|
Weaning
Weaning is the process of gradually introducing an infant human or another mammal to what will be its adult diet while withdrawing the supply of its mother's milk. The process takes place only in mammals, as only mammals produce milk. The infant is considered to be fully weaned once it is no longer fed by any breast milk (or bottled substitute). Humans In some cultures, weaning progresses with the introduction of feeding the child food that has been prechewed by the parent along with continued breastfeeding, a practice known as premastication. The practice was important throughout human history in that it naturally gave a child a greatly improved protein source in addition to preventing iron deficiency. However, premasticated food from caregivers of lower socioeconomic status in areas of endemic diseases can result in the passing of the disease to the child. How and when to wean a human infant is controversial. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends feeding a baby onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
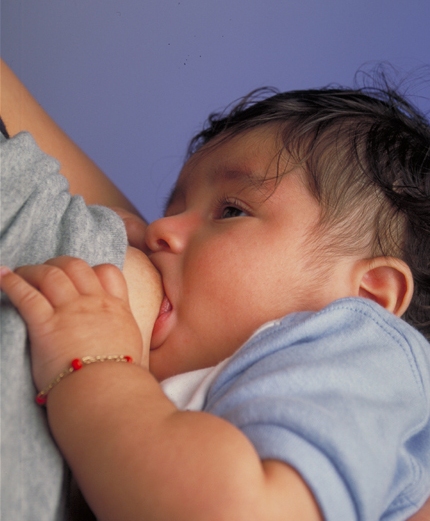
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfeeding has a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calf (animal)
A calf ( : calves) is a young domestic cow or bull. Calves are reared to become adult cattle or are slaughtered for their meat, called veal, and hide. The term ''calf'' is also used for some other species. See " Other animals" below. Terminology "Calf" is the term used from birth to weaning, when it becomes known as a ''weaner'' or ''weaner calf'', though in some areas the term "calf" may be used until the animal is a yearling. The birth of a calf is known as ''calving''. A calf that has lost its mother is an orphan calf, also known as a ''poddy'' or ''poddy-calf'' in British. ''Bobby calves'' are young calves which are to be slaughtered for human consumption. A ''vealer'' is a calf weighing less than about which is at about eight to nine months of age. A young female calf from birth until she has had a calf of her own is called a ''heifer'' (). In the American Old West, a motherless or small, runty calf was sometimes referred to as a dodie. The term "calf" is also used f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns, containing fat, protein, carbohydrates ( lactose and human milk oligosaccharides) and variable minerals and vitamins. Breast milk also contains substances that help protect an infant against infection and inflammation, whilst also contributing to healthy development of the immune system and gut microbiome. Uses and methods of consumption The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, with solids gradually being introduced around this age when signs of readiness are shown. Supplemented breastfeeding is recommended until at least age two and then for as long as the mother and child wish. Some newborn babies that are alert and healthy have the ability to latch on to the mother's breast within one hour of birth, however, on a glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant Formula
Infant formula, baby formula, or simply formula (American English); or baby milk, infant milk or first milk (British English), is a manufactured food designed and marketed for feeding to babies and infants under 12 months of age, usually prepared for bottle-feeding or cup-feeding from powder (mixed with water) or liquid (with or without additional water). The U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) defines infant formula as "a food which purports to be or is represented for special dietary use solely as a food for infants by reason of its simulation of human milk or its suitability as a complete or partial substitute for human milk". Manufacturers state that the composition of infant formula is designed to be roughly based on a human mother's milk at approximately one to three months postpartum; however, there are significant differences in the nutrient content of these products. The most commonly used infant formulas contain purified cow's milk whey and casein as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katherine Ann Dettwyler
Katherine Ann Dettwyler is an American anthropologist and advocate of breastfeeding. She was an adjunct professor at the University of Delaware. In 2017, she gained media attention for her comments regarding Otto Warmbier, a 22-year-old college student who received fatal brain damage while imprisoned in North Korea. Background and education Katherine Ann Dettwyler was born on February 3, 1955. She earned her BS in Anthropology from the University of California, Davis, in 1977, her MA from Indiana University Bloomington in 1981, and her Ph.D. in Anthropology also from IU Bloomington in 1985. Professional career Dettwyler taught as a Visiting Assistant Professor at the Department of Sociology and Anthropology of the University of Southern Mississippi in Hattiesburg, Mississippi from 1985 to 1987. She taught at Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas in the Anthropology department from 1987 until 2000, when she took early retirement from her position as a tenured Associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is Domestication of the dog, derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Dogs were the first species to be domesticated by hunter-gatherers over 15,000 years ago before the development of agriculture. Due to their long association with humans, dogs have expanded to a large number of domestic individuals and gained the ability to thrive on a starch-rich diet that would be inadequate for other Canidae, canids. The dog has been selectively bred over millennia for various behaviors, sensory capabilities, and physical attributes. Dog breeds vary widely in shape, size, and color. They perform many roles for humans, such as Hunting dog, hunting, Herding dog, herding, Sled dog, pulling loads, Guard dog, protection, Police dog, assisting police and the Dogs in warfare, military, Pet, companionsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dairy Cattle
Dairy cattle (also called dairy cows) are cattle bred for the ability to produce large quantities of milk, from which dairy products are made. Dairy cattle generally are of the species '' Bos taurus''. Historically, little distinction was made between dairy cattle and beef cattle, with the same stock often being used for both meat and milk production. Today, the bovine industry is more specialized and most dairy cattle have been bred to produce large volumes of milk. Management Dairy cows may be found either in herds or dairy farms, where dairy farmers own, manage, care for, and collect milk from them, or on commercial farms. Herd sizes vary around the world depending on landholding culture and social structure. The United States has an estimated 9 million cows in around 75,000 dairy herds, with an average herd size of 120 cows. The number of small herds is falling rapidly with the 3,100 herds with over 500 cows producing 51% of U.S. milk in 2007. The United Kingdom d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Mice
The laboratory mouse or lab mouse is a small mammal of the order Rodentia which is bred and used for scientific research or feeders for certain pets. Laboratory mice are usually of the species ''Mus musculus''. They are the most commonly used mammalian research model and are used for research in genetics, physiology, psychology, medicine and other scientific disciplines. Mice belong to the Euarchontoglires clade, which includes humans. This close relationship, the associated high homology with humans, their ease of maintenance and handling, and their high reproduction rate, make mice particularly suitable models for human-oriented research. The laboratory mouse genome has been sequenced and many mouse genes have human homologues. Other mouse species sometimes used in laboratory research include two American species, the white-footed mouse (''Peromyscus leucopus'') and the North American deer mouse ('' Peromyscus maniculatus''). History as a biological model Mice have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premastication
Premastication, pre-chewing, or kiss feeding is the act of chewing food for the purpose of physically breaking it down in order to feed another that is incapable of masticating the food by themselves. This is often done by the mother or relatives of a baby to produce baby food capable of being consumed by the child during the weaning process. The chewed food in the form of a bolus is transferred from the mouth of one individual to another, either directly mouth-to-mouth, via utensils, hands, or is further cooked or processed prior to feeding. The behaviour was common throughout human history and societies and observed in non-human animals. While premastication is less common in present-day Western societies, it was commonly practised, and is still done in more traditional cultures. Although the health benefits of premastication are still being actively studied, the practice appears to confer certain nutritional and immunological benefits to the infant, provided that the caretaker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
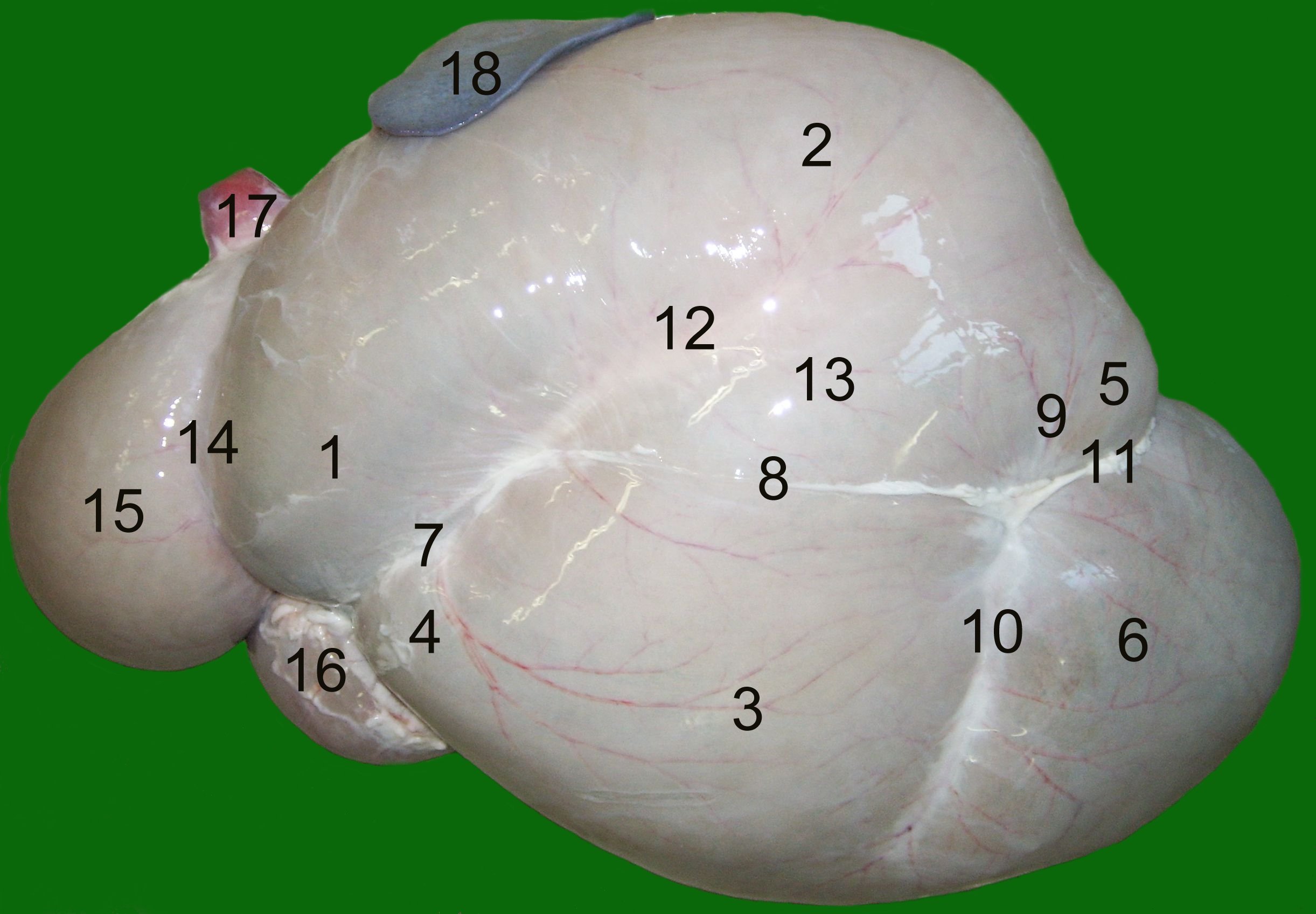
Rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allows it to serve as the primary site for microbial fermentation of ingested feed. The smaller part of the reticulorumen is the reticulum, which is fully continuous with the rumen, but differs from it with regard to the texture of its lining. Brief anatomy The rumen is composed of several muscular sacs, the cranial sac, ventral sac, ventral blindsac, and reticulum. The lining of the rumen wall is covered in small fingerlike projections called papillae, which are flattened, approximately 5mm in length and 3mm wide in cattle. The reticulum is lined with ridges that form a hexagonal honeycomb pattern. The ridges are approximately 0.1–0.2mm wide and are raised 5mm above the reticulum wall. The hexagons in the reticulum are approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla ( hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora ( cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)