|
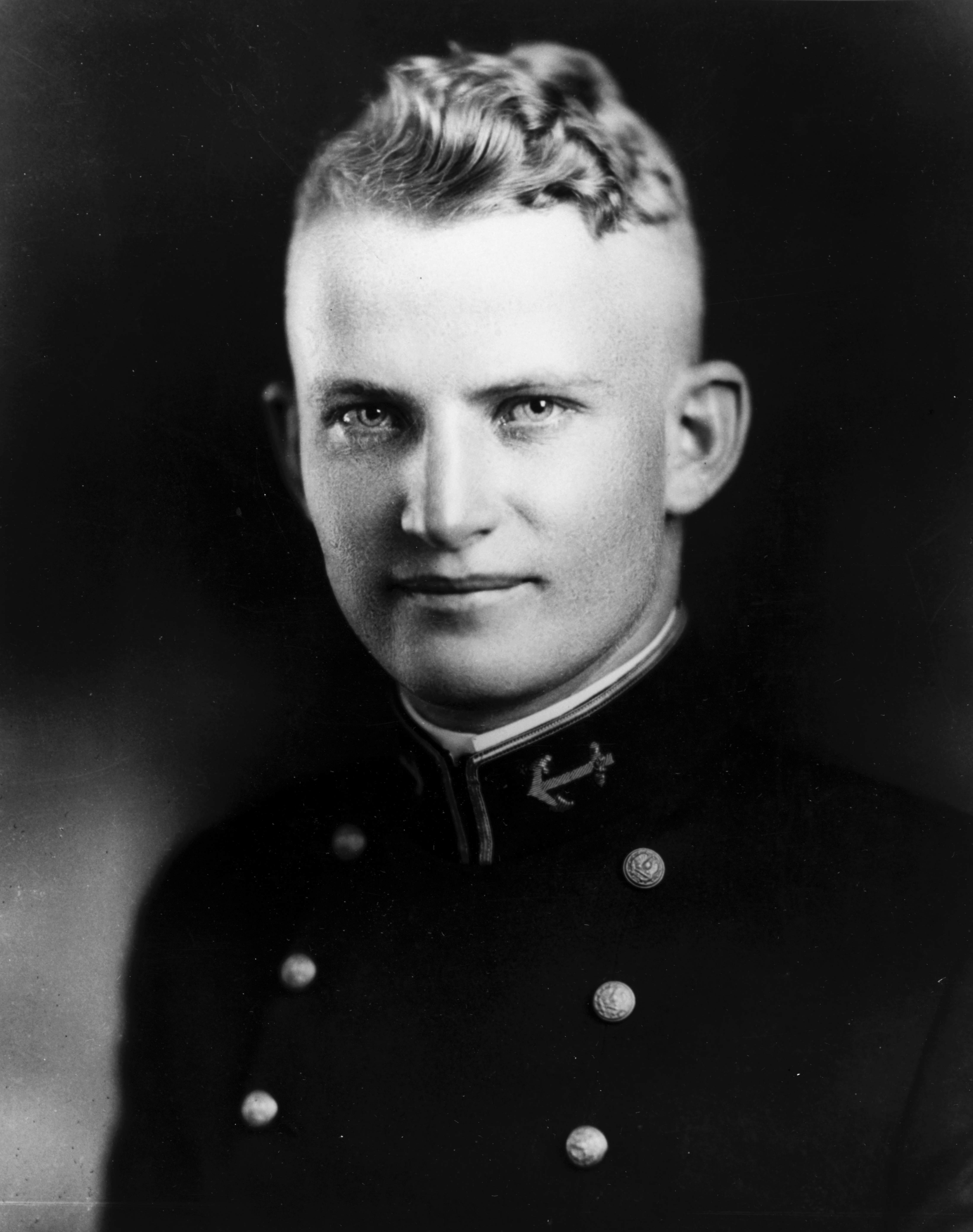
William J. Scheyer
William John Scheyer (March 6, 1900 – May 14, 1956) was a decorated officer of the United States Marine Corps, who reached the rank of major general. He is most noted as executive officer and later commanding officer of the 9th Defense Battalion during the Guadalcanal Campaign and the invasion of Rendova Island. Later he distinguished himself as Personnel Officer of III Marine Amphibious Corps during the Recapture of Guam. Early years William J. Scheyer was born on March 6, 1900, in Dunkirk, New York, the son of William and Lucy Scheyer. Following graduation from high school, he received an appointment to the United States Naval Academy at Annapolis, Maryland, where he was nicknamed "Stoneface"; was active in rifle squad and also served as Manager of the Class Basketball. Many of his classmates became general officers later: Arleigh Burke, Harry D. Felt, Merrill B. Twining, Charles F. Coe, George F. Good Jr., John B. Moss, Frederick Moosbrugger, Stanhope C. Ring, Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk, New York
Dunkirk is a Administrative divisions of New York#City, city in Chautauqua County, New York, United States. It was settled around 1805 and incorporated in 1880. The population was 12,743 as of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census. Dunkirk is bordered on the north by Lake Erie. It shares a border with the Administrative divisions of New York#Village, village of Fredonia, New York, Fredonia to the south, and with the Administrative divisions of New York#Town, town of Dunkirk (town), New York, Dunkirk to the east and west. Dunkirk is the westernmost city in the state of New York (state), New York. History The Iroquoian languages-speaking Erie people occupied this area of the forested lakefront along the southern shore of Lake Erie well into the 1600s, when Europeans, mostly French, started trading around the Great Lakes. They were pushed out by the Seneca people, one of the Iroquois, Five Nations of the powerful Iroquois League, based here and further east in New York. The Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Saipan
The Battle of Saipan was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, fought on the island of Saipan in the Mariana Islands from 15 June to 9 July 1944 as part of Operation Forager. It has been referred to as the "Pacific D-Day" with the invasion fleet departing Pearl Harbor on 5 June 1944, the day before Operation Overlord in Europe was launched, and launching nine days after. The U.S. 2nd Marine Division, 4th Marine Division, and the Army's 27th Infantry Division, commanded by Lieutenant General Holland Smith, defeated the 43rd Infantry Division of the Imperial Japanese Army, commanded by Lieutenant General Yoshitsugu Saitō. The loss of Saipan, with the deaths of at least 29,000 troops and heavy civilian casualties, precipitated the resignation of Prime Minister of Japan Hideki Tōjō and left the Japanese archipelago within the range of United States Army Air Forces B-29 bombers. Background In the campaigns of 1943 and the first half of 1944, the Allies had capt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merrill B
Merrill may refer to: Places in the United States *Merrill Field, Anchorage, Alaska *Merrill, Iowa * Merrill, Maine *Merrill, Michigan *Merrill, Mississippi, an unincorporated community near Lucedale in George County *Merrill, Oregon *Merrill, Wisconsin *Merrill (town), Wisconsin *Merrill Township, Michigan * Merrill Township, North Dakota *Merrill College at the University of California, Santa Cruz People * Merrill Moses (born 1977), Olympic water polo player *Merrill (surname) *Merrill Cook, Utah politician *Merrill Garbus, musician behind the experimental indie project Tune-yards *Merrill Ashley (born 1950), American ballet dancer and ''répétiteur'' Other uses *Merrill (company), a division of Bank of America *Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, architectural firm * USS ''Merrill'' (DD-976) *Nine men's morris, a strategy board game also called ''Merrills'' * Merrill (crater) Merrill is a lunar impact crater. It is located in the high northern latitudes, on the far side. Less than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry D
Harry may refer to: TV shows * ''Harry'' (American TV series), a 1987 American comedy series starring Alan Arkin * ''Harry'' (British TV series), a 1993 BBC drama that ran for two seasons * ''Harry'' (talk show), a 2016 American daytime talk show hosted by Harry Connick Jr. People and fictional characters *Harry (given name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name *Harry (surname), a list of people with the surname *Dirty Harry (musician) (born 1982), British rock singer who has also used the stage name Harry *Harry Potter (character), the main protagonist in a Harry Potter fictional series by J. K. Rowling Other uses *Harry (derogatory term), derogatory term used in Norway * ''Harry'' (album), a 1969 album by Harry Nilsson *The tunnel used in the Stalag Luft III escape ("The Great Escape") of World War II * ''Harry'' (newspaper), an underground newspaper in Baltimore, Maryland See also *Harrying (laying waste), may refer to the following historical events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arleigh Burke
Arleigh Albert Burke (October 19, 1901 – January 1, 1996) was an admiral of the United States Navy who distinguished himself during World War II and the Korean War, and who served as Chief of Naval Operations during the Eisenhower and Kennedy administrations. , the lead ship of its class of Aegis-equipped guided missile destroyers, was commissioned in Burke's honor in 1991. The honor of naming a vessel after a living figure was only the fourth time it had been bestowed since 1861. Early life and naval career Burke was born in Boulder, Colorado, on October 19, 1901, to Oscar Burke and Clara Mokler. His grandfather, August Björkgren, was a Swedish immigrant to the US and changed his surname to 'Burke', a common Irish surname, to sound more 'American'. Due to the 1918 influenza outbreak, schools were closed in Boulder and he never graduated from high school. Burke won an alternate appointment to the United States Naval Academy given by his local congressman. During his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annapolis, Maryland
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east of Washington, D.C., Annapolis forms part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The 2020 census recorded its population as 40,812, an increase of 6.3% since 2010. This city served as the seat of the Confederation Congress, formerly the Second Continental Congress, and temporary national capital of the United States in 1783–1784. At that time, General George Washington came before the body convened in the new Maryland State House and resigned his commission as commander of the Continental Army. A month later, the Congress ratified the Treaty of Paris of 1783, ending the American Revolutionary War, with Great Britain recognizing the independence of the United States. The city and state capitol was also the site of the 1786 An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (US Naval Academy, USNA, or Navy) is a federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy is the second oldest of the five U.S. service academies and it educates midshipmen for service in the officer corps of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. The campus is located on the former grounds of Fort Severn at the confluence of the Severn River and Chesapeake Bay in Anne Arundel County, east of Washington, D.C., and southeast of Baltimore. The entire campus, known colloquially as the Yard, is a National Historic Landmark and home to many historic sites, buildings, and monuments. It replaced Philadelphia Naval Asylum, in Philadelphia, that had served as the first United States Naval Academy from 1838 to 1845, when the Naval Academy formed in Annapolis. Candidates for admission generally must apply directly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landings On Rendova
The Landings on Rendova were amphibious military assaults by United States Army, Marine Corps and Navy forces on Rendova Island in the Solomon Islands on 30 June 1943. The small Japanese garrison was quickly overwhelmed by US troops, but the island was subjected to heavy attack by Japanese aircraft over several days. The landings were some of the first Allied landings during the New Georgia Campaign of the Pacific War and were successful in securing the island and providing a base from which the Allies could support the subsequent invasion of New Georgia island and the eventual capture of Munda airfield in early August 1943. Background Rendova Island forms part of the New Georgia group and is situated off the western coast of mainland New Georgia, separated from it by the Blanche Channel. It is roughly rectangular in shape, oriented northeast, with a southwestern tip that extends like the toe of shoe towards Tetepare Island. At the time of the battle, the island's significance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalcanal Campaign
The Guadalcanal campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by American forces, was a military campaign fought between 7 August 1942 and 9 February 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theater of World War II. It was the first major land offensive by Allied forces against the Empire of Japan. On 7 August 1942, Allied forces, predominantly United States Marines, landed on Guadalcanal, Tulagi, and Florida in the southern Solomon Islands, with the objective of using Guadalcanal and Tulagi as bases in supporting a campaign to eventually capture or neutralize the major Japanese base at Rabaul on New Britain. The Japanese defenders, who had occupied those islands since May 1942, were outnumbered and overwhelmed by the Allies, who captured Tulagi and Florida, as well as the airfield – later named Henderson Field – that was under construction on Guadalcanal. Surprised by the Allied offensive, the Japanese made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th Defense Battalion
The 2nd 90mm Antiaircraft Artillery Gun Battalion was a United States Marine Corps Anti-aircraft warfare, antiaircraft unit that was active during the 1940s & 1950s. Originally formed during World War II as the 9th Defense Battalion, the battalion took part in combat operations on Guadalcanal Campaign, Guadalcanal, Landings on Rendova, Rendova, Battle of Munda Point, Munda Point, and Invasion of Guam, Guam. Like most other Marine Marine defense battalions, defense battalions, the unit was re-designated in September 1944, becoming the 9th Antiaircraft Artillery Battalion. Returning to the United States in 1946, the battalion was again re-designated, this time as the 1st Antiaircraft Artillery Battalion. The battalion received its final designation as the 2nd 90mm Antiaircraft Artillery Battalion on August 21, 1950. It was later decommissioned on September 15, 1956 at Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center Twentynine Palms, Marine Corps Base 29 Palms, California. History World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Star Medal
The Bronze Star Medal (BSM) is a United States Armed Forces decoration awarded to members of the United States Armed Forces for either heroic achievement, heroic service, meritorious achievement, or meritorious service in a combat zone. When the medal is awarded by the Army, Air Force, or Space Force for acts of valor in combat, the "V" device is authorized for wear on the medal. When the medal is awarded by the Navy, Marine Corps, or Coast Guard for acts of valor or meritorious service in combat, the Combat "V" is authorized for wear on the medal. Officers from the other Uniformed Services of the United States are eligible to receive this award, as are foreign soldiers who have served with or alongside a service branch of the United States Armed Forces. Civilians serving with U.S. military forces in combat are also eligible for the award. For example, UPI reporter Joe Galloway was awarded the Bronze Star with "V" device during the Vietnam War for rescuing a badly wound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legion Of Merit
The Legion of Merit (LOM) is a military award of the United States Armed Forces that is given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievements. The decoration is issued to members of the eight uniformed services of the United States Note: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps Amendments Act of 2012 amended the Legion of Merit to be awarded to any uniformed service. as well as to military and political figures of foreign governments. The Legion of Merit (Commander degree) is one of only two United States military decorations to be issued as a (the other being the |