|
Yamatogoto
The ', also called ' and ', is a six- or seven-stringed plucked zither which, unlike the '' koto'' and other stringed instruments, is believed to be truly native to Japan, and not imported from mainland Asia. Both names translate literally to "Japanese stringed instrument." According to Shintō myth as written in the ''Kojiki'', the ''yamatogoto'' played an important role in the origins of Japan itself. In the myth, Amaterasu, goddess of the sun, is insulted by her brother Susano-o no Mikoto and hides in a cave, refusing to emerge. The world is therefore plunged into darkness. Amaterasu is eventually coaxed out of her cave by the goddess Ame-no-Uzume, who performs a dance outside the cave, to music provided by the twanging of six hunting bows. Amused by the music, and by the entertained sounds of the other gods, Amaterasu leaves the cave and returns to the firmament. The six bows are lashed together to form an instrument, and the first ''wagon'' or ''yamatogoto'' is born. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Musical Instruments
Traditional Japanese musical instruments, known as in Japanese, are musical instruments used in the traditional folk music of Japan. They comprise a range of string, wind, and percussion instruments. Percussion instruments *; also spelled – clapper made from wooden slats connected by a rope or cord * – wooden or bamboo clappers * – pellet drum, used as a children's toy * – small, ornately decorated hourglass-shaped drum * – hand-held bell tree with three tiers of pellet bells * – small drum used in * – small flat gong * – a pair of sticks which are beaten together slowly and rhythmically * (also called ) – clapper made from a pair of flat wooden sticks * – woodblock carved in the shape of a fish, struck with a wooden stick; often used in Buddhist chanting * – hand drum * or () – singing bowls used by Buddhist monks in religious practice or rituals * – hourglass-shaped double-headed drum; struck only on one side * – clapper made from wooden slats con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gagaku
is a type of Japanese classical music that was historically used for imperial court music and dances. was developed as court music of the Kyoto Imperial Palace, and its near-current form was established in the Heian period (794-1185) around the 10th century.History of gagaku Nihon gagakukai Today, it is performed by the Board of Ceremonies in the Tokyo Imperial Palace. Gagaku consists of three primary repertoires: #Native Shinto relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ame-no-Uzume
is the goddess of dawn, mirth, meditation, revelry and the arts in the Shinto religion of Japan, and the wife of fellow-god Sarutahiko Ōkami. She famously relates to the tale of the missing sun deity, Amaterasu Omikami. Her name can also be pronounced as Ama-no-Uzume. She is also known as Ōmiyanome-no-Ōkami, an '' inari kami'' possibly due to her relationship with her husband. She is also known as Ame-no-Uzume-no-Mikoto, The Great Persuader, and The Heavenly Alarming Female. She is depicted in kyōgen farce as Okame, a woman who revels in her sensuality. Mythology Amaterasu and the cave Amaterasu's brother, the storm god Susano'o, had vandalized her rice fields, threw a flayed horse at her loom, and brutally killed one of her maidens due to a quarrel between them. In turn, Amaterasu became furious with him and retreated into the Heavenly Rock Cave, Amano-Iwato. The world, without the illumination of the sun, became dark and the gods could not lure Amaterasu out of her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagura
is a type of Shinto ritual ceremonial dance. The term is a contraction of the phrase , indicating the presence of gods () in the practice. One major function of is , involving a procession-trance process. Usually a female shaman will perform the dance and obtain the oracle from the god—in the setting, the dancer herself turns into god during the performance. Once strictly a ceremonial art derived from , has evolved in many directions over the span of more than a millennium. Today, it is very much a living tradition, with rituals tied to the rhythms of the agricultural calendar, thriving primarily in parts of Shimane Prefecture, and urban centers such as Hiroshima. Types of There are two major types of : and . consists of slow circular movement, stressing quiet and elegance, while consists of quick leaping and jumping, stressing activation and energy. The two types can be understood as two phases of : is a preparation process for trance and is the unconscious tranc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zithers
Zithers (; , from the Greek word '' cithara'') are a class of stringed instruments. Historically, the name has been applied to any instrument of the psaltery family, or to an instrument consisting of many strings stretched across a thin, flat body. This article describes the latter variety. Zithers are typically played by strumming or plucking the strings with the fingers or a plectrum. In the Hornbostel–Sachs classification system, the term refers to a larger family of similarly shaped instruments that also includes the hammered dulcimer family and piano and a few rare bowed instruments like the bowed psaltery, bowed dulcimer, and streichmelodion. Like an acoustic guitar or lute, a zither's body serves as a resonating chamber (sound box), but, unlike guitars and lutes, a zither lacks a distinctly separate neck assembly. The number of strings varies, from one to more than fifty. In modern common usage the term "zither" refers to three specific instruments: the concert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Views Of Haniwa Playing A Japanese Harp AAM
3 is a number, numeral, and glyph. 3, three, or III may also refer to: * AD 3, the third year of the AD era * 3 BC, the third year before the AD era * March, the third month Books * '' Three of Them'' (Russian: ', literally, "three"), a 1901 novel by Maksim Gorky * ''Three'', a 1946 novel by William Sansom * ''Three'', a 1970 novel by Sylvia Ashton-Warner * ''Three'' (novel), a 2003 suspense novel by Ted Dekker * ''Three'' (comics), a graphic novel by Kieron Gillen. * ''3'', a 2004 novel by Julie Hilden * ''Three'', a collection of three plays by Lillian Hellman * ''Three By Flannery O'Connor'', collection Flannery O'Connor bibliography Brands * 3 (telecommunications), a global telecommunications brand ** 3Arena, indoor amphitheatre in Ireland operating with the "3" brand ** 3 Hong Kong, telecommunications company operating in Hong Kong ** Three Australia, Australian telecommunications company ** Three Ireland, Irish telecommunications company ** Three UK, British tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glissando
In music, a glissando (; plural: ''glissandi'', abbreviated ''gliss.'') is a glide from one pitch to another (). It is an Italianized musical term derived from the French ''glisser'', "to glide". In some contexts, it is distinguished from the continuous portamento. Some colloquial equivalents are slide, sweep (referring to the "discrete glissando" effects on guitar and harp, respectively), bend, smear, rip (for a loud, violent gliss to the beginning of a note), lip (in jazz terminology, when executed by changing one's embouchure on a wind instrument), plop, or falling hail (a glissando on a harp using the back of the fingernails). On wind instruments, a scoop is a glissando ascending to the onset of a note achieved entirely with the embouchure. Portamento Prescriptive attempts to distinguish the glissando from the portamento by limiting the former to the filling in of discrete intermediate pitches on instruments like the piano, harp, and fretted stringed instruments have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
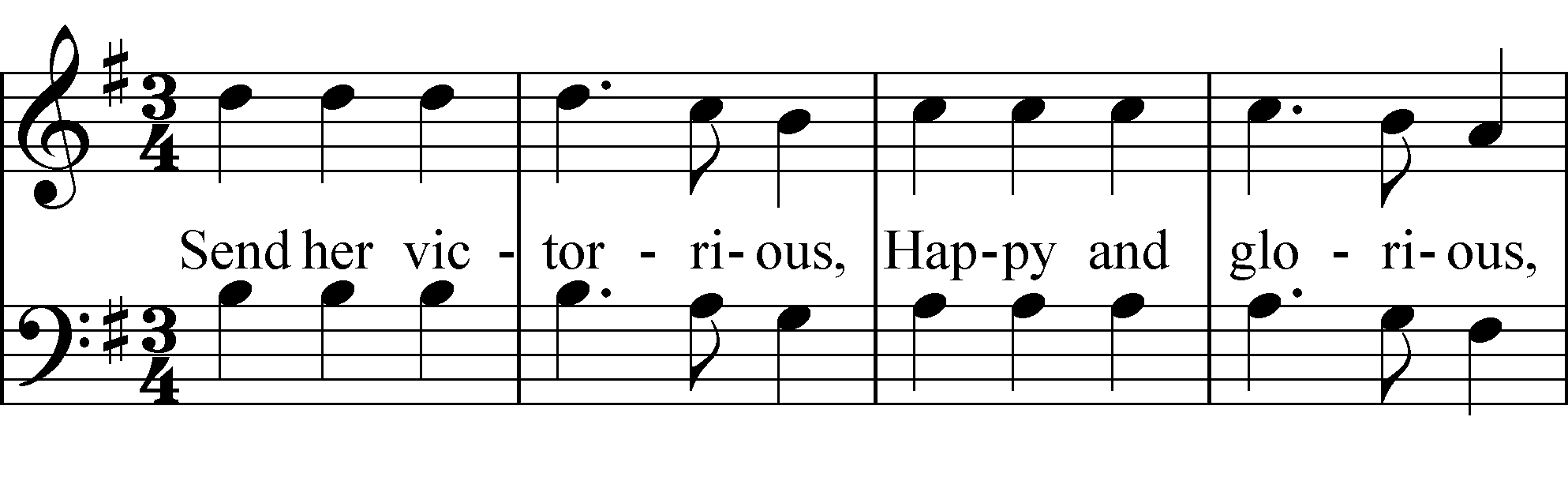
Melodic Sequence
In music and jazz improvisation, a melodic pattern (or motive) is a cell or germ serving as the basis for repetitive pattern. It is a figure that can be used with any scale. It is used primarily for solos because, when practiced enough, it can be extremely useful when improvising Improvisation is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. Improvisation in the performing arts is a very spontaneous performance without specific or scripted preparation. The skills of impr .... "Sequence" refers to the repetition of a part at a higher or lower pitch, and melodic sequence is differentiated from harmonic sequence. One example of melodic motive and sequence are the pitches of the first line, "Send her victorious," repeated, a step lower, in the second line, "Happy and glorious," from " God Save the Queen". "A melodic pattern is just what the name implies: a melody with some sort of fixed pattern to it." "The strong theme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale (music)
In music theory, a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale. Often, especially in the context of the common practice period, most or all of the melody and harmony of a musical work is built using the notes of a single scale, which can be conveniently represented on a staff with a standard key signature. Due to the principle of octave equivalence, scales are generally considered to span a single octave, with higher or lower octaves simply repeating the pattern. A musical scale represents a division of the octave space into a certain number of scale steps, a scale step being the recognizable distance (or interval) between two successive notes of the scale. However, there is no need for scale steps to be equal within any scale and, particularly as demonstrated by microtonal music, there is no limit to how many notes can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yumi
is the Japanese term for a bow. As used in English, refers more specifically to traditional Japanese asymmetrical bows, and includes the longer and the shorter used in the practice of and , or Japanese archery. The was an important weapon of the samurai warrior during the feudal period of Japan. It is typically shot with Japanese arrows known as . The most famous style of is an asymmetrically shaped long bow with a length of more than , characterized by the archer holding the part of the bow below the center to shoot the arrow. History Most of the excavated Jōmon period () bows are in length, while most of the Yayoi period () bows are in length. The bows in these periods were made from a single processed wood, and the bows with this structure were called and were used until the Nara period (710–794 CE). It is unknown when the asymmetrical came into use, but the first written record is found in the ''Book of Wei'', a Chinese historical manuscript dating to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susanoo
__FORCETOC__ Susanoo (; historical orthography: , ) is a in Japanese mythology. The younger brother of Amaterasu, goddess of the sun and mythical ancestress of the Japanese imperial line, he is a multifaceted deity with contradictory characteristics (both good and bad), being portrayed in various stories either as a wild, impetuous god associated with the sea and storms, as a heroic figure who killed a monstrous serpent, or as a local deity linked with the harvest and agriculture. Syncretic beliefs that arose after the introduction of Buddhism to Japan also saw Susanoo becoming conflated with deities of pestilence and disease. Susanoo, alongside Amaterasu and the earthly Ōkuninushi (also Ōnamuchi) – depicted as either Susanoo's son or scion depending on the source – is one of the central deities of the imperial Japanese mythological cycle recorded in the ( CE) and the (720 CE). One of the gazetteer reports () commissioned by the imperial court during the same peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |