seat of the ROC central govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiananmen Square
Tiananmen Square or Tian'anmen Square (; 天安门广场; Pinyin: ''Tiān'ānmén Guǎngchǎng''; Wade–Giles: ''Tʻien1-an1-mên2 Kuang3-chʻang3'') is a city square in the city center of Beijing, China, named after the eponymous Tiananmen ("Gate of Heavenly Peace") located to its north, which separates it from the Forbidden City. The square contains the Monument to the People's Heroes, the Great Hall of the People, the National Museum of China, and the Mausoleum of Mao Zedong. Mao Zedong proclaimed the founding of the People's Republic of China in the square on October 1, 1949; the anniversary of this event is still observed there. The size of Tiananmen Square is 765 x 282 meters (215,730 m2 or 53.31 acres). It has great cultural significance as it was the site of several important events in Chinese history. Outside China, the square is best known for the 1989 protests and massacre that ended with a military crackdown, which is also known as the Tiananmen Square Massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, finance, busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is also applied to the entirety of China proper. Henan is a birthplace of Han Chinese civilization, with over 3,200 years of recorded history and remained China's cultural, economic and political center until approximately 1,000 years ago. Henan Province is home to many heritage sites, including the ruins of Shang dynasty capital city Yin and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the Eight Great Ancient Capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. The practice of tai chi also began here in Chen Jia Gou Village (Chen style), as did the later Yang and Wu styles. Although the name of the province () means "south of the ellowriver.", approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River, also known as the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neixiang County
Neixiang County () is a county under the jurisdiction of Nanyang City, in the southwest of Henan province, China, has an area of and a population of 610,000 as of 2002. Neixiang is best known because it has China's best preserved Yamen, or county government office. The Yamen in Neixiang was built originally in the Yuan Dynasty and has a history of more than 700 years. It was destroyed and rebuilt several times and the existing architecture mostly dates to the Qing Dynasty when it was built by Zhang Bingtao in 1882: it took three years to build. It has an area of and there are more than 260 existing rooms. It is currently China's best preserved feudal county government office. It is home to Neixiang Air Base. Administrative divisions As 2012, this county is divided to 10 towns and 6 townships. ;Towns ;Townships Climate Transport *China National Highway 312 China National Highway 312 (312国道), also referred to as Route 312 or The Mother Road, is a key east-west route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
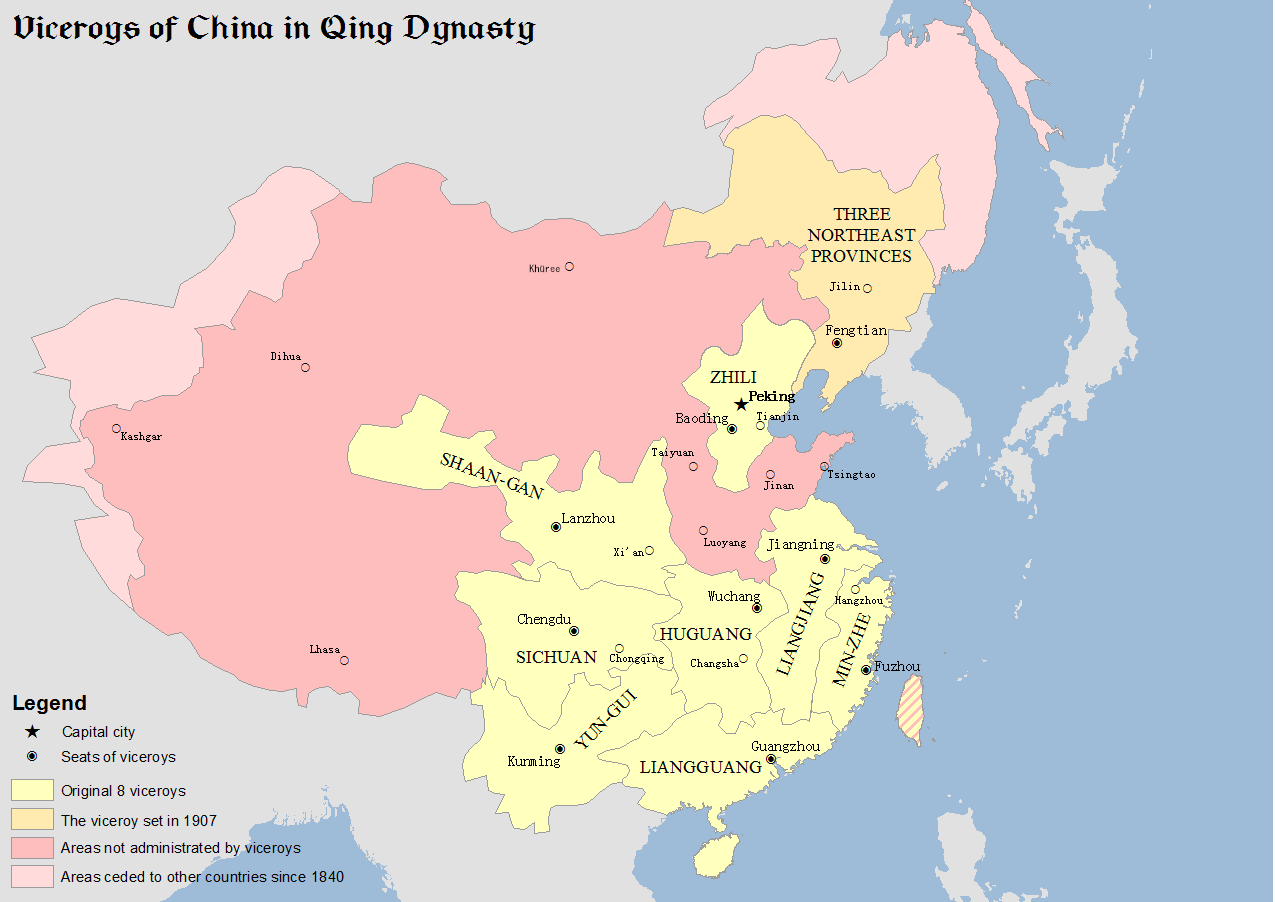
Viceroy Of Liangjiang
The Viceroy of Liangjiang or Viceroy of the Two Jiangs, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of the Two Yangtze Provinces and Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs, Provisions and Funds, Manager of Waterways, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Liangjiang had jurisdiction over Jiangsu, Jiangxi and Anhui provinces. Because Jiangsu and Anhui were previously part of a single province, Jiangnan ("south of the Yangtze"), they were thus known, along with Jiangxi ("west of the Yangtze"), as the two ''jiang''s, hence the name "Liangjiang" ("two Jiangs"). History The office of Viceroy of Liangjiang originated in 1647 during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor. It was called "Viceroy of the Three Provinces of Jiangdong, Jiangxi and Henan" (江東江西河南三省總督) and headquartered in Jiangning (江寧; present-day Nanjing, Jiangsu). In 1652, the office was renamed "Viceroy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |